结构参数对增压器浮环轴承润滑特性和环速比的影响
李佳琪,倪计民,石秀勇,徐晓川,刘 越,李冬冬,陈振斌
结构参数对增压器浮环轴承润滑特性和环速比的影响
李佳琪1,倪计民1※,石秀勇1,徐晓川1,刘 越1,李冬冬1,陈振斌2
(1. 同济大学汽车学院,上海 201804; 2. 海南大学机电工程学院,儋州 571737)
基于以往对增压器的浮环轴承润滑分析中大都忽略浮环的环速比影响,或将润滑性能和环速比独立分析。该文采用数值分析方法研究了增压器浮环轴承的润滑特性和环速比,分析中考虑了转轴、浮环、轴承座之间的传热因素,基于Reynolds方程和浮环平衡方程,建立了浮环轴承润滑模型,对比分析了浮环内、外层间隙,内、外圆半径4个结构参数对浮环轴承润滑特性和环速比的影响。结果表明,实际设计浮环时,需综合考虑结构参数对浮环润滑特性和环速比的影响及影响程度;浮环内层间隙增加,环速比降低,与内层间隙0.02 mm时相比,转速60 000 r/min时,内层间隙0.04 mm时的环速比减幅达23%,内层间隙增加,内、外膜温度减小,摩擦功耗略有增加,内层间隙0.03 mm时,浮环具有较理想的润滑性能和环速比;外层间隙0.06 mm的环速比均比外层间隙0.04 mm的环速比增加30%以上,外层间隙增加,外膜温度减小,且转速越高,外膜温度减幅越大;浮环内圆半径越小,环速比越小,内、外膜温度和摩擦功耗越小,浮环润滑性能越好;浮环外圆半径增加,环速比降低,但内膜温度、外膜温度、总摩擦功耗和总端泄流量变化幅度均在5%以内,外圆半径对浮环润滑性能影响不显著;浮环实际设计时,调整内圆半径比调整外圆半径对改善浮环润滑性能更有效。
轴承;模型;温度;浮环轴承;润滑;结构参数;环速比;传热
0 引 言
增压器浮环轴承由两层油膜组成,中间由浮环隔开,两层油膜分别为转轴与浮环之间的内层油膜(内膜)和浮环与轴承座之间的外层油膜(外膜),浮环轴承具有低功耗、润滑性能好等特点而被广泛应用。
Clarke等[1]对重载荷情况下的浮环轴承进行润滑分析;Koeneke等[2]研究了高速轴承惯性力对油膜破裂的影响;Mokhtar等[3]研究了内、外层外径间隙对最小油膜厚度的影响;Andres等[4-7]在某一给定载荷条件下,考虑了内膜、浮环、外膜之间的传热,对浮环功耗、温度和油膜厚度进行了预测;Li等[8-10]对转子和浮环轴承系统动力学进行了研究;Guo等[11-14]研究了径推联合动静压的静态特性和动态特性;Zhang等[15]研究了气体轴承的稳定性;Dong等[16]研究了浮环轴承在发动机中的应用;Deligant等[17]采用CFD软件对增压器轴承性能进行了预测;Liang 等[18-20]对半浮动轴承、浮环表面织构和浮环失圆等影响因素进行了分析;康召辉等[21-22]考虑了浮环涡动对润滑性能的研究;师占群等[23-25]考虑了贫油条件对浮环轴承润滑性能的影响;宁峰平等[26]研究了过盈量对轴承预紧力的影响;同时,已有一些学者也开展了浮环轴承结构参数、浮环传热的影响研究[27-29]。
上述研究者往往将浮环的环速比脱离浮环轴承润滑性能分析之外,分别对环速比和润滑特性单独分析或不考虑环速比的影响,这显然与浮环轴承的实际工作状况有所差异。浮环实际工作中,转轴向浮环内膜传热,浮环内膜通过端泄带走部分转轴传导内膜和内膜自身摩擦产生的热量,另一部分热量传递到浮环;浮环将内膜吸收的热量传递到外膜,外膜通过端泄带走部分从浮环吸收的热量和外膜自身摩擦产生的热量,其余热量传递到轴承座。因此,转轴、浮环、轴承座之间的传热会影响内、外膜的润滑性能以及作用于浮环上的摩擦力,继而引起环速比的变化。此外,过小的环速比不利于浮环轴承的稳定运转,且环速比的变化也会对润滑性能产生影响。因此,浮环的环速比和润滑性能互相作用、互相影响。在研究结构参数对浮环轴承润滑性能影响时,还应同时考虑其对环速比的影响。
本文以一农用柴油机增压器浮环轴承为研究对象,以浮环轴承润滑模型、转轴、浮环、轴承座热量传递模型和浮环平衡模型为基础,采用有限差分法求解雷诺方程,采用热变形方程求解转轴、浮环和轴承座热变形量,分析探究结构参数对浮环润滑特性和环速比的影响。
1 数学模型与数值分析方法
1.1 浮环轴承动压润滑模型
图1所示为浮环轴承结构示意图。
a. 径向截面
a. Radial cross section
b. 轴向截面
b. Axial cross section
注:J为转轴角速度,rad·s-1;R为浮环角速度,rad·s-1;i、o为内、外膜油膜厚度,m;i、o为浮环内、外圆宽度,mm;o为轴承座坐标系,'''为浮环轴承坐标系。
Note:Jis journal angular velocity, rad·s-1;Ris ring angular velocity, rad·s-1;i,oare the inner and outer film thicknesses,m;i,oare the inner and outer circle widths;ois the coordinate system of bearing block,''' is the coordinate system of floating ring.
图1 浮环轴承结构示意图
Fig.1 Schematic view of structure of floating ring bearing
1.1.1 Reynolds 方程
采用Reynolds方程表征内膜、浮环、外膜系统中内层油膜和外层油膜的压力分布,忽略体积力及惯性力的影响,由式(1)、式(2)表示。
式中i、o分别为浮环内圈半径和外圈半径,mm;J为转轴半径,mm;i、o分别为内膜油膜厚度和外膜油膜厚度,mm;i、o分别为内膜油膜压力和外膜油膜压力,Pa;J、R分别为转轴和浮环角速度,rad/s;i、o分别为内膜和外膜油膜黏度,Pa·s;为油膜角坐标,rad。
1.1.2 浮环油膜厚度方程
浮环油膜厚度方程如式(3)和式(4)所示[4]。
i=i0+iTr−Tj(3)
o=o0−oTr+Tc(4)
不计轴承表面变形的油膜厚度为
浮环受热变形引起的膜厚变化量为
转轴受热变形引起的膜厚变化量为
轴承座受热变形引起的膜厚变化量为
式中i0、o0为不计浮环表面变形的内外油膜厚度,mm;iTr、oTr分别为浮环表面热变形引起的内外油膜厚度变化量,mm,其中浮环热变形使内膜间隙变大,使外膜间隙变小;Tj为转轴热变形引起的内膜油膜厚度变化量,mm,转轴热变形使内膜间隙变小;Tc为轴承座热变形引起的外膜油膜厚度变化量,mm;i0,o0分别为内、外层油膜半径间隙,mm;i、o分别为内外油膜偏心率;i、o分别为内外油膜偏位角,rad;R为浮环热膨胀系数;R为浮环温度,K;ref为参考温度,K;J为转轴热膨胀系数;J为转轴表面温度,K;C为轴承座热膨胀系数;C为轴承座温度,K;C为轴承座半径,mm。
1.1.3 润滑油的黏温关系
黏温关系采用Vogel模型,这里使用CD30级润滑油,其黏温关系表达式为[30]
式中为润滑油黏度,Pa·s;为温度,K。
1.1.4 浮环摩擦功耗
浮环轴承摩擦功耗如式(12)-式(14)所示[4]。
式中i、o为内外油膜摩擦功耗,W;total为浮环摩擦功耗,W;为浮环轴承内圈宽度、外圈宽度,mm。
1.1.5 润滑油端泄流量
浮环轴承润滑油端泄流量如式(15)-式(20)所示[30]。
式中i1、i2分别为内层润滑油前端、后端流量,L/s;o1、o2分别为外层润滑油前端、后端流量,L/s;i、o分别为内、外层润滑油流量,L/s。
1.2 转轴-浮环-轴承座传热模型
增压器转轴-浮环系统运转中,热流由转轴流向轴承座。其中,内膜、浮环和外膜均保持热量平衡。
1.2.1 浮环内膜热平衡方程
浮环内膜热量由转轴向内膜传热和内膜摩擦两部分组成。内膜通过端泄带走部分热量,另一部分热量则传递到浮环,其热平衡方程为
式中Journal-i为转轴对浮环内膜传热量,J;Journal-i=JJi(J−i),其中J为转轴与内膜传热区域面积,m2,Ji为内膜与转轴的对流换热系数;i为内膜温度,K;i=in+∆i,in为进油温度,K;∆i为内膜温升,K;i为内膜摩擦产生热量,J;i=i,i-out为内膜端泄热量散失,J,i-out=cρQi∆i,c为润滑油比热容,J/(kg·K);为润滑油密度,kg/m3;i-ring为内膜对浮环传热量,J,i-ring=RiR(i−R),其中R为油膜与浮环传热区域面积,m2,iR为内膜与浮环的对流换热系数。
1.2.2 浮环热平衡方程
浮环将从内膜吸收的热量传递到外膜,并且浮环从内膜吸收的热量等于浮环传递到外膜的热量,其方程为
式中ring-o为浮环向外膜传递的热量,J;ring-o=RRo(R−o),J,Ro为浮环与外膜的对流换热系数,o为外膜温度,K,o=in+∆o,其中∆o为外膜温升,K。
1.2.3 浮环外膜热平衡方程
浮环外膜热量由浮环向外膜传热和外膜自身摩擦做功两部分组成。同样,外膜通过端泄带走部分热量,另一部分热量则传递到轴承座散失,其热平衡方程为
式中o为外膜摩擦生热量,J,o=o;o-out为外膜端泄热量散失,J,o-out=co∆o;o-casing为外膜传递到轴承座热量散失,J,o-casing=CoC(o−C),C为外膜与轴承座传热区域面积,m2;oC为外膜与轴承座对流换热系数。
1.3 浮环平衡模型
浮环轴承稳定工作时,浮环受到内膜承载力与外膜承载力,且内膜承载力与外膜承载力大小相等,方向相反。内膜作用在浮环上的方向为垂直向下,外膜作用在浮环的方向为垂直向上。力平衡方程为[4]
式中i、o分别为内、外膜承载力,N;ix、ox分别为内、外膜承载力在′,坐标轴方向上的分量,N;iy、oy分别为内、外膜承载力在′,坐标轴方向上的分量,N。
1.3.2 浮环力矩平衡方程
浮环高速运转时,内、外油膜在浮环上产生的摩擦力力矩相等。力矩平衡方程为
1.4 数值分析方法
数值分析流程图如图2所示。
5.从作文内容来看,31%的同学能做到中心明确,内容具体,其余同学有不同层次问题;从结构来看,35%的同学能做到条理清楚,结构完整,其余同学有不同层次问题;从语言来看,31%的同学语言通顺,用语准确,其余同学有不同层次问题。
2 计算模型验证
为验证论文模型正确性,与文献[6]试验结果进行比较。首先,本文模型与文献[4-6]中异同处在于:文献[4-6]中的计算模型没有考虑内膜与转轴之间的传热和外膜与轴承座之间的传热,以转轴温度近似等于内膜温度,轴承座温度近似等于外膜温度作为处理方式,只考虑了内膜、浮环、外膜之间的传热状况,而本文计算模型考虑了转轴、浮环、轴承座之间的传热因素,并且,在本文进一步分析中,考虑了浮环轴承润滑性能和环速比的相互影响关系,研究浮环结构参数对其润滑性能和环速比的综合影响。
在算例中,浮环轴承参数采用试验中轴承性能参数[4-6],并采用本文的模型进行分析,获取不同转速下的环速比与文献[6]相应试验值的对比情况,见图3。由图3可见,本文采取的润滑与传热相结合的模型算法结果与试验值吻合较好,误差在15%内,且变化趋势也较为一致,证明本文模型的可靠性。
4 结果与讨论
表1为分析浮环轴承和润滑油主要参数。
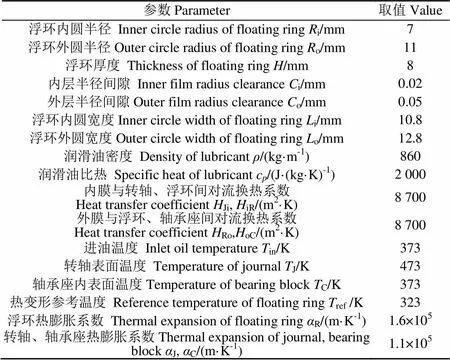
表1 浮环轴承和润滑油主要计算参数
3.1 内层间隙
图4为内层间隙对浮环轴承环速比与润滑特性的影响。由图4a可知,随内层间隙增加,内膜膜厚增加,导致内膜力矩减小,故需减小环速比使内膜力矩与外膜力矩重新达到平衡,因而环速比减小,且转速越小,环速比下降趋势越明显。与内层间隙0.02 mm时相比,转速60 000 r/min时,内层间隙0.04 mm时的环速比减幅达23%。由图4b可知,随内层间隙增加,内膜通过端泄带走更多热量,从而使内膜温度减小。
由图4c可知,外膜温度也随内层间隙增加而减小,主要原因在于环速比减小使浮环转速下降,导致浮环与液膜之间摩擦生热明显减小。由图4d可知,随内层间隙增加,内膜最小膜厚增加,而外膜最小膜厚的变化并不显著,原因在于最小膜厚主要由间隙结构决定,内层间隙增加,浮环内层几何间隙明显变大,因而内膜最小膜厚增加;而外层几何间隙没有发生改变。由图4e可知,总摩擦功耗随内层间隙增加而略有增加。由图4f可知,随内层间隙增加,总端泄流量增加,但增幅基本不随转速变化。因此,在实际设计浮环轴承时,应在避免环速比过小的前提下,适当增加内层间隙从而提高浮环轴承的润滑性能。
在本算例中,尽管内层间隙为0.04 mm时浮环具有最佳的润滑性能,但内层间隙0.04 mm时过小的环速比可能会导致浮环实际工作中失效。综上分析,要获得理想的润滑性能和环速比,内层间隙取0.03 mm较为合适。
3.2 外层间隙
图5为外层间隙对浮环轴承环速比与润滑特性的影响。由图5a可知,外层间隙0.06 mm的环速比均比外层间隙0.04 mm的环速比增加30%以上。由图5b可知,外层间隙对内膜温度几乎没有影响。由图5c可知,尽管环速比随外层间隙增加而增加,导致浮环转速升高,浮环与外膜摩擦产生更多热量,但外膜间隙增加的同时也使液膜端泄带走更多热量,其影响大于外膜摩擦生热影响,故外膜温度反而减少,且随转速升高,外膜温度减幅有扩大趋势。由图5d可知,内膜最小膜厚基本不随外层间隙变化而变化,而外膜最小膜厚随外层间隙增加而增加。由图5f可知,由于外层间隙增加使外膜端泄流量增加,因而总端泄流量增加。综上所述,增加外层间隙以提高浮环的环速比,同时还可降低浮环外膜温度,但对内膜温度的影响并不明显。基于外层间隙对浮环润滑特性和环速比的分析结果,在浮环其他几何结构参数不变的情况下,外层间隙取0.06 mm较为合适。
3.3 内圆半径
图6为内圆半径对浮环轴承环速比和润滑特性的影响。由图6a可知,随内圆半径增加,环速比增加。由图6b可知,由于内圆半径增加使浮环内圆表面与液膜接触面积增加,液膜摩擦做功增加,故内膜温度增加。由图6c可知,外膜温度随内圆半径增加而增加,原因在于浮环转速增加使外膜摩擦生热增多,导致外膜温度增加,且转速越高,外膜温度的增幅有扩大趋势。由图6d可知,随内圆半径增加,内膜最小膜厚与外膜最小膜厚均增加,但外膜最小膜厚增幅明显大于内膜最小膜厚增幅,这是因为内膜膜厚受转轴与浮环转速综合影响,而外膜膜厚只受浮环转速影响。由图6e可知,随着内圆半径的增加,总摩擦功耗增加,同样,总摩擦功耗增幅随转轴转速增加而增加,说明内圆半径对浮环轴承润滑性能与转轴转速有直接联系。由图6f可知,总端泄流量随内圆半径增加而增加。综上所述,由于内、外膜温度和摩擦功耗均随内圆半径减小而减小,因此减小浮环内圆半径可以明显改善浮环润滑性能,但浮环的环速比也相应减小。内圆半径为6 mm时,环速比均在0.1以下,不利于浮环的稳定运转。因此,为确保浮环稳定运行,且同时确保浮环润滑性能最佳,内圆半径取7 mm较为合适。
3.4 外圆半径
图7为外圆半径对浮环轴承环速比和润滑特性的影响。由图7a可知,随外圆半径增加,环速比降低。由图7b可知,内膜温度随外圆半径增加而略有增加,原因在于随着外圆半径增加,浮环转速减小,而转轴与浮环之间的相对速度增加,内膜摩擦生热加剧,导致内膜温度增加。由图7c可知,由于外圆半径增加使浮环外表面与液膜接触面积增加,液膜做功增加,外膜温度略有增加。但是,与内圆半径对内、外膜温度影响程度相比,外圆半径对内、外膜温度的增幅很小。由图7d可知,随外圆半径增加,外膜最小膜厚减小,而内膜最小膜厚基本没有变化。由图7e、7f可知,随外圆半径增加,总摩擦功耗略有增加,总端泄流量略有减小,外圆半径对内膜温度、外膜温度、总摩擦功耗和总端泄流量变化幅度均在5%以内,说明外圆半径对浮环润滑性能的影响并不显著。由于外圆半径为11和12 mm时,环速比较小,为确保浮环稳定运转,外圆半径应取10 mm较为合适,此时浮环在不影响润滑性能的同时也能够保证较大的环速比,从而保证浮环轴承的可靠性。此外,浮环外圆半径对浮环轴承润滑性能的影响程度小于内圆半径对其的影响。因此,想要提高润滑性能,实际设计浮环轴承时,调整浮环内圆半径比调整外圆半径更有效。
4 结 论
1)增压器浮环轴承的环速比和润滑特性存在互相影响、互相作用关系。实际设计浮环轴承时,应综合考虑结构参数对润滑特性和环速比的影响及影响程度。
2)与内层间隙0.02 mm相比,内层间隙0.04 mm时的环速比减幅达23%;内层间隙增加,内膜温度和外膜温度减小,摩擦功耗略有增加,端泄流量增加,浮环润滑性能提高。要获得理想的环速比,内层间隙取0.03 mm较为合适。
3)外层间隙为0.06 mm的环速比均比外层间隙为0.04 mm的环速比增加30%以上;外膜温度减小,且转速越高,外膜温度减幅越大。
4)浮环轴承内圆半径越小,浮环润滑性能越好,但浮环的环速比也相应降低。
5)随浮环外圆半径增加,环速比降低,但内膜温度、外膜温度、总摩擦功耗和总端泄流量变化幅度均在5%以内,润滑性能变化不显著;为提高润滑性能,实际设计浮环轴承时,调整浮环内圆半径比调整外圆半径更有效。
[1] Clarke D M, Fall C,Hayden G N,et al. A steady-state model of a floating ring bearing, including thermal effects[J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 1992, 114(1): 141-149.
[2] Koeneke C E, Tanaka M, Motoi H. Axial oil film rupture in high speed bearings due to the Effect of the centrifugal force[J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 1995,117(3): 394-398.
[3] Mokhtar M M, EI-Butch A M A. Adoption of floating-ring design in automotive applications[C]//SAE World Congress, Detriot, 2005: 3783-3789.
[4] Andres L S, Kerth J. Thermal effects on the performance of floating ring bearings for turbochargers[J]. Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2004, 218(5): 437-450.
[5] Holt C,Andres L S, Sahay S, et al. Test response and nonlinear analysis of a turbocharger supported on floating ring bearings[J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 2005, 127(2): 107-115.
[6] Andres L S, Gjika K G, Larue G. Rotordynamics of small turbochargers supported on floating ring bearings-highlights in bearing analysis and experimental validation[J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 2007, 129(2): 391-397.
[7] Andres L S, Barbarie V C, Bhattacharya A, et al. On the effects of thermal energy transport to the performance of (Semi) floating ring bearing systems for automotive turbochargers[J]. ASME Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbings and Power, 2012, 134(10): 1-10.
[8] Li C H. Dynamics of rotor bearing systems supported by floating ring bearings[J]. Journal of Lubrication Technology, 1982, 104(1): 469-477.
[9] Bouzidane A, Thomas M. Equivalent stiffness and damping investigation of a hydrostatic journal bearing[J]. Tribology Transcation, 2007, 50(2): 257-267.
[10] Chen C H. The influence of orifice restriction and journal eccentricity on the stability of the rotor-hybird bearing system[J]. Tribology International, 2004, 37(3): 227-234.
[11] Guo H, Lai X M, Cen S Q. Theoretical and experimental study of constant restrictor deep/shallow pockets hydrostatic/hydrodynamic conical bearing[J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 2009, 131(4): 041701-041707.
[12] Guo H, Lai X M, Wu X L, et al. Performance of flat capillary compensated deep/Shallow pockets hydrostatic/hydrodynamic journal-thrust floating ring bearing[J]. Tribology Transcations, 2009, 52(2): 204-212.
[13] 郭红,来新民,岑少起,等. 计入气穴影响的径推联合动静压浮环轴承稳定性研究[J]. 润滑与密封,2009,34(9):10-15.
Guo Hong, Lai Xinmin, Cen Shaoqi, et al. A stability analysis for a journal-thrust hybrid floating ring bearing with the cavitations influence[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2009, 34(9): 10-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 郭红,张直明,岑少起,等. 径向浮环动静压轴承稳定性研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2012,31(17):81-85.
Guo Hong, Zhang Zhiming, Cen Shaoqi, et al. Stability of a journal floating ring hybrid bearing[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(17): 81-85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] Zhang R Q, Chang H S. Stability of a new type of hydrostatic/hydrodynamic floating ring gas bearing[J]. Tribology Transcations, 1999, 42(2): 331-337.
[16] Dong X, Zhao Z. Experimental and analytical research on floating-ring bearings for engine applications[J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 1990, 112(1): 119-122.
[17] Deligant M, Podevin P, Descombes G. CFD model for turbocharger journal bearing performance[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 31(5): 811-819.
[18] Liang Feng, Zhou Ming, Xu Quanyong, et al. Effects of semi-floating ring bearing outer clearance on the subsynchronous oscillation of turbocharger rotor[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 29(5): 901-910.
[19] Pei Shiyuan, Xu Hua, Yun Meng, et al. Effects of surface texture on the lubrication performance of the floating ring bearing[J]. Tribology International, 2016, 102(1): 143-153.
[20] Soni S, Vakharia D P. A steady-state performance analysis of a non-circular cylindrical floating ring journal bearing[J]. Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2016, 231(1):1-16.
[21] 康召辉,任兴民,黄金平,等. 浮环轴承系统中浮动环作用机理研究[J]. 振动工程学报,2009,22(5):533-536.
Kang Zhaohui, Ren Xingmin, Huang Jinping, et al. Research of mechanism of a floating ring in the floating ring bearing system[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2009, 22(5): 533-536. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 康召辉,任兴民,何尚文,等. 浮环涡动对浮动轴承油膜压力分布影响的研究[J]. 航空动力学报,2010,25(5):1197-1202.
Kang Zhaohui, Ren Xingmin, He Shangwen, et al. Study on the effects of whirling motion of the floating-ring on distribution of oil pressure in a floating-ring bearing[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2010, 25(5): 1197-1202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 师占群,张浩,宋中越,等. 载荷和供油压力对浮环轴承润滑影响的理论研究[J]. 河北工业大学学报,2013,42(1):61-69.
Shi Zhanqun, Zhang Hao, Song Zhongyue, et al. A theoretical study on the effects of load and lubricant feed pressure on the lubrication of floating ring bearings[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology, 2013, 42(1): 61-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 张浩,师占群,张顺心,等. 基于质量守恒边界条件的浮环轴承贫油润滑特性理论分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2014,50(9):100-107.
Zhang Hao, Shi Zhanqun, Zhang Shunxin, et al. A theoretical investigation on staved lubricating characteristics of the floating ring bearing based on jacobsson-floberg-olsson boundary condition[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(9): 100-107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 张文静,陈渭,李培,等. 系统参数对浮环轴承转速比的动态影响[J]. 四川大学学报:工程科学版,2015,47(3):160-167.
Zhang Wenjing, Chen Wei, Li Pei, et al. Dynamic effects of system parameters on speed ratio of floating ring bearing[J]. Journal of Sichuan University: Engineering Science Edition, 2015, 47(3): 160-167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 宁峰平,姚建涛,安静涛,等. 考虑摩擦特性时过盈量对轴承预紧力的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(14):96-102.
Ning Fengping, Yao Jiantao, An Jingtao, et al. Influence of interference on bearing preload considering frictional properties[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(14): 96-102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 易圣先,赵俊生,李培,等. 结构参数对浮环轴承动态特性的影响研究[J]. 工程设计学报,2013,20(6):512-516.
Yi Shengxian, Zhao Junsheng, Li Pei, et al. Research on effect of structure parameters on dynamic characteristic for floating ring bearing[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Design, 2013, 20(6): 512-516. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] Trippett R J, Li D F. High-speed floating ring bearing, test and analysis[J]. ASLE Transactions, 1987, 27(1): 73-81.
[29] 李佳琪,倪计民,石秀勇,等. 计入浮环传热的增压器浮环轴承润滑分析[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版,2016,44(11):1755-1762.
Li Jiaqi, Ni Jimin, Shi Xiuyong, et al. Influence of heat transfer through floating ring on lubrication performance of floating ring bearing[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2016, 44(11): 1755-1762. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] Sun J, Deng M, Fu Y H, et al. Thermohydrodynamic lubrication analysis of misaligned plain journal bearing with rough surface[J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 2010, 132(1): 111-118.
Effect of structural parameters on lubrication performance of floating ring bearing and ring speed ratio in turbocharger
Li Jiaqi1, Ni Jimin1, Shi Xiuyong1, Xu Xiaochuan1, Liu Yue1, Li Dongdong1,Chen Zhenbin2
(1.,,201804,; 2.,,571737,)
Turbochargers are widely used in internal combustion engines. The floating ring bearing is the most important part in the turbocharger, which is composed of inner film and outer film. The floating ring bearing can reduce the frictional power and oil film temperature. In the past, the lubrication performances of the floating ring bearing were analyzed without considering the heat transfer among the shaft, floating ring and bearing block. Furthermore, some researchers analyzed the lubrication performance of floating ring and the ring speed ratio separately. In reality, there exists heat transfer among the shaft, floating ring and bearing block and this part of heat will directly influence the lubrication performance of the floating ring. Besides, the change of the structural parameters may decrease ring speed ratio, which maybe is unfavorable to the practical operation if it is too small, and the change of the ring speed ratio may also influence the lubrication performance. So there exists a strong coupled relationship between the lubrication performance and ring speed ratio, and they can be studied more comprehensively and systematically with the change of structural parameters. The lubrication performance of floating ring bearing and the floating ring speed ratio in turbocharger were studied by considering the heat transfer among the shaft, floating ring and bearing block. Based on the Reynolds equation and the floating ring balance equation, the lubrication model of floating ring bearing was established. The Reynolds equation was solved by the finite difference method. The thermal deformation of the floating ring bearing was calculated by the thermal deformation equation. Comparative analysis on the influence of structural parameters on lubrication performance of floating ring bearing and floating ring speed ratio was performed, and the parameters included inner film clearance, outer film clearance, inner circle radius and outer circle radius. Results showed the effect and affecting level of structural parameter on lubrication performance and floating ring speed ratio should be considered comprehensively. The ring speed ratio decreased with the increase of inner film clearance. Compared with that inner film clearance is 0.02 mm, the ring speed ratio decreased 23% when inner film clearance is 0.04 mm. The inner film temperature, the outer film temperature decreased and the total friction power loss slightly increased with the increase of inner film clearance. The lubrication performance and ring speed ratio are ideal when inner film clearance is 0.03 mm. Compared with that outer film clearance is 0.04 mm,the ring speed ratio increased more than 30%. The outer film temperature decreased with the increase of outer film clearance. The higher the rotation speed, the greater the decrease amplitude of the outer film temperature. The smaller the inner circle radius, the smaller the floating ring speed ratio, and the smaller the inner film temperature, outer film temperature and total friction power loss. So the lubrication performance of the floating ring bearing will be improved with the decrease of the inner circle radius. The ring speed ratio decreased with the increase of the outer circle radius. But the inner film temperature, the outer film temperature increased, the total friction power loss and total oil leakage flowrate changed less than 5% with the increase of the outer circle radius. The outer circle radius has little effect on the lubrication performance of the floating ring bearing. Compared with the adjustment of the outer circle radius, it is more effective to improve the lubrication performance of floating ring bearing with the adjustment of the inner circle radius. There is a good agreement between the results predicted by the calculation model in this paper and some published experimental data.
bearings; models; temperature; floating ring bearing; lubrication; structural parameters; ring speed ratio; heat transfer
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.02.007
TH133.31
A
1002-6819(2017)-02-0048-08
2016-05-09
2016-12-07
国家自然科学基金资助(51166002);上海市自然基金资助(16ZR1438500)
李佳琪,博士生,主要从事浮环轴承润滑机理研究。上海 同济大学汽车学院,201804。Email:lijiaqi_1987@126.com
倪计民,男,教授,博士生导师,主要从事涡轮增压器润滑系统设计研究。上海 同济大学汽车学院,201804。Email:njmwjyx@hotmail.com
李佳琪,倪计民,石秀勇,徐晓川,刘 越,李冬冬,陈振斌. 结构参数对增压器浮环轴承润滑特性和环速比的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(2):48-55. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.02.007 http://www.tcsae.org
Li Jiaqi, Ni Jimin, Shi Xiuyong, Xu Xiaochuan, Liu Yue, Li Dongdong, Chen Zhenbin. Effect of structural parameters on lubrication performance of floating ring bearing and ring speed ratio in turbocharger[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(2): 48-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.02.007 http://www.tcsae.org

