《非均匀地球中的地震波传播和散射:第二版》引言
Haruo Sato Michael C. Fehler Takuto Maeda
《非均匀地球中的地震波传播和散射:第二版》引言
Haruo SatoMichael C. FehlerTakuto Maeda
1地震波的散射
作为一个例子,我们在图1b中展示了一个MW4.8地震的短周期速度地震波记录(横向水平分量),图中所有地震道都以相同的增益显示。图1c是放大200倍的图。图1a中展示了地震震中和使用的台站。最大振幅随震中距的增加而降低;然而,尾部的振幅却随增加的延迟时间而平滑衰减,并且它们的振幅彼此间基本相等且与大的延迟时间处的震中距无关。Aki(1969)首次将兴趣聚焦在地方震的独特地震波记录的尾部及其连续波列的外观上,以此作为岩石层随机非均质性的直接证据。这些波列,Aki称之为“尾波”,看上去像随机信号,其包络振幅平滑地随延迟时间(由地震起始时间开始测量)的增加而降低。Aki提出尾波是由岩石层中分布的非均匀体散射的非相干波组成的。Rautian和Khalturin (1978)注意到地方震的尾波包络会平稳地衰减而与震中距无关,并且所有距离上的尾波包络都具有相似的延迟时间相关性。那些观测到的地震尾波特征与记录到的地震波历史(用来测量地方震震级的地震记录)和连续使用的持续时间紧密相关(Solov’ev,1965;Tsumura,1967)。

图 1 (a)震源深度为55.3km的MW4.8地震的震中(星形)和日本本州国家地球科学与防灾研究所的Hi-net台网台站(倒三角形)。(b)速度地震波记录(水平横向分量),由下到上按震中距的增加排列,其中所有地震道具有相同增益。(c)200倍放大图
历史上,大多数地方震和区域地震的地震波记录,及那些在300km距离内的地震记录,是由区域台网记录的,这些台网的主要功能就是记录用于定位地震的初始到时。由于这些台网依赖于来自多个台站通过无线线路或电话线的数据模拟传输,其记录的动态范围有限。这就需要台站以高增益运行,从而有利于识别出小的地方震的P波初至。高增益通常会使地震波记录的初期部分限幅。因此第一种分析尾波的方法被发展起来,用于限幅地震波记录的初期部分,尤其是更大地震的地震记录上。尾波分析作为利用高增益和小动态范围的台网数据来获得关于震源和介质性质信息的手段流行起来。
后来,尾波被认为对定量估计随机非均质性提供了有用的地震学证据(Aki and Chouet,1975;Sato,1978)。由于地震仪被放置在井中,与放在地表的地震仪相比环境地震噪声被极大地降低,同时由于数字地震台网的出现,使得动态范围变大,既包括最大振幅部分也包括尾波部分的整个地震波记录的包络都被记录和模拟下来,从而通过利用1~30Hz频率范围可以了解更多关于地球岩石层的随机非均质性。


对于散射介质中来自点源的辐射,忽略了相位信息的辐射传输理论对于解释高频尾波包络是有用的。该理论已被扩展到包括对地球中传播具有重要意义的现象,比如脉冲辐射、各向异性散射和剪切位错地震点源的非球形辐射(例如,Sato,1994a;Shang and Gao,1988;Wu and Aki,1988;Zengetal,1991)。同时,蒙特卡罗模拟也被用来进行基于辐射传输理论的更复杂结构中地震记录包络的数值合成(例如,Gusev and Abubakirov,1987;Hoshiba,1994;Sens-Schönfelderetal,2009;Yoshimoto,2000)。辐射传输理论具有介于P波和S波模式之间的转换散射,它被有效地用于分析在火山下强非均质性区域的人工爆破地震波记录(Yamamoto and Sato,2010)。由于散射损失的概念在地震学界被接受,Wu(1985)提出了地震漫反射系数作为散射衰减对总衰减贡献的现象度量。Fehler等(1992)提出了一种称为多重延迟时间窗口分析的方法,以此方法通过分析整个S波记录包络来估计地震漫反射系数。该方法使用了来自点源球面辐射的多次各向同性散射过程的辐射传输理论解(Hoshibaetal,1991;Zengetal,1991)。已经有很多利用该方法进行散射和固有衰减的区域检测(例如,Carcolé and Sato,2010;Mayedaetal,1992)。
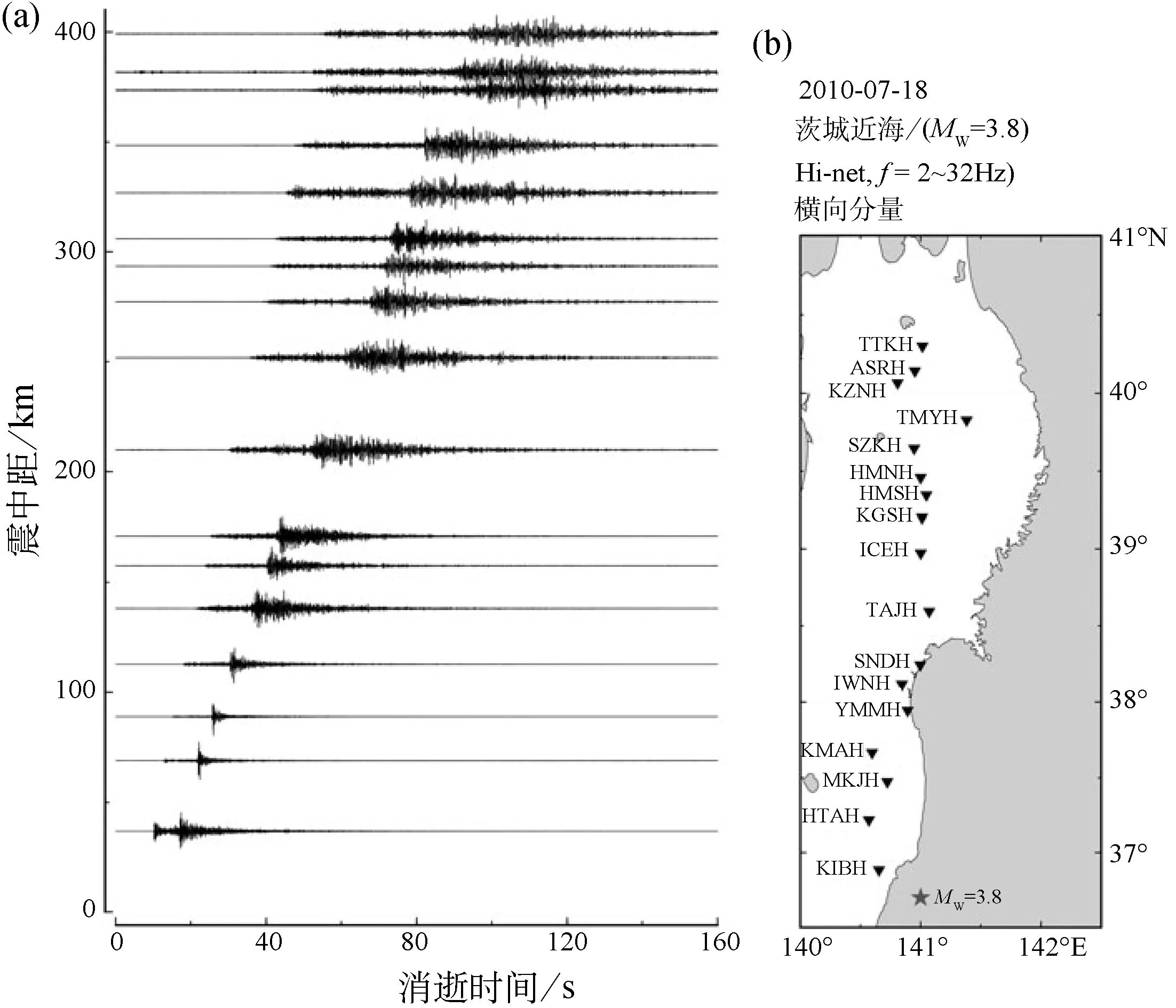
图2 (a)日本本州东北部一个MW3.8地震的速度地震记录的包络随震中距增大而加宽(水平横向分量2~32Hz),其中每个地震道都以其最大振幅进行归一化。(b)地图中星形和倒三角形分别为震中和日本国家地球科学与防灾研究所的Hi-net台网的台站
尽管小的地方震的震源持续时间通常小于1s,但在震中距大于100km的地方,S波的视持续时间仍被发现比1s长很多(Sato,1989)。作为例子,图2展示了按照增加的震中距排列的一个MW3.8地震的水平横向分量地震波记录(2~32Hz)。与图1不同,每个地震道都以其最大振幅进行归一化。当我们关注S波初至到最大振幅一半对应的时间的波形包络时,我们发现S波地震记录的视持续时间随震中距的增加而增加。在距离大于100km时,它会超过几秒,这远远大于地震震级估计的震源持续时间。我们也发现从S波初至算起包络峰值的到时出现了延迟。在距离大于200km时,每个地震波记录看起来就像没有清晰S震相的纺锤。包络的加宽和峰值到时的延迟都利用波动方程抛物线近似的随机平均方法和马尔可夫近似进行定量研究,马尔可夫方法最初用于在波长小于随机非均质尺度时,通过折射率随机变化介质的光波或声波。这一理论对在较大旅行距离时,强烈衍射对观测到的S波包络的初期部分特征的影响给出了很好的解释。包络随距离而加宽的频率相关性由随机速度非均质性的功率谱控制(Saitoetal,2002;Sato,1989)。日本北部火山前沿弧后一侧的包络加宽被发现要强于弧前一侧,该处太平洋板块正向日本岛弧之下俯冲(Obara and Sato,1995)。Shearer和Earle(2004)利用基于结合了玻恩近似的辐射传输理论的包络合成,对远震P波包络进行的分析估计了地幔中的速度非均质性。Kubanza等(2007)将焦点放在远震P波的横向分量的激励上。他们利用随机弹性介质中矢量波的马尔可夫近似得到的横向分量的能量估计了岩石层的非均质性(Sato,2006)。
根据环境噪声互相关函数恢复的格林函数作为提供地球结构信息的一种方法,最近已被广泛关注。该方法不需要任何实际的天然地震震源或人工震源。最初,该方法被用来发现瑞利波速度(Campillo and Paul,2003),后来测量体波速度也成为可能(Rouxetal,2005b)。监测环境噪声的互相关函数(CCF)对检测与地震活动相关的地震波速度的时间变化也有用(例如,Brenguieretal,2008)。学者们已尝试进行检测环境噪声自相关函数尾波部分的时间变化,这可能反映地壳非均质性的变化(例如,Maedaetal,2010;Wegler and Sens-Schönfelder,2007)。根据随机波互相关函数可求得具有尾波尾部形状的格林函数,甚至在非均匀介质中也是可能的(例如,Margerin and Sato,2011a; Sato,2009a, 2010; Snieder and Fleury,2010)。
2岩石层的非均质性
S尾波的激励可以由与平均自由路径互为倒数的S波总散射系数g0很好地量化。岩石层中g0值的测量通常基于来自8倍频带宽度的辐射传输理论。图3总结了最近的g0值对频率的区域测量。大多数测量是基于各向同性散射模型。然而,有一些测量的是单次散射情况下的后散射系数gπ或多次散射情况下各向异性散射过程的有效各向同性散射系数——输运散射系数gm(将会在第7章中讨论)。
对于1~30Hz的频率范围,已报道的岩石层的g0值分布在10-2km-1附近的10-3km-1到5×10-2km-1之间。根据对活火山的人工爆破的分析,发现了较大的值,为g0≈1km-1(Yamamoto and Sato,2010)。利用漫射模型对月震的分析,估计的g0值范围为0.05~0.5km-1(Dainty and Toksöz,1981)。Lee等 (2003, 2006)分析了ScS震相到达前后约900s(由起始时间开始的延迟时间)的区域地震的尾波包络,该分析利用了基于具有速度和总衰减的初步地球参考模型(PREM)的多次散射各向同性模型的数值模拟包络。他们指出,在4s和10s周期波段内,上地幔与岩石层相比具有更低的g0值。而下地幔g0值会变得更小。为了对比,完全在地球内传播的长周期瑞利波的g0值为10-6km-1的量级,这比岩石层中短周期S波的值小得多(Sato and Nohechi,2001)。
基于随机介质的随机波动理论,已有对速度相对扰动δV(x)/V0的功率谱密度函数(PSDF)P(m)的测量。图4总结了最近对岩石层和地幔的功率谱密度函数(km3)对波数m(单位是km-1)的测量结果。利用结合了玻恩近似的辐射传输理论散射系数的远震事件的P波包络加宽的频率相关分析,发现下地幔的功率谱密度函数(图4中线1.2)比岩石层和上地幔的值(线1.1)小。在太平洋板块向日本岛弧下俯冲的日本北部,对功率谱密度函数进行了密集测量,该测量是利用马尔可夫近似对小的地方震的S波地震波记录包络加宽的频率相关分析进行的。与火山前沿的弧前一侧(东侧)(线3.1,3.2,3.3)相比,第四纪火山下的功率谱密度函数(线4.1和4.2)更大,并且它们随波数的衰减率更小。线5.1和5.2展示了根据岩石层微震记录的S波散射损失和尾波激励分析揭示的功率谱密度函数。线6是根据挪威地壳地震测得的S波包络,线7是根据日本日光上地壳中的P波和S波的尾波激励测得的,该测量结合了玻恩近似的辐射传输理论的散射系数。

图3 S波总散射系数的区域测量(K.Emoto提供):1 日本关东 (Sato,1978);2 日本关东—东海 (Fehler et al,1992); 3 美国加利福尼亚长谷; 4 美国加利福尼亚中部; 5 美国夏威夷(Mayeda et al,1992); 6 日本平均值 (Hoshiba,1993);7 美国加利福尼亚南部(Jin et al,1994); 8 美国加利福尼亚南部(Leary and Abercrombie,1994);9 希腊北部 (Hatzidimitriou,1994);10 西班牙南部 (Δ=0~170 km) (Akinci et al,1995); 11 美国加利福尼亚南部(Adams and Abercrombie,1998);12 委内瑞拉东北(Ugalde et al,1998);13 土耳其东部(Akinci and Eyidogan,2000);14 长周期瑞利波 (Sato and Nohechi,2001);15 意大利亚平宁山脉南部(Bianco et al,2002);16 法国中部(Lacombe et al,2003);17 美国阿拉斯加中南部(Dutta et al,2004);18 荷兰南部(Goutbeek et al,2004);19 哥伦比亚东北部;(Vargas et al,2004);20 意大利东北部(Bianco et al,2005);21 意大利西西里岛南部 (Giampiccolo et al,2006);22 岩石层和上地幔 (0 ~ 670 km) (Lee et al,2003, 2006);23下地幔(>670 km)(Lee et al,2003,2006);24 德国 (Sens-Schönfelder and Wegler,2006);25 日本平均值 (Carcolé and Sato,2010);26 日本浅间火山(Yamamoto and Sato,2010);27月震 (Dainty and Toksöz,1981);28 挪威地壳输运散射系数gm(Przybilla et al,2009)

图4 岩石层和地幔中以小数表示的速度扰动分式功率谱密度函数的测量结果。远震P波包络:1.1上地幔;1.2下地幔 (0.5~2.5Hz)(Shearer and Earle 2004);2 波罗的海地盾(0.5~5Hz)(Hock et al,2000)。S波包络: 3.1,3.2,3.3日本弧前(2~16Hz)(Saito et al,2002,2005;Takahashi et al,2009);4.1,4.2日本东北部栗驹和岩手火山(2~16Hz,深度20~60km)(Takahashi et al,2009);5.1,5.2散射损失和S尾波激励(1~30Hz)(Sato,1984a,1990);6挪威地壳(2~10Hz)(Przybilla et al,2009)。P波和S波包络:7日本日光上地壳(8~16Hz)(Yoshimoto et al,1997b)。灰色条纹显示的是速度为4km/s时相应的频率范围
3篇章结构
本书关注过去40年随机非均匀地球结构特别是岩石层中地震波传播与散射领域的发展。本书既介绍了观测到的短周期地震波的散射现象,还介绍了描述介质非均质性和随机介质中波的传播与散射的数学工具。
第2章中,我们将会简单地回顾经典测量和观测结果,这些结果都支持岩石层可被视为随机非均质性的假定。我们也介绍了描述随机非均质性的基本数学公式。第3章介绍了尾波激励的现象描述,它构成了尾波分析和尾波归一化方法的基础。我们还讨论了不同的散射现象。
第4章提供了非均匀弹性介质中散射的玻恩近似。为了介绍公式提到了标量波理论。在第5章中,我们首先回顾了观测到的衰减频率相关性,并讨论了几个提出的内部吸收的机制。然后我们会介绍一种与观测方法一致的改进的随机平均方法。该方法描述了随机介质中散射衰减的频率相关性。在第6章,我们将会提出一种合成地方震三分量地震波记录包络的方法,该方法以被随机弹性不均匀体单次散射的波功率求和为基础。该模型包含了剪切位错点源非球面辐射的影响以及来自非均匀体各向异性散射的影响。
第7章提供了推导随机介质中平均波频散关系的一阶平滑方法,以及利用多尺度分析进行的辐射传递方程的统计推导方法。根据辐射传递理论推导了扩散方程。在第8章中,我们将会讨论球面源辐射和多次各向同性散射情况下,基于辐射传递理论的地震记录包络的合成。在理论形成后,我们将会介绍估计地震漫反射系数的多重流逝时间窗分析方法。我们也会描述该理论向非球面源辐射、各向异性散射以及P波和S波振型转换情况下的扩展。
在第9章中,我们回顾了随机介质中标量波的抛物线近似及其统计处理。然后我们会提供马尔可夫近似,为随机介质中标量和矢量波包络的合成做准备。该近似很好地解释了观测到的包络加宽。第10章介绍了根据随机波互相关函数反推格林函数的理论。提供了几个数据应用的例子。
在第11章,我们总结了现状并讨论了未来可能的发展。
4数学符号

(1)

式中,波浪符~和帽形符^分别表示关于空间坐标和时间坐标的傅里叶变换。我们在第7章和第8章讲解辐射传递理论时,我们注意到帽形符也用来表示关于时间的拉普拉斯变换,用自变量s区分:
(2)

5进一步阅读
以下书籍和专著适合本书讨论的主题。Chandrasekhar (1960) 是一本辐射传递理论的经典教材。Ishimaru (1978) 和 Rytov 等(1989)为随机介质中波的传播研究提供了先进的数学工具。Shapiro和Hubral (1999) 重点研究层状随机介质中波的传播。Goff和Holliger (2003)总结了观测到的地壳非均质性。Apresyan和Kravtsov (1996)介绍了随机介质中的波理论与辐射传递理论之间的数学关系。国际地震学与地球内部物理学协会(IASPEI)工作组两篇关于“散射与非均质性”的报告:Wu和Maupin (2007) 编辑了非均匀介质中波传播的数学模型,Sato 和 Fehler(2008)编辑了关于地震波散射和地球介质非均匀性研究的最新进展。有几个期刊的专辑集中探讨了这些主题(例如, Husebye,1981;Kornetal,1997;Sato 1991b;Wu and Aki,1988b,1989,1990)。
参考文献
Adams DA, Abercrombie RE (1998) Seismic attenu-ation above 10 Hz in southern California from coda waves recorded in the Cajon Pass borehole.J Geophys Res 103:24,257-24,270, DOI10.1029/98JB01757Aki K (1969) Analysis of seismic coda of local earthquakes as scattered waves.J Geophys Res 74:615-631, DOI 10.1029/JB074i002p00615
Aki K (1980a) Attenuation of shear-waves in the lithosphere for frequencies from 0.05 to 25 Hz.Phys Earth Planet Inter 21:50-60, DOI 10.1016/0031-9201(80)90019-9
Aki K, Christoffersson A, Husebye ES (1976) Three-dimensional seismic structure of the litho-sphere under Montana LASA.Bull Seism Soc Am 66:501-524
Aki K, Chouet B (1975) Origin of coda waves: Source, attenuation and scattering effects.Geophys Res 80:3322-3342, DOI 10.1029/JB080i023p03322
Aki K, Lee WHK (1976) Determination of three-dimensional velocity anomalies under a seismic array using first P arrival times from local earthquakes, Part I.A homogeneous initial model.J Geophys Res 81:4381-4399, DOI 10.1029/JB081i023p04381
Aki K, Tsujiura M (1959) Correlation study of near earthquake waves.Bull Earthq Res Inst UnivTokyo 37:207-232
Akinci A, Pezzo ED, Ibanez JM (1995) Separation of scattering and intrinsic attenuation in sou-thern Spain and western Anatolia (Turkey).Geophys J Int 121:337-353, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1995.tb05715.x
Akinci A, Eyidogan H (2000) Scattering and anelastic attenuation of seismic energy in the vicinity of north Anatolian fault zone, eastern Turkey.Phys Earth Planet Inter 122:229-239, DOI 10.1016/S0031-9201(00)00196-5
Apresyan LA, Kravtsov YA (1996) Radiation Transfer: Statistical and Wave Aspects.Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Amsterdam
Bianco F, Pezzo ED, Castellano M, Ibanez J, Lu-ccio FD (2002) Separation of intrinsic and sca-ttering seismic attenuation in the Southern Apennine zone, Italy.Geophys J Int 150(1):10-22,DOI 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01696.x
Bianco F, Pezzo ED, Malagnini L, Luccio FD, Akinci A (2005) Separation of depth-dependent intrinsic and scattering seismic attenuation in the northeastern sector of the Italian Peninsula.Geophys J Int 161(1):130-142, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02555.x
Brenguier F, Campillo M, Hadziioannou C, Shapiro N, Nadeau R, Larose E (2008) Post seismic relaxation along the San Andreas Fault at Parkfield from continuous seismological observations.Science 321(5895):1478, DOI 10.1126/science.1160943
Campillo M, Paul A (2003) Long-range correlations in the diffuse seismic coda.Science 299(5606):547-549, DOI 10.1126/science.1078551Carcolé E, Sato H (2010) Spatial distribution of scatte-ring loss and intrinsic absorption of short period S waves in the lithosphere of Japan on the basis of the Multiple Lapse Time Window Analysis of Hi-net data.Geophys J Int 180:268-290, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04394.x
Chandrasekhar S (1960) Radiative transfer.Dover, New York
Conrad V (1925) Laufzeitkurven des Tauernbebens vom 28.November, 1923.Mitt Erdb KommWien Akad Wiss 59:1-23
Dainty AM, Toksöz MN (1981) Seismic codas on the Earth and the Moon: a comparison.Phys Earth Planet Inter 26:250-260, DOI 10.1016/0031-9201(81)90029-7
Dutta U, Biswas N, Adams D, Papageorgiou A (2004) Analysis of S-wave attenuation in South-Central Alaska.Bull Seism Soc Am 94(1):16-28, DOI 10.1785/0120030072
Fehler M, Hoshiba M, Sato H, Obara K (1992) Separation of scattering and intrinsic attenu-ation for the Kanto-Tokai region, Japan, using measurements of S-wave energy versus hypocentral distance.Geophys J Int 108:787-800, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1992.tb03470.xGiampiccolo E, Tuve T, Gresta S, Patane D (2006) S-waves attenuation and separation of scattering and intrinsic absorption of seismic energy in southeas-tern Sicily (Italy).Geophys J Int 165:211-222, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.02881.x
Goff J, Holliger K (2003) Heterogeneity in the crust and upper mantle: nature, scaling, and seismic properties.Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New YorkGoutbeek FH, Dost B, van Eck T (2004) Intrinsic absorption and scattering attenuation in the southern part of the Netherlands.J Seis 8:11-23, DOI 10.1023/B:JOSE.0000009511.27033.79Gusev AA, Abubakirov IR (1987)Monte-Carlo simu-lation of record envelope of a near earthquake.Phys Earth Planet Inter 49:30-36, DOI 10.1016/0031-9201(87)90130-0
Gusev AA, Lemzikov VK (1985) Properties of sca-ttered elastic waves in the lithosphere of Kamchatka: Parameters and temporal variations.Tectonophysics 112:137-153, DOI 10.1016/0040-1951(85)90177-5
Hatzidimitriou PM (1994) Scattering and anelastic attenuation of seismic energy in northern Greece.Pure Appl Geophys 143:587-601, DOI 10.1007/BF00879499
Hock S, Korn M, the TOR Working group (2000) Random heterogeneity of the lithosphere across the Trans-European Structure Zone.Geophys J Int 141:57-70, DOI 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2000.00078.xHolliger K (1996) Upper-crustal seismic velocity hete-rogeneity as derived from a variety of P-wave sonic logs.Geophys J Int 125(3):813-829, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1996.tb06025.xHoshiba M (1991) Simulation of multiple-scattered coda wave excitation based on the energy conservation law.Phys Earth Planet Inter 67:123-136, DOI 10.1016/0031-9201(91)90066-Q
Hoshiba M (1993) Separation of scattering attenuation and intrinsic absorption in Japan using the multiple lapse time window analysis of full seismogram envelope.J Geophys Res 98:15,809-15,824, DOI 10.1029/93JB00347
Hoshiba M(1994) Simulation of coda wave envelope in depth dependent scattering and absorption structure.Geophys Res Lett 21:2853-2856, DOI 10.1029/94GL02718
Husebye ES (ed) (1981) Contribution of scattering to the complexity of seismograms.Phys Earth Planet Inter 26:233-291
Ishimaru A (1978) Wave Propagation and Scattering in Random Media, Vols.1 and 2.Academic Press, New York
Jin A, Aki K (1986) Temporal change in coda Q before the Tangshan earthquake of 1976 and the Haicheng earthquake of 1975.J Geophys Res 91:665-673, DOI 10.1029/JB091iB01p00665
Jin A, Mayeda K, Adams D, Aki K (1994) Separation of intrinsic and scattering attenuation in southern California using TERRA scope data.J Geophys Res 99:17,835-17,848, DOI 10.1029/94JB01468
Kopnichev YF (1975) A model of generation of the tail of the seismogram.Dok Akad Nauk, SSSR(Engl trans) 222:333-335
Korn M, Sato H and Scherbaum F (eds) (1997) Stochastic Seismology: Stochastic Seismic Wave Fields and Realistic Media.Phys Earth Planet Inter 104:1-281, DOI 10.1016/S0031-9201(97)00040-X
Kubanza M, Nishimura T, Sato H (2007) Evalu-ation of strength of heterogeneity in the lithosphere from peak amplitude analyses of teleseismic short-period vector P waves.Geophys J Int171(1):390-398, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03544.x
Lacombe C, Campillo M, Paul A, Margerin L (2003) Separation of intrinsic absorption and scattering attenuation from Lg coda decay in central France using acoustic radiative transfer theory.Geophys J Int 154:417-425, DOI 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01976.x
Leary P, Abercrombie R (1994) Frequency depen-dent crustal scattering and absorption at 5-160Hz from coda decay observed at 2.5 km depth.Geophys Res Lett 21:971-974, DOI 10.1029/94GL00977
Lee WS, Sato H, Lee K (2003) Estimation of S-wave scattering coefficient in the mantle from envelope characteristics before and after the ScS arrival.Geophys Res Lett 30(24):2248, DOI10.1029/2003GL018413
Lee WS, Sato H, Lee K (2006) Scattering coefficients in the mantle revealed from the seismogram envelope analysis based on the multiple isotropic scattering model.Earth Planet Sci Lett241:888-900, DOI 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.10.035
Maeda T, Obara K, Yukutake Y (2010) Seismic velocity decrease and recovery related to earthquake swarms in a geothermal area.Earth Planets Space 62(9):685-691, DOI 10.5047/eps.2010.08.006
Margerin L, Sato H (2011a) Reconstruction of multiply-scattered arrivals from the cross-correlation of waves excited by random noise sources in a heterogeneous dissipative medium.Wave Motion 48:146-160, DOI 10.1016/j.wavemoti.2010.10.001
Mayeda K, Koyanagi S, Hoshiba M, Aki K, Zeng Y (1992) A comparative study of scattering,intrinsic, and coda Q1 for Hawaii, Long Valley and Central California between 1.5 and 15 Hz.J Geophys Res 97:6643-6659, DOI 10.1029/91JB03094
Obara K, Sato H (1995) Regional differences of random inhomogeneities around the volcanic frontin the Kanto-Tokai area, Japan, revealed from the broadening of S wave seismogram envelopes.J Geophys Res 100:2103-2121, DOI 10.1029/94JB02644
Przybilla J, Wegler U, Korn M (2009) Estimation of crustal scattering parameters with elastic radiative transfer theory.Geophys J Int 178(2):1105-1111, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04204.x
Rautian TG, Khalturin VI (1978) The use of the coda for determination of the earthquake source spectrum.Bull Seism Soc Am 68:923-948
Roux P, Sabra KG, Gerstoft P, Kuperman WA, Fehler MC (2005b) P-waves from cross-correlation of seismic noise.Geophys Res Lett 32, DOI 10.1029/2005GL023803
Rytov SM, Kravstov YA, Tatarskii VI (1989) Principles of statistical radiophysics (Vol.4) Wave propagation through random media.Springer-Verlag, BerlinSaito T, Sato H, Ohtake M (2002) Envelope broade-ning of spherically outgoing waves in three dimensional random media having power-law spectra.J Geophys Res 107(10.1029), DOI 10.1029/2001JB000264
Saito T, Sato H, Ohtake M, Obara K (2005) Unified explanation of envelope broadening and maximum-amplitude decay of high-frequency seismograms based on the envelope simulationusing the Markov approximation: Forearc side of the volcanic front in northeastern Honshu,Japan.J Geophys Res 110, DOI 10.1029/2004JB003225
Sato H (1977a) Energy propagation including sca-ttering effects: Single isotropic scattering approximation.J Phys Earth 25:27-41
Sato H (1978) Mean free path of S-waves under the Kanto district of Japan.J Phys Earth26:185-198
Sato H (1982a) Amplitude attenuation of impulsive waves in random media based on travel time corrected mean wave formalism.J Acoust Soc Am 71:559-564, DOI 10.1121/1.387525
Sato H (1984a) Attenuation and envelope formation of three-component seismograms of small local earthquakes in randomly inhomogeneous lithosphere.J Geophys Res 89:1221-1241, DOI10.1029/JB089iB02p01221Sato H (1990) Unified approach to amplitude attenu-ation and coda excitation in the randomly inhomogeneous lithosphere.Pure Appl Geophys 132:93-121, DOI 10.1007/BF00874359
Sato H (1989) Broadening of seismogram envelopes in the randomly inhomogeneous lithosphere based on the parabolic approximation: Southeastern Honshu, Japan.J Geophys Res 94:17,735-17,747, DOI 10.1029/JB094iB12p17735
Sato H (ed) (1991b) Scattering and attenuation of seismic waves.Phys.Earth Planet.Inter.67:1-210Sato H (1994a) Multiple isotropic scattering model including P-S conversions for the seismogram envelope formation.Geophys J Int 117:487-494, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1994.tb03946.x
Sato H (2006) Synthesis of vector wave envelopes in three-dimensional random elastic media characterized by a Gaussian autocorrelation function based on the Markov approximation: Plane wave case.J Geophys Res 111(B6):B06,306, DOI 10.1029/2005JB004036Sato H (2009a) Retrieval of Green’s function having coda from the cross-correlation function in a sca-ttering medium illuminated by surrounding noise sources on the basis of the first order Born appro-ximation.Geophys J Int 179(1):408-412, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04296.x
Sato H, Fehler M (eds) (2008) Advances in geophysics (Series Ed.: R.Dmowska): Earth heterogeneity and scattering effects on seismic waves, vol 50.Academic Press, New York
Sato H, Nohechi M (2001) Envelope formation of long-period Rayleigh waves in vertical component seismograms: Single isotropic scattering model.J Geophys Res 106:6589-6594,DOI 10.1029/2000JB900383
Schilt S, Oliver J, Brown L, Kaufman S, Albauch D, Brewer J, Cook F, Jensen L, Krumhansl P, Long G, Steiner D (1979) The heterogeneity of the continental crust: Results from deep crustal reflection profiling using the Vibroseis technique.Rev Geophys Space Phys 17:354-368, DOI 10.1029/RG017i002p00354Sens-Schönfelder C, Margerin L, Campillo M (2009) Laterally heterogeneous scattering explainsLg blockage in the Pyrenees.J Geophys Res 114:B07,309, DOI 10.1029/2008JB006107
Sens-Schönfelder C, Wegler U (2006) Radiative transfer theory for estimation of the seismic moment.Geophys J Int 167:1363-1372, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03139.x
Shang T, Gao L (1988) Transportation theory of multiple scattering and its application to seismic coda waves of impulsive source.Scientia Sinica (series B, China) 31:1503-1514
Shapiro S, Hubral P (1999) Elastic waves in random media.Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences,Springer, Berlin 80Shearer PM, Earle PS (2004) The global short-period wavefield modelled with a Monte Carlo seismic phonon method.Geophys J Int 158:1103-1117, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02378.x
Shiomi K, Sato H, Ohtake M (1997) Broad-band power-law spectra of well-log data in Japan.Geophys J Int 130:57-64, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1997.tb00987.x
Snieder R, Fleury C (2010) Cancellation of spurious arrivals in the Green’s function retrieval of multiple scattered waves.J Acoust Soc Am 128:1598-1605, DOI 10.1121/1.348372
Solov’ev SL (1965) Seismicity of sakhalin.Bull Earthquake Res Inst Univ Tokyo 43:95-102
Takahashi T, Sato H, Nishimura T, Obara K (2009) Tomographic inversion of the peak delay times to reveal random velocity fluctuations in the lithosphere: method and application to north eastern Japan.Geophys J Int 178(47):1437-1455, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04227.x
Tsumura K (1967) Determination of Earthquake Magnitude from Total Duration of Oscillation.Bull Earthquake Res Inst 45:7-18
Ugalde A, Pujades LG, Canas JA, Villasenor A (1998) Estimation of the intrinsic absorption and scattering attenuation in northeastern Venezuela (southeastern Caribbean) using coda waves.Pure Appl Geophys 153:685-702, DOI 10.1007/s000240050214
Vargas CA, Ugalde A, Pujades LG, Canas JA (2004) Spatial variation of coda wave attenuation in north western Colombia.Geophys J Int 158:609-624, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02307.x
Wegler U, Sens-Schönfelder C (2007) Fault zone monitoring with passive image interferometry.Geophys J Int 168(3):1029-1033, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03284.x
Wesley JP (1965) Diffusion of seismic energy in the near range.J Geophys Res 70:5099-5106,DOI 10.1029/JZ070i020p05099
Wu R S (1982b) Mean field attenuation and amplitude attenuation due to wave scattering.Wave Motion 4:305-316, DOI 10.1016/0165-2125(82)90026-9Wu R S (1985) Multiple scattering and energy transfer of seismic waves-separation of scattering effect from intrinsic attenuation - I.Theoretical mode-ling.Geophys J R Astron Soc 82:57-80,DOI 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1985.tb05128.x
Wu R S, Aki K (1988) Multiple scattering and energy transfer of seismic waves-Separation of scattering effect from intrinsic attenuation.II.Application of the theory to Hindu-Kush region.Pure Appl Geophys 128:49-80, DOI 10.1007/BF01772590
Wu R S, Aki K (eds) (1988b) Seismic wave sca-ttering in three-dimensionally heterogeneous earth,Part I.Pure Appl Geophys 128:1-447
Wu R S, Aki K (eds) (1989) Seismic wave scatte-ring in three-dimensionally heterogeneous earth,Part II.Pure Appl Geophys 131:551-739
Wu R S, Aki K (eds) (1990) Seismic wave scatte-ring in three-dimensionally heterogeneous earth,Part III.Pure Appl Geophys 132:1-244
Wu R, Maupin V (eds) (2007) Advances in wave propagation in heterogeneous earth, Advances in geophysics (Series Ed.: R.Dmowska), vol 48.Academic Press
Wu R S, Xu Z, Li X P (1994) Heterogeneity spectrum and scale-anisotropy in the upper crust revealed by the German Continental Deep-Drilling (KTB) holes.Geophys Res Lett 21:911-914,DOI 10.1029/94GL00772
Yamamoto M, Sato H (2010) Multiple scattering and mode conversion revealed by an active seismic experiment at Asama volcano, Japan.J Geophys Res 115:B07304, DOI 10.1029/2009JB007109
Yoshimoto K (2000) Monte-Carlo simulation of seismogram envelope in scattering media.J Geophys Res 105:6153-6161, DOI 10.1029/1999JB900437
Yoshimoto K, Sato H, Ohtake M (1997b) Three-component seismogram envelope synthesis in randomly inhomogeneous semi-infinite media based on the single scattering approximation.Phys Earth Planet Inter 104:37-61, DOI 10.1016/S0031-9201(97)00061-7
Zeng Y, Su F, Aki K (1991) Scattering wave energy propagation in a random isotropic scattering medium 1.Theory.J Geophys Res 96:607-619, DOI 10.1029/90JB02012
Zhang H, Thurber C (2003)Double-difference tomography: The method and its application to the Hayward fault, California.Bull Seism Soc Am 93(5):1875, DOI 10.1785/0120020190Zhao D, Wang Z, Umino N, Hasegawa A (2009) Mapping the mantle wedge and interplate thrust zone of the northeast Japan arc.Tectonophysics 467:89-106, DOI 10.1016/j.tecto.2008.12.01
译 者 简 介

朱维(1989-),男,中国地震局地球物理研究所地球探测与信息技术专业硕士研究生,主要从事编码激励在岩石超声成像方面的研究。E-mail:cjdxzw2008@126.com。
Haruo Sato,Michael C. Fehler,Takuto Maeda. 2012. Seismic wave propagation and scattering in the heterogeneous earth: second edition,Chapter 1:1-11
朱维 译. 2016. 《非均匀地球中的地震波传播和散射:第二版》引言.世界地震译丛.47(4): 269-281. doi:10.16738/j. cnki.issn.1003-3238.201604001
中国地震局地球物理研究所朱维译
中国地震局地球物理研究所吴何珍校

