基于随机等价线性化法的悬浮隧道锚索随机振动研究
第一作者 苏志彬 男,硕士,讲师,1980年生
通信作者 孙胜男 女,博士,副教授,1982年生
sunshengnan1982@163.com
基于随机等价线性化法的悬浮隧道锚索随机振动研究
苏志彬,孙胜男
(聊城大学 建筑工程学院,山东 聊城252059)
摘要:为了得到悬浮隧道锚索在随机环境激励作用下的响应,建立了悬浮隧道锚索非线性随机振动方程,并在方程中考虑了锚索的垂度效应,随后采用随机等价线性化法对随机激励作用下锚索的振动响应进行了分析。研究结果表明:在零均值高斯白噪声环境激励作用下,锚索的跨中位移和速度均方根响应经过一定时间后将趋于定值,位移和速度的互相关函数趋于零;锚索的阻尼比越大,锚索跨中横向位移均方根响应越小;激励的功率谱密度强度越大,锚索跨中横向位移均方根响应越大;由于水体阻尼力的存在,悬浮隧道锚索的位移和速度均方根响应比空气中锚索的响应大幅减小。
关键词:悬浮隧道;随机等价线性化法;随机振动;垂度
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助(51108224);山东省自然科学基金资助项目(ZR2013EEL006)
收稿日期:2013-09-13修改稿收到日期:2014-03-03
中图分类号:U459.5文献标志码: A
Random vibration analysis of a submerged floating tunnel’s tether based on stochastic equivalent linearization method
SUZhi-bin,SUNSheng-nan(School of Architecture & Civil Engineering, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng 252059, China)
Abstract:To study the random vibration response of a submerged floating tunnel’s tether subjected to random ambient excitation, a non-linear random vibration equation of the tether was established considering the effect of tether sag. Subsequently, the vibration response of the tether was analyzed by means of the stochastic equivalent linearization method. The results indicated that the mid-span displacement and velocity root mean square responses of the tether to zero-mean Gaussian white noise excitation tend to stable values after a certain period of time, while the cross-correlation function between mid-span displacement and velocity tends to zero; the mid-span displacement root mean square response of the tether decreases with increase in the tether’s damping ratio, whereas it increases with increase in the power spectral density of the excitation; due to the existence of the water damping force, the displacement and velocity root mean square responses of the tether decreases greatly compared with those of the tether in air.
Key words: submerged floating tunnel; stochastic equivalent linearization method; random vibration; sag
长期以来,为解决深水水道穿越问题,研究人员一直在寻找一种更有效、更安全、与环境更为协调的运输系统。一种合适的跨越水道的方式,无疑会给两岸带来极大的便利与经济效益。在我国,以何种方式跨越渤海海峡、琼州海峡一直是专家学者们关注的焦点[1-2]。悬浮隧道(亦称作“阿基米德桥”)是一种跨越水域的新型结构形式,此结构形式可跨越不同类型的水域,如海湾、河流、海峡、湖泊等,并与航道互不干扰。自从这种结构形式问世以来,这种跨越水域的创新方案得到了国内外专家的广泛关注[3-5]。
悬浮隧道锚索具有质量轻、阻尼小、柔度大的特性,极易发生振动。作为悬浮隧道的关键受力构件,许多学者对锚索的振动问题进行了研究。葛斐等[6]建立了悬浮隧道锚索在波流场中顺流向涡激振动的数学模型,考虑了波浪作用下悬浮隧道管体的运动引起的强迫激励和参数激励对锚索涡激振动的影响。陈健云等[7]将悬浮隧道的锚索简化为受张力的梁,建立了锚索涡激振动方程,讨论了锚索倾角、张力和长度对其最大动剪力和最大动弯矩的影响。葛斐等[8]通过Hamilton原理推导了悬浮隧道管体和锚索的运动控制方程,方程中引入了锚索轴向和横向变形之间的耦合作用,并在时域内求解运动控制方程。罗刚等[9]考虑流体-结构耦合效应以及悬浮隧道锚索的几何非线性特点,建立了锚索的非线性振动方程,并通过有限元软件ANSYS的二次开发,分析了悬浮隧道锚索在横向升力作用下的动力特性。项贻强等[10]利用Hamilton原理,考虑悬浮隧道管体和锚索的耦合效应,建立锚索-管体耦合系统的运动方程,对5种典型工况的锚索跨中和管体跨中的位移时程曲线进行了比较。Wittig[11]研究了线性绳索承受平稳宽带点载荷激励下的速度均方动力响应,从而得到了拉索振动的动能响应分布规律。Rega[12]综述性的论述了悬索结构的随机振动,振动稳定特性和流体介质中的拉索振动特性。Yong[13]通过建立索-梁结构面内、面外三自由度振动微分方程组,采用随机线性化法分析了索梁结构中拉索面外自参数随机振动特性。
随机等价线性化法是非线性确定性振动的等价线性化法对随机问题的推广,它的基本思想是把受随机干扰的非线性体系的运动方程用一个等价的线性方程来近似,然后使两个方程之差的误差项的某种量度最小的原则来确定等价线性方程中的参数。这种方法既适用于弱非线性体系,也适用于强非线性体系,在工程实际中应用较广,是目前解决工程结构非线性随机振动问题最有效的方法之一[14]。
锚索处于复杂的波流环境中,其所受的环境激励具有很强的随机性,因此研究锚索在随机环境激励作用下的振动响应问题变得尤为重要。为了得到悬浮隧道锚索在随机环境激励作用下的响应,建立了锚索的非线性随机振动方程,方程中考虑了锚索的垂度效应,随后,采用随机等价线性化法对随机环境激励作用下悬浮隧道锚索的振动响应进行了分析。
1运动方程的建立

图1 锚索振动模型 Fig.1 Vibration model of tether

令θ、LE、m、E和A分别为静力作用下锚索的倾角、长度、锚索无应力状态下的单位长度质量、弹性模量和横截面积,锚索在静力状态下的张力为T0=T0(s),s为弧长坐标。用位移u表示在动荷载作用下的动力构形,u为沿锚索轴向的法线方向偏离静力平衡位置的位移。
(1)
采用Hamilton原理得到锚索的振动方程为[15]
FD=F(t)
(2)
(3)
式中:FD为锚索振动引起的水体对其产生的作用力;CS为锚索的黏性阻尼系数;由小垂度假设,T0约为沿z向的锚索初张力H0;F(t)为均值为零的高斯白噪声激励荷载;ΔH为锚索振动引起的附加张力。
根据线性化的Morison公式,锚索振动引起水体对其单位长度上的总作用力可以表示为附加惯性力和水体阻尼力之和[16]
(4)

索的振动模态近似取为标准弦的振动模态[17]
(5)
采用伽辽金法化简式(2),得

j=1,2,…,∞
(6)
式中:R(z,t)称为留函数[7]。
取一阶振动模态化简式(6),得:
(7)

采用随机等价线性化法对式(7)进行求解,设与式(7)等价的线性方程为:
(8)
式中:βe、ωe分别为等效线性方程表征阻尼和刚度的系数。
式(7)和式(8)之差的误差项为:
(9)
式中:
(10)
ce=2(βe-β0)
(11)
根据随机等价线性理论有:
(12)
(13)
将式(12)代入式(10)
(14)
解得:
(15)

将式(13)代入式(11)得:
(16)
解得:
(17)
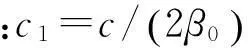

(18)
(19)
式中:S0是激励的功率谱密度。

2数值分析与结果
目前全球范围内并无一座悬浮隧道建成,悬浮隧道锚索的参数取值参考了国外拟建悬浮隧道的设计参数。总水深取为170 m,隧道管体置于水面下30 m处,其它参数取值见表1[18],锚索的速度位移均方根响应采用Matlab编制程序求得。

表1 基本参数



图2 跨中位移均方根响应Fig.2Rootmeansquareofmid-spandisplacement图3 跨中速度均方根响应Fig.3Rootmeansquareofmid-spanvelocity图4 跨中位移和速度的互相关函数Fig.4Cross-correlationfunctionofmid-spandisplacementandvelocity
2.2结构阻尼和激励谱密度强度的影响
锚索的跨中位移均方根和锚索的阻尼比之间的关系(见图5)。由图5可知,由于阻尼对锚索振动的抑制作用,随着阻尼比的增大,锚索跨中位移均方根响应值变小,即振动的动能变小,且锚索振动趋于稳定所用的时间越来越少。从图6可知,随着激励谱密度强度的增大,锚索跨中位移均方根响应也随之增大。

图5 跨中位移均方根和ξ S的关系 Fig.5 Relationship between root mean square of mid-span displacement and ξ S
2.3水体阻尼力的影响
空气中的锚索没有考虑空气阻力和升力的影响,水下锚索考虑了流体阻尼力和附加惯性力的影响,随机激励的功率谱密度相同时,悬浮隧道锚索和空气中锚索的位移和速度均方根响应(见图7和图8)。可以看出,空气中的锚索跨中位移均方根趋于稳定值时为1.29 m,速度均方根为13.2 m/s;水下锚索由于水体阻尼力的作用,跨中位移均方根趋于稳定值时为0.11 m,速度均方根为0.79 m/s。水下锚索由于水体阻尼力的存在使得锚索的跨中位移和速度均方根响应均大幅减小。
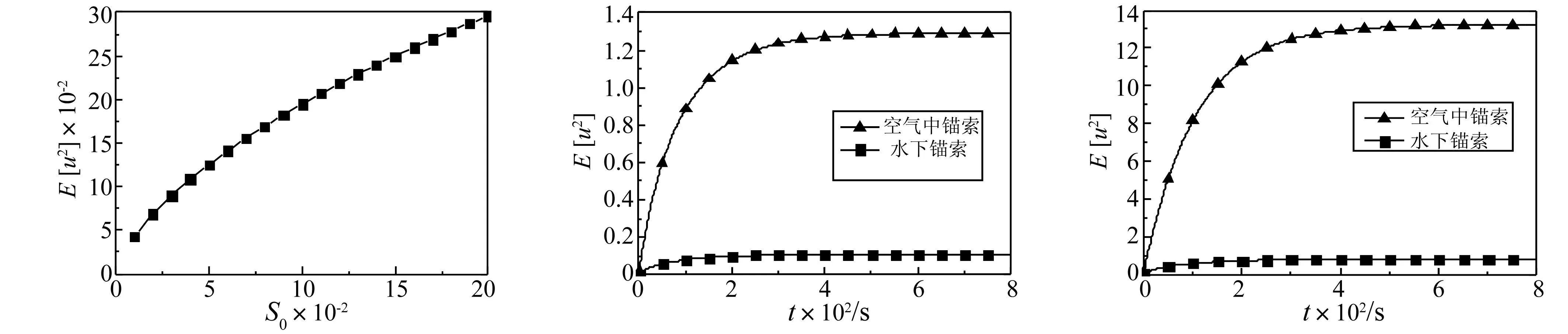

图6 激励的功率谱密度和跨中位移均方根的关系Fig.6Relationshipbetweenpowerspectraldensityofexcitationandrootmeansquareofmid-spandisplacement图7 水体阻尼力对位移均方根的影响Fig.7Effectofwaterdampingforceonrootmeansquareofdisplacement图8 水体阻尼力对速度均方根的影响Fig.8Effectofwaterdampingforceonrootmeansquareofvelocity
3结论
(1) 在零均值高斯白噪声激励作用下,经过较短的时间后,悬浮隧道锚索的振动趋于平稳,位移均方根响应和速度均方根响应均趋于定值,锚索位移和速度互相关函数趋于零。
(2) 随机等价线性化法和蒙特卡罗数值方法进行对比,当锚索的振动趋于平稳后两种方法的计算结果比较接近,证明本方法对锚索随机振动分析的可靠性。
(3) 随着锚索阻尼比的增大,锚索跨中位移均方根响应趋于稳定所用时间越短。
(4) 随机激励的功率谱密度相同时,水下锚索的速度和位移均方根响应比空气中的锚索小,所以水体阻尼力对锚索随机振动具有抑制作用。
参 考 文 献
[1] 宋克志, 王梦恕. 烟大渤海海峡隧道的可行性研究探讨[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2006, 43(6): 1-8.
SONG Ke-zhi, WANG Meng-shu. Feasibility study on Bohai Channel tunnel connecting yantai and dalian [J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2006, 43(6): 1-8.
[2] 麦继婷, 关宝树. 琼州海峡悬浮隧道的可行性研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2003, 80(4): 93-96.
MAI Ji-ting, GUAN Bao-shu. A feasibility study on Qiongzhou strait submerged floating tunnel [J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2003, 80(4): 93-96.
[3] Wu Xiao-dong, Ge Fei, Hong You-shi. Effect of travelling wave on vortex-induced vibrations of submerged floating tunnel tethers [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2010, 4: 153-160.
[4] Lu Wei, Ge Fei, Wang Lei, et al. On the slack phenomena and snap force in tethers of submerged floating tunnels [J]. Marine Structures, 2011, 24: 358-376.
[5] Felch J. The seattle-bellevue loop with still-water submerged floating tunnel [C]// Proceedings of the 4th Symposium on Strait Crossing, Bergen, Norway, 2001, 581-590.
[6] 葛斐,董满生,惠磊,等. 水中悬浮隧道锚索在波流场中的涡激动力响应 [J]. 工程力学,2006,23(S1): 217-221.
GE Fei, DONG Man-sheng, HU Lei, et al. Vortex-induced vibration of submerged floating tunnel tethers under wave and current effects [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2006, 23(S1): 217-221.
[7] 陈健云,孙胜男,王变革. 悬浮隧道锚索的动力分析[J].计算力学学报, 2008, 25(4): 488-493.
CHEN Jian-yun, SUN Sheng-nan, WANG Bian-ge. Dynamic analysis for the tether of submerged floating tunnel [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2008, 25(4): 488-493.
[8] 葛斐, 龙旭, 王雷, 等. 水中悬浮隧道管段锚索耦合模型涡激振动研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2009, 22(3): 83-88.
GE Fei, LONG Xu, WANG Lei, et al. Study of vortex-induced vibration of submerged floating tunnel tube-tether coupled model [J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2009, 22(3): 83-88, 100.
[9] 罗刚, 石研玉, 申奇, 等. 水中悬浮隧道锚索横向动力特性分析[J]. 长安大学学报, 2012, 32(3): 73-78.
LUO Gang, SHI Yan-yu, SHEN Qi, et al. Lateral dynamic characteristics analysis for cable of submerged floating tunnel in water [J]. Journal of Changan University, 2012, 32(3): 73-78.
[10] 项贻强, 晁春峰. 悬浮隧道管体及锚索耦合作用的涡激动力响应[J]. 浙江大学学报, 2012, 46(3): 409-415.
XIANG Yi-qiang, CHAO Chun-feng. Vortex-induced dynamic response for combined action of tube and cable of submerged floating tunnel [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University, 2012, 46(3): 409-415.
[11] Wittig L E. Random vibration of a point-driven strings and plates [D]. PhD thesis, MIT. 1971.
[12] Rega G. Nonlinear vibrations of suspended cables-part Ⅲ: Random excitation and interaction with fluid flow [J].Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2004, 57(6): 515-549.
[13] Yong Xia, Yozo Fu-jino. Auto-parametric vibration of a cable-stayed-beam structure under random excitation [J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2006, 5: 279-286.
[14] 欧进萍, 王光远. 结构随机振动[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1998.
[15] SUN Sheng-nan, CHEN Jian-yun, LI Jing. Non-linear response of tethers subjected to parametric excitation in submerged floating tunnels [J]. China Ocean Engineering. 2009, 23(1): 167-174.
[16] 孙胜男. 悬浮隧道动力响应分析[D].大连: 大连理工大学, 2008: 105-107.
[17] Irvine H M. Cable Structures [M]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, Cambridge, MA, 1981.
[18] Faggiano B, Landolfo R, Mazzolani F M. Design and modelling aspects concerning the submerged floating tunnels: an application to the Messina strait crossing [C]// Krobeborg. Strait Crossing 2001. Swets & Zeitlinger Publishers Lisse, 2001: 511-519.


