Mechanism of Baihu Renshen decoction on T2DM rats based on mitochondrial autophagy mediated by PINK1/Parkin
Han-Zhou Li,Hui Zhang,2,Bao-Chao Pan,2,Yuan-Song Wang,Xiu-Hai Su,Shu-Fang Zhang,Shu-Quan Lyu*,Zhai-Yi Zhang
1Endocrinology Department, Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Affiliated to Hebei University of Chinese Medicine,Cangzhou 061001, China. 2Graduate School, Hebei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050091, China. 3School of Basic Medical Sciences,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 301617,China.
Abstract Background: This study will be aimed at investigating the effects of Baihu Renshen decoction (BHRS) on type 2 diabetes rats and on macromolecular enzyme 1 (PINK1)/E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (Parkin) pathway. Methods: The experiment was divided into four groups: control group, model group, metformin group and BHRS low‑dose group and high‑dose group. Forty male rats were selected as samples and randomly assigned to at least one test group.Finally,there are 18 rats in each group.Except for the control group,the rats within the different teams got a high‑fat diet associate in nursing an intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin to make a type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rat model. The organic chemistry and inflammatory indexes of rats in every cluster were analyzed and compared once four weeks of intragastric administration of comparable reagents to review the therapeutic impact of BHRS on T2DM. In addition, we determined the pathological changes of ductal gland tissue of T2DM rats after treatment,and compared the expression of mitochondrial phagocytosis related proteins in ductal gland tissue of rats in each group.Results:FBG,LDL‑C,TC,TG,MDA,IL‑1,IL‑6,TNF‑,and mitophagy‑related proteins COXIV,P62, VDAC1, and TOM20 were elevated in the model group compared to the control group,while HDL‑C, SOD, GSH‑Px, and mitophagy‑related proteins PINK1, Parkin, and LC3II/I were decreased (P<0.05 or P< 0.01).The expressions of FBG, TC,TG, LDL‑C, MDA,IL‑1,IL‑6, TNF‑, and mitophagy‑related proteins COXIV, P62, VDAC1, and TOM20 were lowered in the BHRS group, while the expressions of HOMA‑, HDL‑C, SOD, GSH‑Px, and mitophagy‑related proteins PINK1, Parkin, and LC3II/I were (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). After therapy with BHRS, hematoxylin‑eosin staining showed that the intensity of pancreatic acinar staining increased, and islet cells became clear boundaries that were, regularly arranged, and with reduced vacuoles reduced. Conclusion: BHRS has a clear therapeutic effect on T2DM,which may be achieved by regulating mitochondrial autophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus; mitophagy; Baihu Renshen decoction; PINK1/Parkin pathway
Highlights
This study will be aimed at investigating the effects of Baihu Renshen decoction(BHRS)on type 2 diabetes rats and on macromolecular enzyme 1(PINK1)/E3 ubiquitin protein ligase(Parkin)pathway.After therapy with BHRS,it has lowered the relevant indicators.Thus,BHRS has a clear therapeutic effect on type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM),which may be achieved by regulating mitochondrial autophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway.
Medical history of objective
BHRS is composed ofGypsum Fibrosum,Rhizoma Anemarrhenae,Panax Ginseng,Glycyrrhiza Uralensis,and japonica rice.BHRS has the effect of clearing heat,replenishing Qi(In traditional Chinese medicine theory,Qi is one of the basic substances that constitute human body and maintain human life activities.)and promoting fluid production in the treatment of T2DM,which was first recorded in Zhang Zhongjing’sTreatise on Typhoid and Miscellaneous Diseases(200–210 C.E.).According to a number of clinical observations,BHRS can reduce body mass index of T2DM patients,improve the metabolism of blood glucose and blood lipid,and effectively reduce blood glucose levels,regulate blood lipids,and reduce oxidative stress.
Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM)pertains to a chronic disease,marked by comparatively low insulin production, which is brought on by a combination of hereditary, environmental, and behavioral factors [1].With the progression of the disease,diabetic patients with T2DM often appear show mitochondrial dysfunction under the action of oxidative stress and chronic inflammation caused by glucolipid toxicity [2, 3].At the same time, under the effect of oxidative stress injury, the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate in the mitochondria of islet β cells is inhibited, the synthesis of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate is inhibited and proton leakage occurs, causing disorder of mitochondrial membrane components, including the respiratory chain, eventually leading to decreased insulin secretion as well as,damage and even apoptosis of islet β cells [4, 5]. The primary mechanisms for mitophagy activation during oxidative stress are protein kinase 1 (PINK1) and E3 ubiquitin‑protein ligase (Parkin) [6,7]. This pathways can regulate mitophagy, remove damaged and redundant mitochondria,maintain mitochondrial homeostasis in cells,improve cell metabolism, reduce the production of reactive oxygen species, reduce oxidative stress injury and lipid accumulation in islet cells, and maintain cell function [8, 9]. It can be seen that improving islet β‑cell function through the PINK1/Parkin pathway is a potential strategy to intervene in the development of T2DM.
Baihu Renshen decoction (BHRS) is composed ofGypsum Fibrosum,Rhizoma Anemarrhenae,Panax Ginseng,Glycyrrhiza Uralensis, and japonica rice. BHRS has the effect of clearing heat, replenishing Qi(In traditional Chinese medicine theory, Qi is one of the basic substances that constitute human body and maintain human life activities.) and promoting fluid production in the treatment of T2DM, which was first recorded in Zhang Zhongjing’sTreatise on Typhoid and Miscellaneous Diseases(200–210 C.E.). According to a number of clinical observations, BHRS can reduce body mass index of T2DM patients,improve the metabolism of blood glucose and blood lipid, and effectively reduce blood glucose levels, regulate blood lipids, and reduce oxidative stress [10, 11]. However, its precise mechanism remains unknown. As a result, this work constructed a T2DM rat model to investigate the mechanism of BHRS in T2DM therapy via modulating mitophagy via the PINK1/Parkin pathway‑mediated mitophagy.
Materials and methods
Materials
High‑fat diet (40% fat, 17.7% sucrose, 17.7% fructose, 9.4% protein);regular diet (59.4% total sugar, 20% protein and 4.8% fat); and metformin hydrochloride tablets (H13021647, 0.5 g/tablet) were purchased from Hebei Tiancheng Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd. (Cangzhou,China); streptozotocin (STZ, S8050, 1 g)and mitochondrial extraction kits (20201229) were purchased from Beijing Soleibao Co., Ltd.; the detection kits for superoxide dismutase (SOD, A001‑1‑1), glutathione peroxidase (GSH‑Px, A003‑1‑1), malondialdehyde (MDA, A005‑1‑1),total cholesterol (TC, A111‑1‑1), triglycerides (TG, A110‑1‑1),high‑density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL‑C, A113‑1‑1) and low‑density lipoprotein (LDL‑C, A112‑1‑1) are from Nanjing Jiancheng Institute of Biotechnology (Nangjing, China); interleukin(IL)‑1β (EK301B), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF‑α, EK306), and IL‑6(EK382) enzyme‑linked immunosorbent assay kits are from Hangzhou Lianke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China); Rrabbit PINK1(DF7742), Parkin (AF0235), P62 (AF5384), LC3II/I (AF5402), COXⅣ(AF5468), VDAC1(DF6140), TOM20 (AF5206), β‑actin (AF7018) and goat anti‑rabbit IgG (S0001) secondary antibodies are from Affinity(San Francisco, CA, USA).
BHRS preparation
Forty specific pathogen‑free Sprague‑Dawley male rats (6–8 weeks,200 ± 20 g) were provided by Beijing Huafukang Biotechnology Co.,Ltd., animal licence number: SCXK (Beijing) 2021‑0031. The feeding conditions are 25°C temperature,50%humidity,12 hours of light and dark cycle, and adequate water and food. The Cangzhou Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital’s Ethics Committee in Hebei Province approved the experiment(CZX2022‑KY‑026).
After one week of adaptive feeding, we randomly selected 8 rats as the control group and gave them balanced diet,while the other 32 rats were fed a high‑sugar and high‑fat diet. After 8 weeks, except for the control group, all rats were given a intraperitoneal injection of STZ 30 mg/kg (dissolved in 0.1 mol/L citrate buffer, pH = 4.5) once. In contrast,rats in the control group were injected with the same amount of STZ or citric acid buffer,and the blood glucose index was measured from the tail vein 72 hours later. The T2DM model was considered successful when blood glucose levels is greater than 16.7 mmol/L.Following modelling, the rats were randomly assigned to four groups,each with eight rats:one for T2DM,one for positive drugs,one for low dose BHRS, and the last for high dose BHRS. The positive drug group was injected with 0.2 g/kg/d metformin hydrochloride, while the control group and T2DM groups were injected with 2 mL saline.According to the body surface area of rats, the BHRS low and high dose groups received 8.8 g/kg/d and 17.6 g/kg/d, respectively(1:6.25). After 4 weeks of continuous gavage, each group’s fasting blood glucose(FBG) was measured on a weekly basis.
FBG detection
Following the modelling, all rats were forbidden to eat for 8 h with free access to water, and use the blood glucose test strip to draw tail blood to calculate FBG.
Detection of serum biochemical indicators
After modeling, all rats were fasted with free access to water for 8 h.The serum was separated from blood extracted from the abdominal aorta.SOD,MDA,GSH‑Px,TC,TG, LDL‑C and HDL‑C were detected in each group. Rats in each group were sacrificed euthanized by spinal dislocation after intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (50 mg/kg).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
After modeling, the serum levels of IL‑1β, TNF‑α, and IL‑6 in each group were detected, and the specific operation methods were described undertaken according to the kit manufacturer’s instructions.
Pathological staining
After modeling, three samples were randomly selected from each group and the pancreas was dissected. A portion of rat pancreas tissue was fixed in formalin solution, embedded in paraffin,and sliced into 3 mm‑thick tissue slices. Hematoxylin‑eosin (HE) staining was then performed. Finally, the histopathological changes were observed under an optical microscope (100×).
Detection of pancreatic tissue and mitochondrial protein PINK1/Parkin pathway-related protein expression
After modeling and administration, four samples were randomly selected from each group. Part of the pancreatic tissue was taken to separate mitochondria in pancreatic the tissue by using a mitochondrial separation kit. After homogenization on ice, it this was centrifuged at 1,000× g for 5 min at 4 °C. After discarding the precipitate, the centrifugation was repeated once,and the supernatant was transferred to a new tube.Finally,the mixture was centrifuged for 10 min at 12,000 g, and the protein supernatant and mitochondria at the bottom of the tube were separated and stored at 80°C.For 30 min,the rat kidney tissue was placed in an ice bath with radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer. The sample was centrifuged for 10 min at 12,000 rpm/min at 4°C,and the supernatant was transferred to a new EP tube.
Pancreatic tissue from rats was obtained and mixed with 150 L of radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer. The sample was centrifuged for 10 min at 4°C at 12,000 rpm/min,and the supernatant was transferred to a new EP tube.The bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Institute of Biotechnology, Nanjing, China)was used to assess the concentration of certain pancreatic tissue or mitochondrial protein. The remaining pancreatic tissue or extracted mitochondrial protein was denatured by boiling water bath,and 20 μg of denatured protein was separated by electrophoresis on 8%–12%SDS‑PAGE gel. The protein was transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane, which was subsequently blocked for 45 min at room temperature with 5%skimmed milk powder,and PINK1,Parkin,LC3 II/I, P62, TOM20, VDAC1, COXIV, and β‑actin primary antibody(dilution ratios were 1:1,000 (PINK1, Parkin, LC3, and P62), 1:2,000(TOM20, VDAC1, and COXIV), and 1:3,000 (β‑actin )) were,incubated overnight at 4 °C. The membrane was washed three times with TBST (TBS‑Tween), and the corresponding secondary antibody(dilution ratio was 1:4,000) was added for 1 h. The membrane was rinsed three times with TBST before adding the matching secondary antibody (dilution ratio was 1:4,000) for 1 hour. To improve the chemiluminescence kit, the membrane was cleaned with TBST. The quantitative expression of each analytic programme was analysed using Image Pro Plus 6.0 software. PINK1, Parkin, LC3, P62, and TOM20 were compared to better understand mitophagy‑related protein expression in mitochondrial proteins. TOM20, VDAC1, and COXIV were compared to β‑actin to better understand mitochondrial number‑related protein expression in pancreatic tissue proteins.
Statistical processing
SPSS 20.0 software system was used for applied math analysis. The information was drawn as x ± s. unidirectional Analysis of Variance was used for comparisons between teams, and therefore the least significance difference t‑test was used for cluster comparisons. The check level is 0.05.
Results
Changes of FBG in T2DM rats after modeling
When contrasted to the control group, the model group’s blood glucose level was significantly higher (P< 0.01). At the same time,the FBG of rats in the positive drug group (P< 0.05) and the BHRS high dose group (P< 0.01) decreased (P> 0.05) compared to the model group. Figure 1 depicts the results.
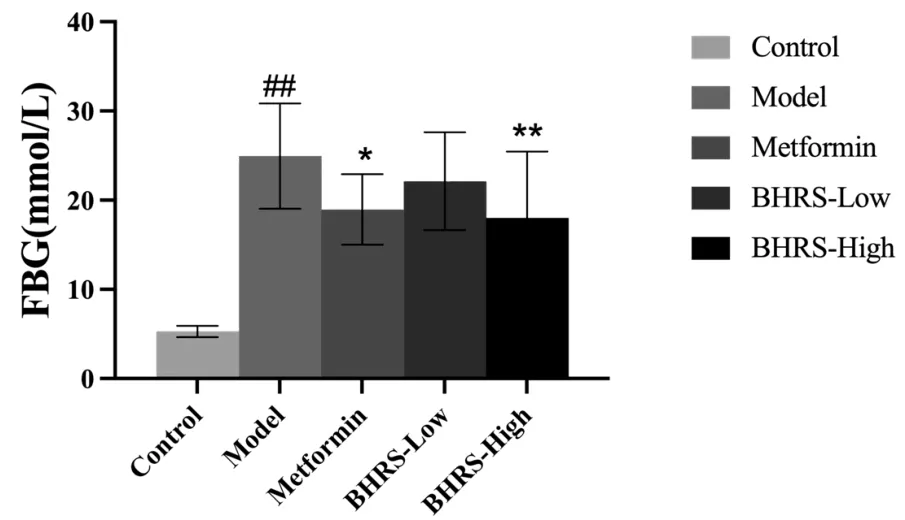
Figure 1 BHRS impact on FBG in T2DM model rats. #, P< 0.05 in contrast to the control group; ##, P < 0.01 in contrast to the control group; *, P < 0.05 in contrast to the model group; **, P < 0.01 in contrast to the model group. BHRS, Baihu Renshen decoction; T2DM,type 2 diabetes mellitus; FBG, fasting blood glucose.
Changes of serum TC, TG, LDL-C, and HDL-C levels in T2DM rats after modeling
When contrasted to the control group, the model group’s levels of TC,TG,and LDL‑C were significantly higher,while the level of HDL‑C was significantly lower (allP< 0.01). In the positive drug group and the high‑dose group of BHRS, TC (allP< 0.05), TG (allP< 0.01), and LDL‑C levels(allP<0.01)were dramatically decreased,while HDL‑C levels were significantly elevated (allP< 0.05). The LDL‑C level of the rats in the low‑dose group of BHRS was much lower than the model group, while the HDL‑C level was significantly higher (P<0.01). Figure 2 depicts the results.

Figure 2 BHRS impact on TC,TG,LDL-C and HDL-C in T2DM model rats.##,P<0.01 in contrast to the control group;*,P<0.05 in contrast to the model group; **, P < 0.01 in contrast to the model group. BHRS, Baihu Renshen decoction; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; HDL‑C, high‑density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL‑C, low‑density lipoprotein.
Changes of SOD, MDA, and GSH-Px levels in the serum of T2DM rats after modeling
SOD and GSH‑Px levels were significantly lower in the model group than in the control group, while MDA levels were significantly higher(allP<0.01).SOD and GSH‑Px levels were significantly higher in the positive drug and high‑dose groups than in the model group, while MDA levels were significantly lower (allP< 0.05). Figure 3 depicts the results.
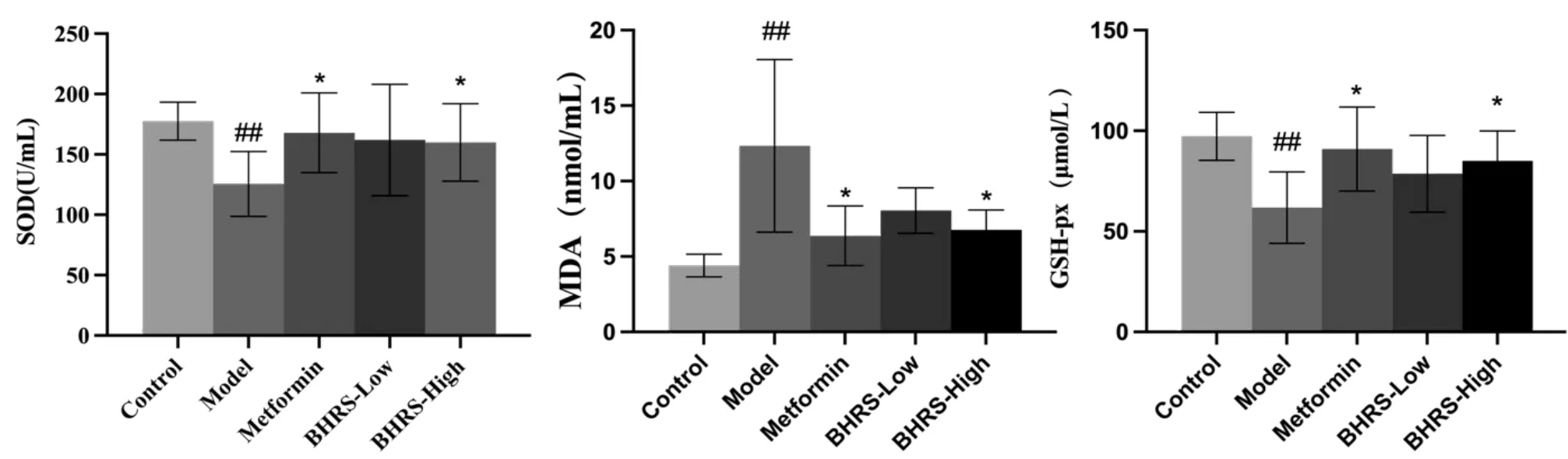
Figure 3 BHRS impact on SOD,MDA and GSH-Px in T2DM model rats.##,P<0.01 in contrast to the control group;*,P<0.05 in contrast to the model group; **, P < 0.01 in contrast to the model group. BHRS, Baihu Renshen decoction; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GSH‑Px, glutathione peroxidase; MDA, malondialdehyde.
Changes of serum IL-1β,IL-6,and TNF-α levels in T2DM rats after modeling
When contrasted to the control group, the model group had significantly higher levels of IL‑1, IL‑6, and TNF‑α (allP<0.01). The levels of IL‑1, IL‑6, and TNF‑α in the positive drug group and the BHRS high‑dose groups were considerably lower than in the model group (allP< 0.05). Figure 4 depicts the results.

Figure 4 BHRS impact on IL-1β,IL-6 and TNF-α in T2DM model rats.##, P < 0.01 in contrast to the control group; *,P <0.05 in contrast to the model group; **, P < 0.01 in contrast to the model group. BHRS, Baihu Renshen decoction; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; IL, interleukin;TNF‑α, tumor necrosis factor α.
Pathological changes of pancreatic tissue in T2DM rats after modeling
HE staining results(Figure 5)showed that the acinar staining intensity of the model group decreased, the boundary of islet β cells was unclear, and vacuole changes appeared. After the intervention of metformin and BHRS low‑dose and high‑dose groups, it was found that the staining intensity of acinar cells increased, the lipid droplet vacuoles of islet β cells decreased, and the boundaries became clear and arranged regularly.
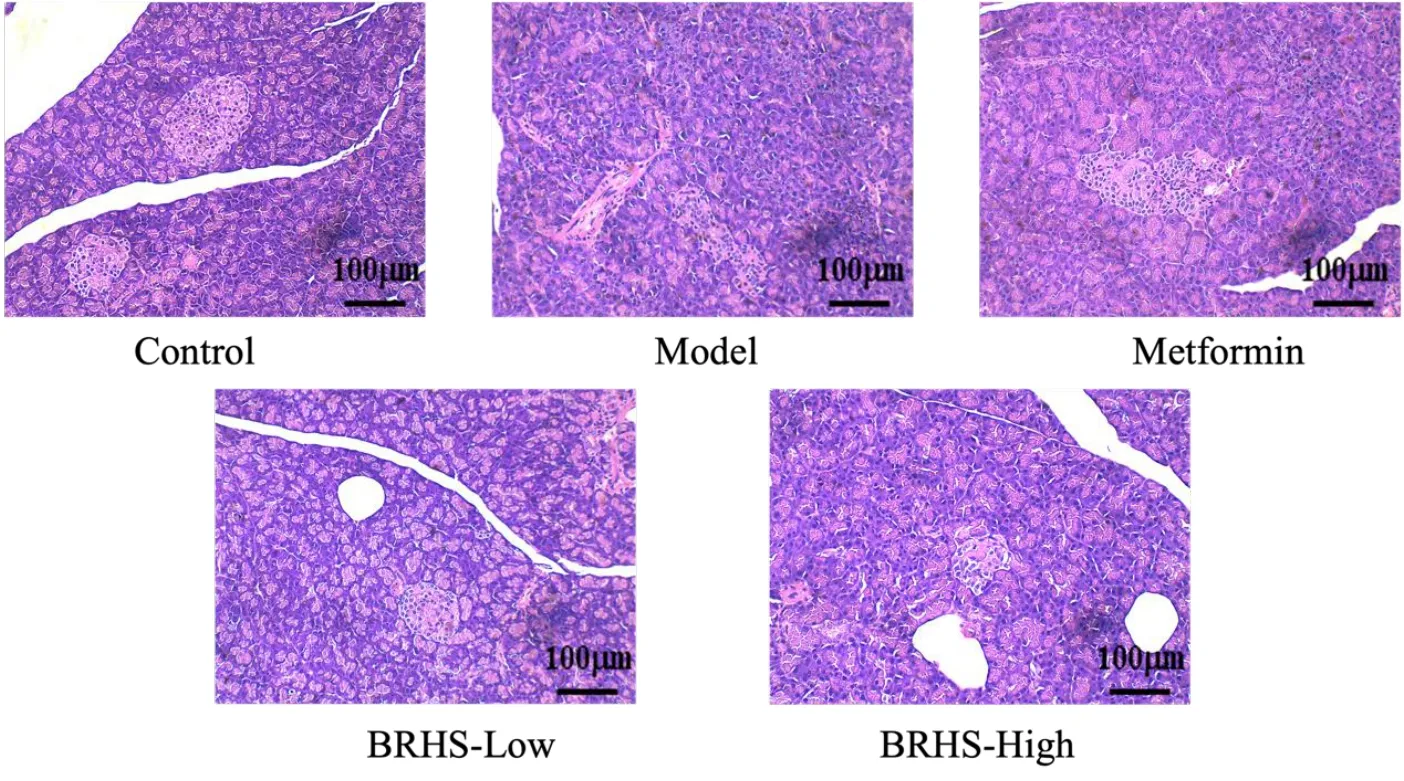
Figure 5 BHRS impact on pancreatic tissue in T2DM model rats. BHRS, Baihu Renshen decoction; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Expression changes of pancreatic mitochondrial proteins PINK1,Parkin, LC3, P62, and pancreatic tissue proteins TOM20, VDAC1,and COXIV in T2DM rats after modeling
The expression of PINK1, Parkin, and LC3 II/I in the pancreatic mitochondrial protein of the model group was significantly lower than that of the control group,while the expression of P62 was significantly higher (allP< 0.01). The protein expression of PINK1, Parkin, and LC3II/I was much higher in the positive drug group than it was in the model group, as well as in the low‑dose and high‑dose BHRS groups(allP< 0.01). P62 protein expression was considerably lower in the positive drug group and the high‑dose BHRS group compared to the model group (P< 0.01). Furthermore, when compared to the control group, the protein expression of TOM20, VDAC1, and COXIV in the model group’s pancreatic tissue increased (allP< 0.01).TOM20 and VDAC1 protein expression levels were lower in the positive drug group, as well as the low‑dose and high‑dose BHRS groups (allP< 0.01). COXIV protein expression was lower in the positive drug group and the BHRS high‑dose group compared to the model group (P< 0.01). Figure 6 depicts the results.

Figure 6 BHRS impact on the relative expression levels of PINK1,Parkin, LC3II/I, P62,TOM20,VDAC1 and COXIV in pancreatic tissue of T2DM model rats. Control group, model group, metformin group, BHRS low‑dose group, BHRS high‑dose group (n = 8 for each group). (A) The Western blot results of PINK1, Parkin, LC3II/I, P62, TOM20, VDAC1 and COXIV. (B) The quantified gray value analysis results of PINK1, Parkin,LC3II/I,P62,TOM20,VDAC1 and COXIV Western blot.##,P<0.01 in contrast to the control group;**,P<0.01 in contrast to the model group.BHRS, Baihu Renshen decoction; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Discussion
The main manifestations of T2DM are dry mouth, polydipsia, hunger,and emaciation. The key pathogenesis is the loss of yin and fluid, and excessive dryness and heat.Plain Questions·Qi Disease Theory(221 B.C.E.; unknown author) proposed that the pathogenesis of diabetes is“several sweet and fat also, fat makes people hot, sweet people full”.BHRS is derived from the classic“Treatise on Typhoid and Miscellaneous Diseases” of traditional Chinese medicine. It is set up after vomiting and purgation of typhoid fever. It can also treat the symptoms of exterior syndrome resolved and internal heat injury. This prescription is composed of BHRS plus ginseng three two, and the meaning purpose of ginseng is to tonify Qi and generate fluid. The whole prescription plays a role of in clearing heat, tonifying Qi, and generating fluid. Throughout the course of the development of diabetes T2DM, its development is a gradual process, and its symptoms causes begin with“internal heat” and the heat is consumed present for a long time. BHRS heat and Qi and Yin (In traditional Chinese medicine theory, Qi refers to energy and Yin refers to matter,the imbalance of Qi and Yin can lead to the development of diseases.)simultaneously, so thus, it can be used as the a main treatment of diabetes for T2DM.
In this study, the therapeutic effect of BHRS on T2DM model rats was then investigated further by detecting and evaluating important biochemical signs.In comparison to the control group,the TC,TG,and LDL‑C values in the T2DM group suggested that these rats had evident hyperlipidemia. Islet cells in pancreatic tissue obviously have showed atrophic blurred boundaries, islet cell damage, the a reduced number of reducedand sparse distribution, and vacuolar degeneration. The above findings are consistent with T2DM pathological manifestations[12, 13]. In addition, it was found that the levels of the inflammatory indexes TNF‑α, IL‑1β, and IL‑6 decreased, and the pathological condition of the pancreatic tissue was improved by HE staining,suggesting that BHRS had a therapeutic effect on T2DM, and the high dose group was showed the most obvious improvement.
One of the key elements in the emergence of T2DM is oxidative stress [14]. According to research, T2DM is associated with abnormalities in glucose and lipid metabolism, which produce a lot of reactive oxygen species, harm mitochondrial function, and cause oxidative stress [15]. We found that BHRS might increase the activity of SOD and GSH‑Px while lowering MDA levels within the blood serum of T2DM rats. Inhibitor enzymes SOD and GSH‑Px show the extent of inhibitor capability [16]. To keep the equilibrium of free radicals and defend the organism from superoxide anions, SOD is an intracellular oxygen‑free radical scavenger that catalyzes the conversion of O2to O2and H2O2[17]. GSH‑Px could be a peroxidase‑degrading accelerator that’s thick within the body. It can catalyze the creation of H2O2by SOD, hence lowering oxidative damage to cells [18]. After oxidative stress occurs, a large number of reactive oxygen species accumulated in vivo, resulting in lipid peroxidation to form MDA,MDA levels are often accustomed infer the extent of oxidative harm in cells [19, 20].
The importance of pro‑inflammatory cytokines including IL‑6,IL‑1β, and TNF‑α. The production of pro‑inflammatory factors, as the key risk factors of an inflammatory islet inflammatory microenvironment, aggravates the induction of insulin resistance, and the metabolic stress of T2DM can stimulate islet cells to produce more inflammatory factors, resulting in a vicious cycle of T2DM [21]. Our found that BHRS could lower serum levels of IL‑6,IL‑1β,and TNF‑α in T2DM model rats. Insulin activity can be reduced by interfering with insulin receptor signaling and impairing β‑cell function, resulting in insulin resistance. This can also be accomplished by inhibiting the activity of insulin receptor signal downstream fragments, thereby inhibiting glycogen synthesis and promoting the development of T2DM [22]. IL‑1β is one of the main pro‑inflammatory factors produced by macrophages,which can activate the NF‑κB pathway and other inflammatory mediators, thus, starting the self‑amplification of inflammatory cells [23]. TNF‑α affects blood glucose regulation metabolism by increasing β‑cell apoptosis while lowering glucose‑stimulated insulin secretion [24, 25].
Recent studies have shown that PINK1/Parkin‑mediated mitophagy is inseparable from T2DM. When the internal environment of hyperglycemia causes oxidative stress to damage mitochondria, the mitochondrial membrane potential decreases, and the outer membrane transporter (TOM) on the mitochondrial outer membrane stops transporting PINK1, causing PINK1 to accumulate on the mitochondrial outer membrane and bind to TOM20. TOM20, as a stable component of the outer membrane of mitochondria, can determine the number of mitochondria by observing changes in its protein [26]. With the self‑ubiquitination of PINK1 and the recruitment of Parkin, the mitochondrial outer membrane is further ubiquitinated, marking that the mitophagy‑activated LC3I begins to flow to LC3II [27] and participates in the formation of autophagic membranes. At the same time, after ubiquitination of mitochondrial proteins, they accumulate to double‑layer autophagic vesicles under the synergistic action of various autophagy receptors regulatory proteins, such as LC3II and P62. After encapsulation and fusion,mitochondria are degraded by hydrolases in mitochondrial autophagosomes[28, 29].
Our present study found that the expression of PINK/Parkin and LC3II/LC3I increased after BHRS intervention, marking the activation of autophagy. Since the damaged mitochondria were degraded by phagocytosis, the expression of the mitophagy substrates P62 and TOM20 decreased accordingly. It was indicated that BHRS can activate mitophagy, repair mitochondrial function, and promote lipid metabolism, in which mitochondria are deposited in cells in islet β cells and,improve the energy metabolism and function of islet β cells,increasinge insulin release to improve glucose and lipid metabolism in the body, and thus, reduce the body’s oxidative stress response and cellular inflammatory damage caused by glycolipid toxicity [30].VDAC1 and COXIV are located on the outer membrane and inner membranes of mitochondria, respectively. By observing their expression, the effect of mitophagy on the number of mitochondria can be reflected. Further other studies have found that mitophagy can reduce the apoptosis of the mitochondrial pathway of islet β cells by improving oxidative stress[31].The outer mitochondrial membrane is where VDAC1 is found, and it functions to lower mitochondrial membrane potential and promote COXIV release [32, 33]. COXIV is a mitochondrial pro‑apoptotic protein that activates mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway, which removes damaged mitochondria,reduces VDAC1 expression and COXIV release, and inhibits apoptosis of the mitochondrial pathway of pancreatic β cells from being over‑initiated [34].Therefore, this study we speculates that BHRS can inhibit the mitochondrial pathway apoptosis of islet β cells by activating mitophagy and, reducing the expression of VDAC1, and the release of COXIV.
Therefore, our findings demonstrated that BHRS may reduce mitochondrial damage and the inflammatory response by encouraging PINK1/Parkin‑mediated mitophagy in pancreatic tissue. These findings supported the therapeutic effect of BHRS on T2DM.
 Traditional Medicine Research2023年5期
Traditional Medicine Research2023年5期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Theanine combined with cisplatin inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of TNBC cells through Akt signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology and verification experiment-based prediction of active components and potential targets of Alpiniae Oxyphyllae Fructus-Saposhnikoviae Radix(Yizhiren-Fangfeng)for treatment of diabetic kidney disease
- Comparison of polysaccharides from 10 species of genera Paris,Trillium,Aspidistra,and Polygonatum
- Research progress of artesunate in diabetes and its complications
- Exploring the compatibility theory of traditional Chinese medicine formulae: the disassembled prescriptions study
