Therapeutic effect observation on acupuncture plus umbilicus application with Chinese medicine in treating detrusor underactivity
Liu Wei-min (刘为民), Hu Hong-yan (胡红燕), Xiao Wei (肖嵬)
Traditional Chinese Medicine Center, Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hangzhou 310006, China
Abstract Objective: To observe the clinical efficacy of acupuncture plus umbilicus application with Chinese medicine for detrusor underactivity.
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Acupoint Sticking Therapy; Point, Shenque (CV 8); Detrusor Underactivity; Urination Disorders; Men
Detrusor underactivity (DU) is a common bladder dysfunction caused by a decrease in contractility of bladder detrusor or a shortened duration of contraction,resulting in delayed bladder emptying or incomplete emptying during normal urination[1]. The main clinical manifestations of DU are lower urinary tract symptoms,such as frequent micturition, urgency of urination,urinary incontinence and dysuria[2], which seriously affects the quality of life (QOL) of patients[3]. At present,there is no unified treatment plan or effective drugs.The muscarinic receptor agonist and cholinesterase inhibitor used at present only have limited effect and may cause many adverse reactions[4]. Based on this circumstance, we used acupuncture plus umbilicus application with Chinese medicine to treat male patients with detrusor underactivity between January and December 2017, which is reported as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
Referring to the literature[5], the diagnostic criteria of DU in this study met the following three points: the diagnosis of neurological diseases leading to bladder urethral dysfunction, such as the nature, location,degree and extent; the diagnosis of lower urinary tract dysfunction and urinary tract complication, such as the type and degree of the dysfunction, and the condition of upper urinary tract; the diagnosis of other related systems or organ dysfunctions.
It should be noted that DU urodynamics is characterized by lower intravesical pressure, shortened contracting duration or wavy contraction, and lower urinary flow rate[6]. The detrusor overactivity, prostatic hyperplasia, urinary tract infection and other related diseases must be excluded. Urodynamics, urine routine,urinary color Doppler and other related auxiliary examinations can help to confirm the diagnosis.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Those who met the diagnostic criteria of DU; male patients in the outpatient clinic of our hospital; aged 18-65 years; with duration of at least 1 month; agreed to participate in this clinical trial and signed informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those who were allergic to Chinese herbal medication; fear of acupuncture, who had unstable emotion after acupuncture, or were intolerant of metal products; coupled with other serious diseases;psychiatric patients.
1.4 Elimination and drop-out criteria
Those who failed to be examined or treated as required, resulting in incomplete clinical data; dropped out because of sudden illness or other accidents during treatment.
1.5 Statistical methods
All data were statistically analyzed by the SPSS 22.0 statistical software. The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s), and t-test was applied. Chi-square test was applied to the comparison of counting data. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
1.6 General data
A total of 46 cases were selected from clinic of our hospital, from January to December 2016. They were randomly divided into an observation group and a control group by the random number table according to the visiting sequence, with 23 cases in each group.There were no statistically significant differences in the general data between the two groups (all P>0.05),indicating that they were comparable (Table 1).
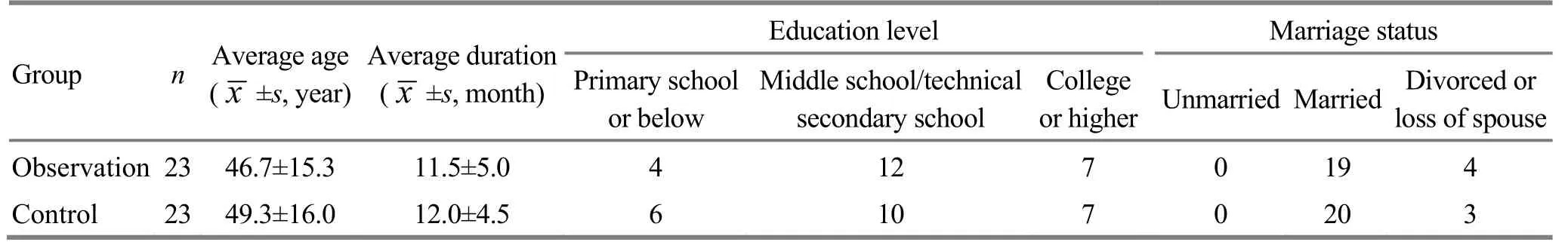
Table 1. Comparison of the general data between the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Control group
Patients in the control group received sterile intermittent catheterization and routine nursing.
The catheterization time depended on the degree of bladder filling. Before the catheterization, if the patient felt better, he could try automatic micturition. In general, the catheterization was performed every 6 h from the first catheterization every day. Physician derived urine 300 mL firstly, and then continued catheterization to 400-500 mL if the patient had no discomfort, and closely monitored the change of residual urine volume. When the residual urine volume was <200 mL, the daily catheterization was changed to twice a day; when the residual urine volume was<150 mL, the daily catheterization was changed to once a day; when the bladder residual urine volume was<100 mL, and the patient was in good physical condition,the catheterization could be stopped.
The patient's daily fluid intake was controlled and maintained at 1 000-1 500 mL. Irregular water drinking should be prevented. At the same time, daily water drinking amount should be average, which meant to drink water after waking up in the morning, after lunch and before dinner. The patients were told not to drink water after dinner or before sleep if it was not necessary, so that the body could develop habitual water drinking, which helped the bladder to keep regular habitual contraction and relaxation.
2.2 Observation group
On the basis of the intervention of the control group,umbilicus application with Chinese medicine and acupuncture treatment were added.
2.2.1 Umbilicus application with Chinese medicine
Medicine: Huang Qi (Radix Astragali) 15 g, Wu Yao(Radix Linderae) 10 g, Yi Zhi Ren (Fructus Alpiniae Oxyphyllae) 10 g, Bai Ji (Pseudobulbus Bletillae) 10 g,Mo Yao (Myrrh) 5 g, and Ru Xiang (Olibanum) 5 g.
Method: The above-mentioned Chinese herbal medicine after stir-fried were mashed and ground into powder, and mixed. Every time, the physician took 3 g of the powder, prepared it into a paste with aged vinegar, and then applied it at the umbilicus, which was covered with sterile gauze and fixed with tape. Then,placed a 40 ℃ hot-water bag on the top for hot medicated compress. The treatment was applied twice a day, lasting 30 min each time. The medicine was changed once a day, 10 d as a treatment course, with a 3-day interval between two courses, for 2 courses in total.
2.2.2 Acupuncture therapy
Acupoints: Guanyuan (CV 4), Sanyinjiao (SP 6),Pangguangshu (BL 28), Shenshu (BL 23), Shenmai(BL 62) and Fuyang (BL 59).
Method: The patient took a supine position. The physician selected the acupoints on one side each time.The two sides of acupoints were used alternatively. The physician used the acupuncture needles of 0.38 mm in diameter and 7.5 cm in length to obliquely puncture Guanyuan (CV 4) at a 45° angle with the tip of the needle downwards by 1.5-3.0 cm in depth, to make the needling sensation spread to perineum. Sanyinjiao (SP 6)was punctured with the tip of the needle upwards to make the needle sensation spread upwards. The needles were retained for 30 min. After needle withdrawal, the patient took a prone position. The physician perpendicularly punctured Shenshu (BL 23)and Pangguangshu (BL 28) by 1.5-2.0 cm in depth. Then,the physician connected two poles of the CMNS6-1 electronic pulser with Shenmai (BL 62) and Fuyang(BL 59) on the same side, with continuous wave, 80 Hz in frequency, and 20 mA in current intensity. The stimulation lasted for 30 min each time, once a day, and 10 times constituted a treatment course. There was a 3-day interval between two courses, and a total of 2 courses were performed.
3 Efficacy Observation
3.1 Criteria of curative efficacy[5]
Cured: The patient felt no urinary incontinence or urinary retention symptoms. After the catheter was removed under self-willingness, the patient was able to urinate regularly and normally; the residual urine was less than 50 mL.
Marked effect: The patient felt a great relief in urinary incontinence or discomfort of urinary retention. The patient could remove the catheter and urinate on time with right quantity every day. The residual urine was >50 mL, but ≤100 mL.
Effective: The patient felt a certain relief in urinary incontinence or discomfort of urinary retention,occasionally had dysuria or unconscious urine discharging; was able to remove the catheter, but occasionally needed in an emergency; residual urine was 100-200 mL.
Invalid: The patient felt no improvement of urinary incontinence or urinary retention, and was unable to remove the catheter; the bladder urine residue was not significantly improved compared with the pretreatment value, or the residual urine >200 mL.
3.2 Results
No dropout cases occurred during the treatment.
3.2.1 Total effective rate
After the intervention, the total effective rate of the observation group was 78.3%, which was higher than that of the control group (52.2%), and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P<0.05), (Table 2).
3.2.2 Bladder urine residue
There was no significant difference in residual urine between the two groups before intervention (P>0.05).After intervention, the residual urine volume of both groups decreased (both P<0.05). The difference in the change of residual urine after intervention was statistically significant between the two groups (P<0.05),(Table 3).
3.2.3 Maximum urine flow rate
There was no significant difference in the maximum urine flow rate between the two groups before intervention (P>0.05). After intervention, the maximum urine flow rate was improved in both groups (both P<0.05); the change in the maximum urinary flow rate was significantly different between the two groups after intervention (P<0.05), (Table 4).

Table 2. Comparison of clinical efficacy between the two groups (case)
Table 3. Comparison of bladder urine residue between the two groups (±s, mL)
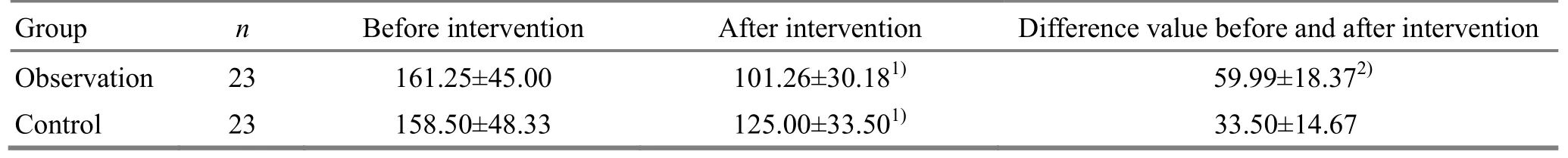
Table 3. Comparison of bladder urine residue between the two groups (±s, mL)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the control group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before intervention After intervention Difference value before and after intervention Observation 23 161.25±45.00 101.26±30.181) 59.99±18.372)Control 23 158.50±48.33 125.00±33.501) 33.50±14.67
Table 4. Comparison of maximum urine flow rate between the two groups (±s, mL)

Table 4. Comparison of maximum urine flow rate between the two groups (±s, mL)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the control group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before intervention After intervention Difference value before and after intervention Observation 23 6.59±1.72 11.95±2.261) 5.36±0.882)Control 23 6.72±1.85 9.33±2.031) 2.61±0.50
4 Discussion
In this study, patients in the control group received sterile intermittent catheterization and routine nursing,which accorded with the current treatment of DU. On the basis of this treatment, patients in the observation group were treated by acupuncture plus umbilicus application with Chinese medicine. The results showed that the total effective rate of the observation group was higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). The changes in residual urine and maximum urine flow rate after intervention in the observation group were higher than those in the control group (both P<0.05). These results suggested that acupuncture plus umbilicus application with Chinese medicine on the basis of sterile intermittent catheterization and routine nursing had a better effect.
Umbilicus application with Chinese medicine is a common external therapy in traditional Chinese medicine[7]. The umbilicus is the last position of the abdominal wall closure during embryonic development.It has the characteristics of weak stratum corneum. It is easy for Chinese herbal medication to penetrate into the stratum corneum. Compared with other regions,external application on umbilicus has the advantages of higher utilization rate and absorption rate[8]. Shenque(CV 8) is located at the umbilical region. With application of Chinese herbal medicine, the veins around the umbilicus can be stimulated, so, qi and blood circulation in Zang-fu organs would be promoted[9]. In this study, Huang Qi (Radix Astragali)has the effect of benefiting qi, supporting yang,nourishing kidney and strengthening spleen; Wu Yao(Radix Linderae) can relieve pain and move qi, eliminate cold and warm kidney; Yi Zhi Ren (Fructus Alpiniae Oxyphyllae) can invigorate yang and warm kidney,secure essence and reduce urination; Bai Ji(Pseudobulbus Bletillae) has the effect of dispersing swelling and promoting tissue regeneration; Mo Yao(Myrrh) and Ru Xiang (Olibanum) have stasis-resolving and qi-moving effects. The combination of the whole formula could tonify the kidney qi and make the bladder open and close properly.
Studies have shown that acupuncture stimulation could improve urinary frequency, urgency and urinary retention[10], which could affect and change urodynamics[11-13]. The clinical efficacy of local acupoints in the treatment of urinary retention has been verified[14-16]. In this study, acupuncture on both sides of Shenshu (BL 23) could tonify the kidney and improve bladder qi transformation; Guanyuan (CV 4) could nourish the primordial qi, which was beneficial to restoring the opening and closing function of the bladder[17-18]; Pangguangshu (BL 28) could regulate qi movement of lower jiao, activate qi to move water,increase urine excretion, and promote the recovery of bladder qi transformation, which helped to regulate the waterways[19-20]. The combination of these acupoints could strengthen the kidney, enhance the effect of bladder qi transformation, regulate the urine storage and discharging capacity of the bladder, and regulate the condition of bladder, to achieve the effect of addressing both the symptoms and root cause.
In summary, acupuncture plus umbilicus application with Chinese medicine on the basis of sterile intermittent catheterization and routine nursing can effectively improve clinical symptoms, reduce bladder residual urine volume, and increase the maximum urinary flow rate. Therefore, it is worth further research and promotion of application.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that there was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Received: 15 April 2018/Accepted: 19 May 2018
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2018年6期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2018年6期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effects of electroacupuncture of different frequencies on SP and VIP expression levels in colon of rats with slow transit constipation
- Experimental study on the effect of An-pressing and Rou-kneading Huantiao (GB 30) on certain brain nuclei of pleasure circuits in rats with chronic neuralgia
- Fire-needle therapy for deglutition disorders in post-stroke pseudobulbar palsy:a randomized controlled trial
- Memory response to manual acupuncture in chronic insomniacs: evidence from event-related potentials
- Effect of tuina exercise on simple obesity in college students
- Clinical observation on tuina plus foot bath with Chinese medicine for diabetic foot in early stage
