Periostin与血管支架内再狭窄关系的研究进展
魏本,郭富强
(1.泸州医学院临床学院,四川 泸州 646000;2.四川省医学科学院,四川省人民医院神经内科,四川 成都 610072)
Periostin与血管支架内再狭窄关系的研究进展
魏本1,郭富强2△
(1.泸州医学院临床学院,四川 泸州 646000;2.四川省医学科学院,四川省人民医院神经内科,四川 成都 610072)
Periostin是一种近年发现的分泌型可溶解性细胞间基质蛋白,可促进血管平滑肌细胞增殖并合成基质蛋白,导致新生内膜的形成,进而使损伤血管的管腔变小。血管再狭窄是血管成形术及支架置入术的主要不良反应之一,其以新生内膜形成为特征,是一个涉及多种能分泌细胞因子及生长因子的细胞参与并引起血管局部炎症反应和增殖的病理过程。Periostin参与血管支架内再狭窄的形成可能与平滑肌细胞相互作用以及其它机制有关,其分子机制需进一步研究。
Periostin;血管内再狭窄;血管内支架置入术;血管成形术
脑卒中作为发病率居首的人类疾病越来越成为人们关注的焦点,其中血管成形术及支架置入术作为颅内外血管狭窄的有效治疗手段之一,已引起临床神经介入工作者的高度重视,但其术后血管再狭窄已成为临床应用中的棘手问题,也是近年来的研究热点。有研究表明Periostin与血管再狭窄的关系密切,本文就Periostin与血管损伤修复及动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS)的关系进行综述。
1 Periostin简介
Periostin是细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)蛋白的一种,最初由日本学者Takeshita等[1]于1993年从小鼠成骨细胞系MC3T3-E1cDNA文库中克隆出的一种黏附分子,曾命名为成骨细胞特异因子-2(osteoblast-specific factor-2,OSF-2)。OSF-2由811个氨基酸组成,其四倍重叠区与成束蛋白(fasciclinⅠ,FASⅠ)具有相似的结构。近年研究发现每1个FASⅠ区域都含有一个γ-羧化酶识别位点和几个能羧化的谷氨酰胺残基,并且FASⅠ区域还含有整合素结合位点,Periostin可与整合素相互作用介导上皮细胞-间质细胞转化(EMT),从而调节细胞的迁移和黏附[2]。
在功能方面,过去认为Periostin蛋白仅特异性表达于骨组织[3],目前证实其存在于许多组织中,如:皮肤[4]、肿瘤、癌细胞[5]、肾脏及心脏瓣膜[6],并且在肌肉损伤[7]、血管损伤[8]和肺血管重构[9]等条件下也有表达。在心脏中,Periostin主要表达在心肌成纤维细胞,并由其直接分泌[10],而在心肌细胞中的表达尚无统一定论[11-12]。进一步研究发现其可在多种组织尤其是在各种创伤愈合和恶性肿瘤组织内过度表达,它不仅能促进细胞的黏附作用,还能调控细胞的迁移与增殖。
2 Periostin促进内皮细胞的迁移和增殖
2.1 Periostin与内皮细胞的趋化性
在参与调控内皮细胞迁移的诸多趋化性细胞因子中,最主要的是血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF),而能够调节内皮细胞的迁移、增殖、分化以及血管的通透性的是VEGF酪氨酸激酶受体-2(VEGFR-2)。研究发现,Periostin是通过上调血管内皮细胞中VEGFR-2的表达,而非通过增加VEGF的量来实现血管损伤后愈合或血管重塑的形成,因此,阻断VEGFR-2的表达能抑制Periostin所诱导的血管形成[13]。所以,Periostin可通过上调VEGF受体的表达,提高敏感性,促进VEGF和VEG-FR-2结合的方式来刺激内皮细胞的趋化性移动,从而促进内皮细胞的迁移和增殖。
2.2 Periostin与内皮细胞的趋触性
细胞基质蛋白是一类细胞外基质相关的分子,其在发育过程中表达水平高,而在出生后仅低表达于正常组织,但在创伤或病理组织中表达量却会明显增高。基于这一特点,Periostin也被归类为细胞基质蛋白。研究证实,细胞基质蛋白能影响细胞的迁移、细胞外基质合成、细胞黏附、细胞的增殖与凋亡等[14]。Periostin能够与包括Ⅰ、Ⅲ和Ⅴ型胶原蛋白、纤连蛋白和腱糖蛋白C等其他细胞外基质成分直接相互作用,并促进细胞外基质的浸润和收缩[15]。Periostin与I型胶原存有共同的分布区域,且其可直接与I型胶原结合,同时发现Periostin基因剔除的小鼠胶原纤维的直径减小,胶原交联水平降低,提示Periostin调节I型胶原纤维的合成[16]。表明Periostin可能通过对I型胶原的调节来促进内皮细胞的迁移,继而参与血管形成或修复过程。
3 Periostin与基质胶原的关系
细胞外基质(ECM)异常积聚是球囊血管成形术后血管再狭窄的重要原因。在病变部位,ECM可达组织总量的90%。胶原是ECM的主要成分,其过度合成不仅是造成ECM异常积聚的原因,而且还影响血管平滑肌细胞(VSMC)的增殖和迁移。因此,胶原合成与降解平衡失调在血管再狭窄的发生发展过程中发挥重要作用[17]。
Periostin无论是在皮肤、肌腱[16],还是在心脏[8]的损伤修复过程中均参与胶原纤维生成。缺乏Periostin可导致心脏瓣膜异位平滑肌和心肌细胞系原始细胞的出现,与成年人或鼠的岛样和口袋样的心脏瓣膜纤维化相吻合[18]。Periostin基因敲除后培养鼠胚胎时期的成纤维细胞,其胶原的合成量仅约为野生型的胚胎鼠胶原合成量的32%。综上可知,Periostin是成纤维细胞合成分泌胶原的信号,或通过与胶原结合来减少细胞间基质中胶原的降解。
4 Periostin与TGF-β的关系
支架置入术后再狭窄的发生是VSMC增殖、迁移以及ECM的分泌和积累的结果,TGF-β1可能起着重要作用。在大鼠颈动脉球囊剥脱术后48 h,TGF-β1、2、3及受体的mRNA在血管中膜即有表达,并可持续较长时间,同时伴有明显的细胞增殖与迁移[19]。对猪冠状动脉行PTCA,并在此部位转染分泌型TGF-β1Ⅱ受体(Ad5-RⅡs)的重组腺病毒,拮抗TGF-β1表达,刺激致密的胶原外膜形成,减少血管腔缩窄,这提示转基因治疗拮抗TGF-β1作用可能预防再狭窄发生[20]。由此可见,TGF-β1可通过调节细胞间基质重构在基质纤维化和血管损伤修复中发挥重要作用。
上调TGF-β水平可导致Periostin蛋白表达,而应用TGF-β中和性抗体将抑制Periostin蛋白的表达。Paige等[21]通过研究Smad6、TGF-β及Periostin基因敲除动物,发现Periostin与TGF-β超家族信号系统有密切关系。TGF-β/Smad6位于Periostin蛋白的上游,能够调节Periostin。在经TGF-β刺激或损伤鼠颈动脉后发现Periostin表达上调[22],且TGF-β信号在原纤维蛋白-1基因突变鼠中出现过表达,Periostin表达亦有上调,而在全身性TGF-β2和心肌细胞局限性Alk3基因敲除后可出现Periostin表达减少[23]。由此提示,在成年动物心血管组织动态平衡中,TGF-β和Periostin作为重要的反应分子在ECM的生成和重构中扮演着重要角色,且TGF-β1可能通过增加perisotin表达的过程来发挥提高血管损伤后修复的效果,从而形成新生内膜并导致血管再狭窄。
5 Periostin与血管损伤修复之间的关系
损伤-反应学说认为血管损伤可促进平滑肌细胞增殖迁移并合成基质蛋白,这有助于新血管内膜的形成并参与受损血管的修复,目前研究发现Periostin与血管损伤修复之间关系密切。在大鼠颈动脉球囊损伤后再狭窄的模型中发现Periostin的mRNA及蛋白表达于血管内膜和外膜大量增殖的平滑肌细胞及肌成纤维细胞中,且伴随胶原蛋白Ⅰ及胶原蛋白在血管壁沉积[8]。同时,体外培养发现,在细胞分化成平滑肌细胞的过程中,Periostin的mRNA表达显著增高;随后,在细胞中过表达Periostin基因能够显著增强细胞迁移能力,而该效应能够被Periostin特异性抗体阻断。在颈动脉球囊损伤血管内膜后3 d及7 d,Periostin分别在血管中膜及内膜中的VSMC中开始表达,其可能通过磷酯酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol3-kinase,PI3K)途径来介导上调,同时PI3K特异性抑制剂Wortmannin却能显著抑制Periostin mRNA的表达及磷酸化Akt的增高[7]。体外试验表明,TGF-β能剂量依赖性的刺激胸主动脉平滑肌细胞Periostin mRNA的表达,成纤维生长因子2(fibroblastgrowthfactor-2,FGF-2)、血管紧张素Ⅱ也都具有类似的效应;免疫荧光显像发现Periostin主要在VSMC胞浆表达。在VSMC迁移试验中[24],Periostin特异性抗体能显著抑制VSMC的迁移。该研究证实,动脉内膜损伤后TGF-β、FGF-2等可促进VSMC表达Periostin,Periostin通过与整合素受体结合,激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,从而促进VSMC的迁移。
在临床实验中,有研究发现Periostin样因子(periostin-like factor,PLF)在正常人VSMC给予促有丝分裂化合物干预后表达水平增高,提示其在VSMC活化中起着重要作用;同时发现不同的PLF表达水平可导致VSMC迁移增殖的变化,提示PLF可能通过VSMC迁移增殖来参与血管增生性疾病的发展过程[25]。综上表明PLF在VSMC活化及血管再狭窄形成中发挥重要的作用。
6 Periostin与动脉粥样硬化(AS)的关系
AS是由各种危险因子综合作用于内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞而在局部产生过度的慢性炎症增生。诸多研究证实Periostin与AS的相互关系。Periostin在高脂血症模型鼠载脂蛋白E敲除的颈动脉损伤模型鼠以及AS模型鼠中均表达增高,可能通过参与泡沫细胞及ECM沉积脂质核心形成来促进AS的形成[22,26]。在动脉粥样硬化病人的血管内皮中Periostin的表达量是正常人群的6.1倍,同时在Periostin高表达部位发现VEGF的表达亦明显增高且伴随弥漫性血管浸润[27]。Periostin通过与整合素蛋白相互作用并激活成簇黏附激酶(focal adhesion kinase,FAK)信号通路来促进平滑肌细胞的迁移(如图1),从而参与AS及血管再狭窄的形成[28]。总之,VSMC增殖及其从动脉中层向内膜迁移是AS斑块形成和血管成形术后再狭窄的主要原因。近年来研究证明,VSMC的迁移和增殖与ECM的降解密切相关。Periostin可能通过与平滑肌细胞相互作用以及其它机制参与AS的形成,其具体的分子机制需进一步研究。
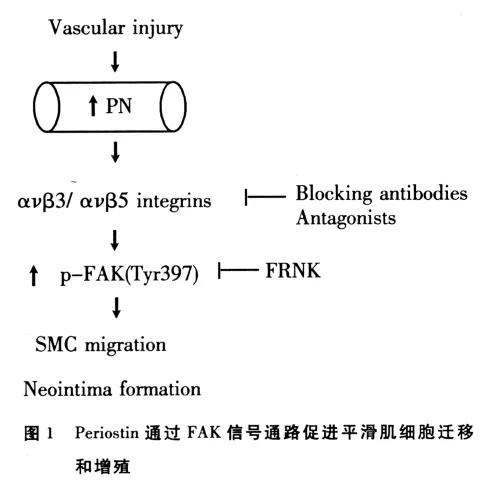
7 结语
综上所述,Periostin与血管再狭窄形成关系密切,但具体分子机制目前尚未明确,阐明其发病机制,寻找新的血管再狭窄防治策略已成为目前临床亟待解决的紧迫问题。病理直接损伤及细胞因子等能够刺激血管VSMC表达Periostin,虽然能进一步促进VSMC的增殖及迁移,参与血管损伤后修复过程,但同时也能导致血管损伤后的再狭窄。Periostin与血管再狭窄的分子机制如何,其能否成为独立预测因子来判断血管再狭窄程度,能否研制出相关药物应用于临床实践,又能否通过这一指标来判断药物疗效或病情进展等,这仍需大量的探索性实验来研究。
[1]Takeshita S,Kikuno R,Tezuka K,et al.Osteoblast-specific factor 2:cloning of a putative bone adhesion protein with homology with the insect protein fasciclin I[J].Biochem J,1993,294(1):271-278
[2]Coutu DL,Wu JH,Monette A,et al.Periostin,amember of anovel family of vitamin K-dependent proteins,is expressed bymesenchymal stromal cells[J].J Biol Chem,2008,283(26):17991-18001
[3]Bonnet N,Standley KN,Bianchi EN,et al.The matricellular protein Periostinis required for sost inhibition and the anabolic response to mechanical loading and physical activity[J].J Biol Chem,2009,284(51):35939-35950
[4]Zhou HM,Wang J,Elliott C,et al.Spatiotemporal expression of Periostin during skin development and incisional wound healing:lessons for human fibrotic scar formation[J].J Cell Commun Signal,2010,4(2):99-107
[5]Contié S,Voorzanger-Rousselot N,Litvin J,et al.Increased expression and serum levels of the stromal cell-secreted protein Periostin in breast cancer bone metastases[J].Int J Cancer,2011,128(2):352-360
[6]Norris RA,Moreno-Rodriguez RA,Sugi Y,et al.Periostin regulates atrioventricular valve maturation[J].Dev Biol,2008,316(2):200-213
[7]LaFramboise WA,Jayaraman RC,Bombach KL,et al.Acute molecular response of mouse hindlimb muscles to chronic stimulation[J].Am J Physiol Cell Physiol,2009,297(3):556-570
[8]Lindner V,Wang Q,Conley BA,et al.Vascular injury induces expression of Periostin:implications for vascular cell differentiation and migration[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2005,25(1):77-83
[9]Li P,Oparil S,Feng W,et al.Hypoxia-responsive growth factors upregulate Periostin and osteo-pontin expression via distinct signaling pathways in rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells[J].J Appl Physiol,2004,97(4):1550-1558
[10]Shimazaki M,Nakamura K,Kii I,et al.Periostin is essential for cardiac healing after acute myocardial infarction[J].J Exp Med,2008,205(2):295-303
[11]Iekushi K,Taniyama Y,Azuma J,et al.Novel mechanisms of valsartan on the treatment of acute myocardial infarction through inhibition of the antiadhesion molecule Periostin[J].Hypertension,2007,49(6):1409-1414
[12]Snider P,Hinton RB,Moreno-Rodriguez RA,et al.Periostin is required for maturation and extracellular matrix stabilization of noncardiomyocyte lineages of the heart[J].Circ Res,2008,102(7):752-760
[13]Shao R,Bao S,Bai X,et al.Acquired expression of Periostin by human breast cancers promotes tumor angiogenesis through up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression[J].Mol Cell Biol,2004,24(9):3992-4003
[14]Hamilton DW.Functional role of Periostin in development and wound repair:implications for connective tissue disease[J].J Cell Commun Signal,2008,2(1):9-17
[15]Butcher JT,Norris RA,Hoffman S,et al.Periostin promotes atrioventricular mesenchyme matrix invasion and remodeling mediated by integrin signaling through Rho/PI3-KInase[J].Dev Biol,2007,302(1):256-266
[16]Norris RA,Damon B,Mironov V,et al.Periostin regulates collagen fibrillogenesis and the biomechanical properties of connective tissues[J].J Cell Biochem,2007,101(3):695-711
[17]Sun Hongxia,Wen Jinkun.CollagenaseⅣand arteriosclerosis[J].Chin Arterioscl,1998,6(3):271-274
[18]Mulholland DL,Gotlieb AI.Cell biology of valvular interstitial cells[J].Can J Cardiol.1996,12(3):231-236
[19]Ryan ST,Koteliansky VE,Gotwals PJ,et al.Transforming growth factor-beta-dependent events in vascular remodeling following arterial injury[J].J Vasc Res,2003,40(1):37
[20]Kingston PA,Sinha S,David A,et al.Adenovirus-mediatedgene transfer of a secreted transforming growth factor-beta typeⅡreceptor inhibits luminal loss and constrictive remodeling after coronary angioplasty and enhances adventitial collagen deposition[J].Circulation,2001,104(21):2595
[21]Snider P,Hinton RB,Jian W,et,al.Periostin Is Required for Maturation and Extracellular Matrix Stabilization of Noncardiomyocyte Lineages of the Heart[J].Circulation Research,2008,102(7):752-760
[22]Li G,Oparil S,Sanders JM,et al.Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling mediates VSMC expression of Periostin vivo and in vitro[J].Atherosclerosis,2006,188(2):292-300
[23]Cohn RD,van Erp C,Habashi JP,et al.Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade attenuates TGF beta-induced failure of muscle regeneration inmultiple myopathic states[J].Nat Med,2007,13(2):204-210
[24]Stansfield WE,Andersen NM,Tang RH,et al.Periostin is a novel factor in cardiac remodeling after experimental and clinical unloading of the failing heart[J].Ann Thorac Surg,2009,88(6):1916-1921
[25]Litvin J,Chen X,Keleman S,et al.Expression and function of Periostin-like factor in vascular smooth muscle cells[J].Am J Physiol Cell Physiol,2007,292(5):1672-1680
[26]Bagnato C,Thumar J,Mayya V,et al.Proteomics analysis of human coronary atherosclerotic plaque:a feasibility study of direct tissue proteomics by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry[J].Mol Cell Proteomics,2007,6(6):1088-1102
[27]Hakuno D,Kimura N,Yoshioka M,et al.Periostin advances atherosclerotic and rheumatic cardiac valve degeneration by inducing angiogenesis and MMP production in humans and rodents[J].J Clin Invest,2010,120(7):2292-306
[28]Li GH,Jina R,Zhang L,et al.Periostin mediates vascular smooth muscle cell migration through the integrins V3 and V5 and focal adhesion kinase(FAK)pathway[J].Atherosclerosis,2010,208(2):358-365
Progress in the study on relationship between periostin and reangiostenosis
WEI Ben1,GUO Fu-qiang2△
(1.Luzhou Medical College,Luzhou 646000,Sichuan,China;2.Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital,Chengdu 610072,Sichuan,China)
Periostin has recently been found as a kind of secretion type which can dissolve between cell matrix proteins.It can promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and synthetize matrix proteinsleading to the formation of neointimal thus lessening the damage toblood vessels lumens.Reangiostenosis is one of major adverse reaction angioplasty or with internal stents,and marked by neointimal formation.It is a kind of the pathological process which is involved with several secreted cell factors and growth factors in the cells.This causeslocal inflammatory reactions and proliferation in the blood vessels.Periostin may be related to reangiostenosis through the interaction with smooth muscle cells and other mechanisms.However,due to the limited research of this aspect,the specific molecular mechanism is still not very clear.Therefore,more and more in-depth research is needed for it to be clarified.
Periostin;Reangiostenosis;Intravascular stenting;Angioplasty
1005-3697(2012)04-0313-05
R363
A
10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2012.04.003
四川省科技厅科技支撑项目(2009FZ0080)
2012-05-12
魏本(1985-),男,安徽桐城人,硕士研究生,主要从事脑血管介入基础与临床工作。
△通讯作者:郭富强,E-mail:guofuqiang2005@126.com网络出版时间:2012-7-80∶29
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1254.R.20120708.0029.201204.313_003.html

