Bibliometric Analysis of the Elderly’s Frailty in China
Xiao-Hui An, Fu-Liang Sun, Shu-Qing Cao
1Graduate School, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, 300193, China;
2Nursing Department, Tianjin Eye Hospital, Tianjin, 300020, China.
Abstract Objective:To analysis the research status of the elderly's frailty in China by bibliometric, in order to provide reference for clinical practices and nursing researches.Methods:Search China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), WanFang Data, CQVIP, China Biology Medicine (CBM) disc to find the studies concerning frailty of older adults in China, and analysis the information of Published year, Provinces, Institutions, Journals, Types, Contents and Funds.Results:A Total of 248 articles were included in this study. From 2011, the numbe of studies about the elderly's frailty was growing rapidly; the province with the largest number of publications was Beijing, with a total of 82 articles; the institution with the largest number of publications was Beijing ospital, with 20 articles; the journal with the largest number of publications was Chinese Journal of Geriatrics, with 27 articles; the research type with the largest number of articles was cross-sectional study, with 92 articles, whose content was mainly about the factors of frailty.Conclusion:The study on the elderly's frailty was just starting in China. oping to carry out interventional studies widely in the future, so as to delay the progress of frailty and improve the quality of life of the elderly.
Keywords:Aged; Frailty; Bibliometrics
Introduction
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Retrieval strategy and Selection criteria
Search the China National Knowledge Infrastructure(CNKI), the Wanfang database, the Chinese Scientific Journal Database (VIP) and China Biology Medicine disc (CBM)for topic-related studies until December 2018. The following search terms were used: (“old people” OR “the elderly” OR “aged” OR “senile” ) and(“ frailty “ OR “ frailty syndrome”). In addition, the reference lists from articles were manually searched for further studies. Studies were eligible if the articles were published journal literature related to the theme of frailty. The exclusion criteria were: 1) Conference papers; 2) Newsletters; 3) Literature seriously missing in content; 4) Duplicate literature. All articles were independently selected by two reviewers (Xiaohui An,Fuliang Sun) in the sequence of title, abstract, and full text. Any inconsistencies were resolved by discussion until a consensus was achieved.
1.2 Data extraction and Quality assessment
The following information was extracted from articles: Year of publication, Province, Institution,Journal, Funds, Research Type and Content. Extracted data were entered into a standardized Microsoft Excel file (Microsoft Corporation, office 2010). Two authors(Xiaohui An, Fuliang Sun) independently finished extraction and quality assessment after reviewing each article, which was then checked by another author(Shuqing Cao). Any disagreements were resolved through discussion and consensus.
2 Results
2.1 Literature screening process and results
133 studies were collected from different databases,59 duplicate articles were excluded, 36 articles were excluded from reading abstracts and titles, 27 articles were excluded from reading the full text, 11 articles met the criteria, and 9 studies were finally carried out quantitative analysis. The flow chart of literature screening is shown in Figure 1. Characteristic tables and quality scores included in the study are shown in Table 1.
2.2 Literature Search
Initial electronic searching retrieved a total of 1,792 citations. Of these, 1,544 were excluded because they were duplicates or irrelevant studies. Finally, 248 eligible studies were remained.
2.2 The Result of Publication Year Overall results
In 1997, China published the first article about frailty;from 1997 to 2010, the research about frailty in China was in a slow development stage, with 4 articles,accounting for 1.61% of the total number of articles published; from 2011 to 2016, the research about frailty in China entered a rapid recovery stage, with 62 articles, accounting for 25% of the total number of articles published; from 2017 to now, the research about frailty in China has entered a fast stage, and 183 papers were published, accounting for 73.79% of the total volume. The annual volume about frailty in China is shown in Figure 1.
2.3 The Result of Provinces ranking Overall results
Analysis of the location of units where the first author works, 248 articles were from 27 provinces. The Frailty is a common geriatric syndrome. Because of the physical function decreasing, the elderly are vulnerability increasing and anti-stress ability reducing[1]. The pathophysiological mechanisms of frailty are complex. Studies have shown that inflammatory factors, senescence factor and low 25-hydroxyvitamin D are independent risk factors for frailty[2,3], and individual nutrition, medication use and cognitive function are also related to frailty[4-6]. The study shows that the incidence of frailty is 7%-14% for the elderly over 65 years old, and more than 30% for the elderly over 80 years old in the community[7]. Fried believes that the main symptoms of frailty are muscle weakening, slow walking speed,self-reported fatigue, low vitality and weight loss[8].Frailty not only affects the physical activities of the elderly, but also increases the risk of falls, depression,infection and death in the elderly[9,10]. The research on frailty of the elderly in China is still in a starting stage. This study in order to explore the status and trend of senile frailty in China by bibliometric analysis, and provide data support for future research.provinces publishing volume more than 20 include Beijing, Sichuan and Hebei provinces, adding up to 130 articles (52.42%); the provinces publishing volume between10 and 20 include Jiangsu, Shandong and Shanghai provinces, adding up to 48 articles (19.35%);and the provinces only publishing one article include Yunnan, Hainan, Heilongjiang, Qinghai, Ningxia and Tibet provinces, with 6 articles totally(2.42%). The top 8 provinces in the ranking are shown in Figure 2.
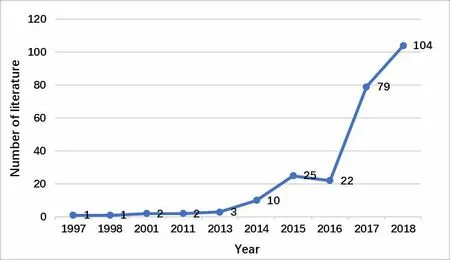
Figure 1. The result of publication year about frailty in China
2.4 The Result of Institutions ranking Overall results
According to the unit of the first author, this study involved 111 institutions, including 72 hospitals(64.86%), 31 universities (27.93%) and 8 other institutions (7.21%). Among them, Beijing Hospital has the largest number of articles, with a total of 20(8.06%). Contrarily, there are 72 institutions that publish only one. It can be seen easily that there are a large number of institutions to carry out researches about frailty in China, but the concentration of literature is low, and there is a significant difference in the depth and breadth about the research in different institutions.The top 7 institutions in the ranking are shown in Table 1.

?
2.5 The Result of Journals ranking Overall results
248 articles were published in 103 journals, of which 71 published only one article, accounting for 68.93% of the total number of journals; while only 5 journals with more than 10 articles, accounting for 7.04% of the total number of journals. There were 64 core journals of science and technology in China, accounting for 62.14% of the total number of journals, and 199 articles were included, accounting for 80.24% of the total number of articles. There were 17 nursing journals,accounting for 16.5% of the total number of journals,and 53 articles were included, accounting for 21.37%of the total number of articles. The ranking of journals is shown in Table 2.
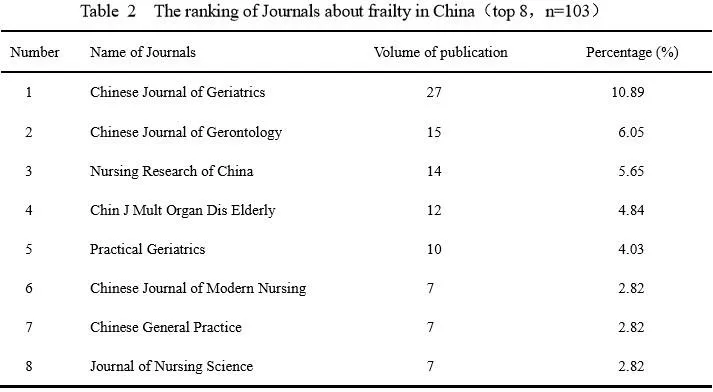
?
2.6 The Result of Research types Overall results
Research types are divided into interventional study,descriptive study, literature review, personal summary,case studies and others. Among them, descriptive study is the most, literature review is the second, and intervention study is less. The results are shown in Figure 3.
2.7 The Result of Research contents Overall results
The research contents can be refined into six aspects,including frailty status, frailty screening, related factors of frailty, measurement tools of frailty,treatment for frailty and management of frailty. The specific contents are shown in Figure 4.
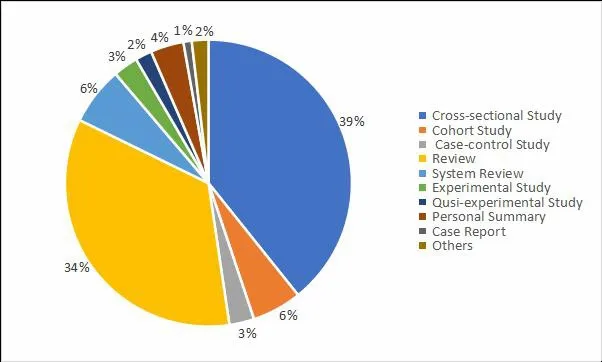
Figure 3. The results of research types about frailty in China (n=248)
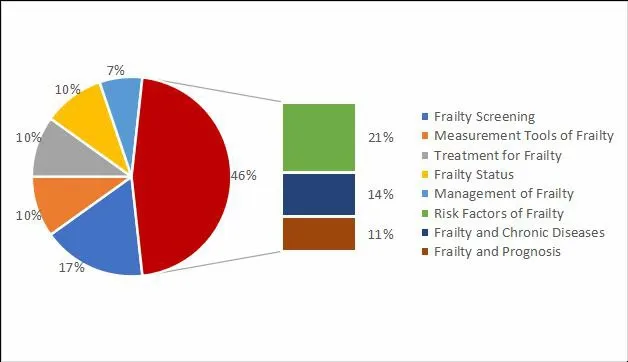
Figure 4. The result of research contents about frailty in China (n=248)
2.8 The Result of Research funds Overall results
There were 139 articles supported by funds at different levels, accounting for 56.05% of the total number of articles. Among them, 95 articles were supported by one fund, 30 articles by two funds, 11 articles by three funds, and 3 articles by four funds, adding up to 200 funds. Among them, there were 49 national funds(24.5%),100 provincial funds (50%), 17 urban funds(8.5%), 24 college funds (12%) and 10 others (5%).
3 Discussion
3.1 Pay attention to the Frailty of the Elderly
With the progress of aging accelerating, the population of the frailty will become more and more.After WHO first proposed the goal of "healthy aging"at Copenhagen Conference, a large number of studies about the relevant theories and definitions of frailty began to emerge abroad. Domestic relevant researches began to increase gradually after 2011 as shown in Figure 1 but the number of publications has shown an explosive growth trend in the past two years, which indicates that the research about frailty in China started relatively late, but developed rapidly. This also reflects from the side that the Chinese government is paying more attention to the issue of frailty. Frailty not only brings pain to the body and spirit of the elderly, but also brings a serious burden to society and family [11]. The problem of the elderly's frailty should not be underestimated. In the future, nurses should pay full attention to the issue of frailty of the elderly and implement the task of prevention, health care,rehabilitation and nursing for the elderly no matter in hospital or community in order to delay the process of frailty as far as possible, further to improve the quality of life of the elderly.
3.2 Carry out Comprehensive Screening of Frailty
From the point of province distribution, there is obvious regional imbalance in the study of seniority frailty in China. The most productive areas are mainly concentrated in the peripheral provinces centered on Beijing, while less publications are distributed in the remote areas like Gansu, Heilongjiang, Yunnan, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia and Tibet. This may be related to the level of policy, economy, medicine and education among various provinces. Comprehensive screening can predict the health status of the elderly [12,13].Especially, early screening and intervention of frailty can reduce the occurrence of adverse outcomes and significantly improve the prognosis of diseases.Comprehensive screening of the elderly has been widely used in hospitals, communities and nursing homes abroad [14]. However, there is an obvious imbalance on the study of the elderly's frailty in China.About 64.86% of the study is carried out in hospitals in major cities, but the remote and rural areas are often ignored. It is suggested that we should support remote and backward areas with preferential policies,talents, technology and funds in order to promote the development of the geriatric medical enterprise in China.
3.3 Carry out Longitudinal and Qualitative Research
From the point of institutional distribution, there were 111 institutions totally, 72 of which published only one article, accounting for more than half of the total number of institutions. This shows that most institutions have just started on the study of the elderly's frailty, and have not yet formed a powerful research team. The number of hospitals in the institutions is the largest, accounting for 64.86% of the total number of institutions, followed by colleges and universities, accounting for 27.93% of the total number of institutions. It can be seen that related research on elderly's frailty has been widely carried out in major hospitals and universities. At present, the study about the elderly's frailty is mostly concentrated on crosssectional research in China. Its shortcoming is that it can’t monitor the dynamic changes of the elderly's frailty, nor can it check the relationship between frailty and other factors. Therefore, in the future, we should carry out longitudinal research, through which to observe the dynamic changes and health outcomes of the elderly, in order to provide reference for making individualized intervention programs; should carry out qualitative research, through which to get the real feelings and care needs of the elderly, in order to provide reference for the development of assessment tools for the elderly in China.
3.4 Prevent Chronic Diseases Actively
According to the ranking of journals, we knew more than 100 kinds of journals publishing related articles,but more than half of which published only one article.It showed that there were abundant types of journals,but the distribution of articles is relatively scattered.More than half of the journals belong to the core journals in China, which published more than 80% of the articles. It can be seen that the quality of the articles about the elderly's frailty is high in China. Thus, it can provide a reliable evidence-based basis for clinical and scientific researchers. But nursing journals were few and only one fifth of the total number of articles were published. It can be inferred that the study about the elderly's frailty in nursing field has just started at home.Frailty is a clinical syndrome caused by degenerative changes of the body and various chronic diseases,which is closely related to health status and geriatric syndrome [15]. Chronic diseases can accelerate the progress of the elderly’s frailty, and frailty can also lead to poor prognosis of chronic diseases [16-18]. Park showed that patients with cardiovascular disease, COPD, diabetes and chronic arthritis had a significantly increased risk of frailty in a short period of time[19]. Therefore, it is the key to prevent the elderly's frailty that carrying out multidisciplinary intervention and active prevention of chronic diseases.Therefore, it is necessary to direct patients to use drugs timely and scientifically, have physical examinations regularly and prevent complications actively.
3.5 Carry out Nursing Intervention
According to the content of the studies, we knew that the researches about prevention and treatment of frailty were few, accounting for only 4.84% of the total number of articles. This may be explained by the reason that it was still in the preliminary stage where the studies about the elderly's frailty was just stared in China. The main content of the researches were the status and influencing factors of the elderly's frailty, while researches on the prevention and intervention of frailty were less. It may be related to the insufficient attention by nurses to the prevention of frailty. Foreign studies have shown that nutrition,exercises, rehabilitation and comprehensive nursing intervention can improve the symptoms of patients'frailty effectively [20-22]. It was suggested that nurses should establish evidence-based, scientific and feasible comprehensive intervention model from the fields of physiology, psychology and sociology to delay the process of the elderly's frailty. In addition, the concept of "preventive treatment of diseases" in traditional Chinese medicine can be integrated into the clinical practices of prevention of the elderly's frailty, guiding the elderly to take appropriate exercises and reasonable nutrition, so as to reduce the incidence of frailty.
4 Summary
In China, the study on the elderly's frailty is just starting. There are some problems, such as unbalanced regional development, low concentration of research institutions, and research type single. In the future,medical staff should pay full attention to the early screening and prevention of the elderly's frailty to delay the process of frailty, so that the elderly can really achieve healthy aging. At the same time, the government should provide research institutions with many preferential policies and more investments, and encourage them to conduct in-depth studies, so as to promote the development of the enterprise for elderly population in China.
- Medical Data Mining的其它文章
- Curcumin in The Treatment of in Animals Myocardial ischemia reperfusion: A Systematic review and Meta-analysis
- The application effect of swaddling bath in neonates: A meta-analysis
- Efficacy of empowerment education in self-management with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis

