Ginseng and Angiogenesis: Promotion or Inhibition?
Jun-Ju Zou, Xiao-Tao Zhou, Wen-Yi Li, Chao-Xi Zhu, Yue-Rong Ma
1Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
2Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu,Sichuan,China.
Abstract: Ginseng has a unique pharmacological activity, which can treat ischemic diseases through angiogenesis, and inhibit tumor growth and metastasis by anti-angiogenesis. Angiogenesis is a common target for tumors and ischemic diseases. How could the ginseng regulateblood vessels in different diseases?Here, the mechanism of ginseng bidirectional regulation of angiogenesis in different pathological environments is reviewed,and the role of bidirectional regulation is elucidated.
Key words: Ginseng, Tumor, Angiogenesis, Bidirectional regulation, Research progress
Introduction
P anax ginseng C. A. Mey. is the dried root and rhizome of the ginseng of the Araliaceae plant.As a traditional and precious Chinese medicinal material, Panax ginseng is known as the king of herbs. Its properties are smooth,sweet and slightly bitter and mild.As a tonic, it can tonify vital energy, invigorate the arteries,remove fluid, relieve thirst,invigorate the spleen, invigorate the lungs, and calm the mind.
Angiogenesis can be divided into two types, physiological and pathological. Physiological angiogenesis plays an important role in angiogenesis, formation,m a t u r a t i o n, r e m o d e l i n g o r d e g r a d a t i o n; p a t h o l o g i c a l angiogenesis is an important feature of tumors, various ischemic diseases, and inflammatory diseases. The essence of the tumor is"positive deficiency and poisonous poly", and the key to the emergence of metastasis is "weakness of the body". Neovascularization of tumors is one of the important mechanisms of its metastasis. In related research, it is found that ginseng and its active ingredients have a two-way regulation of angiogenesis.How can ginseng have both pro-angiogenic effects and inhibition of angiogenesis?This article will review the mechanism of action of ginseng on ischemic angiogenesis and antitumor angiogenesis to elucidate its role in bidirectional regulation.
1 Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis, also known as neovascularization, is a physiological phenomenon in the process of normal growth and development, wound repair, etc.,through the proliferation, migration,vascular division and branching of Vascular endothelial cells (VEC)to form new capillaries [1]. In the process of angiogenesis, related series of cytokines are involved harmoniously. If the expression of these factors is insufficient or over-expressed, it will lead to abnormal angiogenesis. This coincides with the "yin and yang"in Chinese medicine theory, that is, yin and yang coordination is the basis of balance. Therefore,the angiogenesis needs to promote the coordination of factors and inhibitors to maintain the angiogenesis; when the promotion factor increases or the inhibitory factor decreases, the angiogenesis will be initiated, and vice versa,the angiogenesis trend will be controlled [2]. During tumor progression, ischemia and hypoxia lead to activation of hypoxia induced factors (HIFs), which promotes activation of a series of angiogenic cytokines such as VEC growth factor (VEGF), activates the proliferation and motivation of VEC, and forms new blood vessels [3]. In this process,fibroblast growth factor (FGF),epidermal growth factor (EGF),angiopoietin (Ang-1) and their receptors can promote VEC mitosis[4]; mesenchymal cell-derived factor SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4, integrin Integrinαvβ3 regulate cellto-cell interstitial adhesion, promote EC migration,and increase VEC permeability to form angiogenesis(Figure 1) [5-6]; transforming growth factor-1 (TGF-1)can induce MMPs, which participate in the regulation of ECM and basement membrane degradation, promote cell invasion [7]; hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α)induces VEC or tumor cells to express and secrete angiogenesis-related factors, up-regulate CXCR4 expression and enhance the stability of CXCR4mRN A [8]; Ras/Raf-1 /MEK/ERK, PI3K/Akt and eNOS/NO also regulate VEGF, PDGF, FGF, and control many processes in the angiogenesis process [9-10].
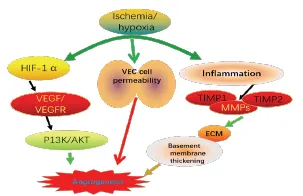
Figure 1: Angiogenesis in ischemia/hypoxic conditions
2 Ginseng inhibits tumor angiogenesis
The formation of tumor blood vessels is an infinite circulation phenomenon. Hypoxia is one of the basic characteristics of tumor microenvironment. Hypoxia induces the activation of related pro-angiogenic factors,promotes the formation of blood vessels, thereby promoting tumor growth, and at the same time, tumor growth can also induce hypoxia, and this cycle leads to the continuous formation of tumor blood vessels.In recent studies, it has been found that many active ingredients in ginseng have inhibitory effects on tumor angiogenesis, including: (1)direct inhibition of vascular endothelial cell proliferation.(2)inhibition of tumor angiogenesis factor (mainly VEGF) signal transduction pathway.(3) inhibition of the activities of MMPs.(4) promotes the expression of tumor angiogenesis inhibitory factors(Figure 2).
2.1 Regulation of proangiogenic factors such as HIFs, VEGF, MVD
Hypoxia is a common feature of solid tumor adaptation. Studies have shown that hypoxia-induced HIF-1αplays an important role in tumor formation,development, invasion and metastasis [11].It is a pivotal link for tumor cells to adapt to hypoxic environment and produce hypoxic behavior, and can also enhance VEGF, MVD and other gene expression related to hypoxia adaptation [12].In the process of UVB irradiation of HaCaT cells, Zhang Hongchanget al. [13]found that the biochemical extract of ginseng can regulate the expression of many genes including VEGF by affecting the expression of HIF-1α in cells,and prevent UVB-induced skin cancer. Li Guodong et al. [14]found that ginsenoside Rg3 can inhibit the expression of HIF-1α and down-regulate the expression of downstream pathway genes VEGF-A and MMP9, and inhibit the angiogenesis of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Tian Junhai et al. [15]found that ginsenoside Rg3 can regulate the expression of HIF-1αof human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell line under hypoxic conditions, inhibiting the expression of VEGF protein and reducing the proliferation of secretory VEGF to promote endothelial cell proliferation. Gengliang [16]found that Rg3 and Rg3 nanoparticles can inhibit the invasion ability and microtubule formation ability of endothelial cells.The main mechanism may be related to the inhibition of the expression of MMP-9, HIF-1 alpha and VEGF proteins.Lu pei [17]found that ginsenoside Rg3 could inhibit the expression of VEGF, MMP-2 and MMP-9 and thus inhibit the formation of tumor blood vessels.Studies have shown that ginsenoside Rg3 can increase the angiogenesis of sorafenib in nude mice xenografts, inhibit the expression of VEGF and its receptor VEGFR-2 by stronginhibition ofHIF-1α[18].Ginsenoside Rg3 can inhibit P38 signaling/ERK(downregulation of VEGF (eg, VEGF-A, VEGF-B and VEGF-C) expression [19], and also by inhibiting hypoxia-induced multiple signals, such as HIF-1α ,COX-2, NF-κB, STAT3, ERK1/2, and JNK (reduced VEGF expression in tumor cells [20-22]. Recent researchindicates that Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits translation of VEGF-A mRNA by elevated miR-497 in the treatment of glioblastoma [23]. Ginsenoside CK inhibits the production of SP1 by inhibiting the activity of SPHK1 in HUVEC, and can regulate the expression of MMPs to inhibit the migration of HUVEC [24]; The decrease of S1P can inhibit the signal of p38MAPK protein, and the p38MAPK protein can induce the migration of cells, so the inhibition of p38MAPK can inhibit the formation of new blood vessels [25]. Further analysis of angiogenesis-related gene expression in saponin Rg3-treated CRC cells, and found 22 proangiogenic Genes ANGPT1, ANGPT2,CCL13, COL18A, CSF3, CXCL1, EGF, FGF-2, IL1A,IL1B, IL8, KDR, MMP-1, PGF, PIGF, PLAUR, TEK,THPO, TIMP1 and TIMP2 were all significantly downregulated [26].
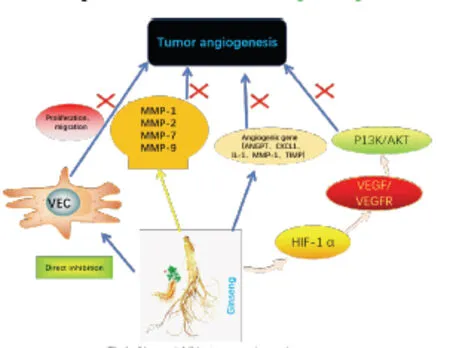
Figure 2: Ginseng inhibits tumor angiogenesis
2.2 Direct inhibition of vascular endothelial cell proliferation
Vascular endothelial cells proliferate and migrate to form a lumen, which plays a very important role in various tumor angiogenesis. It has been confirmed that the proliferation of endothelial cells is 30-40 times faster in tumor tissues than in normal tissues [27].Therefore, the activated VEC will accelerate the growth of tumor blood vessels and inhibit the proliferation of VEC in the tumor state, and is a vital method for inhibiting tumor proliferation and migration. Kim J W et al. [28]co-cultured Rg3 with endothelial cells and found that it inhibits cell proliferation, cell migration and angiogenesis. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits tumor growth by inhibiting endothelial progenitor cells from mobilizing the peripheral circulation of the bone marrow microenvironment. QIHuaicheng et al. [29]used the chicken chorioallantoic membrane model to study the in vitro effects of Rg3 on blood vessels, and showed that it significantly inhibited the formation of angiogenesis through anti-proliferationin chick chorioallantoic membrane. CAO Liang et al.[30]through the effect of Rg3 on the proliferation of HRCEC was observed by MTT colorimetric assay,and found theproliferationinhibition of Rg3was concentration- and time-dependent. WANGJiejun et al.[31]found that ginsenoside Rg3 can inhibit the growth of VEC in gastric cancer cell conditioned medium.Wang Bing et al. [32]detected the proliferation of VEC induced by VEC and gastric cancer cell culture medium with different concentrations of Rg3, and found that when Rg3 concentration was 0.125-0.5mmol/L, it inhibited VEC cells induced by MKN-45 cells.Zhang Guocheng et al. [33]investigated the inhibitory effect of protopanaxadiol (PPd) on the proliferation of gastric cancer-induced vascular endothelial cells(VEC), and found that PPd inhibited the proliferation of VEC induced by conditioned medium in gastric cancer cells. XIN Ying et al. [34]used B16 melanoma cell conditioned medium to induce proliferation and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. It was found that 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 can inhibit the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells by tumor cells.
2.3 Inhibition of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase activity
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are zincdependent endopeptidases that are capable of degrading extracellular matrix (ECM) and basement membrane components under physiological conditions [35].Their activity is mainly caused by metalloproteinase inhibitors. In oncology, matrix metalloproteinases have been considered necessary through ECM (degradation promotes tumor invasion and metastasis molecules)[36]. It has been reported that MMP-2 and MMP-9 have been thought to inhibit the effect of ECM on the basement membrane by decomposing type IV collagen [37]; Studies have shown that in the process of tumor angiogenesis, tumor cells in addition to their own secretion of MMPs,it can also indirectly promote the production of MMPs by vascular endothelial cells by interfering with the expression of VEGF, which confirms that MMPs and VEGF are involved in tumor angiogenesis [38-39]. Ginsenosides have been shown to negatively regulate the expression of MMPs.Ginsenoside RB2, saponin Rg1, ginsenoside Rg3,RH saponins Rh2, Rd and CK prevent ECM barrier damage by preventing the expression of MMP-1, 2, 3,7, 9, 13 and thereby preventing invasion and migration of cancer cells. In addition, ginsenosides Rh1 and Rh2 reduce AP-1 expression and downstream transcription through MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways,and down-regulate the pivotal factors NF-κB and AP-1, and reduce the metalloproteinase gene by recruiting HDAC4's transcription factor activity [40]; ginsenoside RH3 can inhibit the activation of p38MAPK pathway(inhibition of MMP-2 expression) [41]; RH2 inhibits pancreatic cancer cells by down-regulating the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9, ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits angiogenesis induced by ovarian cancer SKOV-3 tumor cells and metastasis by reducing the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 [42]; other studies have shown that ginsenoside RD can reduce the expression of MMP-1, MMP-2 and MMP-7, down-regulating ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signal transduction pathways to prevent migration of hepatoma cells [43]. Wang et al. [44]found that ginsenoside Rg3 can reduce the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF by inhibiting the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF.
3 Ginseng promotes angiogenesis (Figure 3)
Angiogenesis is a physiological mechanism under strict regulation of tissues, several of which affect the active processes at the molecular level, including several soluble peptides, such as VEGF, Ang, FGF,PDGF, TGF-β, ECM. In ischemic diseases, the balance of angiogenesis is broken, affecting the expression of genes involved in neovascularization, endothelial cell proliferation, apoptosis, adhesion and migration, and also reducing vascular tone and vascular reactivity. At home and abroad, it has been found to have significant effects on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases through pharmacological studies of ginseng [45]. Early studies have shown that ginsenoside Rg1 is a stable pro-angiogenic active ingredient that promotes HUVEC proliferation, migration, and official cavity formation[46]. Other studies have confirmed that ginsenoside Rg1 interferes the expression of VEGF protein to adjust HUVEC ,in addition, via the further intervention of HUVEC by p38MAPK inhibitor and p13K inhibitor, it was found that ginsenoside Rg1 can induce cardiovascular production by activating p13K/Akt signaling pathway and inhibiting p38MAPK signaling pathway [47]; In order to prove ginseng not only has the ability to promote angiogenesis but also has the ability to promote tissue regeneration,Huang Chunya et al. [48]implanted into the rat through the extracellular matrix and found that ginsenoside Rg1 does have this function. Some researchers have used ginsenoside Rg1 in rAMI model experiments to confirm the promotion of angiogenesis by up-regulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF)-1α, VEGF, and FGF [49]. Ginseng triol saponin (PTS), ginsenoside Rg1 and ginsenoside Re are thought to play a role in promoting angiogenesis in HUVECs and zebrafish chemically induced vascular loss models [50]. Zhen hui et al. [51]found that PTS can increase cerebral blood flow, promote cerebral angiogenesis and regulate the expression of VEGF and Ang-1. Further studies have shown that 20(S)-protopanaxadiol (PPD) phosphorylates by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Raf/MEK/ ERK signaling pathways and their downstream p70S6 kinase (p70S6K)Accelerating HIF-1α-mediated VEGF secretion induces angiogenesis [52].
4 The therapeutic value of ginseng
Chinese medicine advocates "preventing before the onset of the disease, prevention of progress after the onset of the disease, prevention of recurrence after the disease has healed."
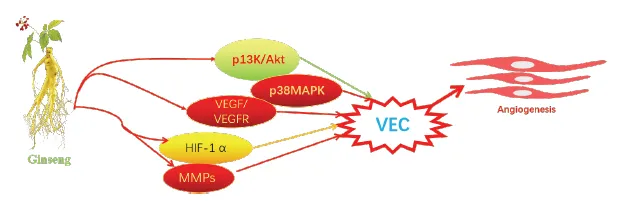
Figure 3: Ginseng promotes angiogenesis
When our body functions in a sub-health state,such as fatigue, susceptibility to colds, drowsiness,weakness, cold hands and feet, etc. , the hormone level or immunity is low. People's chances of getting sick are greatly increased.At this time, taking tonic or tonic food will get people out of this state. As the king of Herbs, ginseng has the strongest qi effect and can improve the immunity of human body and mice [53-54]. It can also enhance the inhibition and killing effect of cancer cells on cancer cells during cancer patients[55-57]. Therefore, the combination of diet therapy plays an important role in the functional recovery of cancer patients.. At present, people are accustomed to using ginseng combined with some food and meat after the disease or when the body is weak. This type of health porridge is suitable forpeople who eat less vomiting, weight loss and fatigue are eating [58-60].In the traditional way of health of the Manchu, the various uses of ginseng, such as stewing, making cakes,creaming - turtle age collection (The precious and healthy products of the Palace royal) and making wine,these methods can enhance the human body immunity[61]. Nowadays, ginseng is used as a supplementary and complementary therapy for cancer treatment, and has been advocated. It is believed that ginseng contains anti-cancer ingredients, which can improve the vitality of the human body, relieve fatigue and help the patient's recovery. In addition, it can reduce the patient's depression symptoms, protect the heart and arterial blood vessels, and improve digestion and absorption.[62-64].According to the researchers, ginsengol and similar compounds can reduce the peripheral nerve damage caused by the anticancer drug paclitaxel and the weight loss caused by nausea, and can reduce the damage of the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil to red blood cells and white blood cells, thereby reducing the risk of infection and anemia [65-66]. Using the special ginseng preparation (Sun Ginseng, SG for short)provided by the Seoul Ginseng Academy of Korea,it was found that SG can improve the quality of life of cancer patients [67]. Malaysia uses a combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine to treat cancer. By using self-made double-salt drinking in the treatment of patients with cancer radiation therapy, it is found that the number of lymphocytes and the number of B cells can be significantly increased; and the quality of life, such as emotional function and cognitive function, is improved, social function, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, insomnia, loss of appetite, financial difficulties, overall life [68]. Clinical studies have found that single-flavored ginseng or ginseng Saponins can improve the fatigue remission rate of cancer patients to a certain extent, reduce the body's fatigue and inertia, and improve the quality of life of patients.Ginseng and ginseng saponins are safe and have no serious side effects. From the evidence of systematic research, it is concluded that the clinical application of ginseng is almost similar to the use of ginseng in diet therapy [69]. From the above research results, it can be concluded that ginseng has a good recovery effect on cancer patients or people with sub-health, and can improve people's quality of life. However, there is a saying in TCM: All drugs are poisonous. even if it is a diet, it should be used in a reasonable way.
5 Discussion and prospect
In summary, the production or inhibition of angiogenesis by ginseng depends on thechanges in the internal and external environment. When in the pathological condition of ischemic pathology, ginseng produces a stress response to repair the damage.By activating HIF-1α, it promotes the transcription of VEGF and its receptor VEGFR, and increases the permeability of blood vessels and also induces EC migrationthrough activation and release of metalloproteinases (MMPs) and growth factors (such as bFGF, VEGF and IGF1). The hypoxic state of the tumor stimulates the increase of endothelial cells and some vascular growth factors, then leads to the growth of tumor blood vessels. The ginseng passes direct inhibition of VEC proliferation in tumors through inhibitingthe signal transduction pathway of angiogenic factors such as VEGF, VEGF, MVD, inhibits the activity of extracellular matrix metalloproteinases,decreases the thickening and weakening migration of EC basement membrane, and further promotes the expression of tumor angiogenesis inhibitors, thereby inhibiting tumor blood vessel growth. Ginseng can act on the same or different targets for tumor and ischemic tissue angiogenesis. Angiogenesis is a multi-cell and multi-molecular process that is coordinated by proangiogenic and inhibitory factors and regulated by many growth factors and signaling pathways. Therefore,under these two different pathological conditions,the effect of ginseng on angiogenesis is different or even completely opposite, which is related to the twoway regulation function of ginseng. This is also the profound and profound point of traditional Chinese medicine. the balance of Yin and Yang is essential for healthy, and the drug's medicinal effect is different according to the state of the body, “Interdependence between yin and yang” is the fundamental of each other, and it is the embodiment of the two-way regulation of drugs. In the study of Chinese medicine in the future, I hope that there will be more researches from the "two-way regulation" of traditional Chinese medicine, reflecting that the treatment of Chinese medicine is not only about treating diseases, but also treating the roots and reconciling yin and yang, which is the basis of treatment.

