便携式血糖仪检测汞离子
石维平 蔡杰 杨雅妮 罗欢欢 刘冰倩 付秋平


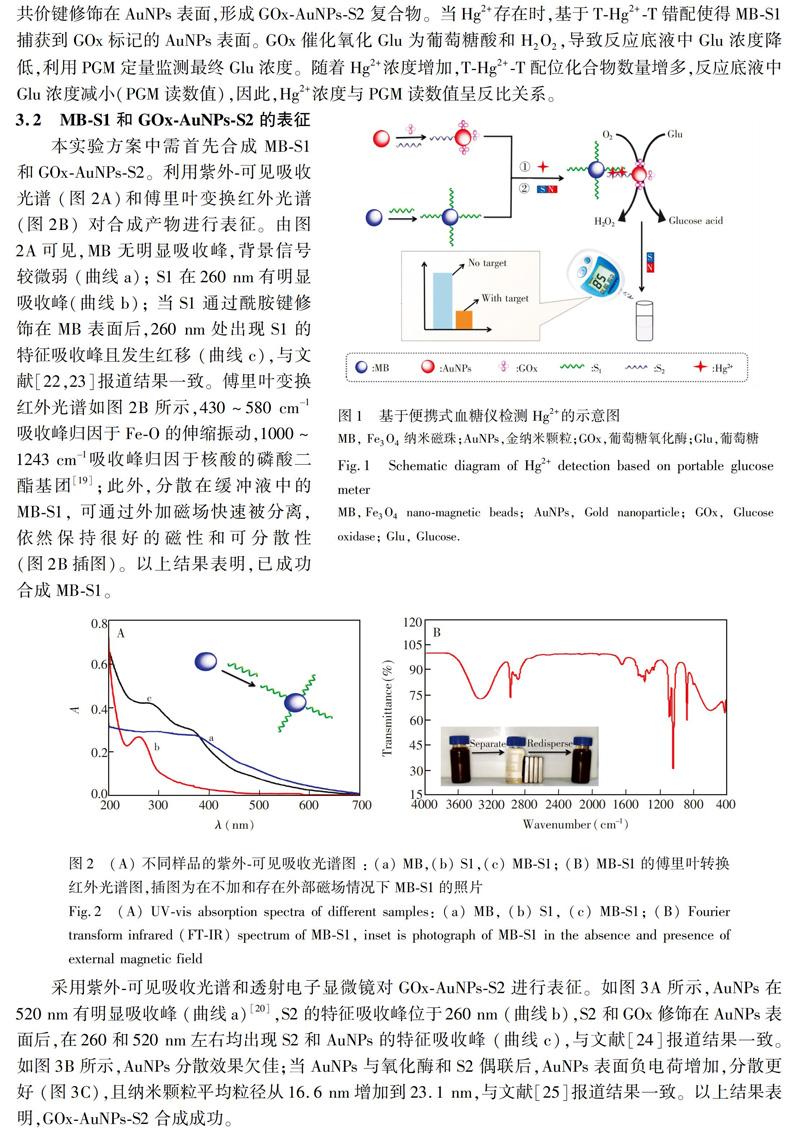

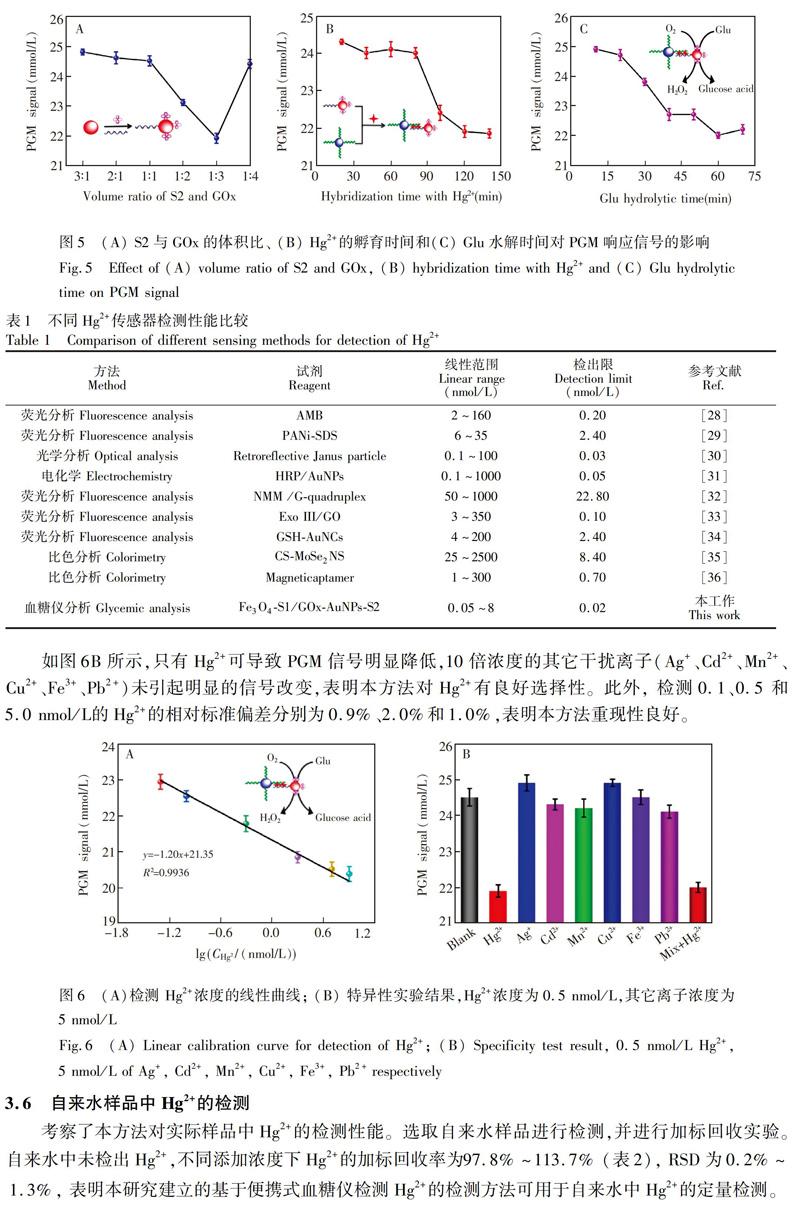
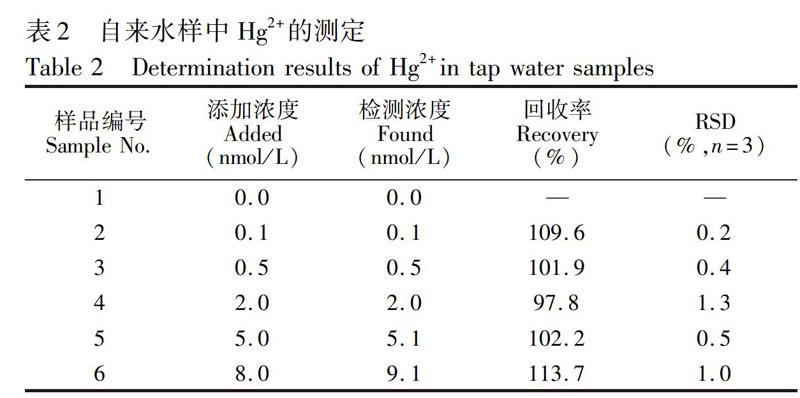
4 結 论
利用Hg2+和T碱基特异性结合形成THg2+T碱基错配,以Fe3O4纳米磁珠为反应平台,富T单链DNA和葡萄糖氧化酶标记的金纳米颗粒为信号传导标签,建立了基于便携式血糖仪检测Hg2+的新方法。本方法操作简单,具有良好的灵敏度和特异性,携带性好,成本低,可用于自来水样本中Hg2的检测。本研究不仅为样品筛选提供了有效方案,也为便携式Hg2+检测仪的开发提供了新思路。
References
1 Chen G Q, Guo Z, Zeng G M, Tang L. Analyst, 2015, 140(16): 5400-5443
2 Hadi P, To M H, Hui C W, Lin C S K, Mc Kay G. Water Res., 2015, 73(15): 37-55
3 Chen C H, Lin Y C, Chang H H, Lee A S Y. Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(8): 4546-4551
4 Baughman T A. Environ. Health Perspect., 2006, 114(2): 147-152
5 Erxleben H, Rμzicka J. Anal. Chem., 2005, 77(16): 5124-5128
6 Luis G, Rubio C, Revert C, Espinosa A, GonzálezWeller D, Gutiérrez A J, Hardisson A. J. Food Compos. Anal., 2015, 39: 48-54
7 Zhu Z Q, Su Y Y, Li J, Li D, Zhang J, Song S P, Zhao Y, Li G X, Fan C H. Anal. Chem., 2009, 81(18): 7660-7666
8 Sun Z Z, Zhang N, Si Y M, Li S, Wen J W, Zhu X B, Wang H. Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(65): 9196-9199
9 Shih T T, Hsu I H, Chen S N, Chen P H, Deng M J, Chen Y, Lin Y W, Sun Y C. Analyst, 2015, 140(2): 600-608
10 Miyake Y, Togashi H, Tashiro M, Yamaguchi H, Oda S, Kudo M, Tanaka Y, Kondo Y, Sawa R, Fujimoto T, Machinami T, Ono A. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(7): 2172-2173
11 Tanaka Y, Oda S, Yamaguchi H, Kondo Y, Kojima C, Ono A. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(2): 244-245
12 Li L Y, Wen Y L, Xu L, Xu Q, Song S P, Zuo X L, Yan J, Zhang W J, Liu G. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 75(15): 433-445
13 Zhan S S, Xu H C, Zhang D W, Xia B, Zhan X J, Wang L M, Lv J, Zhou P. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 72(15): 95-99
14 Xiong E, Wu L, Zhou J W, Yu P, Zhang X H, Chen J H. Anal. Chim. Acta, 2015, 853(1): 242-248
15 Qiu Z L, Shu J, Jin G X, Xu M D, Wein Q H, Chen G N, Tang D P. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 77(15) : 681-686
16 Zhao Y T, Du D, Lin Y H. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 72(15): 348-354
17 Zhang J, Tang Y, Teng L M, Lu M H, Tang D P. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 68(15): 232-238
18 Liang X L, Wang L, Wang D, Zeng L G, Fang Z Y. Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(10): 2192-2194
19 Cao L L, Zhang Q, Dai H, Fu Y C, Li Y B. Electroanalysis, 2018, 30(3): 517-524
20 Gao Z Q, Xu M D, Hou L, Chen G N, Tang D P. Anal. Chem., 2013, 85(14): 6945-6952
21 Zhang J, Tang Y, Teng L M, Lu M H, Tang D P. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 68(15): 232-238
22 Liu B Q, Zhang B, Chen G N, Yang H H, Tang D P. Anal. Chem., 2014, 86(15): 7773-7781
23 Liu Y L, Li J, Chang G, Zhu R Z, He H P, Zhang X H, Wang S F. New J. Chem., 2018, 42(12): 9757-9763
24 Zhang J, Tang Y, Teng L M, Lu M H, Tang D P. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 68(15): 232-238
25 Lin Y X, Zhou Q, Lin Y P, Tang D P, Niessner R, Knopp D. Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(16): 8531-8540
26 EPA 816F02013, National Primary Drinking Water Regulations, USA.
27 GB/57492006, Standards for Drinking Water Quality. National Standards of the People's Republic of China
生活饮用水卫生标准. 中华人民共和国国家标准. GB/5749-2006
28 Sun C Y, Sun R, Chen Y Q, Tong Y, Zhu J W, Bai H, Zhang S Y, Zheng H R, Ye H Q. Sens. Actuators B, 2018, 255(1): 775-780
29 Nguyen H L, Cao H H, Nguyen D T, Nguyen V A. Electroanalysis, 2017, 29(2): 595-601
30 Chun H J, Kim S, Han Y D, Kim D W, Kim K R, Kim H S, Kim J H, Yoon H C. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2018, 104(1): 138-144
31 Wang G F, Huang H, Zhang X J, Wang L. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2012, 35(1): 108-114
32 LIU ChenGuang, WANG JiuJun, ZHANG XingPing, YANG HuaLin. Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2017, 45(2): 163-168
劉晨光, 王久军, 张兴平, 杨华林. 分析化学, 2017, 45(2): 163-168
33 Zhang Y L, Tang L N, Yang F, Sun Z Y, Zhang G J. Microchim. Acta, 2015, 182(7): 1535-1541
34 ZHANG Guo, FENG JianJun, CHAI RuiTao, ZHU WeiHuang, KANG QianWen, LI Hui. Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2019, 47(4): 583-590
张 国, 冯建军, 柴瑞涛, 朱维晃, 康倩文, 李 卉. 分析化学, 2019, 47(4): 583-590
35 Huang L J, Zhu Q R, Zhu J, Luo L P, Pu S H, Zhang W T, Zhu W X, Sun J, Wang J L. Inorg. Chem., 2019, 58(2): 1638-1646
36 Wang L N, Liu F Y, Sui N, Liu M H, Yu W W. Microchim. Acta, 2016, 183(11): 2855-2860
Abstract Based on the specific recognition of THg2+T mismatched for mercury ions (Hg2+), a simple and sensitive method for detecting Hg2+ was developed by using Fe3O4 nanomagnetic beads (MB) as reaction platform and portable blood glucose meter (PGM) as detection means. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were prepared by sodium citrate reduction. The surface of AuNPs was modified with sulfhydryl terminalrich thymine (T) oligonucleotide probe (S1) and glucose oxidase (GOx). In the presence of Hg2+, functionalized AuNPs were captured by captureprobe (S2)modified MB due to THg2+T coordination. The labeled GOx oxidized glucose (Glu) to gluconic acid and H2O2. Thus, the concentration of Glu in the reaction solution was reduced and could be detected quantitatively by PGM. The optimal conditions of the assay were as follows: the volume ratio of S2 and GOx was 1∶3, the reaction time of Hg2+ was 2 h, and the hydrolysis time of Glu was 1 h. Under optimized conditions, the PGM response of the system had a good linear relationship with the logarithm of Hg2+ concentration. The linear range was 0.05-8.00 nmol/L, and the detection limit was 0.02 nmol/L (3σ). The recovery of Hg2+ in actual water samples was 97.8%-113.7%, and the relative standard deviation was 0.2%-1.3%, which met the detection requirements of Hg2+ in actual water samples.
Keywords ThymineHg2+Thymine; Fe3O4 nanomagnetic beads; Gold nanoparticles; Portable glucose meter; Mercury ion

