Effects of Three Kinds of Chinese Medicine Polysaccharides on the Immune Effect of Newcastle Disease Vaccine
Qingfang YANG, Kanglin YANG, Jing YAO, Chunmao JIANG,
1. Jinzhong Vocational & Technical College, Jinzhong 030600, China;
2. Tibet Vocational Technical College, Lhasa 850000, China;
3. Wuxi Agricultural Technology Promotion Center, Wuxi 214000, China;
4. Jiangsu Agri-husbandry Vocational College, Taizhou 225300, China
As one of the most abundant and important biomacromolecules in the natural world,polysaccharide forms the most basic four living matters with protein, nucleic acid and lipid[1], its structure and function have received extensive attention,thus it has become the third milestone of exploring the life after protein and nucleic acid[2]. In recent years, some studies found that Chinese medicine polysaccharide, as the active ingredient of traditional Chinese medicine, its most important function is immunoregulatory activity[3].In the experiment, the polysaccharides were extracted from three kinds of traditional Chinese medicines like Astragalus,Epimedium and Isatis indigotica Fort.As the adjuvants to vaccinate the chicken with Newcastle disease vaccine, then the dynamic changes of weight gain rate, serum antibody titer and the proliferation of peripheral T lymphocyte were determined, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the development of immunopotentiator of Chinese medicine polysaccharides.
Materials and Methods
Experimental materials
Astragalus, Epimedium and Isatis indigotica Fort. were purchased from local medical companies, and water extraction and alcohol sedimentation technique was used to extract Astragalus polysaccharides (ASP),Epimedium polysaccharides (EPP)and Isatis root polysaccharides(IRPS); and the contents of the three polysaccharides were determined using sulfuric acid-anthrone method,which were 68.5%,63.8% and 53.4%,respectively.Each polysaccharide was diluted as high-dose concentration(H,8 mg/ml)and low-dose concentration(L,4 mg/ml) using deionized water according to net content,then high pressure disinfection was carried out routinely for reserving.
Experimental animals and grouping
240 one-day-old healthy and nonimmune Roman chicken were randomly divided into 8 groups, including blank control group (BC group), immune control group(IC group),immunity groups of each Chinese medicine(ASPHgroup,ASPLgroup,EPPHgroup,EPPLgroup, IRPSHgroup and IRPSLgroup), each group had 30 chicken.Until 14 days old of the chicken, except BC group which adopted normal saline to drop noses and eyes, IC group and immunity groups of each Chinese medicine used Newcastle disease vaccine to drop noses and eyes(2 doses/chick)as the first immunity, then the second immunity was carried out at the 28-day-old. On the day of the first immunity,3 d before the second immunity, the day of the second immunity and 3 d after the second immunity,high-dose concentration and low-dose concentration of ASP, EPP and IRPS were used for the immunity groups of each Chinese medicine using the gavage, and 0.5 ml for each chick.
Sample collection and item measurement
On the 7th, 14th, 21stand 28thday after the first immunity, 10 chicken of each group were randomly got and weighed, and the weight of each was recorded and the weight gain rate was calculated;on the 7th,14th,21stand 28thday after the immunity,0.5 ml blood of each chick was collected from the wing vein, then the serum was separated,the antibody titer was measured using HI[4];the anticoagulation was collected from the heart (the anticoagulant was sodium citrate) using MTT[5],the absorbancy D570nm, as a proliferation index of T lymphocyte, was measured on enzyme linked immunity instrument.
Data processing
The statistical analysis of difference was carried out for experimental data using SPSS software.
Results
The change of weight gain rate of different day-old chicken
As shown in Table 1, on the 7thd after the immunity, there was not statistical difference on weight gain rate among different groups of chicken(P>0.05); on the 14thd after the immunity,the weight gain rate of each treatment group was significantly higher than that of blank control group (P <0.05),but it had not significant difference with immune control group (P >0.05), and there was not statistical difference between immune control group and blank control group(P>0.05); on the 21stand 28thd after the immunity,except ASPH group, the weight gain rate of other treatment groups was all significantly higher than that of immune control group and blank control group (P <0.05), but there was not statistical difference between immune control group and blank control group (P >0.05).
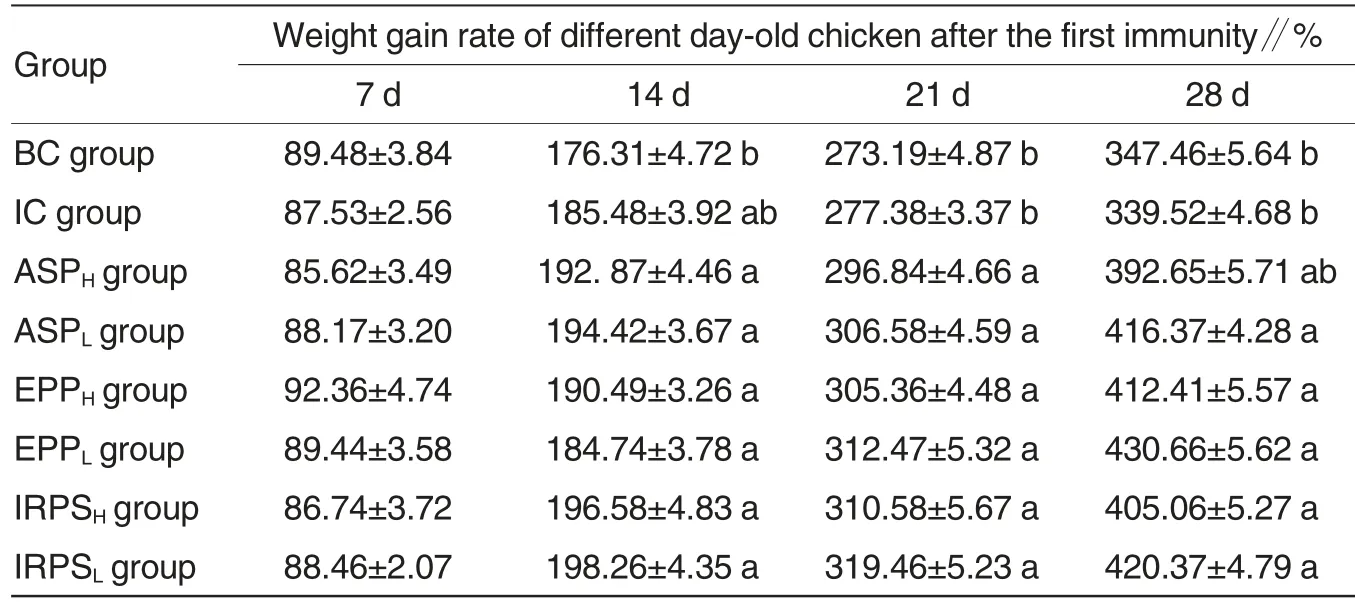
Table 1 The change of weight gain rate of different day-old chicken after the immunity

Table 2 The change of serum HI antibody titer of different day-old chicken after the immunity(log2)
The change of serum antibody titer of different day-old chicken
As shown in Table 2, on the 7thand 14thd after the immunity, there was not significant difference on serum antibody titer among different immunity groups of chicken (P>0.05),but that of immunity groups was all significantly higher than that of blank control group(P<0.05); on the 21stand 28thd after the immunity, the antibody titer of traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharide immune groups was all significantly higher than that of immune control group and blank control group (P<0.05);hereinto,on the 21std of the immunity, the antibody titer of ASPH, ASPL and IRPSL groups was all significantly higher than that of other treatment groups (P>0.05); on the 28th d of the immunity, except IRPSH group, there was not statistical difference among other treatment groups(P>0.05). These indicated that appropriate concentration of traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharide can im-prove the antibody titer of vaccine immunity,and the immune enhancement effects of ASPLand IRPSLgroups were better.
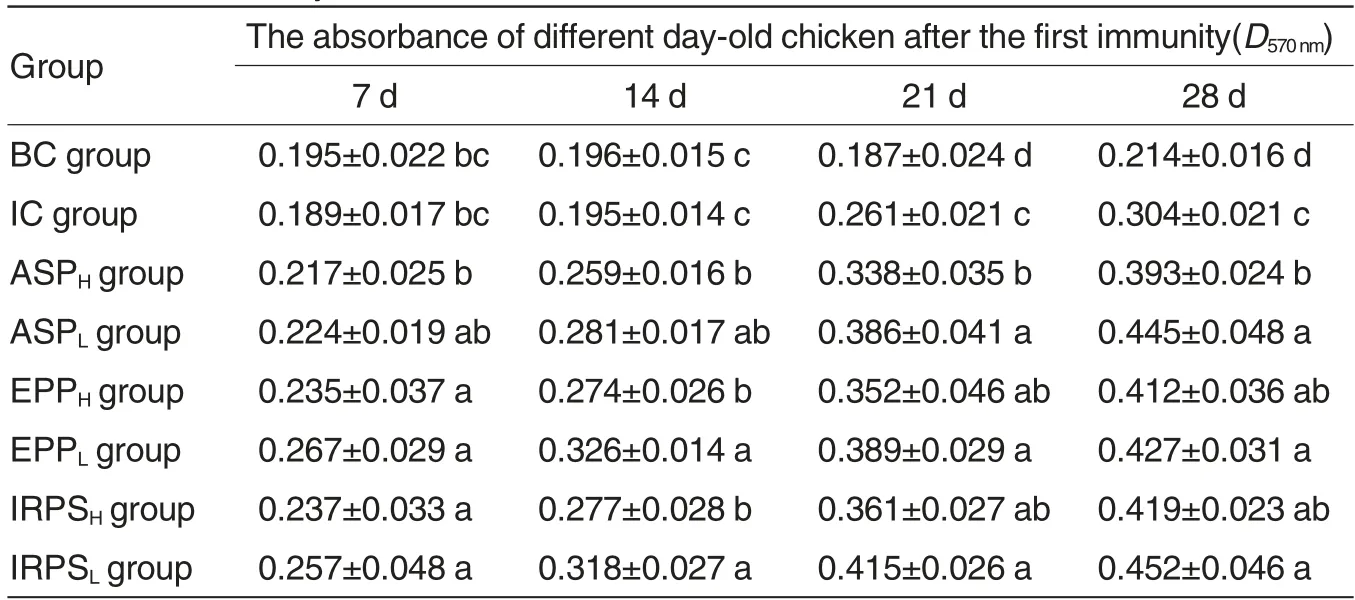
Table 3 The dynamic change of lymphocyte proliferation of different day-old chicken after the immunity
The change of the proliferation of peripheral T lymphocyte of different day-old chicken
As seen in Table 3,on the 7thd after the immunity, except ASPH and ASPLgroups, the D570nmvalue of other treatment groups was significantly higher than that of immune control group and blank control group (P <0.05); among all treatment groups,except ASPHgroup,there was not significant difference among other groups(P>0.05).On the 14th,21stand 28thd after the immunity, the D570nmvalue of each treatment group was all significantly higher than that of immune control group and blank control group (P<0.05); among all treatment groups, on the 14thd after the immunity,there was not significant difference among all low-dose groups, and so did all highdose groups and ASPLgroup(P>0.05);on the 21stand 28thd after the immunity,except ASPH group,there was not statistical difference among all treatment groups(P>0.05).
Discussions
Many researches showed that the polysaccharide of traditional Chinese medicine has growth-promoting effect.Wang Xuebin et al.[6]showed that APS powder and APS injection can promote the growth of chicken. The research carried out by Liang Ying et al.[7]also indicated that adding appropriate polysaccharide of Scutellaria baicalensis into the diet can improve the growth performance of broiler chicken. In the experiment, the results showed that except ASPHgroup, the weight gain rate of chicken of other treatment groups is increased significantly, this may be caused by the complexing of high-dose ASP and fat,which inhibits the absorption of fat,thereby reducing the growth performance of chicken[8].
Serum antibody titer reflects specific humoral immunity mediated by B lymphocyte. The higher the antibody titer,the stronger the antiviral ability of chicken, and the stronger the ability of anti-infection of chicken[9]. This experiment results showed that appropriate polysaccharide of traditional Chinese medicine can significantly enhance the humoral immunity of chicken, improve the antibody titer of ND vaccine, and enhance the anti-ND infection ability of chicken,the results are consistent with the research results of Qiu Yan et al.[10]and Wang et al.[11].
T lymphocyte is the immune regulating hub of the body,its proliferation reflects the immune level of body cells[12].The immunological competence of T lymphocyte is related to anti-viral ability of the body; when the viability function of T cell reduces,the generation of different cytokines (such as interleukin, interferon and tumor factors,etc.) decreases, and the assistant role of helper T lymphocyte to B cell antibody is affected[13]. The experiment results indicated that 3 polysaccharides of traditional Chinese medicine can promote the proliferation of peripheral T lymphocyte, and show certain doseeffect and time-effect relationship.These show that appropriate polysaccharide of traditional Chinese medicine can promote the proliferation of T lymphocyte.
In the experiment, taking ASP which has already been applied in animal production as the reference, the immunological enhancement effects of EPP and IRPS were observed, and the results showed that the growth promotion and immunomodulatory effects of Chinese herbal polysaccharide show certain dose-effect relationship,the weight-increasing and immunological enhancement effects of IRPS at low dosage are the best, high-dosage IRPS and EPP also have certain weight-increasing and immunological enhancement effects. Therefore, it is necessary to further screen the effective dose in the application and development of traditional Chinese medicine.
[1]JB LOWE, JD MARTH. A genetic approach to mammalian glycan function[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry,2003,72(1):643-691.
[2]BERTOZZI CR,KIESSLING LL.Chemical glycobiology [J]. Science, 2001, 291(5512):2357-2364.
[3]XIE MY(谢明勇),NIE SP(聂少平).Areview about the research of structure and function of polysaccharides from natural products (天然产物活性多糖结构与功能研究进展)[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology (中国食品学报), 2010, 10(2):1-11.
[4]THEKISOE MM, MBATI PA, BISSCHOP SPR. Different approaches to the vaccination of free ranging village chickens against Newcastle disease in Qwa-Qwa,South Africa [J]. Veterinary Microbiology,2004,101:23-30.
[5]GUO ZH(郭振环),HU YL(胡元亮),MA X(马霞), et al. Adjuvanticity of sulfated lentinan for Newcastle disease vaccine(硫酸化香菇多糖对新城疫疫苗免疫效果的影响)[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University(南京农业大学学报),2010,33(1):76-80.
[6]WANG XB(王学斌),CHEN GY(陈功义),WEI ZY (魏战勇),et al.Comparison on effect of astragalus polysaccnaride powders and injects on immune function and growth of chickens (黄芪多糖粉剂和注射剂对雏鸡免疫功能和生长的影响比较)[J].China Poultry(中国家禽),2007,29(3):21-23.
[7]LIANG Y(梁英),JIANG N(姜宁),HE WJ(何雯娟), et al. Effects of astragalus polysaccharide on growth performance and immune function of broilers(黄芩多糖对肉仔鸡生长性能和免疫功能的影响)[J].Acta Zoonutrimenta Sinica(动物营养学报),2010,22(4):1031-1036.
[8]HE G (赫刚). Effects of chitosan on growth performance and immune functions in broilers(壳聚糖对肉仔鸡生长性能与免疫功能的影响)[J]. China Feed(中国饲料),2005(24):19-21.
[9]XUE F (薛峰),WU SL (吴胜龙),TANG YH(唐应华),et al.Monitoring of hemagglutination inhibition antibody titers specific to Newcastle disease virus and avian influenza virus in field chickens immunized with different immune program and it’s potential relationship to the protection from Newcastle disease and avian influenza (不同免疫程序的鸡群新城疫和禽流感抗体水平与免疫保护之间的相关性试验)[J].Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine (中国兽医杂志),2005,41(9):23-25.
[10]QIU Y(邱妍),CUI BA(崔保安), HU YL(胡元亮),et al.Effects of four polysaccharides on antibody titer and T lymphocyte in vaccinated chicken (4 种多糖对免疫雏鸡抗体效价和T 淋巴细胞的影响)[J].Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University (南京农业大学学报),2008,31(1):77-81.
[11]WANG DY, HU YL, SUN JL, et al.Comparative study on adjuvanticity of compound Chinese herbal medicinal ingredients [J]. Vaccine, 2005, 23(28):3704-3708.
[12]KIM HM,HAN SB,OH GT,et al.Stimulation of humoral and cell mediated immunity by polysaccharide from mushroom Phellinus linteus [J]. International Journal of Immunopharmacology,1996,18(5):295-303.
[13]WANG DY (王德云), HU YL(胡元亮),ZHANG BK (张宝康),et al. Comparison on immune synergism of several Chinese herbal medicinal ingredients with interleukin-2(几种中药成分与IL-2 免疫协同作用的比较)[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University(南京农业大学学报),2005,28(3):140-142.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Specific Gravity-based Seed Grading on Seed Germination,Seedling Emergence and Grain Yield of Hybrid Rice
- Effects of NaCl Stress on Seed Germination of Four Canavium album Raeuseh Cultivars
- Application Effects of Ultra-fine Powder Shaped Maize Seed Coating Agent in Spring Sowing areas in northeast China
- Breeding and Application of a Japonic Rice Cytoplasmic Male Sterility Line,E-Jing A
- Effect of Low Temperature and Sparse Light Conditions on Cold Tolerance of Different Rice Lines at Seedling Stage
- Molecular Marker Assisted Selection for Fusarium Wilt Resistance Breeding in Watermelon(Citrullus lanatus)
