Cluster Analysis of Polyphenols and Organic Acids in 11 Different Brand Cigarette Samples at Home and Abroad
Lan MI, Bilong DAI, Yu QIN, Wenjun ZHANG, Zhen XIONG, Yanhong WANG, Ting ZHU
China Tobacco Schweitzer (Yunnan) Reconstituted Tobacco Project Meeting minutes, Yuxi 653100, China
Polyphenols are the essential aroma precursors in tobacco,which are positively correlated with the level of tobacco products. Tobacco is a higher-grade with higher content of polyphenols than those lower-grade[1-2],the contents of polyphenols are related to the color of tobacco after curing and the aroma of cigarette[3], and polyphenols and the morphologies also have direct effects on cigarette smoke because they are moved into the smoke in the course of inhaled[4]. So it can be considered that polyphonols are one of the primary components in the process of generating the tobacco aroma,due to they can endows the tobacco products with fine and elegant aroma, increase the aroma quality of tobacco products and play an important role in improving the tobacco products quality. Meanwhile,phenolic compounds cause an acidic chemical reaction over the course of the tobacco burn,which can neutralize some alkaline substances and make the smoking velvety.
Organic acid is an important part of tobacco and it means mainly these organic acid that outside the amino acide[5]. They are various of kinds and have a greater difference on content that includes volatile lower fatty acid,semi-volatile high grade fatty and nonvolatile binary acids, trimacinic acide.The nonvolatile organic acids in tobacco are one of the major chemical compositions affecting the quality of tobacco smoking, especially malic acid, citric acid, olaxic acid, malonic acid[6]. The acidic fragments by decomposition of nonvolatile organic acids over the course of the tobacco burn can adjust the ratio of nicotine that protonated and free, maintain the smoke PH balance, relieve the irritating of tobacco and keep smoking levels up, which is important for tobacco quality[7].Some organic acid are commonly used in cigarette casing, such as malic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid and oxalic acid.Because of the importance of the research of organic acid and polyphenol, it makes the cluster analysis of polyphenols and organic acids in 11 different brand cigarette samples at home and abroad, which are intended to supply a base for improving the quality of different brand cigarette.
Materials and Methods
Materials
There are 11 different cigarette samples, which include Su smoke,Baisha smoke, Double Xi smoke, Hibiscus king smoke, Chinese smoke,Hongta tobacco, Waboro, plaza, pacific Blue.
Sample preparation and GC-FID analysis
Break the cigarette samples and then filter it over 40mesh screen.Take 1.00g tobacco smails into the 100ml polypropylene tube that had added to 25 ml 10% H2SO4-CH3OH and 0.5ml adipic acid as internal standard and then oscillate it about 22 h, filter it.Pour the filtrate into the 100ml separatory funnel which had added to 40 ml waters, and use CH2Cl3to extracts 3 times and 10 ml one time,then wash it by 30 ml saturated NaCl solution and drying with anhydrous sodium sulfate,take 1ml filtrate for GC analysis.
The gas chromatographic analyses were carried out on an PE 500 GC system (PE, USA) equipped with an autosampler. Separations were conducted using a PE17, 30 m×0.25 mm capillary column coated with a 0.25 μm stationary phase film. Nitrogen was used as the carrier gas at 140 kpa.The column temperature was pro-grammed at 90 ℃for 2 min, raised to 180 ℃at 10 ℃/min and then raised to 260 ℃at15 ℃/min. Finally, the temperature was held at 260 ℃for 10 min.All of the samples were analyzed in split mode (1 μl injection, split rate,10∶1).The FID heater temperature was held at 250 ℃[8]. The flow rates of air and nitrogen in the FID were 40, 500,respectively.
Sample preparation and HPLC analysis
Tobacco(0.2g)was extracted with 40 ml 80%methanol(include the internal standard C9H6O4and 0.5% ascorbic acid) in a 100 ml polypropylene tube.After vigorous shaking the samples were subjected to ultrasound for 20 min, Prior to HPLC analysis, the samples were filtered through a 0.45 mm membrane and then take the filtrate 2 ml for HPLC analysis.
The HPLC instrument consisted of an Alliance 2695 separation module and column oven, equipped with a built-in online degasser (Waters, Milford, MA, USA). The specifications of the analytical column is 4.6×250 mm,5 μm (Beckman Coulter USPH ODS).Mobile phase A was methanol and mobile phase B was 0.05 mol/L KH2PO4.The flow rate was 0.2 ml/min.The initial conditions of the binary gradient were 95% mobile phase B and 5%mobile phase A.The mobile phase composition was changed from 95%to 5%mobile phase B within 25 min.After maintaining the system for 3 min at 100%it was then set to the initial conditions and equilibrated for 15 min resulting in an overall run time of 43 min.
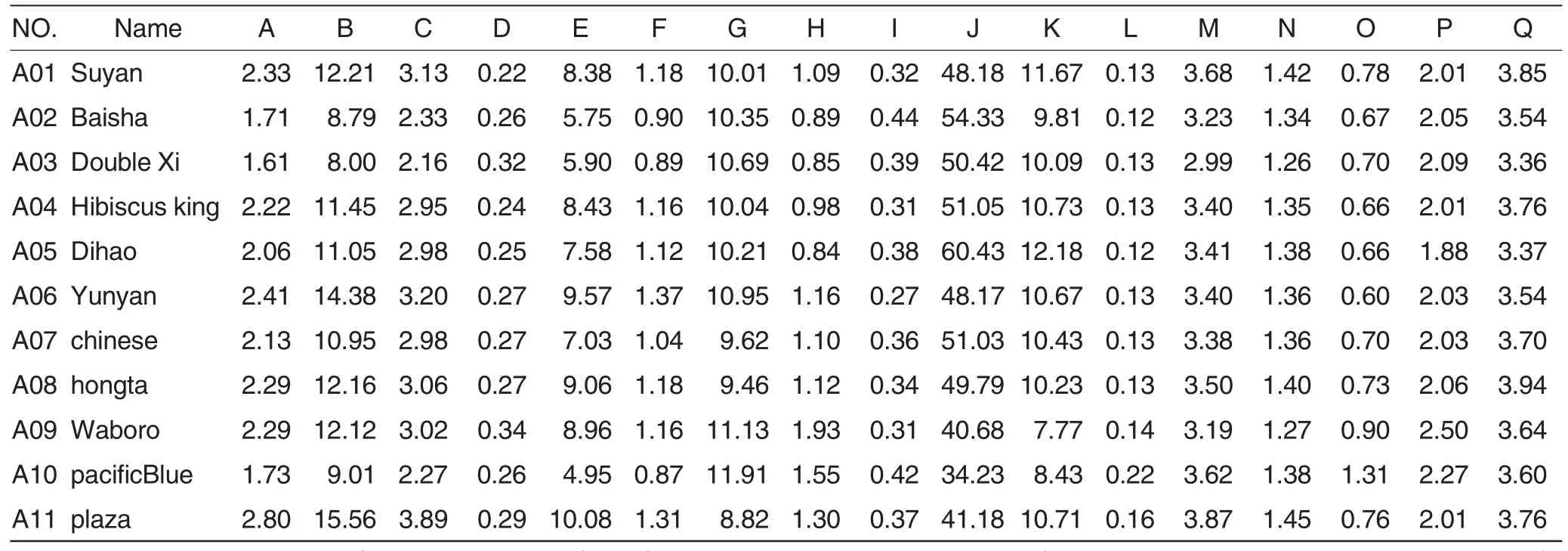
Table 1 The amount and the kinds of the polyphenols and organic acids in 11 different brand cigarette samples mg/g
The data processing
All the data was processed with the hierarchical clustering by the SPSS software (v16.0) and between the two groups were compared with independent-test.
Results
From the cluster analysis(Q hierarchical clustering)of polyphenols and organic acids (Fig.1)it is showed that the 11 different samples could be classified two types.The first type included A01, A02, A03, A04, A05, A06, A07 and A08,and the second type refers to those that A09, A10 and A11. The analysis of the sample origin showed that the first type include Su smoke,Baisha smoke, Double Xi smoke, Hibiscus king smoke, Chinese smoke,Hongta tobacco, and the second type are those that Waboro, plaza and pacific Blue.
T-test of independent sample of the two groups (Table 2)showed that Neochlorogenic acid, Chlorogenic acid, 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid, Beta-DGlucose, Bioflavonoid, Nicotiflorin,Etheanedioic, Succinic acid, Myristic acid, palmitic acid, Stearic acid, Oleic acid, Linoleic acid and Linolenic acid had no significant difference but Malonic acid, Malic acid and Citric acid had significant difference in the two types between the two groups were compared with independent T-test.Malonic acid has the higher content in the second type sample than in the first type sample. Malic acid and Citric acid has the higher content in the first type sample than in the second type.
Conclusion and Discussion
It can be concluded that the 11 different samples can be clustered two kinds, the first kind is domestic samples and the second kind is foreign samples.It also can be found the clustered kinds are closely related to the source of the samples if from the source of sample analyzing.The quality of different tobacco samples at home and abroad have some difference and this differentia different basically is behaved in the content of the chemical composition that influence the tobacco quality, for example, the Malonic acid, Malic acid and Citric acid.
The nonvolatile organic acids in tobacco are one of the major chemical compositions affecting the quality of tobacco smoking, especially malic acid, citric acid, olaxic acid, malonic acid[5]. The acidic fragments by decomposition of nonvolatile organic acids over the course of the tobacco burn can adjust the ratio of nicotine that protonated and free, maintain the smoke PH balance, relieve the irritating of tobacco and keep smoking levels up, which is important for tobacco quality[6]. Some organic acid are commonly used in cigarette casing, such as malic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid and oxalic acid.The cluster analysis of polyphenols and organic acids for the 11 different tobacco sample shows that the difference of different tobaccosamples at home and abroad in quality basically is behaved in the content of Malonic acid, Malic acid and Citric acid. However compared with foreign cigarette in quality there are many shortcoming about Chinese tobacco and the incongruity of the tobacco chemical composition also largely restricts the development of Chinese tobacco industry.So,compared with foreign tobacco, determining the content of Chinese tobacco chemical composition and finding the difference will improve the quality, raise market competitiveness and promote the development of Chinese tobacco.
The research used the GC[9]and HPLC to determine tobacco polyphenols and organic acids, and recent years Some researchers also used the HPLC[10]to determine the content of tobacco polyphenols and organic acids simultaneous, used mass spectroscopy to determine the tobacco organic acids[11], used micro-HPLC system to determine polyphenols[10], no matter the method of GC, HPLC and GC-MS, the determination of tobacco polyphenols and organic acids got a good effect. In recent years, with the development of modern analytical instrument it make the analysis of tobacco chemical composition a new phase that accurately, rapidly and efficiently.

Table 2 T-test of independent sample of the two groups
[1]YAN KY.Tobacco Chemistry[M].Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University Press.2002,273-274.
[2]HAN JF.Physiology of Tobacco Cultivation[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press.2003,199-202.
[3]SHI HZ,LIU GS.Aroma of Tobacco[M].Beijing: China Agriculture Press. 1998,68-70.
[4]XU XY,SUN WS,WANG NR.Synthesis of polyphenolic compounds and their effects on tobacco quality [J].Chinese Tobacco Science.2003,1:3-5.
[5]Tobacco Chemistry and Analysis [M]Beijing:Chinese financial and Economic Publishing House.1992.
[6]YANG HQ,ZHOU JH,GUO ZM.Difference of the content of nonvolatile organic acidsin flue-cured tobacco varieties in Hunan Province [J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica.2006,12,44-46.
[7]QUAN L, TAN KL, GUO R, Research Progress in Organic Acids in Tobacco[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi. 2010, 22,68-72.
[8]FANG DH, SONG CM, SHAO Y. Cluster analysis of polybasic acids and higher fatty acids in flue-cured tobacco leaves inYunnan and overseas [J].Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University.2006,35:562-564.
[9]YI J.Determination of organic acids and polyphenols in tobacco by HPLC and Research on Sunlight-Conversion Film for tobacco in Field Experiments [D].Journal of Hunan Normal University.2006,90,183.
[10]ZHANG T, DONG XC, Wu FP, Determination of polyphenols in tobacco by microcolumn-HPLC and mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis.2004,23,274-275.
[11]LI Fl, LU XM, WEI YW. Analysis on Changes of Key Nonvolatile Organic Acids in Tobacco Leaves during Its Growth by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences. 2011, 39, 1780 -1786.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Specific Gravity-based Seed Grading on Seed Germination,Seedling Emergence and Grain Yield of Hybrid Rice
- Effects of NaCl Stress on Seed Germination of Four Canavium album Raeuseh Cultivars
- Application Effects of Ultra-fine Powder Shaped Maize Seed Coating Agent in Spring Sowing areas in northeast China
- Breeding and Application of a Japonic Rice Cytoplasmic Male Sterility Line,E-Jing A
- Effect of Low Temperature and Sparse Light Conditions on Cold Tolerance of Different Rice Lines at Seedling Stage
- Molecular Marker Assisted Selection for Fusarium Wilt Resistance Breeding in Watermelon(Citrullus lanatus)
