三七叶、人参叶和西洋参叶皂苷类成分的研究
张兰兰,高文远,周水平,朱永宏,宋兆辉,黄芝娟
1天津大学药学院,天津300072;2天津天士力集团研究院中药所,天津300410
三七叶、人参叶和西洋参叶皂苷类成分的研究
张兰兰1,2,高文远1*,周水平2,朱永宏2,宋兆辉2,黄芝娟2
1天津大学药学院,天津300072;2天津天士力集团研究院中药所,天津300410
三七叶、人参叶和西洋参叶其皂苷类成分相近,但专属性成分各异,皂苷类成分的分布比例也各不相同。本文建立了HPLC-UV法测定上述皂苷成分的方法,经过方法学考察,各种皂苷成分精密度好、加样回收率高,方法可靠。11种皂苷成分总含量顺序为:西洋参叶>人参叶>三七叶;二醇组皂苷成分含量:西洋参叶>三七叶>人参叶;三醇组皂苷成分含量:人参叶>西洋参叶>三七叶。西洋参叶中二醇组皂苷和人参叶中三醇组皂苷含量明显高于其他。西洋参叶中人参皂苷Rb3和Rd的含量之和占11种皂苷成分的60%以上。鉴于其中人参皂苷的高含量,三七叶、人参叶和西洋参叶应该作为皂苷来源得到充分利用;不同的皂苷成分有不同的药理活性,应基于它们的皂苷组成和比例选择性进行研究和开发。
三七;人参;西洋参;叶;人参皂苷
Instruction
Panax ginseng,P.notoginseng and P.quinquefolius are valuable agriculture commodity used in many traditional medicinal therapies.In the past years,much attention has been paid to analyze the active saponins in the rootof P.ginseng,P.notoginseng and P.quinquefolius.For example,P.notoginseng has been used as creditable drug for the treatment of haemoptysis,haemostatic and haematoma in China for more than 400 years.Modern pharmacological studies have shown that P.notoginseng has anticarcinogenic and hepatoprotective activities,as well as protective effects on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems[1].P.ginseng has been a tonic,sedative,anti-fatigue drug,and also has anti-diabetic and anti-tumor activities[2].P.quinquefolius,which is apopular herb for patients suffering from nervous system and cardiovascular,is also a dietary supplement.Its extract has been included as a component in many supplement formulations[3].Drammarane triterpene saponins are considered as the major bioactive constitutes in Panax genus.According to the different aglycone,these neutral saponins were classified into two groups:protopanaxatriol saponins(PTS,such as ginsenoside Re,Rg1,Rf,Rh1,and notoginsenosideR1)and protopanaxadiol saponins(PDS,such as ginsenoside Rc,Rd,Rb1,Rb2,Rb3).However,the biological activities of ginsenosides are related with their structures[4].Therefore,it is valuable to separate different types of saponins for further pharmacological research.Pharmacological studies suggested that ginsenoside Rb3may contribute to improve learning and memory[5],and ginsenoside Rg3and Rh2showed anticancer effects[6].However,ginsenoside Rg1,Rb1,Re showed strong protective effects on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems[7].
Nowadays,several studies have demonstrated that the leaves of P.ginseng,P.notoginseng and P.quinquefolius also contain ginsenosides.Liu et al.reported the separation of ginsenoside Rb3and Rc from extracts of leaves of P.notoginseng[8].Shi et al.compared the ginsenoside content of the leaves with the root of P.ginseng and investigated their changes with age[9].Qu et al.studied on ginsenosides in different parts and ages of P.quinquefolius.In recent years,their leaves extract have been frequently used as food additives and raw materials of healthy food[10].Therefore,more systematic studies and comparisons on these Panax leaves become necessary,which will provide more data and information in the field of food and medicine.
In the recent years,the macroporous resins have been extensively applied to separate and purify the bioactive components of herbs[11,12].In this paper,we used the macroporous resins D101to purify and prepare the ginsenoside extract.As for the analytical method,HPLCUV,which uses acetonitrile and water as elution solvents and measured the absorbance at the wavelength of 203 nm,is a general method to determine the content of ginsensosides,because of its good linear and precision.
Experiment
Materials and instruments
The standards of ginsenoside Rg1,Re,Rb1,Rb2,Rb3,Rc,Rd,Rh2,Rg3,Rfand notoginsenoside R1were purchased from Chinese Medical and Biological Products Institute(Beijing China).Methanol and acetonitrile were products of Merck.The deionized water was purified by Milli-Q purification system(Millipore Bedford,USA).Macroreticular resins D101were products of Tianjin Nankai Haiguang Chemicals Co.,Ltd.All the other reagents were of analytical grade.Agillent 1100 liquid chromatography(Agilent Technologies,USA)equipped with quaternary gradient pump was used to separate the ginsenosides,UV detector coupled with a Chromatograph Workstation was used for detecting the ginsenosides.The fresh leaves of P.ginseng,P.notoginseng,P.quinquefolius materials were harvested in fall,and P.notoginseng leaves obtained from Wenshan in Yunnan Province,P.ginseng leaves and P.quinquefolius leaves were obtained from Jingyu in Jilin Province.The leaves were dried at 38℃in ventilated drier.The dried leaves were crushed into small pieces of sizes of 1-2 cm.
Sample preparation
Heat reflux extraction
Samples of the leaves(1 kg)was mixed with 12 kg water in a 20 L extractor,heated in 100℃for 2 h.The extraction process repeated for 3 times,with the extract filtrated each time,then all the extracts were combined and cooled down to room temperature.
Macroreticular resins separation and purification
The 800 g macroreticular resins,which were pretreated,were placed into a 10 cm id glass column,and then washed several times with deionized water.The extract solution was flowed through the column at the rate of 0.5 BV/h.After adsorption equilibrium,the adsorbents were flushed with water for 6 BV at 1BV/h,70%aqueous ethanol for 7 BV at 1 BV/h.All the 70%aqueous ethanol were collected and condensed to 1000 mL,then 3000 mL 95%aqueous ethanol was added,placed overnight,filtered and evaporated by a rotary evaporator at 50℃.The dried residue was sealed to preserve untilused.
Analytical methods
The separation was carried out on a Kinetex-C18column (100×4.6 mm,2.6 μm,phenomenex,at 30℃).For HPLC analysis,a 20 μL sample was injected into the column and eluted at 30℃at a constant flow rate of 1.0 mL/min.Acetonitrile(A)and 0.05%Phosphoric acid aqueous solution(B)with a gradient elution:0-15 min,19%A,81%B;15-30 min,19%-31%A,81%-69%B;30-50 min,31%-53%A,69%-47%B;50-60 min,53%-70%A,47%-30%B.Then the elution solvent was kept at 19%A and 81%B for 10 min at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min before analyzing the next sample.
Notoginsenoside R1(0.5075 mg/mL),ginsenoside Rg1(0.5156 mg/mL),Re(0.5015 mg/mL),Rb1(0.5037mg/mL),Rb2(0.5014mg/mL),Rb3(0.5116mg/mL),Rc(0.4975mg/mL),Rd (0.5125mg/mL),Rh2(0.5081mg/mL),Rg3(0.5103 mg/mL),and Rf(0.5062 mg/mL)mixed standard stork solution were prepared in methanol.A series of standard operating solution of different concentrations were obtained by diluting the mixed standard stock solution.The concentrations of these compounds in the samples were calculated according to the regressionparametersderivedfromthestandard curves.
Results
Evaluation of macroreticular resins for sample preparation method
Macroreticular resins adsorption process for ginsenosides have been reported many times.In Fig.1-3,elution curve was depicted to show the effect of 70%ethanol on the desorption behavior.The elution curves
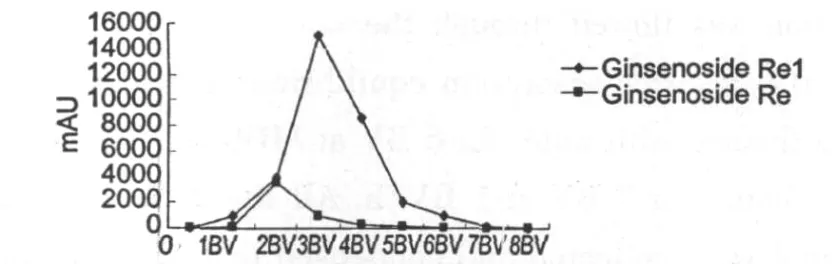
Fig.1 The elution curve of P.ginseng main ginsenosides from D101desorpted by 70%ethanol.Note:Ywas the peak area and Xwas elution volume.6BVmeans that elution volume was six times of the column volume.The same below.
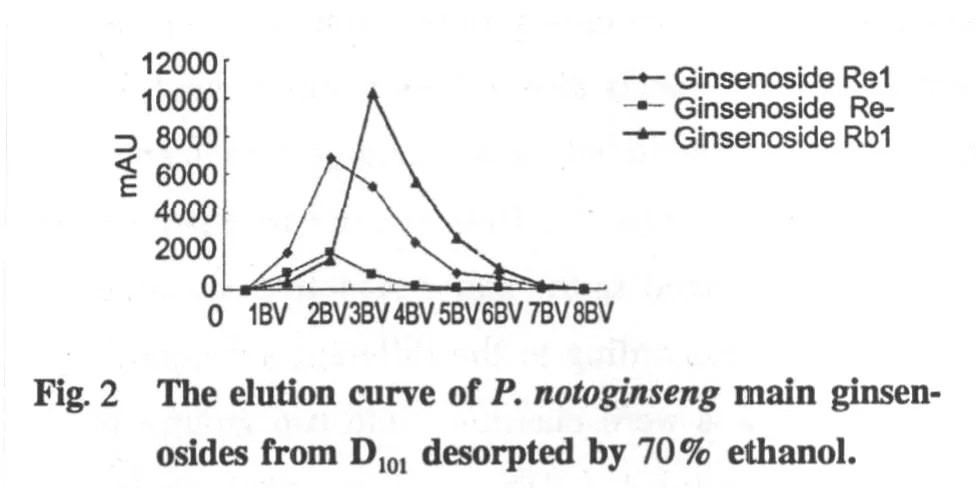

showed that the column was successfully washed by 7BV 70%ethanol.The order of desorption efficiency was Ginsenoside Re,-R1>GinsenosideRg1>Ginsenoside Rb1>Ginsenoside Rb3,-Rd.
Evaluation of the analytical methods
The calibration curves and precision were shown in Table 1.All the correlation coefficients exceeded 0.99,suggesting good linearity.Precision was obtained by six parallel experiments.The accuracy of this method was evaluated by the recovery experiment.The recoveries rate were calculated by the following formula:recovery (%)=(found amount-original amount)/added amount×100%.50 mg of the extracts of P.quinquefolius leaves,P.notoginseng leaves,P.ginseng leaves were treated,respectively,as described in Sections 2.3.to get the original amounts of these ginsenosides.Then the fixed quantities of 11 ginsenosides were added into 25 mg of the extract of leaves and analyzed in the same way.All the data were the average values obtained by six parallel experiments.The recovery rates of the 11 ginsenosides were listed in Table1.The recoveries are between 96.95%and 104.17%.The relative standard deviations(RSD)were no more than 5%.These results demonstrated that the method proposed in this paper was accurate for the quantitative determination of the 11 ginsenosides in samples.The standards and typical sample chromatograms were shown in Fig.4.
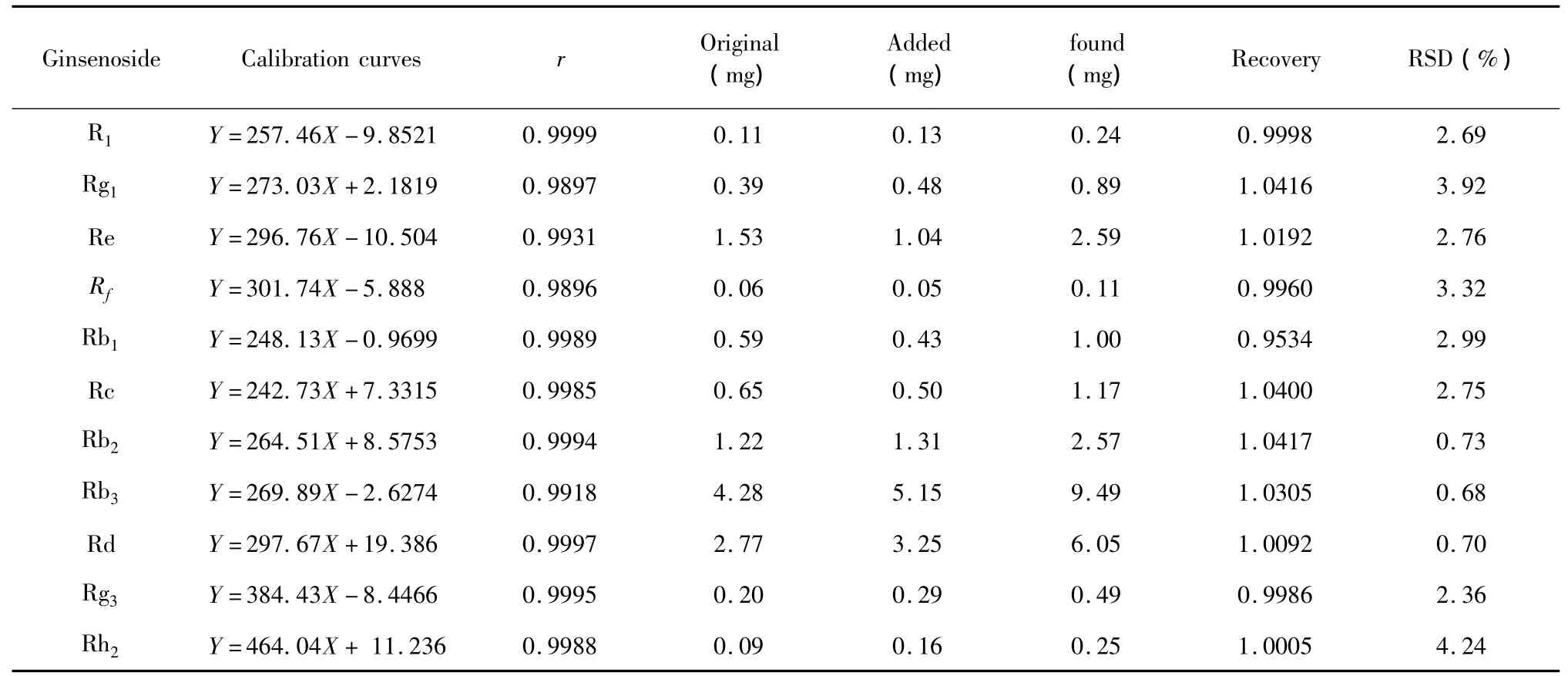
Table 1 The calibration curves and recovery of ginsenosides determined by standard addition method.
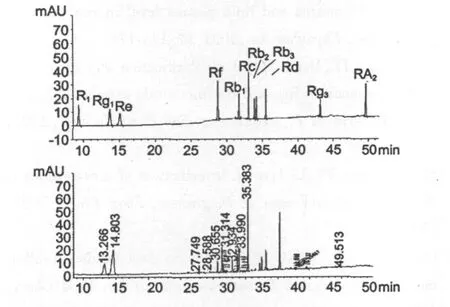
Fig.4 The standards(A)and typical sample(B) chromatograms.
Ginsenoside contents in the leaves of different ginseng species
The ginsenoside contents in the leaves of different ginseng species were shown in Table 2,which revealed that the total content of 11 ginsenosides followed this order:P.quinquefolius leaves>P.ginseng leaves>P.notoginseng leaves.The contents of protopanaxadiol saponins(Rb1,Rb2,Rb3,Rc,Rd,Rg3,Rh2)ranked as:P.quinquefolius leaves>P.notoginseng leaves>P.ginseng leaves,The content of protopanaxatriol saponins(R1,Rg1,Re,Rf)ranked as:P.ginseng leaves>P.quinquefolius leaves>P.notoginseng leaves.Ginsenosides Rb3and Rd were the main constituents of P.quinquefolius leaves.The total contents Ginsenoside Rb3and Rd accounted for above 60%of total the total amount of the 11 ginsenoside in P.quinquefolius leaves.Ginsenoside Rg1and Re were the main constituents of P.ginseng leaves.The total contents of Ginsenoside Rg1and Re accounted for above 58%of the total amount of 11 ginsenoside in P.gingseng leaves.As for the individual ginsenoside,Ginsenoside Rb3was the dominant component in P.quinquefolius leaves and P.notoginseng leaves.Ginsenoside Re was dominant component in P.ginseng.The content of ginsenoside Rb3in P.quinquefolius leaves is more than 48 times in P.ginseng leaves,and more than 3 times in P.notoginseng leaves.Ginsenoside Rd was of similar amount in P.notoginseng leaves and P.ginseng leaves,however,the amount in P.quinquefolius leaves was 2 times higher.Ginsenoside Rf,the chemical marker of P.ginseng was also detected in P.ginseng leaves,but not found in the two others.Only trace amount of ginsenoside Rh2was found in P.quinquefolius leaves,and notoginsenoside R1was undetectable in P.gingseng leaves and P.quinquefolius leaves.

Table 2 Contents of ginsenosides in the leaves of different ginseng Species(mg·g-1)
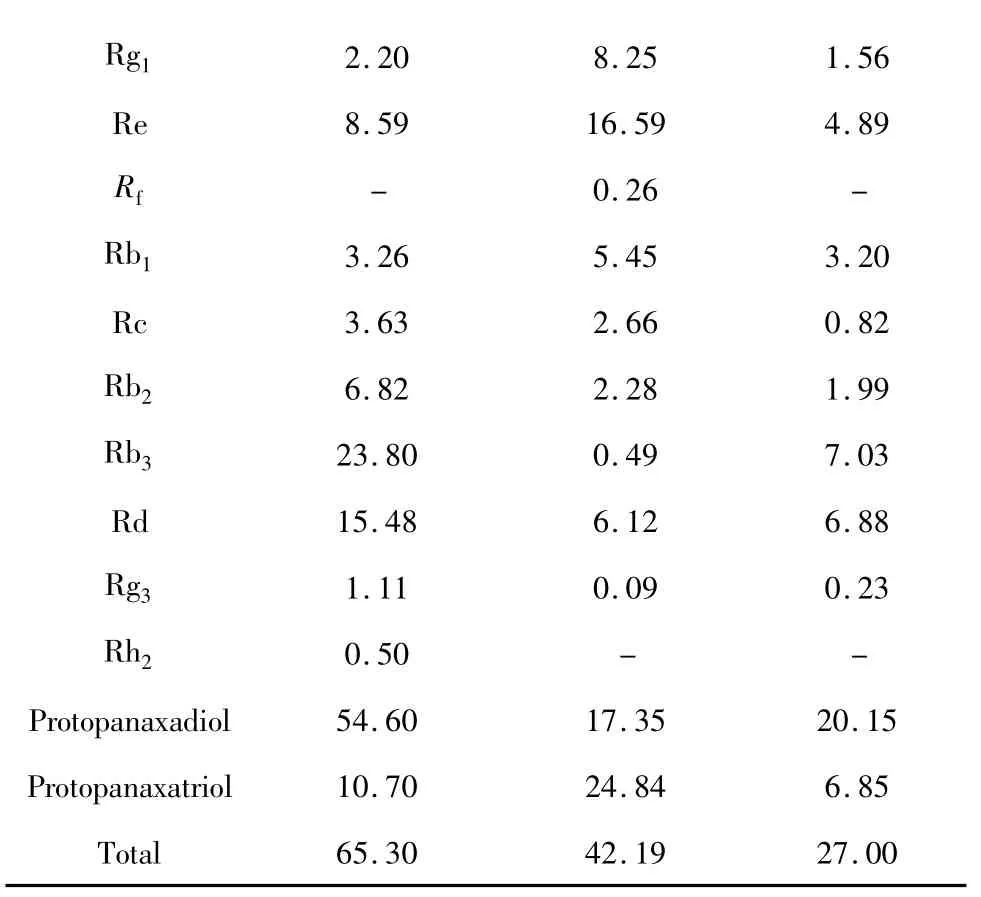
Rg12.208.251.56 Re8.5916.594.89 Rf-0.26-Rb13.265.453.20 Rc3.632.660.82 Rb26.822.281.99 Rb323.800.497.03 Rd15.486.126.88 Rg31.110.090.23 Rh20.50--Protopanaxadiol54.6017.3520.15 Protopanaxatriol10.7024.846.85 Total65.3042.1927.00
Conclusion and Discussion
The results revealed that not only the total saponins content were different among different ginseng species leaves,but also the proportions of individual ginsenoside were different.The result was similar with other reports[13].
Our study indicated that P.quinquefolius leaves and P.notoginseng leaves were good sources of protopanaxadiol saponins,especially ginsenoside Rb3and Rd,and P.ginseng leaves was good sources of protopanaxatriol saponins,especially ginsenoside Rg1and Re.
Due to the the high content of ginsenosides in the leaves of different ginseng species,the leaves should be throughtly used as a new ginsenoside supplier.Different ginsenosides have different pharmacological effects,so we can perform the extraction,separation and purification based on the content differences in leaves of different ginseng species.
1Konoshima M,Takasaki H,Tokuda.Anti-carcinogenic activity of the roots of naxnotoginseng II.Biol Pharm Bull,1999,22:1150-1152.
2Shin YW,Bae EA,Kim DH.Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg5and its metabolite ginsenoside Rh3in an oxazolone-induced mouse chronic dermatitis model.Arch Pharm Res,2006,29:685-690.
3Assinewe VA,Baum BR,Gagnon D,et al.Phytochemistry of wild populations of Panax quinquefolius L.(North P.quinquefolius).J Agric Food Chem,2003,51:4549-4553.
4Sun H,Yang Z,Ye Y.Structure and biological activity of protopanaxatriol-type saponins from the roots of P.notoginseng.Int Immunopharmacol,2006,6:14-25.
5Zou K,Zhu S,Meselhy MR,et al.Dammarane-type saponins from Panax japonicus and their neurite outgrowth activity in SK-N-SH cells.J Nat Prod,2002,65:1288-1292.
6Lee Y,Jin Y,Lim W,et al.A ginsenoside-Rh1,a component of ginseng saponin,activates estrogen receptor in human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol,2003,84:463-468.
7Cicero AF,Vitale G,Savino G,et al.P.notoginseng(Burk.) effects on fibrinogen and lipid plasma level in rats fed on a high-fat diet.Phytother Res,2003,17:174-178.
8Liu C,Han JY,Duan YQ,et al.Purification and quantification of ginsenoside Rb3and Rc from crude extracts of caudexes and leaves of P.notoginseng.Sep Purif Technol,2007,54:198-203.
9Shi W,Wang YT,Li J,et al.Investigation of ginsenosides of different parts and ages of P.ginseng.Food Chem,2007,102:664-668.
10 Qu CL,Bai YP,Jin XQ,et al.Study on ginsenosides in different parts and ages of Panax quinquefolius L..Food Chem,2009,115:340-346.
11 Wang CZ,Wu JA,McEntee E,et al.Saponins composition in P.quinquefolius leaf and berry assayed by high performance liquid chromatography.J Agr Food Chem,2006,54:2261-2266.
12 Zhao Y,Chen B,Yao SZ.Separation of 20(S)-protopanaxdiol type ginsenosides and 20(S)-protopanaxtriol type ginsenosides with the help of macroporous resin adsorption and microwave assisted desorption.Sep Purif Technol,2007,52: 533-538.
13 Fuzzati N.Analysis methods of ginsenosides.J Chromatogr B,2004,812:119-133.
Ginsenosides in Leaves of Panax notoginseng,P.ginseng and P.quinquefolius
ZHANG Lan-lan1,2,GAO Wen-yuan1*,ZHOU Shui-ping2,ZHU Yong-hong2,SONG Zhao-hui2,HUANG Zhi-juan21College of Pharmaceutical&Biotechnology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China;2Modern TCM R&D Institute,Tianjin Tasly Group Co.Ltd.,Tianjin 300410,China
Leaves of Panax notoginseng,P.ginseng and P.quinquefolius have similar saponin components but with different exclusive components.In this work,the contents of saponins in the leaves of Panax notoginseng,P.ginseng and P.quinquefolius were determined with reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography.The chromatographic separation was achieved by using a Kinetex-C18column(100×4.6 mm,2.6 μm,phenomenex,at 30℃).Eleven compounds were separated with a gradient elution and detected at 203 nm.The results showed that the order of total content of saponins,protopanaxadiol saponins and protopanaxatriol saponins in three kinds of leaves was P.quinquefolius>P.ginseng>P.notoginseng,P.quinquefolius>P.notoginseng>P.ginseng,and P.ginseng>P.quinquefolius>P.notoginseng,respectively.The content of protopanaxadiol saponins in the leaves of P.quinquefolius and the content of protopanaxatriol saponins in the leaves of P.ginseng obviously were higher than those in others.And the total content of Ginsenosides Rb3and Rd was accounted for over 60%of the total 11 ginsenosides in P.quinquefolius leaves.Conclusively,the leaves of Panax notoginseng,P.ginseng and P.quinquefolius should be well used as a wonderful source for saponins due to their high contents.In addition,all the three kinds of saponins should be exploited on the basis of their contents and compositions.
Panax notoginseng;P.ginseng;P.quinquefolius;leaves;ginsenoside
January 6,2010;Accepted June 12,2010
book=2011,ebook=1
R284.1
A
1001-6880(2011)06-1064-05
*Corresponding author Tel:86-22-87401895;E-mail:pharmgao@tju.edu.cn

