饲料中添加两株乳酸菌及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾消化酶活性的影响
沙玉杰,王 雷,孙国琼,刘 梅,王宝杰
饲料中添加两株乳酸菌及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾消化酶活性的影响
沙玉杰1,2,3,王雷1,2,孙国琼1,2,刘梅1,2,王宝杰1,2
(1.中国科学院 海洋研究所 海洋生物学重点实验室,山东 青岛 266071; 2.青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室海洋生物学与生物技术功能实验室,山东 青岛 266237; 3.中国科学院大学,北京 100049)
摘要:为了探讨前期实验获得的益生菌及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾消化功能的影响,将初始体质量3.5 g ± 0.06 g的凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei)在30℃± 2℃环境下于水族箱中养殖4周。以基础饲料为对照组,在基础饲料中分别添加戊糖乳杆菌(Lactobacillus pentosus)HC-2、粪肠球菌(Enterococcus faecium)NRW- 2、戊糖乳杆菌HC-2的发酵上清液,最终每克基础饲料中含有1.0×107 CFU益生菌或此菌量所对应的发酵上清液,共配制3组实验饲料。实验结果如下: 与对照组相比,各实验组对虾肠道中蛋白酶活力显著提高(P<0.05),但肝胰腺中蛋白酶活力无显著差异; 添加 NRW-2的实验组与对照组相比,肠道和肝胰腺中淀粉酶和脂肪酶活力均显著提高(P<0.05),HC-2组对虾肝胰腺中淀粉酶及肠道中脂肪酶的活力显著提高(P<0.05),而HC-2发酵上清液的添加仅显著提高了对虾肠道蛋白酶和淀粉酶的活性。结果表明饲料中添加 NRW-2、HC-2及其发酵上清液可以提高凡纳滨对虾肠道及肝胰腺中消化酶的活力,但在不同组织中提高消化酶活性的种类是不同的,为水产养殖安全投入品的开发及乳酸菌在水产养殖中的推广应用提供一定的科学依据。
关键词:戊糖乳杆菌(Lactobacillus pentosus)HC-2; 粪肠球菌(Enterococcus faecium)NRW-2; 凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei); 消化酶活性
[Foundation: The National Key Technology R&D Program of China,No.2012BAD17B03]
凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei),原产于南美洲太平洋沿岸,因其具有生长周期短、抗病力强、对水环境适应力强等优点,在中国得到了迅速推广[1]。然而在对虾养殖中,由于病害泛滥给对虾养殖业造成了巨大损失[2]。但是目前尚无有效的治疗措施,主要以预防为主,其中采用益生菌提高对虾的生理健康水平和清洁养殖环境已成为预防病害的重要措施。
益生菌是一类对宿主有益的活性微生物,其对水产动物有诸多有利影响,如拮抗病原菌、与病原菌竞争粘附位点和营养以及提高宿主免疫力等[3-4]。乳酸菌是一种被广泛应用的益生菌,其在畜禽养殖的研究应用较多,研究表明其可以增强畜禽的免疫力、调节肠道微生物菌群平衡、分泌抑菌物质如乙酸、乳酸和细菌素及提高畜禽的成活率和日增重等[5-12]。近年来,乳酸菌如短乳杆菌(Lactobacillus breris)、嗜酸乳杆菌(Lactobacillus acidophilus)及植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)等也被广泛的应用于水产中以提高水产动物的免疫机能及生长性能[13]。但这些菌株大部分来自于畜禽,考虑到水陆两类动物生活习性的迥然差异,作者自水产动物中分离得到两株乳酸菌: 戊糖乳杆菌(Lactobacillus pentosus)和粪肠球菌(Enterococcus faecium),前期实验结果说明两株菌具有促进对虾生长的作用。
本实验研究了饲料中添加水生动物来源的粪肠球菌、戊糖乳杆菌及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾消化酶活性的影响,探讨了益生菌及其代谢产物对凡纳滨对虾消化酶的调节作用,以期为水产养殖安全投入品的开发及乳酸菌在水产养殖中的推广应用提供一定的科学依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1实验材料
实验菌株: 粪肠球菌 NRW-2和戊糖乳杆菌HC-2均分离自健康的矛尾刺虾虎鱼(Acanthogobius hasta),预研究发现 NRW-2对凡纳滨对虾肠道粗黏液具有较好的黏附性,而 HC-2对副溶血弧菌ATCC17802具有较强的抑菌活性。两株菌分别接种于MRS液体培养基在37℃条件下静置培养24 h后,对发酵液进行离心(12 000 r/min,10 min),保留HC-2上清液备用,菌体用无菌海水洗涤 3次后重悬于无菌海水中备用。
健康的凡纳滨对虾由青岛瑞兹海珍品发展有限公司提供,1 200只对虾平均分配于12个水族箱(640 L/个)暂养驯化1周,暂养期间每天饲喂3次基础日粮。所有对虾均饲养于海水中(盐度30),温度为(30 ± 2)℃,持续通气,每天日换水量为60%。饲料每日投喂量为对虾体质量的10%,投喂时间分别为7: 00,11: 00 和 19: 00,投喂量分别占每日投喂量的35%,20% 和 45%。驯化期(7 d)结束后,每个水族箱中凡纳滨对虾的平均体质量约为3.5 g。
基础饲料为烟台大乐饲料有限公司生产的南美白对虾饲料 1#料,粗蛋白 42%,粗脂肪 7%,灰分15%,水分11%。
1.2实验设计
将12个水族箱随机分成4组(3个实验组,1个对照组),每组3个重复,每个重复90只虾。实验组1:基础饲料中含有戊糖乳杆菌活菌(1×107CFU/g饲料);实验组 2: 对虾投喂的基础饲料中含有粪肠球菌活菌(1×107CFU/g饲料); 实验组3: 对虾投喂的饲料中含有戊糖乳杆菌的上清液(对应每克饲料中含有1×107CFU戊糖乳杆菌上清液的量); 对照组只投喂基础饲料。养殖周期为 4周。饲养条件与驯化时期一致。
1.3样品处理
实验结束后,自12个水族箱中分别随机选取20只对虾,用 75%酒精对其表面消毒后进行解剖,分别取其肝胰腺和肠道,去除肠道的内容物并且在滤纸上将表面的水分吸干,每个样品均为20只对虾的混样,所有操作均在冰浴中进行。
分别称取 1 g肠道及肝胰腺样品置于预冷的匀浆器,并加入 4倍体积预冷的磷酸缓冲液(pH7.4)匀浆,随后12 000 r/min、4℃离心10 min,留上清,4℃储存,样品在24 h之内测定,每组样品3个平行。
1.4消化酶测定
蛋白酶活力测定采用Rathore[14]的方法进行,在此条件下水解底物偶氮酪蛋白,将每分钟 OD值增加0.001所需的酶量定义为一个酶活单位。
淀粉酶活力测定参照黄凯等[15]的淀粉酶测定方法。在 25℃下,每分钟每毫升淀粉酶将可溶性淀粉降解成麦芽糖,麦芽糖含量每升高1 µg作为1个酶活单位。
脂肪酶活力测定参照 Aryee等[16]的方法进行,在 25℃条件下,催化对硝基苯酚每分钟 OD值增加0.01所需酶量定义为一个酶活单位。
各种酶活力以比活力进行表示,即每毫克可溶性蛋白所含酶活单位数(U/mg)。蛋白质浓度采用考马斯亮蓝G-250法测定。
1.5数据分析
所有数据由 SPSS 17.0软件进行单因素方差和LSD多重比较分析,显著水平P值采用0.05。
2 结果
2.1饲料中添加 NRW-2、HC-2及其发酵
上清液对凡纳滨对虾蛋白酶活力的影响
实验结果表明,与对照组相比,饲料中添加NRW-2、HC-2及其发酵上清液显著提高了凡纳滨对虾肠道中蛋白酶的活力,其中 NRW-2处理组的蛋白酶活力最高,并且显著高于其他两个处理组(P<0.05); 凡纳滨对虾肝胰腺中蛋白酶活力在 3个处理组中虽然有不同程度的提高,但与对照组相比差异不显著,并且 3个处理组之间也没有显著差异(图1)。
2.2饲料中添加 NRW-2、HC-2及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾淀粉酶活力的影响
由图 2可见,HC-2(S)处理组与对照组相比,其对虾肠道中淀粉酶活力显著提高(P < 0.05),但是与NRW-2处理组相比没有显著差异,并且 HC-2及NRW-2处理组对凡纳滨对虾肠道淀粉酶活性的影响与对照组相比均不显著; 与对照组相比,HC-2和NRW-2处理组对虾肝胰腺中淀粉酶活力显著提高(P<0.05),而 HC-2(S)处理组对虾肝胰腺中淀粉酶活力与对照组相比差异不显著。

图1 饲料中添加NRW-2、HC-2及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾肠道和肝胰腺蛋白酶活力的影响Fig.1 Effects of probiotics and the corresponding supernatant on protease activities in the intestine and hepatopancreas of Litopenaeus vannamei
HC-2.戊糖乳杆菌HC-2; NRW-2.粪肠球菌NRW-2; HC-2(S).戊糖乳杆菌HC-2上清液
HC-2,NRW-2,and HC-2(S)represent Lactobacillus pentosus HC-2,Enterococcus faecium NRW-2,and the supernatant of L.pentosus HC-2,respectively
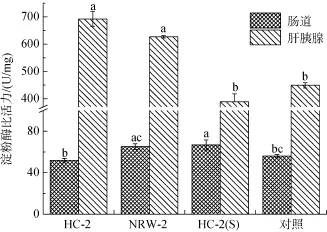
图2 饲料中添加NRW-2、HC-2及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾肠道和肝胰腺淀粉酶活力的影响Fig.2 Effects of probiotics and the corresponding supernatant on amylase activities in the intestine and hepatopancreas of Litopenaeus vannamei
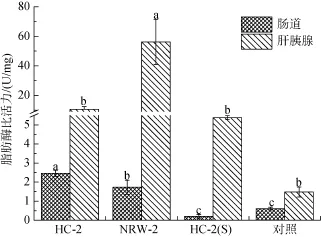
2.3饲料中添加 NRW-2、HC-2及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾脂肪酶活力的影响
由图3可见,HC-2处理组与NRW-2处理组对虾肠道脂肪酶的活性显著高于对照组(P<0.05),其中HC-2处理组的脂肪酶活力最高且显著高于 NRW-2处理组,而HC-2(S)处理组与对照组相比反而抑制了凡纳滨对虾肠道中脂肪酶活力; NRW-2处理组与对照组相比对虾肝胰腺脂肪酶活力显著提高(P<0.05),HC-2处理组和 HC-2(S)处理组与对照组相比虽然提高了脂肪酶活力,但差异不显著。
3 讨论
消化酶(蛋白酶、淀粉酶和脂肪酶等)在营养物质分解中发挥着重要作用。蛋白酶是水解蛋白质肽链一类酶的总称,可以将蛋白质分解为利于机体吸收的氨基酸; 淀粉酶和脂肪酶则分别降解碳水化合物和脂肪,最终生成的单体及能量供给机体生长及发育。动物的消化器官对饲料组成具有较高的敏感性,进而调节体内消化酶的活性,最终影响动物的生理状态[17-18]。
本实验中,NRW-2和HC-2的添加显著提高了凡纳滨对虾肠道中蛋白酶和脂肪酶活力,但均未显著提高淀粉酶活力,其中HC-2的添加对淀粉酶活力反而出现了一定的抑制作用。Ye等[19]发现饲料中添加益生菌或者益生元可以增强肠道中蛋白酶和淀粉酶的活性,其中对蛋白酶的作用优于淀粉酶,而王彦波等[20]的研究报告证实复合益生菌的添加显著提高了凡纳滨对虾肠道中蛋白酶、淀粉酶和脂肪酶的活力,与本实验的结果不完全一致,这可能是由于所采用的菌株种类与搭配不同所致。动物肠道中消化酶的活性受到诸多因素的影响,如温度、盐度、pH及肠道菌群等[21]。细菌具有分泌一系列胞外酶的特性,乳酸菌也不例外[22],但经过预实验本实验所用的粪肠球菌NRW-2和戊糖乳杆菌HC-2均无分泌可检测到的淀粉酶、蛋白酶和脂肪酶,因此本实验中的实验结果可能与粪肠球菌和戊糖乳杆菌的加入影响了对虾肠道的 pH或原肠道菌群中参与分泌消化酶及影响消化酶活性的微生物有关,但是此猜测还需要实验的进一步验证。
肝胰腺作为对虾消化系统中的重要器官,是众多生物大分子的主要合成场所,在对虾代谢上发挥着重要作用[23]。本实验中HC-2处理组显著提高了对虾肝胰腺中淀粉酶活力,而NRW-2处理组显著提高了对虾肝胰腺中淀粉酶和脂肪酶活力,但两者均未显著提高蛋白酶活力,此结果与 Sun等[24]研究的结果截然相反,其研究显示乳酸菌的加入显著提高了斜带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides)肝胰腺中蛋白酶活力,但对肝胰腺中淀粉酶和脂肪酶活力没有显著差异,并且Liu等[25]研究结果显示,饲料中芽孢杆菌的添加也没有显著提高凡纳滨对虾肝胰腺中蛋白酶活力,甚至随着菌量的增加而出现不同程度的抑制作用。这说明益生菌对机体消化酶活性的影响是各异的,与菌种本身表面成分及代谢有关,同样也与水生动物有关,如食性、环境条件、个体发育的不同阶段[26]及机体自身代谢需求等。
由于戊糖乳杆菌HC-2具有较强的抑菌作用,本实验将其活菌与发酵液分离后分别探讨它们的添加对凡纳滨对虾消化酶活性的影响。结果表明戊糖乳杆菌 HC-2上清液的添加提高了凡纳滨对虾肠道中蛋白酶和淀粉酶活力,对肠道中脂肪酶和肝胰腺中蛋白酶、淀粉酶和脂肪酶活力均没有显著差异; 而戊糖乳杆菌 HC-2菌体的添加显著提高了凡纳滨对虾肠道及肝胰腺中3种消化酶活力; 此外,前期实验显示戊糖乳杆菌 HC-2菌体的添加显著提高了凡纳滨对虾的特定生长率,而HC-2菌株发酵上清液实验组的特定生长率低于对照组(P>0.05),因此推测益生菌菌体在此菌量的情况下对机体的益生效果或许优于其发酵上清液。本实验就水生动物来源的两株乳酸菌及其发酵上清液对凡纳滨对虾消化酶活性影响的探讨,期望为水产养殖安全投入品的开发及乳酸菌在水产养殖的推广应用提供一定的科学依据。
参考文献:
[1]黄凯,王武.南美白对虾国外养殖发展概况及我国养殖现状,存在的问题与对策[J].内陆水产,2002,8:11-14.Huang Kai,Wang Wu.The development of Litopenaeus vannamei abroad and its situation,problems and countermeasures in China[J].Journal of Inland Fisheries,2002,8: 11-14.
[2]Zhang Y,Wang L L,Wang L L,et al.An integrin from
shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei mediated microbial agglutination and cell proliferation[J].Plos one,2012,7(7): 1-8.
[3]Verschuere L,Rombaut G,Sorgeloos P,et al.Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture[J].Microbiol Mol Biol R,2000,64(4): 655-671.
[4]宋奔奔,傅松哲,刘志培,等.水体中添加两种菌剂对凡纳滨对虾存活、生长及消化酶活力的影响[J].海洋科学,2009,33(4): 1-5.
Song Benben,Fu Songzhe,Liu Zhipei,et al.Effect of
adding two microbes to aquaculture water on shrimps' survival,growth and digestive enzyme activity[J].Marine Science,2009,33(4): 1-5.
[5]Bednorz C,Guenther S,Oelgeschläger K,et al.Feeding
the probiotic Enterococcus faecium strain NCIMB 10415 to piglets specifically reduces the number of Escherichia coli pathotypes that adhere to the gut mucosa[J].Appl Environ Microb,2013,79(24): 7896-7904.[6]Styková E,Nemcová R,Valocký I,et al.Adherence of bacteria to mucus collected from different parts of the reproductive tract of heifers and cows[J].Can J Microbiol,2013,59(11): 720-725.
[7]Larsen N,Thorsen L,Kpikpi E N,et al.Characterization of Bacillus spp.strains for use as probiotic additives in pig feed[J].Appl Microbiol Biot,2014,98(3):1105-1118.
[8]Villena J,Chiba E,Vizoso-Pinto M G,et al.Immunobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains differentially modulate antiviral immune response in porcine intestinal epithelial and antigen presenting cells[J].BMC Microbiol,2014,14(1): 126.
[9]Clarke G,Cryan J F,Dinan T G,et al.Review article:probiotics for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome-focus on lactic acid bacteria[J].Aliment Pharm Ther,2012,35(4): 403-413.
[10]Huang M K,Choi Y J,Houde R,et al.Effects of Lactobacilli and an acidophilic fungus on the production performance and immune responses in broiler chickens[J].Poultry Science,2004,83: 788-795.
[11]Brzóska F,Buluchevskij S,Stecka K,et al.The effects of lactic acid bacteria and mannan oligosaccharide,with or without fumaric acid,on chicken performance,slaughter yield and digestive tract microflora[J].Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences,2007,16(2): 241-251.
[12]Chen C Y,Tsen H Y,Lin C L,et al.Oral administration of a combination of select lactic acid bacteria strains to reduce the Salmonella invasion and inflammation of broiler chicks[J].Poultry Science,2012,91(9): 2139-2147.
[13]高鹏飞,张善亭,赵树平,等.乳酸菌在水产养殖业中的应用[J].家畜生态学报,2014,35(7): 82-86.
Gao Pengfei,Zhang Shanting,Zhao Shuping,et al.The application of lactic acid bacteria in animal breeders[J].Acta Ecologiae Aminalis Domastici,2014,35(7): 82-86.
[14]Rathore R M,Kumar S,Chakrabarti R.Digestive enzyme patterns and evaluation of protease classes in Catla catla(Family: Cyprinidae)during early developmental stages[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biol-ogy,2005,142(1): 98-106.
[15]黄凯,杨鸿昆,战歌,等.盐度对凡纳滨对虾幼虾消化酶活性的影响[J].海洋科学,2007,31(3): 37-40.Huang Kai,Yang Hongkun,Zhan Ge,et al.Effects of salinities on digestive enzyme activities of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei boone[J].Marine Science,2007,31(3): 37-40.
[16]Aryee A N A,Simpson B K,Villalonga R.Lipase fraction from the viscera of grey mullet(Mugil cephalus):Isolation,partial purification and some biochemical characteristics[J].Enzyme Microb Tech,2007,40(3):394-402.
[17]Bolasina S,Pérez A,Yamashita Y.Digestive enzymes activity during ontogenetic development and effect of starvation in Japanese flounder,Paralichthys olivaceus[J].Aquaculture,2006,252(2): 503-515.
[18]Shan X,Xiao Z,Huang W,et al.Effects of photoperiod on growth,mortality and digestive enzymes in miiuy croaker larvae and juveniles[J].Aquaculture,2008,281(1): 70-76.
[19]Ye J D,Wang K,LI F D,et al.Single or combined effects of fructo and mannan oligosaccharide supplements and Bacillus clausii on the growth,feed utilization,body composition,digestive enzyme activity,innate immune response and lipid metabolism of the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus[J].Aquacult Nutr,2011,17(4): 902-911.
[20]王彦波,傅玲琳.益生菌对凡纳对虾生长性能和消化酶活性的影响研究[J].饲料工业,2010,31(20):12-14.Wang Yanbo,Fu Linglin.The effects of probiotic on the performance and digestive enzyme activities of Litopenaeus vannamei[J].Feed Industry,2010,31(20):12-14.
[21]Wang J,Zhao L,Liu J,et al.Effect of potential probiotic Rhodotorula benthica D30 on the growth performance,digestive enzyme activity and immunity in juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus[J].Fish Shellfish Immun,2015,43(2): 330-336.
[22]Papamanoli E,Tzanetakis N,Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E,et al.Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from a Greek dry-fermented sausage in respect of their technological and probiotic properties[J].Meat Science,2003,65(2): 859-867.
[23]朱孟凯,姚翠鸾.温度胁迫对凡纳滨对虾肝胰腺氧代谢及能量代谢的影响[J].水产学报,2015,39(5):669-678.Zhu Mengkai,Yao Cuiluan.The impact of temperature stress on the oxygen metabolism and energy metabolism in the hepatopancreas of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei[J].Journal of Fisheries of China,2015,39(5):669-678.
[24]Sun Y Z,Yang H L,Ma R L,et al.Effect of Lactococcus lactis and Enterococcus faecium on growth performance,digestive enzymes and immune response of grouper Epinephelus coioides[J].AquacultNutr,2012,18(3): 281-289.
[25]Liu C H,Chiu C S,Ho P L,et al.Improvement in the growth performance of white shrimp,Litopenaeus vannamei,by a protease-producing probiotic,Bacillus subtilis E20,from natto[J].J Appl Microbiol,2009,107(3): 1031-1041.
[26]Gamboa-delgado J,Molina-poveda C,Cahu C.Digestive enzyme activity and food ingesta in juvenile shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei(Boone,1931)as a function of body weight[J].Aquac Res,2003,34(15):1403-1411.
(本文编辑: 谭雪静)
Effects of two lactic acid bacteria species and the corresponding supernatants on the activities of digestive enzymes in Litopenaeus vannamei
SHA Yu-jie1,2,3,WANG Lei1,2,SUN Guo-qiong1,2,LIU Mei1,2,WANG Bao-jie1,2
(1.Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology,Institute of Oceanology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Qingdao 266071,China; 2.Laboratory for Marine Biology and Biotechnology,Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology,Qingdao 266237,China; 3.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China)
Received: Apr.27,2015
Key words:Lactobacillus pentosus HC-2; Enterococcus faecium NRW-2; Litopenaeus vannamei; digestive enzyme
Abstract:To investigate the effects of probiotics and the corresponding supernatants on the activities of digestive enzymes in Litopenaeus vannamei,several groups of L.vannamei(approximately 3.5 g)were reared at a temperature of 30 ± 2°C in an aquaria for 4 weeks.The following four trials(three treated and one control)were conducted:T1,shrimp fed with a commercial diet + strain Lactobacillus pentosus HC-2(1×107CFU/g feed); T2,shrimp fed with a commercial diet + strain Enterococcus faecium NRW-2(1×107-CFU/g feed); T3,shrimp fed with a commercial diet + the supernatant of strain L.pentosus HC-2(the corresponding supernatant of 1×107CFU/g feed of L.pentosus HC-2); and T4,shrimp fed with a commercial diet alone as a control.The results demonstrated that the protease activities were significantly(P<0.05)increased in the intestines of three treatment groups compared with those in the control group,but they were not significantly increased in the hepatopancreas.The amylase and lipase activities were significantly(P<0.05)increased in the intestines and hepatopancreas of shrimp fed with E.faecium NRW-2 compared with those in the control group.The amylase and lipase activities were significantly(P<0.05)increased in the hepatopancreas and intestines,respectively,in the group of shrimp fed with L.pentosus HC-2,whereas the protease and amylase activities were just increased significantly in the intestines of shrimp fed with the supernatant of L.pentosus HC-2.This study suggested that the activities of digestive enzymes in L.vannamei can increase by NRW-2,HC-2,and the corresponding supernatant but vary in different tissues.These results provide a solid foundation for the application of probiotics in aquaculture.
中图分类号:S963.73+9
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1000-3096(2016)03-0059-06
doi:10.11759//hykx20150427001
收稿日期:2015-04-27; 修回日期: 2015-10-22
基金项目:国家科技支撑计划(2012BAD17B03)
作者简介:沙玉杰(1989-),女,山东德州人,博士研究生,主要从事水生动物微生态制剂的研究与开发,电话: 0532-82898723,E-mail:syjlw89@163.com; 王宝杰,通信作者,电话: 0532-82898722,E-mail:wangbaojie@qdio.ac.cn

