嗜酸硫杆菌双组分信号转导系统多样性分析
余水静,彭 涛,周 丹,潘 涛,董 伟,陈江安,邱廷省*(1.江西理工大学资源与环境工程学院,江西 赣州 341000;2.江西理工大学,江西省矿冶环境污染控制重点实验室,江西 赣州 341000;3.江西理工大学,江西省矿业工程重点实验室,江西 赣州 341000)
嗜酸硫杆菌双组分信号转导系统多样性分析
余水静1,2,彭涛1,2,周丹1,2,潘涛1,2,董伟1,2,陈江安1,3,邱廷省1,3*(1.江西理工大学资源与环境工程学院,江西 赣州 341000;2.江西理工大学,江西省矿冶环境污染控制重点实验室,江西 赣州 341000;3.江西理工大学,江西省矿业工程重点实验室,江西 赣州 341000)
为探索嗜酸硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus)对极端矿山环境条件感知和反应分子机制的差异,利用生物信息学方法鉴定和分析了两株嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌、一株喜温嗜酸硫杆菌和一株耐冷嗜酸硫杆菌的双组分信号转导系统(TCS)结构多样性特征.结果表明,4株嗜酸硫杆菌拥有27~38个TCS蛋白,聚类分析显示有16组配对的TCS族、4组孤儿组氨酸蛋白激酶(HK)和9组孤儿反应调节蛋白(RR),与其进化分支有较好的相关性;其中9个配对和5个不配对的TCS 蛋白族为嗜酸硫杆菌菌株所共有,其余特有TCS均在一个或几个菌株中缺失.嗜酸硫杆菌菌株共有的TCS功能涉及氮素固定及代谢调节、柠檬酸/苹果酸代谢调节等,特有TCS功能涉及如趋化性调控、重金属响应、铜抗性调控等,这可能有助于菌株在极端矿山环境中生存.
嗜酸硫杆菌;双组分信号转导系统;多样性分析
嗜酸硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus)可通过氧化硫和还原态无机硫化物获得能量,能在极酸(pH 值1~3)、高浓度重金属环境中生长繁殖[1],已广泛应用于生物冶金、生物脱硫和含硫废水的处理等领域.
嗜酸硫杆菌属主要代表菌有中温嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌(A. ferrooxidans)、喜温嗜酸硫杆菌(A. caldus)和耐冷嗜酸硫杆菌(A. ferrivorans). A. ferrooxidans为专性好氧菌,最佳生长 pH值为2~2.5,最佳生长温度 28~35℃,能耐受多种重金属[2]; A. caldus能在含砷、含重金属离子、45℃和pH 1.6的极端环境中旺盛生长[3];A. ferrivorans为兼性厌氧菌,能在7℃条件下浸出多金属硫化矿[4].由此可见,嗜酸硫杆菌各菌株生存的极端环境条件具有明显差异.
细菌在生长繁殖过程中,需对变化的环境条件进行感知和反应,通常这个功能是由双组分信号转导系统(Two-component signal transduction system,TCS)来完成的.双组分信号转导系统由组氨酸蛋白激酶(Histidine protein kinase,HK)和反应调节蛋白(Response regulator protein,RR)组成[5],具有参与调控细胞生长、分化、代谢、渗透调节、致病性、趋化性及耐药性等多种重要生物学功能.
许多科学工作者试图从基因组学角度探究微生物遗传型和表型之间的相关性,从生物信息学角度揭示嗜酸硫杆菌 TCS的多样性特征,理解这些菌株对多变极端环境条件响应的分子机制.然而,目前嗜酸硫杆菌TCS多样性方面的研究国内外还鲜见.
嗜酸硫杆菌基因组测序已完成的有 A. ferrooxidans、A. caldus和A. ferrivorans菌株[6-8],因此,本研究拟对已测序的 4株嗜酸硫杆菌菌株(A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270、A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993、A. caldus SM-1、A. ferrivorans SS3)的TCS进行发掘鉴定,并从 TCS的聚类和进化关系、功能域、共有和特有TCS功能分析等方面阐释嗜酸硫杆菌TCS多样性特征.
1 材料与方法
1.1基因组数据收集
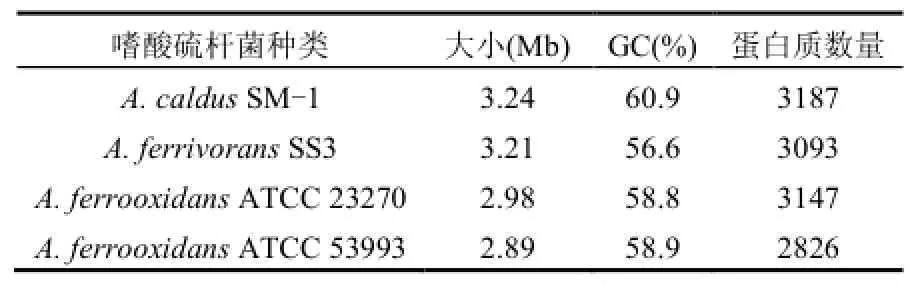
表1 四株已测序的嗜酸硫杆菌基因组信息Table 1 The information of four sequenced Acidithiobacillus genomes used in this study
从美国国立生物技术信息中心网站(National Center for Biotechnology Information,NCBI)收集4株嗜酸硫杆菌A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270、A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993、A. caldus SM-1、A. ferrivorans SS3的基因组信息(包括后缀名为.ffn、.faa、.ptt三种类型文件),见表1.
1.2HK和RR鉴定
根据Song等[9]报道的方法鉴定4株嗜酸硫杆菌包括 A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270、A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993、A. caldus SM-1、A. ferrivorans SS3菌株的HK和RR.方法如下:将嗜酸硫杆菌的.faa文件提交至Pfam蛋白序列数据库[10]进行批量搜索(Cut-off选择 Gathering threshold),其中HK预测不设e值,RR预测设e值为1e-6.在返回的结果中用PF00512、PF07568、PF07730、PF07536、PF06580、PF01627、PF02895(HK的保守结构域)搜索可能的 HK,用PF00072(RR的保守结构域)搜索RR[9].
然后将获得的HK和RR序列提交NCBI网站的BLASTp程序在线比对,根据以下原则确认HK和RR:(1) 催化结构域HATPase_c必须位于HK的C-末端(末端2/3);(2) HATPase_c的上游具有H-box;(3) RR的N-末端通常具有磷酸受体结构域REC;(4) Response_reg结构域位于RR的C-末端.基因间距小于 300bp且转录同向的HK-RR鉴定为 HK-RR基因对(HK-RR gene pairs),同时拥有 HK 的磷酸转移酶结构域(phosphotransferase domainn)和 RR磷酰基接受域(phosphoryl-accepting domain)的HK-RR为杂合蛋白(HK-RR Fusion),单个的HK或RR基因鉴定为“Orphan”[11].
1.3TCS聚类分析与进化
利用OrthoMCL在线工具[12]对4株嗜酸硫杆菌聚类分析,将鉴定的 HK蛋白序列提交至OrthoMCL-DB数据库比对,获得HK蛋白的聚类分组,属于同一聚类分组的HK蛋白鉴定为嗜酸硫杆菌共有TCS,在一株或几株菌缺失的HK蛋白组鉴定为特有TCS.利用phylogeny.fr[13]工具对TCS的 HK序列进行多重序列比对并建立系统发育树.
1.4HK功能域分析
HK 功能域采用 SMART分析[14]或BLASTp程序相似性比对分析[15],应用TMHMM Server[16]分析HK蛋白跨膜结构区域. 从NCBI网站的Genebannk数据库中获取TCS功能信息.
2 结果与讨论
2.1嗜酸硫杆菌TCS多样性分布
利用保守结构域对 4株嗜酸硫杆菌菌株的TCS进行全基因组搜寻,结果表明,在4株嗜酸硫杆菌中,TCS蛋白总数为 27~38个,其中成对的TCS (HK-RR)为11~14对,孤儿HK和RR分别为2~5和3~9个,发现3个HK蛋白(Atc_1719、Acife_1338和Acife_1591)同时拥有RR磷酰基接受域,为杂合蛋白(见表2).
从表2可以看出,嗜酸硫杆菌A. ferrooxidans、A. caldus、A. ferrivorans菌种之间TCS数量差异较明显;即使同一菌种不同菌株之间,如 A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270和ATCC 53993在Orphan RR的数量上也有细微的差异,这可能与其生存环境条件及进化的不同有关.
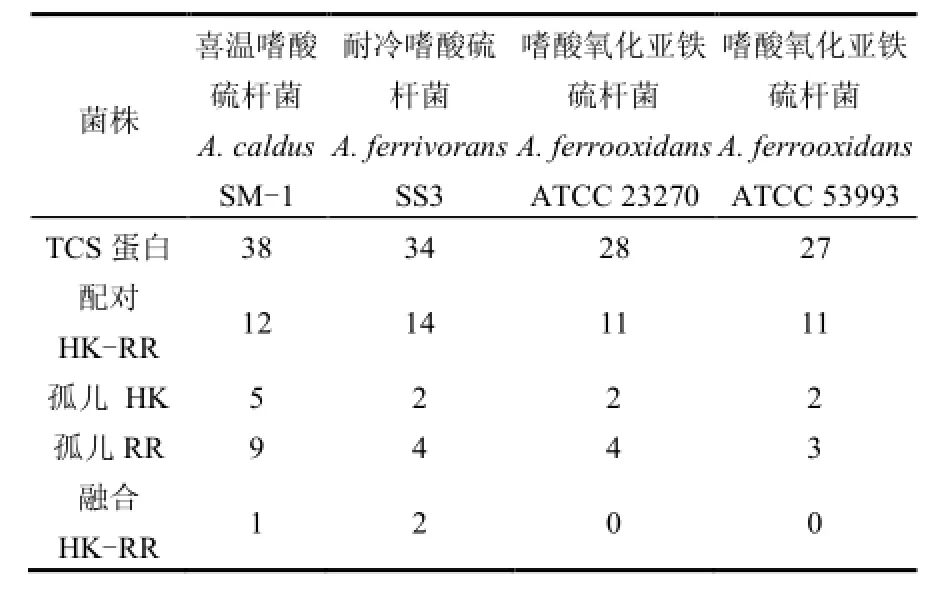
表2 四株嗜酸硫杆菌双组份信号转导系统Table 2 Identification of the TCSs in four Acidithiobacillus strains
2.2嗜酸硫杆菌TCS聚类与进化分析
本研究对4株嗜酸硫杆菌的TCS蛋白聚类分析结果显示,有 16组不同的 TCS族、4组 orphan HK和9组orphan RR (表3).
在16个配对的TCS族中,9个TCS族为4株嗜酸硫杆菌菌株所共有,包括TCS-1、TCS-2、TCS-3、TCS-4、TCS-6、TCS-7、TCS-11、TCS-13、TCS-14;其余 7个 TCS 族(TCS-5、TCS-8、TCS-9、TCS-10、TCS-12、TCS-15、TCS-16)在一个或几个菌株中缺失.如 TCS-9、TCS-12只存在于 A. ferrivorans SS3菌株中;TCS-15、TCS-16只存在于A. caldus SM-1菌株中.而TCS-5、TCS-10仅在A. caldus SM-1菌株中缺失;TCS-8在A. ferrooxidans菌株中缺失.对于不配对的 TCS蛋白,聚类分析显示:Orphan HK2、Orphan HK3、Orphan RR4、Orphan RR5族为4株嗜酸硫杆菌菌株所共有,其余均在一个或几个菌株中缺失(表3).
利用phylogeny.fr工具对嗜酸硫杆菌TCS的HK构建了进化树(图1),从图1中可以看出HK基因进化关系的远近.通过对比嗜酸硫杆菌 TCS 中HK的进化关系和聚类分析,发现进化分支和聚类分组之间具有较好的相关性.
2.3嗜酸硫杆菌HK结构域组成及功能分析
根据Mascher等[17]的分类方法,HK蛋白可分为3个不同的组别:胞外敏感型HK、胞内敏感型HK和细胞膜敏感型HK.本研究中对嗜酸硫杆菌HK结构域组成分析发现:仅有TCS-1的HK蛋白属于胞外敏感型HK;TCS-6、TCS-9、TCS-10、TCS-14的HK蛋白属于细胞膜敏感型敏感型HK;其余TCS的HK蛋白属于胞内敏感型HK(图2).
TCS-1、TCS-4、TCS-7、TCS-8、TCS-14、TCS-15的HK蛋白中含有PAS (Per-Arnt-Sim)结构域. PAS结构域作为传感分子在感应外界环境中氧浓度、细胞氧化还原态或光强度中扮演着重要的角色[18].大多数含有 PAS结构域的HK蛋白位于细胞内,通过感应细胞内外的氧化还原电位变化引起电子传递系统的改变来监控细胞内外环境[19].此外,TCS-8的 HK蛋白中还含有PAC (proxy auto-config)结构域,PAC结构域常与PAS结构域结合形成保守的三维PAS折叠[20].
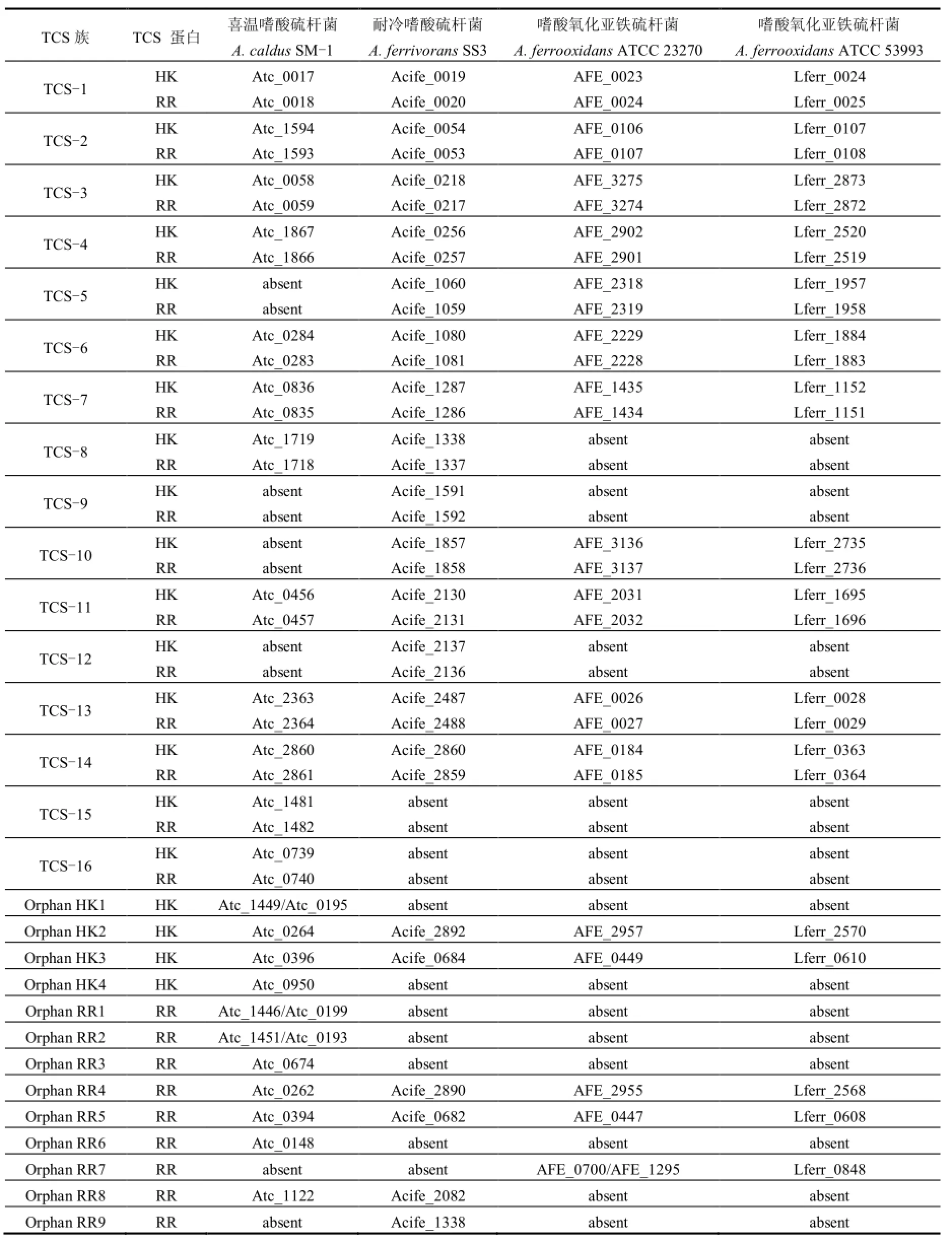
表3 嗜酸硫杆菌TCS聚类分析Table 3 Ortholog analysis of the TCS proteins in the four Acidithiobacillus strains
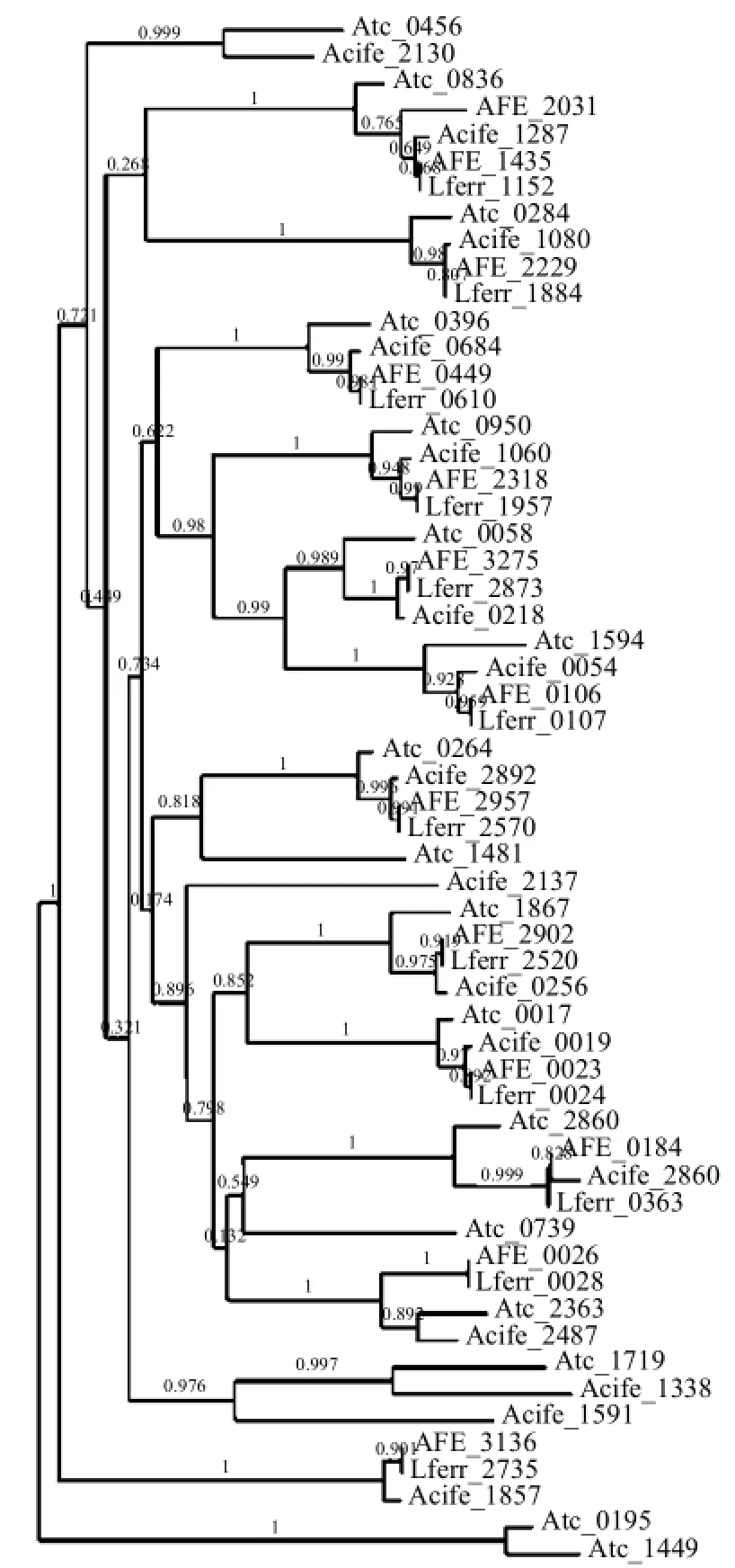
图1 利用phylogeny.fr构建的嗜酸硫杆菌HK进化树.Fig.1 Phylogenetic tree of the identified putative HKs inthe Acidithiobacillus strains using the web tool. phylogeny. fr
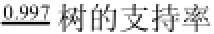
TCS-1、TCS-2、TCS-3、TCS-12、TCS-13、TCS-16的 HK蛋白及 Orphan HK2、Orphan HK3、Orphan HK4中均含有HAMP (Histidine kinases,Adenylyl cyclases,Methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins and Phosphatases)结构域. HAMP扮演着跨膜螺旋和信号传送区域连接器的角色[21].
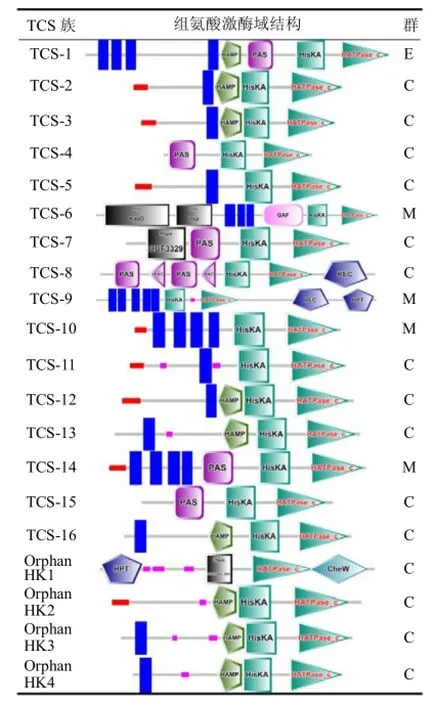
图2 嗜酸硫杆菌双组分信号转导系统中HKs结构域Fig.2 Domain architectures of histidine kinases representativeof TCS clusters in the Acidithiobacillus
2.4嗜酸硫杆菌共有TCS蛋白及功能分析
亲缘关系密切的微生物菌株TCS蛋白序列是保守的[22-24].在不同的细菌中,保守的 TCS一方面可能维持基本生物学功能,另一方面对于存在于特殊生境中的一些细菌也可能进化成新的功能.
本研究中聚类分析发现有 4株嗜酸硫杆菌菌株所共有TCS的 HK蛋白族包括 TCS-1、TCS-2、TCS-3、TCS-4、TCS-6、TCS-7、TCS-11、TCS-13、TCS-14、Orphan HK2、Orphan HK3.
对嗜酸硫杆菌共有的 TCS功能注释(来自NCBI数据库,见表 4)进行分析,发现 TCS-1、TCS-4、TCS-13涉及氮素固定及代谢调节;TCS-1、TCS-7响应环境中光和氧的变化;TCS-2、TCS-3响应环境渗透压胁迫;TCS-4、TCS-6、TCS-7、Orphan HK3可对渗透压敏感型K离子通道调节;TCS-7、TCS-14可响应磷酸盐饥饿及磷酸盐代谢;TCS-13涉及柠檬酸/苹果酸代谢调节;TCS-14参与鞭毛生物合成调控;Orphan HK2、Orphan HK3参与氨基糖代谢调控(表4).分析发现这些共有功能与嗜酸硫杆菌基本生物学功能和主要表型特征相关.
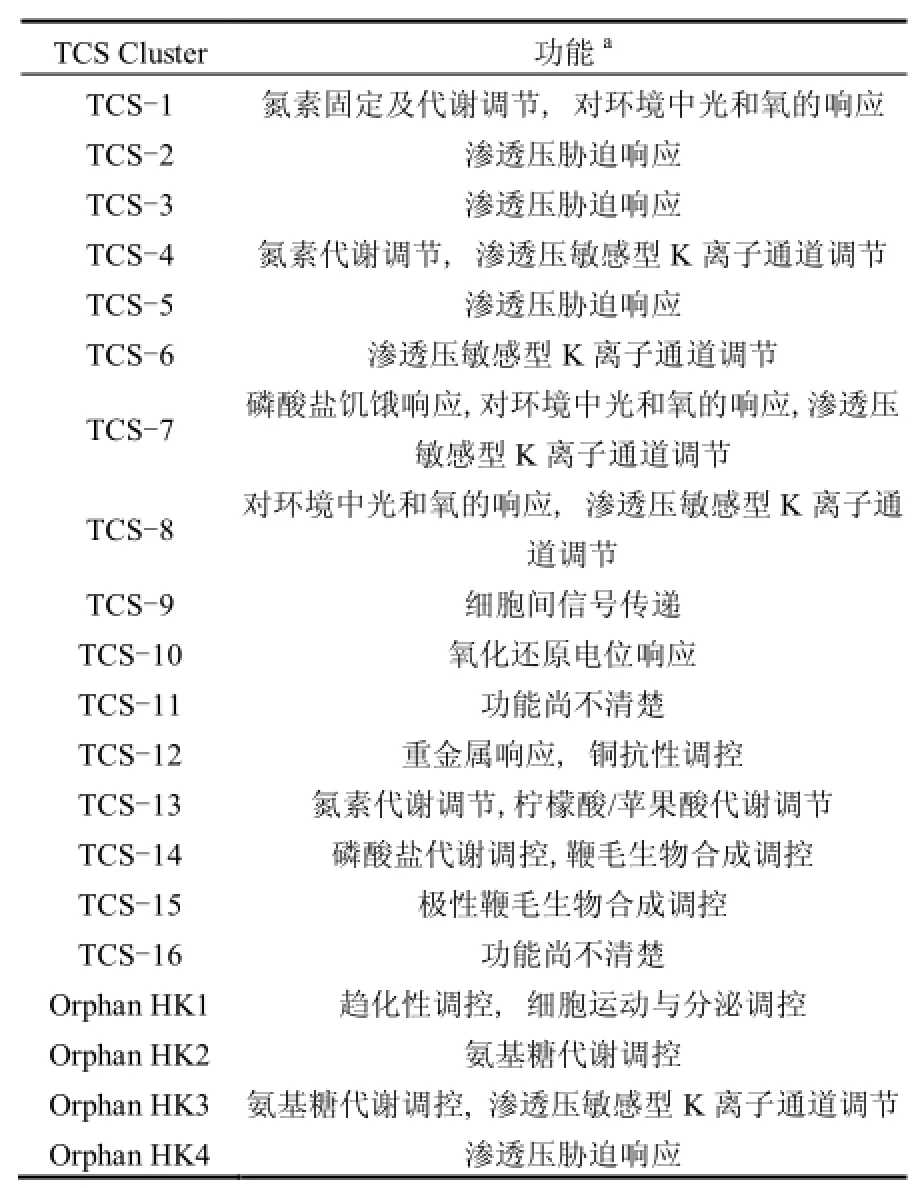
表4 嗜酸硫杆菌TCS功能小结Table 4 A brief summary of known/putative functions of the TCSs in Acidithiobacillus strains
2.5嗜酸硫杆菌特有TCS 蛋白及功能分析
特有TCS只存在于在一个或几个菌株中,体现了细菌对复杂环境因素响应的多样性,一般与某些特别的生物代谢途径和环境适应相关,如产抗生素、耐受性、毒力等方面.
本研究中聚类分析发现 TCS-5、TCS-8、TCS-9、TCS-10、TCS-12、TCS-15、TCS-16、 Orphan HK1、Orphan HK4、Orphan RR1、Orphan RR2、Orphan RR3、Orphan RR6、Orphan RR7、Orphan RR8、Orphan RR9族均在嗜酸硫杆菌一个或几个菌株中缺失,为特有TCS蛋白(表3).
TCS-9、TCS-12只存在于A. ferrivorans SS3菌株中,涉及细胞间信号传递、重金属响应,铜抗性调控等功能;TCS-15、TCS-16只存在于 A. caldus SM-1菌株中,涉及极性鞭毛生物合成调控等功能;TCS-5、TCS-10存在于A. ferrivorans SS3、A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270和ATCC 53993菌株中,仅在A. caldus SM-1菌株中缺失,涉及渗透压胁迫响应、氧化还原电位响应等功能;而TCS-8存在于A. ferrivorans SS3、A. caldus SM-1菌株中,在A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270和ATCC 53993菌株中缺失,涉及对环境中光和氧的响应,渗透压敏感型 K离子通道调节等功能; Orphan HK1、Orphan HK4仅存在于A. caldus SM-1菌株中,涉及趋化性调控,细胞运动与分泌调控、渗透压胁迫响应等功能(表4).
特有TCS功能分析显示出嗜酸硫杆菌菌种间TCS的多样性特征,反映出嗜酸硫杆菌属不同菌种对其特定生存环境条件响应机制的差异.
3 结论
3.1鉴定和比较了4株嗜酸硫杆菌TCS,发现嗜酸硫杆菌菌种之间TCS数量差异较明显,即使同一菌种不同菌株之间在数量上也有细微的差异.这些TCS基因分散在基因组中,并不局限于某一区域,暗示着嗜酸硫杆菌存在着一个复杂的调控网络.
3.2嗜酸硫杆菌包含已知功能结构域有HAMP、HATPase_c、HisKA、HPT、PAC、PAS、CheW、REC、Trans_regC等,这些结构域可感应环境中氧浓度、氧化还原电位、光强度等的变化,从而调控其多种生理生化过程来适应外界环境的变化.
3.3聚类分析鉴定了4株嗜酸硫杆菌共有TCS和特有TCS,其中特有TCS功能体现了嗜酸硫杆菌 TCS的多样性特征,如极性鞭毛生物合成调控、趋化性调控、重金属响应、铜抗性调控等,反映出嗜酸硫杆菌属不同菌种对其特定生存环境条件响应机制的差异.
[1] Rawlings D E. Characteristics and adaptability of iron- and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms used for the recovery of metals from minerals and their concentrates [J]. Microb. Cell Fact,2005,4(1):13.
[2] Zheng C L,Chen M J,Tao Z L,et al. Differential expression of sulfur assimilation pathway genes in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans under Cd2+stress: evidence from transcriptional,enzymatic,and metabolic profiles [J]. Extremophiles,2015,19(2):429-436.
[3] Acuña L G,Cárdenas J P,Covarrubias P C,et al. Architecture and gene repertoire of the flexible genome of the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus caldus [J]. Plos One,2013,8(11):e78237.
[4] Dopson M,Halinen A K,Rahunen N,et al. Mineral and iron oxidation at low temperatures by pure and mixed cultures of acidophilic microorganisms [J]. Biotechnol. Bioeng.,2007,97(5):1205-1215.
[5] West A H,Stock A M. Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems [J]. Trends Biochem. Sci.,2001,26(6):369-376.
[6] Liljeqvist M,Valdes J,Holmes D S,et al. Draft genome of the psychrotolerant acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans SS3 [J]. J. Bacteriol.,2011,193(16):4304-4305.
[7] You X Y,Guo X,Zheng H J,et al. Unraveling the Acidithiobacillus caldus complete genome and its central metabolisms for carbon assimilation [J]. J. Genet. Genomics,2011,38(6):243-252.
[8] Valdes J,Pedroso I,Quatrini R,et al. Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans metabolism: from genome sequence to industrial applications [J]. BMC Genomics,2008,9:597.
[9] Song L,Sudhakar P,Wang W,et al. A genome-wide study of two-component signal transduction systems in eight newly sequenced mutans streptococci strains [J]. BMC Genomics,2012,13(1):128.
[10] Punta M,Coggill P C,Eberhardt R Y,et al. The Pfam protein families database [J]. Nucleic Acids Res.,2012,40(Database issue):D290-301.
[11] de Been M,Francke C,Moezelaar R,et al. Comparative analysis of two-component signal transduction systems of Bacillus cereus,Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus anthracis [J]. Microbiology,2006,152(Pt 10):3035-3048.
[12] Fischer S,Brunk B P,Chen F,et al. Using OrthoMCL to assign proteins to OrthoMCL-DB groups or to cluster proteomes into new ortholog groups [J]. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics,2011,Chapter 6:Unit 6(12):11-19.
[13] Dereeper A,Guignon V,Blanc G,et al. Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist [J]. Nucleic Acids Res.,2008,36(Web Server issue):W465-469.
[14] Letunic I,Copley R R,Pils B,et al. SMART 5: domains in the context of genomes and networks [J]. Nucleic Acids Res.,2006,34(Database issue):D257-260.
[15] Marchler-Bauer A,Anderson J B,Cherukuri P F,et al. CDD: a conserved domain database for protein classification [J]. Nucleic Acids Res.,2005,33(Database issue):D192-196.
[16] Krogh A,Larsson B,von Heijne G,et al. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes [J]. J. Mol. Biol.,2001,305(3):567-380.
[17] Mascher T,Helmann J D,Unden G. Stimulus perception in bacterial signal-transducing histidine kinases [J]. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R.,2006,70(4):910-938.
[18] Taylor B L,Zhulin I B. PAS domains: Internal sensors of oxygen,redox potential,and light [J]. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R.,1999,63(2):479-506.
[19] Zhulin I B,Taylor B L. PAS domain S-boxes in Archaea,bacteria and sensors for oxygen and redox [J]. Trends Biochem. Sci.,1997,22(9):331-333.
[20] Hefti M H,Francoijs K J,de Vries S C,et al. The PAS fold - A redefinition of the PAS domain based upon structural prediction [J]. Eur. J. Biochem.,2004,271(6):1198-1208.
[21] Aravind L,Ponting C P. The cytoplasmic helical linker domain of receptor histidine kinase and methyl-accepting proteins is common to many prokaryotic signalling proteins [J]. FEMS Microbiol. Lett.,1999,176(1):111-116.
[22] Lavin J L,Kiil K,Resano O,et al. Comparative genomic analysis of two-component regulatory proteins in Pseudomonas syringae [J]. BMC Genomics,2007,8:397.
[23] Qian W,Han Z J,He C Z. Two-component signal transduction systems of Xanthomonas spp.: A lesson from genomics [J]. Mol. Plant Microbe. In.,2008,21(2):151-161.
[24] Zhao Y F,Wang D P,Nakka S,et al. Systems level analysis of two-component signal transduction systems in Erwinia amylovora: Role in virulence,regulation of amylovoran biosynthesis and swarming motility [J]. BMC Genomics,2009,10:245.
Diversity analysis of two-component signal transduction systems in the genus Acidithiobacillus.
YU Shui-jing1,2,PENG Tao1,2,ZHOU Dan1,2,PAN Tao1,2,DONG Wei1,2,CHEN Jiang-an1,3,QIU Ting-sheng1,3*(1.School of Resources and Environment,Jiangxi University of Science and Technology,Ganzhou 341000,China;2.Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Mining and Metallurgy Environmental Pollution Control,Jiangxi University of Science and Technology,Ganzhou 341000 China;3.Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Mining Engineering,Jiangxi University of Science and Technology,Ganzhou 341000,China).
China Environmental Science,2015,35(7):2146~2152
To investigate the difference in the molecular mechanism of the genus Acidithiobacillus responding to extreme mine environment,two A. ferrooxidans strains,one A. caldus strain and one A. ferrivorans strain were analyzed in the diversity of two-component signal transduction systems (TCS) by using the bioinformatics method. The results showed that 27~38 TCS proteins were respectively identified from the four Acidithiobacillus strains. These TCS proteins were clustered into 16 paired groups,four groups of orphan histidine protein kinases,and nine groups of orphan response regulator proteins,demonstrating significant correlationship with their evolutionary branches. Among TCS proteins,nine groups of paired TCSs and five groups of non-paired TCSs were shared by the four strains of Acidithiobacillus,while the other TCSs were absent at least in one strain. Common TCS proteins of the four strains played basic biological roles including nitrogen fixation and citrate/malate metabolism regulation. Specific TCS proteins got involved in chemotaxis regulation,heavy metal response,and copper resistance regulation,which might contribute to survival of bacterial strains under the extreme mine environment.
Acidithiobacillus;two-component signal transduction system;diversity analysis
X172
A
1000-6923(2015)07-2146-07
2014-12-20
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51474114);江西省科技厅科技支撑计划项目(20121BBG70004);江西省教育厅科技项目(GJJ13397)
* 责任作者,教授,qiutingsheng@163.com
余水静(1976-),男,江西樟树人,副教授,博士,主要从事环境微生物学及基因组学等领域研究.

