正电子冲击下氦电离三重微分截面的理论计算
周雅君,刘 芳,程勇军,王 旸,焦利光,马 佳,王远程,于荣梅,张永志,姜平辉0,柯友启,胡小颖,吴 勇
(1.吉林大学原子与分子物理研究所,长春130012 ;2.哈尔滨理工大学理学院,哈尔滨150080 ;3.陕西师范大学物理学与信息技术学院,西安710119 ;4.哈尔滨工业大学物理学院,哈尔滨150080 ;5.吉林大学物理学院,长春130012 ;6.沈阳航空航天大学理学院,沈阳110136 ;7.沈阳师范大学物理科学与技术学院,沈阳110034 ;8.南阳师范大学物理与电子工程学院,南阳473000 ;9.黑龙江大学物理科学与技术学校,150080;10.黑龙江工程学院理学院计算原子与分子物理研究所,哈尔滨150050 ;11.上海科技大学物质科学与技术学院,上海201210 ;12.长春大学理学院材料设计与量子模拟实验室,长春130022 ;13.北京应用物理与计算数学研究所,北京 100088)
1 Introduction
The main task of atomic physics is to understand the interaction dynamics of many body systems via explaining for electron correlations.The electron-atom collision is a powerful tool to achieve this object.Ionization of atoms is one of the most interesting processes in the field of atomic collisions.The correlated dynamics of few interacting particles is a fundamental physics problem that may be exemplified through the process of ionization[1].Despite the fact that the study of atomic and molecular ionizations has expanded rapidly and achieved tremendous progress in past decades,the agreement between theory and measurement for many important systems is still not satisfactory and some problems still remain unsolved in the theoretical description and experiment.In this work,we studied the special position -atom collision process,which involves two different light particles including an electron and a positron in the final state.Such studies are very sensitive to the role of the projectile charge and mass on collision dynamics[1],providing an ideal candidate to investigate the correlation effects of many body systems.
The process of electron/positron-atom collisions is genreally characterized by scattering cross sections.Although a large body of cross section data,for electron,photon and ion impact,has been obtained by using the(e,2e)collision theoretical method and experimental technique,the studies of differential cross sections for the ionization of atoms with positrons are still very limited.In the case of electron impact,the determination of the momentum of the target electron is significantly distorted by the interaction of the external electrons with the remainder of the system.The strong distortion can be accounted for by the distorted-wave Born or impulse approximation(DWBA or DWIA),in which the motion of the external electron is represented by elastic-scattering functions,calculated in a suitable potential,rather than by plane waves[2].Up to date,the distorting potential has been the static-exchange potential for the appropriate system(atom or ion),averaged over spin states.This treatment has given an excellent agreement with experimental data.
2 Theoretical methodology
The goal of our present work is to investigate the differential cross sections in the case of positron impact that have not been consistently described by ab initio approaches.In Ref.[3],distorted -wave Born approximation model has been employed to study the ionization of atoms impact by positron,but positronium formation channels are not considered.Recently,the triple differential cross sections of atom target for ionization by positron impact have been determined,some unexpected phenomena are observed[1].At present,the data has no acknowledged theoretical description,however,these observations have suggested that the positronium formation channels can strongly influence the shape and magnitudes of cross sections at lower energies[1].To the best of our knowledge,such theoretical calculation that can consider positronium(Ps)formation channels for differential cross section of ionization of atoms by positron impact has not been reported.In this article,to understand the effects of positronium formation channels on the ionization of atoms by positron impact,we calculated the differential cross sections at incident positron energy of 50 eV using the distorted -wave Born approximation with the Ps formation channels treated by adding an ab initio complex potential to the static distorted potentials[4,5].
The distorted -wave Born approximation for the ionization amplitude[2]is

The incident positron,ejected electron and scattered positron momenta are k0,keand kp,respectively.The positron -electron potential is v.The T matrix element is half shell with energy E,at which it is calculated,corresponding to the final-state relative momentum.The distorted waves are described by the following scattering equation:
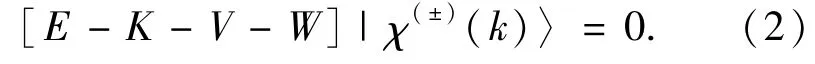
where K is the kinetic energy,V is the static potential appropriate to the scattering system and W is the complex polarization potential describing the effects of rearrangement channels,namely positronium formation that have not been otherwise treated.The superscript plus and minus denote respectively outgoing and ingoing spherical-wave boundary conditions.
It is a simple matter to calculate the static potential for positron scattering on atoms,since the whole potential depends only on the electron density.However,as a two-center problem,a calculation for the Ps formation potential W is difficult,in which an equivalent local approximation in momentum space is used.The form of the Ps potential in momentum space with the approximation of Zhou et al.[6]and Cheng et al.[7]is:
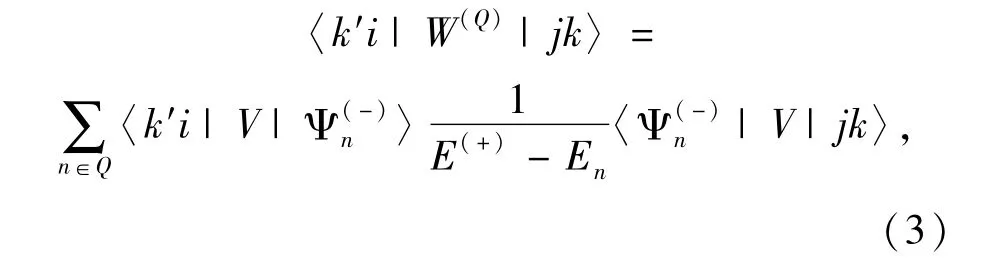

whereφμis a bound state of the positronium and kPsis the momentum of positronium center of mass.〈R|kPs〉represents the motion of positronium,since only short-range terms in the positronium-ion potential survive.In Eq(4),r is the relative coordinate

where rpand reare the respective coordinates of the positron and the electron,and R is the coordinate of the positronium center of mass,

The detail calculations for positronium formation potential can be found in Refs.[6]and [7].
Then,the triple differential cross sections can be obtained as:
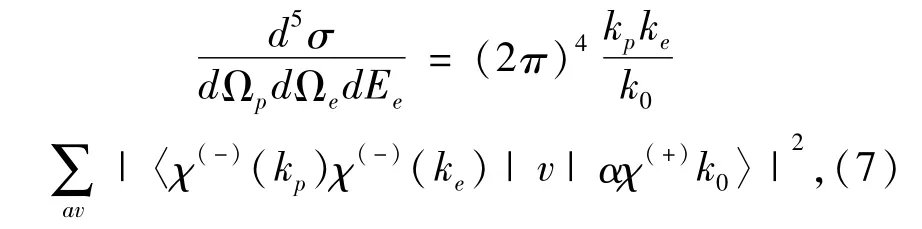
whereΩpand Ωeare the solid angles of scattered positron and ejected electron,respectively.The notionrepresents a sum over final and average over initial magnetic and spin degeneracy.A Fourier transformation is also adopted since the positroniun formation potentials are calculated in momentum space while the distorted-wave approximation is set up in the coordinate space.In the present calculations,the coplanar asymmetric kinematic condition is used[2].
3 Resultsand discussion
In this work,we have calculated the triple differential cross sections(TDCS)at an incident energy of 50 eV.The effect of positronium formation in its n=1 and n=2 bound states as a polarization potential is added to the static distorted potential.In Fig.1,we presented our calculation results and compared with the experiment measurements from Arcidiacono et al.[1]and results of BBK model from Campeanu[8].

Fig.1 Experimental and theoretical results for the triple differential ionization cross sections versus ejected electrons in 50 eV positron collision with atomic helium:solid line,present results;black dot,experiment from Arcidiacono et al.[1];dashed line,BBK from Campeanu[8].
We can find good agreement with the experimental data[1]except at the ejected kinetic energies around 16 eV,where our results are a little higher than experimental and BBK' s results[4].However,the BBK calculation results are much higher than both the present results and experimental data in the impact energy region below 16 eV.This difference may be due to the absence of positronium formation channels in BBK model which are believed to play an important role either as an open or closed channel.Around the ejected kinetic energy 16 eV,thephenomenon of electron capture to the continuum(ECC)that the ejected electron is captured by the projectile to a bound or low-lying continuum[9]is remarkable because of the similar velocities of scattered positron and ejected electron.This post-collision process arises from the dominance of the final-state Coulomb attraction between the scattered positron and ionized electron.However,the ECC process is not considered in present calculation.It is a possible explanation for the discrepancy that our TDCS is higher than the experiment at this energy region[10].
4 Conclusions
In conclusion,the triple differential cross sections(TDCS)for positron impact ionization of helium at 50 eV have been obtained using the distorted -wave Born approximation.The influence of positronium formation channels has been taken into account via a polarization potential.Present results are in better agreement with experimental data[1]than calculations of Campeanu[3],owing to the inclusion of positronium formation process.The investigation of ECC process in the ionization of atom impacted by positron is a project we plan to work on in the future.Furthermore,it is highly desired to carry out more experimental and theoretical studies to establish the reliable data set of TDCS for ionization of helium by positron impact.
———理学院

