不同麻醉方式对重型颅脑损伤急诊手术患者的影响
张玮

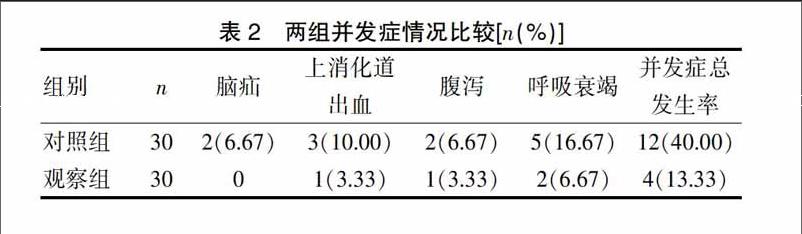
[摘要] 目的 探讨不同麻醉方式对重型颅脑损伤急诊手术患者的影响。 方法 收集2014年1月~2017年1月期间我院急诊科收治的重型颅脑损伤患者共60例作为研究对象,将其按照不同的麻醉方法分为两组,对照组和观察组各30例,两组均给予相同的术前准备,对照组静吸复合麻醉,观察组全凭静脉麻醉,比较两组插管前、插管后10 min、插管后1 h、手术结束HR、SBP、DBP,并发症情况、致残及死亡情况。 结果 观察组插管前、插管后10 min、插管后1 h、手术结束后HR、SBP、DBP与对照组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),观察组呼吸衰竭发生率、并发症总发生率、致残率、死亡率均低于对照组,两组差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 重型颅脑损伤急诊手术患者使用全凭静脉麻醉效果更好,不会对患者形成明显的影响,且并发症发生率、死亡率及致残率均较低,可在临床推广应用。
[关键词] 颅脑损伤;麻醉;急诊;静吸复合麻醉;全凭静脉麻醉
[中图分类号] R614;R651.1+5 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2017)13-0122-03
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of different anesthesia methods on the emergency surgery in the patients with severe craniocerebral injury. Methods A total of 60 patients with severe craniocerebral injury who were admitted to the emergency department in our hospital from January 2014 to January 2017 were collected as the study subjects. The patients were divided into two groups according to different anesthesia methods, with 30 cases each in the control group and the observation group. Both groups were given the same preoperative preparation. The control group was given intravenous inhalational anesthesia. The observation group was given total intravenous anesthesia. HR, SBP, DBP, complications, disability and death before intubation, 10 min after intubation, 1 h after intubation and at the end of surgery were compared between the two groups. Results There were no statistically significant differences in HR, SBP and DBP between the observation group and the control group before intubation, 10 min after intubation, 1 h after intubation and at the end of surgery(P>0.05). The incidence rate of respiratory failure, total incidence rate of complications, morbidity rate and mortality rate in the observation group were lower than those in the control group, and there were statistically significant differences between the two groups(P<0.05). Conclusion Total intravenous anesthesia in the emergency surgery in the patients with severe craniocerebral has a better effect, which does not have a significant impact on the patients, and the incidence rate of complications, mortality rate and morbidity rate are low, which can be popularized and applied clinically.
[Key words] Craniocerebral injury;Anesthesia;Emergency;Intravenous inhalational anesthesia; Total intravenous anesthesia
顱脑损伤是指暴力作用于头部引起的脑组织损伤,多由锐器伤、交通事故及坠跌伤等导致,重型颅脑损伤是指颅脑损伤患者伤后昏迷时间超过6 h 或再次昏迷者,是临床中比较严重的急危症,患者以意识障碍、头晕、恶心、失语等为主要的临床表现[1],病情危重紧急,需要及时救治,否则可能会导致患者死亡或残疾。重型颅脑损伤患者受伤程度不同,其病情也会发生相应的变化,临床多开颅手术治疗,在急诊手术中,为了使患者的疼痛舒缓、确保手术顺利进行,麻醉的实施是非常重要的环节,手术的成功率及手术后并发症发生率会受到麻醉方法及麻醉剂量的直接影响[2-3]。本文对60例重型颅脑损伤急诊手术患者进行分析,根据不同的麻醉方式分组,比较不同麻醉方式对患者的影响,现报道如下。

