V-Ti基脱硝催化剂去除汞和PCDDs/PCDFs的研究现状
田军吉,杨胜芬,陆 邹,石 宇
(1.贵州省六盘水市钟山区经济和信息化局,贵州 六盘水 553001;2.信和汇金信息咨询(北京)有限公司,贵州 六盘水 553001)
综述与展望
V-Ti基脱硝催化剂去除汞和PCDDs/PCDFs的研究现状
田军吉1*,杨胜芬2,陆邹1,石宇1
(1.贵州省六盘水市钟山区经济和信息化局,贵州 六盘水 553001;2.信和汇金信息咨询(北京)有限公司,贵州 六盘水 553001)
摘要:将柔软纤维与折皱钢网复合制成波纹式支撑骨架,将V-Ti基脱硝催化剂负载到波纹式支撑骨架上制成整体波纹式脱硝催化剂。介绍V-Ti基波纹式整体脱硝催化剂的主要制备工艺、优点以及国内外对V-Ti基波纹式整体脱硝催化剂的研究现状;对V-Ti基脱硝催化剂与贵金属脱硝催化剂的制造成本以及PCDDs/PCDFs催化分解效果进行对比,两者具有相同的催化分解效果,V-Ti基脱硝催化剂成本低得多;活性组分、V质量分数以及活性温度不同,V-Ti基脱硝催化剂催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs的效果也不同,催化分解率最高可达97.7%;研究者得出V-Ti基脱硝催化剂催化氧化Hg0的不同效果,介绍V-Ti基脱硝催化剂催化氧化Hg0的研究现状。
关键词:三废处理与综合利用;V-Ti基脱硝催化剂;波纹式脱硝催化剂;汞;PCDDs/PCDFs
CLC number:TQ426.6;X701Document code: AArticle ID: 1008-1143(2016)05-0025-06
目前,火电厂、高炉转炉炼铁和炼钢、水泥行业燃煤烟气脱硝处理最有效的手段是SCR喷氨脱硝系统[1-9 ]。SCR喷氨系统核心是脱硝催化剂,工业常用的脱硝催化剂为V-Ti基催化剂,其催化反应活性温度窗口宽,为(300~420)℃。脱硝催化剂使用较多的是蜂窝式和波纹式,波纹式脱硝催化剂具有接触面积和压降大的特点,备受燃煤工厂青睐。研究发现,V-Ti基催化剂不仅可用于烟气脱硝处理,还可将烟气中PCDDs/PCDFs催化氧化分解为H2O、CO2和HCl[10-11],将Hg0催化氧化为Hg2+[12]。
本文综述波纹式脱硝催化剂的制备工艺、主要特点以及脱硝催化剂催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs和催化氧化汞的主要特性。
1波纹式脱硝催化剂的特点及制备工艺
波纹式脱硝催化剂属非均质催化剂,以柔软纤维和折皱钢网复合制成载体,将活性组分V2O5和V2O5-WO3等涂覆在载体上而制成。波纹式脱硝催化剂以玻璃纤维、陶瓷纤维或复合式载体作为支撑骨架,结构坚硬,承载能力强,还具有以下特点[13]:(1) 主要采用玻璃纤维作为基体材料,与传统的蜂窝式和板式脱硝催化剂相比,在制造工艺和结构上,融合了两种催化剂的优点;(2) 具有较大的比表面积,脱硝率高于90%,同体积条件下,催化效率优于其他脱硝催化剂;(3) 相同的催化效率,波纹式催化剂使用的活性原料少,每立方米质量比蜂窝式轻(50~100) kg,以100 m3计算,催化剂原料使用量降低(5~10) t;(4) 制备工艺相对简单,生产自动化程度高。
自20世纪60年代末开始,日本的三菱、武田化工和日立三家公司研制出以TiO2为基材的催化剂,并逐渐取代Pt-Rh和Pt系列催化剂。该类催化剂主要由V2O5(WO3)、Fe2O3、CrOx、CuO、MnOx、MoO3、NiO和MgO等金属氧化物或有联合作用的混和物构成,通常以TiO2、ZrO2、Al2O3、SiO2和AC等作为载体,与SCR系统中的液氨或CO(NH2)2等还原剂发生还原反应,成为电厂SCR脱硝工程中应用较广泛的主流催化剂产品。
国内主流SCR脱硝催化剂核心技术为美国、日本、韩国、丹麦和德国等国家垄断,技术壁垒高,我国主要靠高成本引进技术进行生产经营。大荣环保科技有限公司引进韩国先进技术,建成国内首个9 000 m3·a-1波纹式脱硝催化剂项目,现已在西安经济开发区启源装备园区投产。
2脱硝催化剂催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs
PCDDs/PCDFs化学性质相对稳定,对生物具有很大的毒害性,因此,如何去除PCDDs/PCDFs的研究受到重视。能催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs的催化剂有贵金属催化剂和过渡金属催化剂,虽然贵金属催化剂催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs的效率最高可达90%,但贵金属资源稀缺,价格昂贵,在批量生产和应用中受到限制;以过渡金属作为催化剂活性组分的主要有VOx、MnOx、CrOx和FeOx等,其中,VOx催化活性最高,V2O5/TiO2催化剂分解PCDDs/PCDFs的效果最好[14]。V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂可同时用于催化还原NOx和催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs[15]。
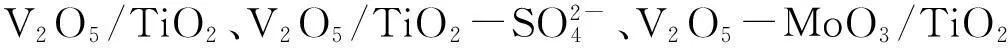
3脱硝催化剂催化氧化汞的性能
燃煤产生的汞约占人为释放量的30%,在燃煤烟气中,汞通常以单质汞Hg0、气态二价汞Hg2+及固态颗粒汞Hgp形式存在,其中,Hg0约占烟气中汞含量的70%[25]。Hg2+与固态颗粒汞Hgp可通过湿法脱硫、烟气除尘和MCFB烟气净化系统去除[26-27]。但Hg0易挥发且不溶于水,可通过吸附剂除去烟气中的Hg0[28-32]。通过对煤采用沉重分离、程序升温热解、酸性提取和SSE技术等研究无烟煤、褐煤和沥青煤释放汞的温度条件以及吸收方法进行预处理[33],研究[34-36]发现,在温度低于150℃、(150~250)℃、(250~400)℃和(400~600)℃时,汞分别以单质汞Hg0、HgCl2、HgS和硫铁矿键配位Hg形式释放,HNO3提取法对除去硫铁键配位汞具有较好的效果。工业用V-Ti基脱硝催化剂通过催化氧化能够有效地将Hg0氧化成Hg2+[37-38 ]。
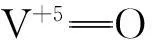
4结语与展望
虽然V系脱硝催化剂在催化氧化汞和催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs方面已有研究,但V-Ti基催化剂催化氧化Hg0和催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs的条件与催化还原NOx的条件存在差异,一是活性温度不同,催化氧化Hg0的最佳活性温度为(300~350)℃,催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs的最佳活性温度为(200~300)℃,而催化还原NOx的最佳活性温度为(300~420)℃;二是修饰剂的影响,在V-Ti基催化剂中加入修饰成分WO3(MoO3)后有利于促进Hg0和NOx的催化氧化还原反应,但对PCDDs/PCDFs的催化分解有抑制作用。研究V-Ti基催化剂催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs时,PCDDs/PCDFs主要是采用多氯苯和芳香烃混合而成的模拟气体进行研究,所得实验结果可能存在一定偏差。针对V-Ti基催化剂应用技术研究还有待进一步深入:
(1) 深入对V-Ti基催化剂成型工艺研究。虽然在国外波纹式V-Ti基脱硝催化剂技术已成熟,但由于国内烟气成分和相应成分含量不同,因此,研究适合国内生产的波纹式V-Ti基脱硝催化剂应用技术或催化剂成型产品迫在眉睫。
(2) 深入对V-Ti基催化剂催化氧化Hg0和催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs的机理及影响因素研究。研究加入不同修饰剂修饰V-Ti基催化剂催化氧化Hg0的机理影响,进一步提高V-Ti基催化剂催化氧化Hg0的效率;研究催化分解真正的PCDDs/PCDFs,真正了解催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs的机理和影响因素。
(3) 深入对工业用V-Ti催化剂改性研究。加深对现有V-Ti基催化剂改性研究,使改性后的V2O5-WO3(MoO3)/TiO2催化剂在最佳脱硝条件下能同时得到催化氧化Hg0和催化分解PCDDs/PCDFs的效率。
参考文献:
[1]曹志勇,谭城军,李建中,等.燃煤锅炉SCR烟气脱硝系统喷氨优化调整试验[J].中国电力,2011,44(11):55-58.
Cao Zhiyong,Tan Chengjun,Li Jianzhong,et al.Experiment of optimization adjustment for ammonia injection of selective catalytic reduction flue gas denitration system in coal-fired boiler[J].Electric Power,2011,44(11):55-58.
[2]方朝君,金理鹏,宋玉宝,等.SCR脱硝系统喷氨优化及最大脱硝效率试验研究[J].热力发电,2014,43(7):157-160.
Fang Zhaojun,Jin Lipeng,Song Yubao,et al.Performance optimization and maximum denitration efficiency analysis for SCR-DeNOx power plants[J].Thermal Power Generation,2014,43(7):157-160.
[3]中国环境保护产业协会脱硫脱硝委员会.我国脱硫脱硝行业2013年发展综述[J].中国环保产业,2014,(9):4-15.
[4]武宝会,崔利.火电厂SCR烟气脱硝控制方式及其优化[J].热力发电,2013,42(10):116-119.
Wu Baohui,Cui Li.SCR flue gas denitrification control and optimization in thermal power plants[J].Thermal Power Generation,2013,42(10):116-119.
[5]Patrick G W A Kompio,Angelika Bruckner,Frank Hipler,et al.A new view on the relations between tungsten and vanadium in V2O5-WO3/TiO2catalysts for the selective reduction of NO with NH3[J].Journal of Catalysis,2012,286:237-247
[6]尤振丰,丁明,方文仓,等.水泥行业烟气脱硝技术综述及展望[J].广东建材,2013,29(5):29-33.
[7]邢雨薇.钢铁行业烧结烟气脱硫工序节能减排方案研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2014.
Xing Yuwei.Study on sintering flue gas desulfurization process of energy-saving emission reduction of iron and steel industry[D].Chuangchun:Jilin Agricultural University,2014.
[8]刘庆祎.水泥窑炉SCR反应器流场数值模拟研究[D].北京:北京工业大学,2014.
Liu Qingyi.The numerical simulation of flow field in cement kilns SCR reactor[D].Beijing:Beijing University of Technology,2014.
[9]佘志伟,隋荣禄,孙振海.水泥窑炉烟气脱硝技术的比选分析与工程实践[J].江西建材,2015,(2):4-5.
[10]陈佳琦,高爽,李军,等.2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-1-氧自由基促进的钒基催化剂催化苯直接氧化制苯酚[J].催化学报,2011,32(9):1446-1451.
Chen Jiaqi,Gao Shuang,Li Jun,et al.2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxy-promoted hydroxylation of benzene to phenol over a vanadium-based catalyst using molecular oxygen[J].Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2011,32(9):1446-1451.
[11]Sindra L Summoogum,Dominika Wojtalewicz,Mohammednoor Altarawneh,et al.Formation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDD/F) by precursor pathways in oxidation of pesticide alpha-cypermethrin[J].Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2013,34:3499-3507.
[12]Raik Stollea,Heinz Koesera,Heinz Gutberletb.Oxidation and reduction of mercury by SCR DeNOx catalysts under flue gas conditions in coal fired power plants[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2014,144:486-497.
[13]宋存义,常冠钦,董震松,等.一种波纹板式SCR脱硝催化剂结构:中国,CN202263606U[P].2012-06-06.
[14]Chia Cheng Yang,Shu Hao Chang,Bao Zhen Hong,et al.Innovative PCDD/F-containing gas stream generating system applied in catalytic decomposition of gaseous dioxins over V2O5-WO3/TiO2based catalysts[J].Chemosphere,2008,73:890-895.
[15]Grzegorz Wielgosiński.The possibilities of reduction of polychlorinated dibenzo-pdioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans emission[J].International Journal of Chemical Engineering,2010,7(10):1-11.
[16]Bertinchamps F,Gregoire C,Gaigneaux E M.Systematic investigation of supported transition metal oxide based formulations for the catalytic oxidative elimination of (chloro)-aromatics:part Ⅱ:Influence of the nature and addition protocol of secondary phases to VOx/TiO2[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2006,66:10-22.
[17]Albonetti S,Mengou J E,Trifiro F.Polyfunctionality of DeNOx catalysts in other pollutant abatement[J].Catalysis Today,2007,119:295-300.
[18]Debecker D P,Bertinchamps F,Blangenois N,et al.On the impact of the choice of model VOC in the evaluation of V-based catalysts for the total oxidation of dioxins:furan vs. chlorobenzene[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2007,74:223-232.
[19]Debecker D P,Delaigle R,Eloy P,et al.Abatement of model molecules for dioxin total oxidation on V2O5-WO3/TiO2catalysts:the case of substituted oxygen-containing VOC[J].Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical,2008,289(1/2):38-43.
[20]Damien P Debecker,Romain Delaigle,Pao Chen Hung,et al.Evaluation of PCDD/F oxidation catalysts:confronting studies on modelmolecules with tests on PCDD/F-containing gas stream[J].Chemosphere,2011,82:1337-1342.
[21]Roland Weber,Takeshi Sakurai,Hanspaul Hagenmaier.Low temperature decomposition of PCDD/PCDF,chlorobenzenes and PAHs by TiO2-based V2O5-WO3catalysts[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,1999,20:49-256.
[22]Ji Shasha,Li Xiaodong,Ren Yong,et al.Ozone-enhanced oxidation of PCDD/Fs over V2O5-TiO2-based catalyst[J].Chemosphere,2013,92:265-272.
[23]Chang Shu Hao,Chi Kai Hsien,Young Chi Wei,et al.Effect of fly ash on catalytic removal of gaseous dioxins over V2O5-WO3catalyst of a sinter plant[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2009,43(19):7523-7530.
[24]Stieglitz L.The oxidative degradation of carbon and its role in the de-novo-synthesis of organohalogen compounds in fly ash[J].Chemosphere,1993,27:343-350.
[25]李建荣,何炽,商雪松,等.SCR脱硝催化剂对烟气中零价汞的氧化效率研究[J].燃料化学学报,2012,40(2):241-246.
Li Jianrong,He Chi,Shang Xuesong,et al.Oxidation efficiency of elemental mercury in flue gas by SCR De-NOx catalysts[J].Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2012,40(2):241-246.
[26]庄烨,刘科伟,路光杰.用于烟气除汞的烟气调质剂及其复合烟气净化方法:中国,CN103223290A[P].2013-07-31.
[27]刘海蛟.MCFB烟气净化系统的多种污染物协同脱除研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2009.
Liu Haijiao.Study on simultaneous removal of multi pollutant in MCFB flue gas cleaning system[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2009.
[28]孔凡海.铁基纳米吸附剂烟气脱汞实验及机理研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2010.
Kong Fanhai.Experimental and mechanism study of elemental mercury removal in flue gas by Fe-based nano-sorbent[D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2010.
[29]丁峰.矿物吸附剂对燃煤烟气中汞的脱除机制的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012.
Ding Feng.Mechanism study of elemental mercury removal from coal combustion flue gases by mineral sorbents[D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2012.
[30]谭增强.改性竹炭基吸附剂脱汞的实验及机理研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012.
Tan Zengqiang.Experimental and mechanism study of elemental mercury removal in flue gas by modified bamboo-based sorbents[D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2012.
[31]张润圃.P84掺炭纤维性能表征及其脱除燃煤烟气Hg0的试验研究[D].武汉:东华大学,2010.
Zhang Renpu.Performance of modificated P84-MCF and experimental study on adsorption of mercury[D].Wuhan:Donghua University,2010.
[32]刘松涛.烟气同时脱除Hg0、SO2和NOx的实验研究[D].保定:华北电力大学,2009.
Liu Songtao.Experimental study on simultaneous removal of Hg0,SO2and NOx from flue gas[D].Baoding:North China Electric Power University,2009.
[33]Luo Guangqian,Ma Jingjing,Han Jun,et al.Hg occurrence in coal and its removal before coal utilization[J].Fuel,2013,104:70-76.
[34]郭志航.褐煤热解分级转化多联产工艺的关键问题研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2015.
Guo Zhihang.Research on key issues of lignite pyrolysis-based staged conversion polygeneration technology[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2015.
[35]王钦.煤燃烧过程中易挥发元素(Hg、As、Se)迁移规律研究[D].天津:天津大学,2014.
Wang Qin.The study of transformation regularities of volatile trace elements(Hg,As,Se) during coal combustion[D].Tianjin:Tianjin University,2014.
[36]罗光前.燃煤汞形态识别及其脱除的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2009.
Luo Guangqian.Study of species identification and removal of mercury in coal and during coal combustion[D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2009.
[37]Pudasainee Deepak,Lee Sung Jun,Lee Sang-Hyeob,et al.Effect of selective catalytic reactor on oxidation and enhanced removal of mercury in coal-fired power plant[J].Fuel,2010,89(4):804-809.
[38]Li Hailong,Li Ying,Wu Changyu,et al.Oxidation and capture of elemental mercury over SiO2-TiO2-V2O5catalysts in simulated low-rank coal combustion flue gas[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2011,169(1/3):186-193.
[39]Manuela Rallo,Barna Heidel,Kevin Brechtel,et al.Effect of SCR operation variables on mercury speciation[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,198:87-94.
[40]Sandhya Eswaran,Harvey G Stenger.Effect of halogens on mercury conversion in SCR catalysts[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2008,89(11):1153-1159.
[41]Raik Stolle,Heinz Koser,Heinz Gutberlet.Oxidation and reduction of mercury by SCR DeNOx catalysts under flue gas conditions in coal fired power plants[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2014,144:486-497.
[42]Gao Wei,Liu Qingcai,Wu Changyu,et al.Kinetics of mercury oxidation in the presence of hydrochloric acid and oxygen over a commercial SCR catalyst[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,220:53-60.
[43]周黎明.基于量子化学计算的汞氧化动力学研究[D].北京:华北电力大学,2014.
Zhou Liming.Study on oxidation kinetics of mercury based on quantum chemistry calculation[D].Beijing:North China Electric Power University,2014.
[44]侯文慧.模拟煤气条件下金属氧化物吸附脱除单质汞的机理研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2015.
Hou Wenhui.Mechanism study on the removal of elemental mercury from simulated syngass over matal oxide sorbents[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2015.
[45]Wan Qi,Duan Lei,Li Junhua,et al.Deactivation performance and mechanism of alkali (earth) metals on V2O5-WO3/TiO2catalyst for oxidation of gaseous elemental mercury in simulated coal-fired flue gas[J].Catalysis Today,2011,175(1):189-195.
[46]云端,宋蔷,姚强.V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂的失活机理及分析[J].煤炭转换,2009,32(1):91-95.
Yun Duan,Song Qiang,Yao Qiang.Mechanism and analysis of SCR catalyst deactivation[J].Coal Conversion,2009,32(1):91-95.
Research status of V-Ti-based denitrification catalysts for removal of Hg and PCDDs/PCDFs
Tian Junji1*, Yang Shengfen2, Lu Zou1, Shi Yu1
(1.Economic and Information Bureau of Zhong Mountain Area of Liupanshui City, Liupanshui 553001,Guizhou, China; 2.Xinhe Huijin Consulting (Beijing) Co. Ltd, Liupanshui 553001, Guizhou, China)
Abstract:The composite corrugated support frames were prepared by using the soft fibers and creasing steel mesh.The monolithic corrugated denitrification catalysts were prepared by loading V-Ti-based De-NOx catalysts onto corrugated support frames.The current major preparation processes,main advantages and research status of V-Ti-based corrugated denitrification catalysts at home and abroad were reviewed.Compared V-Ti-based denitrification catalysts with noble metal denitrification catalysts,both catalysts possessed the same catalytic decomposition effects of PCDDs/PCDFs,but the manufacturing cost of V-Ti-based denitrification catalysts was lower than those of noble metal denitrification catalysts.V-Ti-based denitrification catalysts with different active components,vanadium contents and reaction activity temperatures exhibited different catalytic decomposition effects of PCDDs/PCDFs.The highest catalytic decomposition rate was 97.7%.The researchers obtained different catalytic effects of V-Ti-based denitrification catalysts for oxidation of Hg0.The research status of V-Ti-based denitrification catalyst for catalytic oxidation of Hg0 oxidation was introduced.
Key words:three waste disposal and comprehensive utilization; V-Ti based denitrification catalyst; corrugated denitrification catalyst; Hg; PCDDs/PCDFs
收稿日期:2015-11-12;修回日期:2016-04-12
作者简介:田军吉,1987年生,男,贵州省铜仁市人,主要从事新型环保材料、工业烟气排放后处理技术和柴油烟气催化净化研究。
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2016.05.005 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2016.05.005
中图分类号:TQ426.6;X701
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1008-1143(2016)05-0025-06
通讯联系人:田军吉。

