Effects of electroacupuncture on conjunctival cell apoptosis and the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins Caspase-3, Fas and Bcl-2 in rabbits with dry eye syndrome
Yang Yan-ting (杨延婷), Wei Bang-ji (魏邦基), Zhao Yue (赵越), Zhang Dan (张丹), Liu Jie (刘婕), Zhang Cui-hong(张翠红), Wu Ling-xiang (吴凌翔), Dong Xiao-qing (董小庆), Liu Xiao-xu (刘晓旭), Zhang Lin-lin (张琳琳), Hong Jue(洪珏), Ma Xiao-peng (马晓芃),
1 Shanghai Research Institute of Acupuncture and Meridian, Shanghai 200030, China
2 Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
3 Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Dry Eye Syndrome; Apoptosis; Caspase-3 Protein; Fas Protein;Bcl-2 Protein; Rabbits
Dry eye syndrome (DES) is one of the most common medical issues in ophthalmology, mainly manifested as dryness, photophobia, soreness, pain, redness and fatigue of the eyes, and conjunctival congestion.The causes include tear film instability, hyperpermeability,ocular surface inflammatory damages and neurosensory abnormalities[1].Due to the popularity of smartphone and computer, along with increasing environmental pollution, frequent wearing of contact lenses and other reasons, the incidence of DES is getting higher and higher.Epidemiological study showed that the incidence of DES in Asians was 17%-33%[2].So far,there is no targeted treatment for this intractable medical issue[3-4].Acupuncture-moxibustion therapy has been proved effective in treating DES, and electroacupuncture (EA) has displayed its advantage in improving eye symptoms and tear secretion compared with manual acupuncture[5-7].However, the mechanism of EA in producing therapeutic efficacy is yet unclear.
Apoptosis is closely related to the development of DES.Studies have found that lacrimal glands and ocular surface epithelial tissues present active apoptosis in DES patients[8-10].Increased apoptosis has also been found in the lacrimal glands and conjunctival epithelial cells of animal models of DES: except Bcl-2, the apoptotic factors including P53 and Fas all presented an increased expression[11], suggesting that pathological apoptosis may be one of the key mechanisms in the development of DES.Based on the successful preparation of an experimental DES rabbit model, this study observed the effects of EA on the apoptosis of conjunctival cells of DES rabbits and the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins Caspase-3, Fas and Bcl-2, to explore the mechanism of EA in the treatment of DES.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental animals
Twenty-four healthy male New Zealand rabbits weighing (2.2±0.2) kg were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.The rabbits were housed separately in standard rabbit cages, with the indoor temperature at (20±2) ℃, relative humidity at 50%-70%, 12 h light/dark cycle, and free access to food and water.The animals were adaptively reared for one week.The rabbits all underwent ocular surface examination, and only those with normal function were used for experiments.The treatments during this study were consistent with the basic and 3R principles for experimental animals.
1.2 Main reagents and instruments
Benzalkonium chloride (Sigma, USA); absolute ethanol, formaldehyde, paraformaldehyde, xylene,neutral gum adhesive, disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate, potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China); terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferasemediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) kit (Roche Ltd., Swiss); Fas (GeneTex, USA); Caspase-3 (Abcam,USA); Bcl-2 (Abnova, USA); fluorescein ophthalmic test strip, tear test filter strip (Tianjin Jingming New Technology Development Co., Ltd., China); filiform needles (Wujiang Cloud & Dragon Medical Device Co.,Ltd., China); slit lamp microscope (Suzhou 66 Vision Tech Co., Ltd., China); optical microscope and analysis software (Olympus, Japan); Han's EA apparatus (Nanjing Jisheng Medical Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.,China).
1.3 Model development
DES rabbit model was developed by eye drop of 0.1%benzalkonium chloride[12-13], 1 drop each time, twice a day, 7 d a week, for a total of 4 weeks.At the end of modeling, the tear production and tear film break-up time (BUT) were observed to verify the model.
1.4 Grouping and interventions
The 24 New Zealand rabbits were randomized into a normal group (NG), a model group (MG), an EA group(EAG) and a sham EA group (SEAG), with 6 rabbits in each group.Except the NG, the other three groups were developed into DES models.When the DES rabbit model was verified, the interventions began.
The NG did not receive modeling or any intervention.The MG only underwent modeling with 0.1%benzalkonium chloride eye drop without any intervention.The EAG was given EA intervention after modeling.Bilateral Cuanzhu (BL 2), Taiyang (EX-HN 5),Sizhukong (TE 23) and Fengchi (GB 20) were selected based on the acupoint location in theExperimental Acupuncture Scienceand relevant references[14-15].Filiform needles of 0.25 mm in diameter and 0.20 mm in length were used for acupuncture.After needling qi was achieved, bilateral Cuanzhu (BL 2) and Taiyang(EX-HN 5) were connected to Han’s EA apparatus, with continuous wave of 2 Hz and 2 mA, and the needles were retained for 20 min.The EA intervention was performed once a day for a total of 7 d.For the SEAG,the same acupoints as those in the EAG were punctured while the needle tips only reached the cutaneous layer.Bilateral Cuanzhu (BL 2) and Taiyang (EX-HN 5) were connected to Han’s EA apparatus but without power.The needles were retained for 20 min.The intervention was also conducted once a day for a total of 7 d.During the study, 1 rabbit in the SEAG died.The cause of death was indefinite, but it was supposed to be enteritis since the rabbit presented with lassitude, poor appetite,diarrhea and significant weight loss.
1.5 Specimen collection
The rabbits were sacrificed by air embolization.The rabbit bulbar conjunctiva was separated with ophthalmic scissors and then divided into two parts.The nasal part was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde solution, and the temporal part was frozen at -80 ℃.
1.6 Detections
1.6.1 Detection of tear secretion
Schirmer test I (STI) was used to measure the tear production.The tip of tear secretion test strip was folded back at 5 mm, and placed in the middle and outer 1/3 of the rabbit's conjunctival sac.The trips were removed 5 min later and observed to record how long the strip was wet[16].The measure was repeated 3 times and the mean value was obtained.
1.6.2 Detection of BUT
Fluorescein sodium ophthalmic strips were socked with normal saline.Gently touched the inside of the lower eyelid with the top of the test strip, and closed and gently rubbed the eyes of rabbit, to evenly stain the surface of the eyes with fluorescein sodium.Two eyes were observed under the slit lamp in turn to record the BUT from the moment that the rabbit opened its eye till the appearance of the first dark spot[16].The measurement was repeated 3 times and the average value was taken.
1.6.3 Detection of conjunctival cell apoptosis
The conjunctival cell apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay mediated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase.The tissue sections were baked at 60 ℃for 2 h, then dewaxed into water, rinsed 3 times with PBS solution, treated with proteinase K solution for 20 min, washed 3 times with PBS again, added with 50 μL TUNEL mixture, put into a wet box, and incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 h.After rinsed 3 times with PBS, each sample was added with 50 μL POD solution, incubated at 37 ℃ for 30 min; added with 50 μL DAB mixture for 3-5 min for color developing; counterstained with hematoxylin; differentiated with 1% hydrochloric acid alcohol; dehydrated through graded alcohol;transparentized by xylene; sealed by neutral gum, and then observed and analyzed under light microscope.
1.6.4 Detection of Caspase-3, Fas and Bcl-2 protein expressions in conjunctival cells
Immunohistochemistry was used for detection.The tissue sections were baked at 60 ℃ for 2 h, then dewaxed into water and washed 3 times with PBS; then the tissue sections were placed in citrate buffer and heated in a microwave oven for antigen retrieval.After washed 3 times with PBS, the samples were added with hydrogen peroxide solution and incubate for 25 min in shade; then washed with PBS 3 times; added 50 μL diluted primary antibody solution into the tissue sections with the concentrations as: Caspase-3 (1:500),Fas (1:500) and Bcl-2 (1:300); put them in a wet box at 4 ℃ for incubation overnight; re-incubated at 37 ℃for 45 min the next day; rinsed 3 times with PBS and added with 50 μL diluted second antibody solution for each section, and incubated in a wet box at 37 ℃ for 1 h; washed 3 times with PBS and added with appropriate amount of DAB mixture to develop color,counterstained with hematoxylin and differentiated with 1% hydrochloric acid alcohol; dehydrated with graded alcohol; transparentized with xylene; sealed by neutral gum and observed under a light microscope.
1.7 Statistical methods
The SPSS 21.0 software was used for statistical analysis.The data were first checked for normal distribution and those in normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s) and those did not conform to normal distribution were expressed as median (min, max).Then the homogeneity of variance was tested.If the data conformed to normal distribution and homogeneity of variance, one-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data and the least significant difference (LSD) test was used for betweengroup comparisons.For data that followed normal distribution but showed heterogeneity of variance,Games-Howell test was adopted for between-group comparisons.The test level was set atα=0.05, andP<0.05 indicated stat istical significance.
2 Results
2.1 Effect of EA on the tear production of DES rabbits
After modeling and prior to intervention, the tear production in the MG, EAG and SEAG declined significantly compared with the NG (allP<0.01); there were no significant inter-group difference in the tear production among the MG, EAG and SEAG (allP>0.05).After intervention, the tear production increased significantly in the EAG compared with that before intervention (P<0.01), while no significant difference was found in the other groups (allP>0.05).After intervention, the tear production was significantly lower in the MG, EAG and SEAG than in the NG (allP<0.01);compared with the MG, the tear production was higher in the EAG (P<0.01); compared with the EAG, the tear production was lower in the SEAG (P<0.05), (Figure 1).
2.2 Effect of EA on the BUT of DES rabbits
After modeling and prior to intervention, the BUT in the MG, EAG and SEAG declined significantly compared with the NG (allP<0.01).After intervention, the BUT increased significantly in the EAG compared with that before intervention (P<0.01), while no significant change was found in the other groups (allP>0.05).After intervention, the BUT was significantly shorter in the MG, EAG and SEAG than in the NG (allP<0.01);compared with the MG, the BUT was longer in the EAG(P<0.01); compared with the SEAG, the BUT was longer in the EAG (P<0.01), (Figure 2).
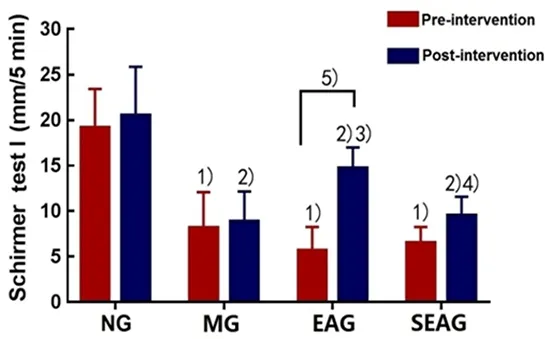
Figure 1.Changes of the tear production
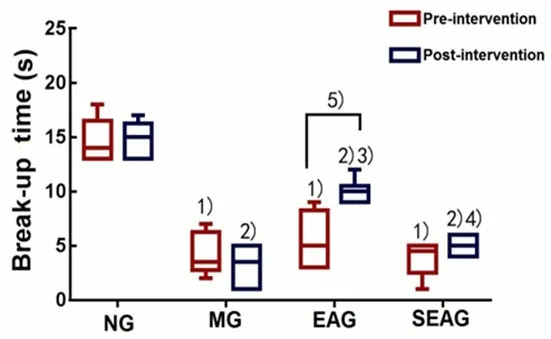
Figure 2.Changes of the BUT
2.3 Effect of EA on the conjunctival cell apoptosis of DES rabbits
The TUNEL staining results showed that the arrangement of rabbit conjunctival cells in the MG was disordered, scattered with brown-yellow stained nuclei and nucleus rupture or chromatin concentration,indicating cell apoptosis (Figure 3).Compared with the NG, the apoptosis in rabbit conjunctival cells was more significant in the MG, EAG and SEAG (P<0.01).Compared with the MG, the apoptosis of rabbit conjunctival cells was significantly reduced in the EAG(P<0.01), while the SEAG did not show significant difference (P>0.05).Compared with the EAG, the apoptosis of rabbit conjunctival cells was more significant in the SEAG (P<0.01), (Figure 4).
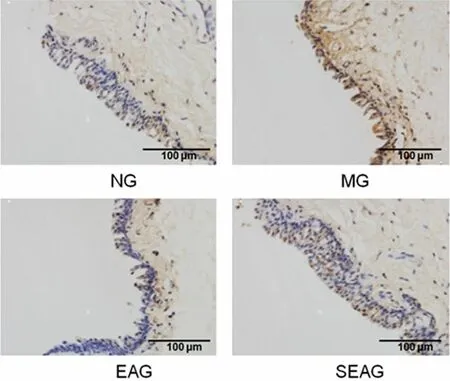
Figure 3.TUNEL staining result of the conjunctival cell apoptosis (×400)
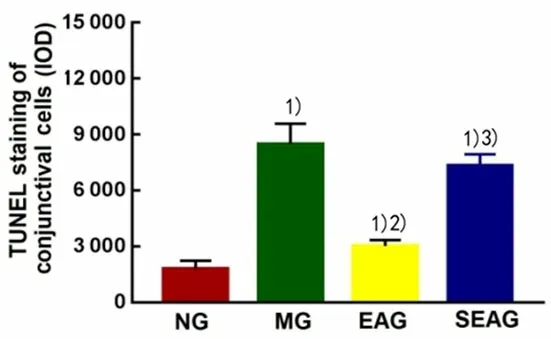
Figure 4.Comparison of TUNEL result of the conjunctival cell apoptosis
2.4 Effect of EA on Caspase-3 protein expression in conjunctival cells of DES rabbits
Positive Caspase-3 cells were mainly stained at the cytoplasm presenting with brown particles (Figure 5).Compared with the NG, the expression of Caspase-3 protein in conjunctival cells was increased in the MG,EAG and SEAG (P<0.05).Compared with the MG, the expression of Caspase-3 protein in conjunctival cells was significantly decreased in the EAG (P<0.01), while the SEAG did not show significant difference (P>0.05).Compared with the EAG, the expression of Caspase-3 protein in conjunctival cells was increased in the SEAG(P<0.01), (Figure 6).
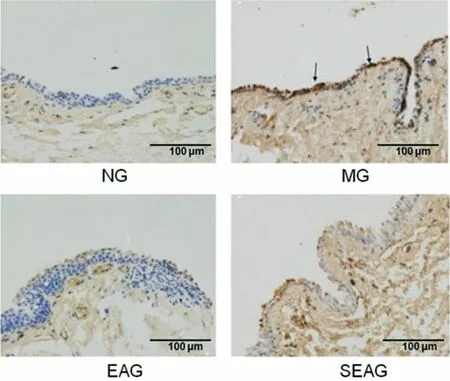
Figure 5.Immunohistochemistry result of Caspase-3 protein expression in conjunctival cells (×400)
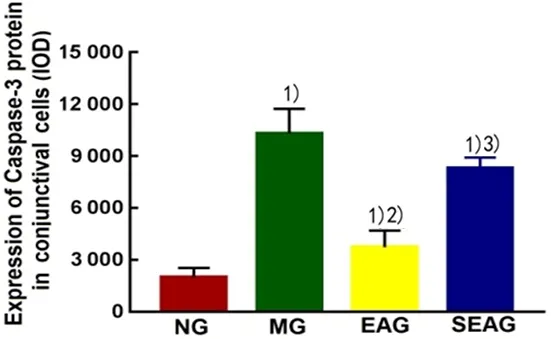
Figure 6.Comparison of immunohistochemistry result of Caspase-3 protein expression in conjunctival cells
2.5 Effect of EA on Fas protein expression in conjunctival cells of DES rabbits
Positive Fas cells were mainly stained at the cell membrane presenting with dark brown granules(Figure 7).Compared with the NG, the expression of Fas protein in conjunctival cells was significantly increased in the MG, EAG and SEAG (P<0.01).Compared with the MG, the expression of Fas protein in conjunctival cells was significantly decreased in the EAG (P<0.01), while the SEAG did not show significant difference (P>0.05).Compared with the EAG, the expression of Fas protein in conjunctival cells was significantly increased in the SEAG (P<0.01), (Figure 8).
2.6 Effect of EA on Bcl-2 protein expression in conjunctival cells of DES rabbits
Positive Bcl-2 cells were mainly stained at the nuclear membrane presenting with dark brown granules(Figure 9).Compared with the NG, the expression of Bcl-2 protein in conjunctival cells was significantly decreased in the MG, EAG and SEAG (P<0.01).Compared with the MG, the expression of Bcl-2 protein in conjunctival cells was significantly increased in the EAG (P<0.01), while the SEAG did not show significant difference (P>0.05).Compared with the EAG, the expression of Bcl-2 protein in conjunctival cells was significantly decreased in the SEAG (P<0.01),(Figure 10).
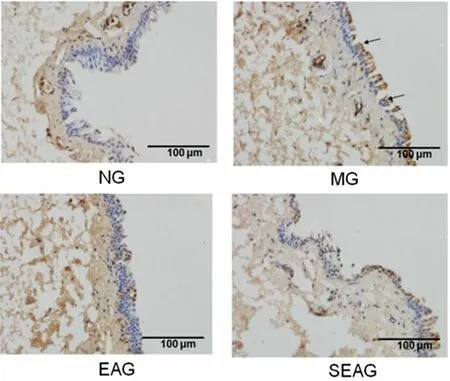
Figure 7.Immunohistochemistry result of Fas protein expression in conjunctival cells (×400)
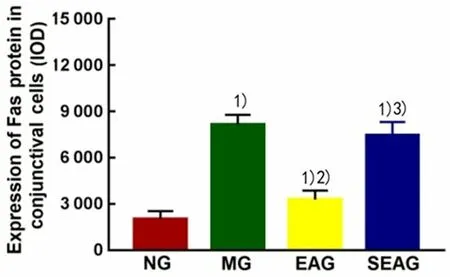
Figure 8.Comparison of immunohistochemistry result of Fas protein expression in conjunctival cells
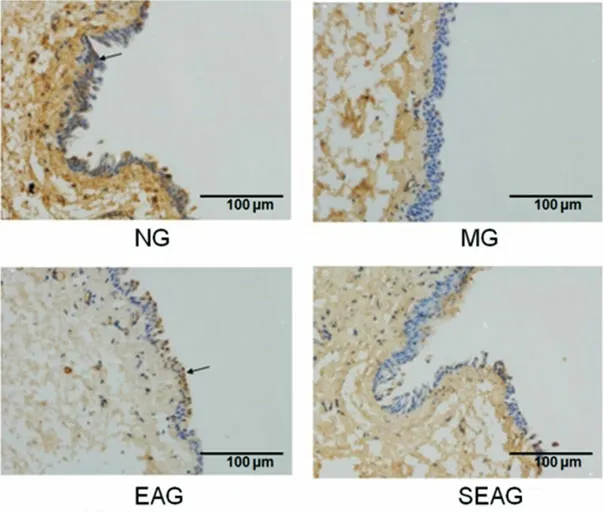
Figure 9.Immunohistochemistry result of Bcl-2 protein expression in conjunctival cells (×400)
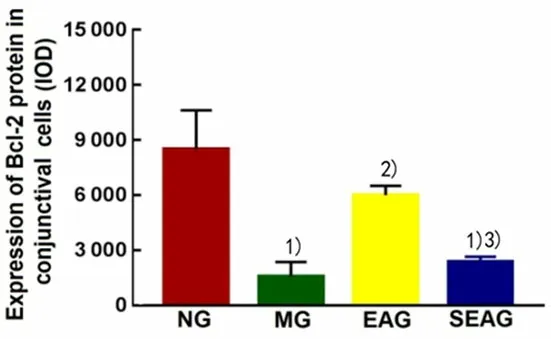
Figure 10.Comparison of immunohistochemistry result of Bcl-2 protein expression in conjunctival cells
3 Discussion
DES belongs to the categories of Bai Se Zheng, Shen Shui Jiang Ku, Zao Zheng, etc.in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).There is a lack of effective treatments for this medical issue.Meanwhile, using artificial tears,anti-inflammatory drugs such as cyclosporine A and glucocorticoid may cause tingling, allergy or drug resistance, affecting the efficacy and reducing the quality of life of the patients.Acupuncture therapy has been proved effective in treating DES and showed certain advantages.Research has found that EA can promote tear secretion and improve ocular surface damage; the current stimulation can make up for the single and insufficient stimulation of manual acupuncture to certain extent, and can be applied to patients with different degrees of dry eye[17-18].This study used benzalkonium chloride to induce DES rabbit model to observe the effects of EA on tear secretion and BUT of DES rabbits.The results showed that the tear production and BUT reduced significantly at the end of modeling, suggesting the success of the DES model; the rabbit tear production and BUT increased after EA intervention, while the changes in the SEAG were not significant, indicating that EA can effectively improve the ocular surface function in DES.
It was found that the expressions of apoptosis markers (Fas, Fas ligand, etc.) in conjunctival epithelial cells were positively correlated with the expressions of immune activation markers class Ⅱ leukocyte antigen DR (HLA-DR) antigens in DES patients[19].The conjunctival epithelial cells play an important role in the defense mechanism of ocular surface.In addition to the anatomical barrier to the external environment, the conjunctival epithelial cells can produce cell adhesion molecules such as histocompatibility complex class Ⅱ(MHC-Ⅱ) and HLA-DR through leukocyte migration to cause an inflammatory response[20].It reminds that the occurrence of inflammation in conjunctival tissues may be accompanied by apoptosis.Clinical and experimental studies have all shown that pathological apoptosis plays a key role in the pathogenesis of DES and may become a new target for treatment[21].In this study, TUNEL staining of the conjunctival tissues of DES rabbits demonstrated sparse cells and disordered cell arrangement, with scattered brown-yellow colored nuclei, ruptured nuclei or concentrated chromatin.After EA intervention, the apoptosis of conjunctival cells was inhibited, which suggested that reducing conjunctival cell apoptosis may be one of the mechanisms of EA in improving ocular surface function in DES.
Most of the Caspase family proteins are promoters or effectors during the apoptotic process, playing a critical role.The over-expression and activation of Caspase-3 can cause apoptosis, so it is also called death protease.It promotes apoptosis in two ways, mitochondrialdependent and mitochondrial-independent[22-23].Studies found higher Caspase-3 expression in the conjunctival cells of DES animal models compared with the normal controls[24-25].Fas protein belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)/nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR) family and is widely present in a variety of cells.It is a major pro-apoptotic factor and can activate apoptosis-related signaling pathways when over-expressed[26].Study found that the expression of Fas was significantly increased in lacrimal gland cells of male rabbits with DES[27].Bcl-2 proteins are a class of regulatory proteins that play an important role in the process of apoptosis and belong to anti-apoptotic factors.They are isolated as integral membrane proteins of the organelle membrane when there is no death signal, but interact with pro-apoptotic proteins translocated from the cytosol when stimulated by death signals, to prevent the loss of organelles and the consequent cell apoptosis[28].It has been confirmed that corneal epithelial cell apoptosis may cause dry eye symptoms, which is related to the increased Fas expression and decreased Bcl-2 expression[29].This study found that compared with the NG, the expressions of Caspase-3 and Fas proteins in the conjunctival cells increased significantly in the MG, and the expression of Bcl-2 protein decreased significantly,consistent with the previous reports[30-31].After EA intervention, conjunctival cell apoptosis in DES rabbits decreased, the expressions of Caspase-3 and Fas proteins decreased, and the Bcl-2 protein expression increased, along with the improvement of ocular surface function.The results suggested that EA can reduce the expressions of Caspase-3 and Fas proteins in conjunctival cells of DES rabbits, and increase the expression of Bcl-2 protein, thereby inhibiting the apoptosis of conjunctival cells, and these effects may be one of the mechanisms of EA in treating DES and improving the associated ocular surface functions.As apoptosis is regulated by multiple genes and their products, it still requires further research to understand whether EA affects other factors that regulate apoptosis and in which section of the regulatory pathways that it plays a key role.
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年1期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年1期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effect of electroacupuncture on the learning and memory abilities in type 2 diabetic model rats with cognitive impairment
- Effects of electroacupuncture of different frequencies on electromyography, NOS and ICC of colon in rats with slow transit constipation
- Acupuncture for premature ovarian insufficiency:a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of heat-sensitive moxibustion for adjuvant treatment of depression in Parkinson disease
- Clinical study on Jin’s three-needle therapy for post-stroke cognitive impairment
- Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of heat-sensitive moxibustion for vascular dementia
