基于婴儿下肢留置针致血栓性浅静脉炎的反馈-前馈控制研究
牛晓桂 高贵霞 李化娉 苗银芳 王梅林

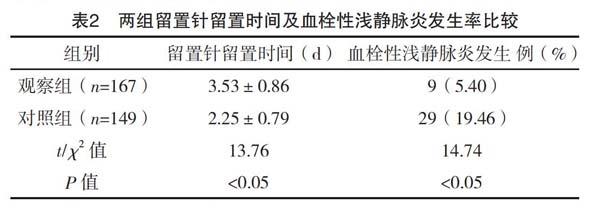

【摘要】 目的:研究反馈-前馈控制方法在降低婴儿下肢静脉留置针致血栓性浅静脉炎中的应用效果。方法:选择2019年4-9月某院儿科住院婴儿316例作为研究对象,根据时间顺序分为对照组和观察组,对照组149例给予留置针常规护理,观察组167例采用反馈-前馈控制措施进行护理,记录两组血栓性浅静脉炎发生率、留置针留置时间、家属满意度并进行比较。结果:观察组留置针留置时间长于对照组,血栓性浅静脉炎发生率低于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组家属总满意度(95.21%)高于对照组(87.92%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:运用反馈-前馈控制可以有效降低婴儿血栓性浅静脉炎发生率,延长留置针留置时间,提高患儿家属满意度。
【关键词】 反馈控制 前馈控制 血栓性浅静脉炎 婴儿 下肢静脉 静脉留置针
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2020.17.040 文献标识码 B 文章编号 1674-6805(2020)17-00-03
Study on Feedback-feedforward Control of Thrombotic Superficial Phlebitis Induced by Indwelling Needle in Veins of Lower Extremity in Infants/NIU Xiaogui, GAO Guixia, LI Huaping, MIAO Yinfang, WANG Meilin. //Chinese and Foreign Medical Research, 2020, 18(17): -98
[Abstract] Objective: To study the effect of feedback-feedforward control in reducing thrombotic superficial phlebitis induced by venous indwelling needles in infant lower limbs. Method: A total of 316 pediatric infants in a hospital from April to September 2019 were selected as study subjects, according to the time sequence, they were divided into the control group and the observation group, 149 patients in the control group were given routine nursing care of indwelling needle, 167 patients in the observation group were given nursing care with feedback-feedforward control measures. The incidence of superficial thrombotic phlebitis, the time of indwelling needle and the satisfaction of family members were recorded and compared between the two groups. Result: The duration of indwelling needle indwelling in the observation group was longer than that in the control group, and the incidence of superficial thrombophlebitis in the observation group was lower than that in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The total satisfaction of family members in the observation group (95.21%) was higher than that in the control group (87.92%), the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Feedback-feedforward control can effectively reduce the incidence of thrombotic superficial phlebitis in infants, prolong the indwelling time,and improve the satisfaction of the families.
[Key words] Feedback control Feedforward control Thrombotic superficial phlebitis Infants Veins of lower extremity Venous indwelling needle
First-authors address: Binzhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, Binzhou 256603, China
外周靜脉留置针是儿科静脉输液治疗的主要方式,能够减少反复穿刺给患儿带来的痛苦,有利于临床用药及紧急抢救,已广泛应用于临床[1]。2016版INS实践标准指出,儿童穿刺部位首先考虑手部、前臂及腋窝以下的上臂部位静脉,不走路时可选用下肢静脉[2]。临床工作中,因为疾病或患儿自身因素,常常不可避免地选择下肢静脉穿刺。血栓性浅静脉炎是婴儿留置针输液的常见并发症[3],下肢静脉穿刺相对于其他部位,发生血栓性浅静脉炎和其他并发症的机会更高,护理中应该提供更多的措施,以保证护理安全。反馈控制又称“事后控制”,是一种作用发生在行动之后最常用的传统控制方法,其目的是力求改进未来行动的质量[4-5]。前馈控制又称“超前控制”,指在管理工作开始前,对所产生的后果进行预测,并采取预防措施,使可能出现的偏差在事前得到避免,是一种预防性的控制方式[6]。笔者运用反馈-前馈复合控制的方法,分析其在下肢静脉留置针致婴儿血栓性浅静脉炎中的应用效果,现报告如下。
综上所述,通过反馈-前馈控制措施,能有效降低血栓性浅静脉炎发生率,延长静脉留置针使用时间,从而减轻患儿痛苦,提高家属满意度。該措施简单易行,适合在儿科输液治疗中全面推广。
参考文献
[1]高贵霞,牛晓桂,李化娉,等.整合式心理干预对住院婴儿头皮静脉留置针穿刺的影响[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2019,40(6):776-778.
[2] INS.Infusion therapy standards of practice[M].7th ed. Norwood:Infusion Nurses Society,2016:56-79.
[3] Arias-Fernández L,Suérez-Mier B,Martínez-Ortega M D,et al.
Incidence and risk factors of phlebitis associated to peripheral intravenous catheters.Incidenciay factores de riesgo de flebitis asociadas a catéteres venosos periféricos[J].Enferm Clin,2017,27(2):79-86.
[4]蒋文娟.3M液体敷料预防婴幼儿留置针相关性静脉炎的效果观察[J].当代护士:中旬刊,2018,25(12):124-126.
[5]吴欣娟,王艳梅.护理管理学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2017:215.
[6]沈鸣雁,卢芳燕,卢婕楠.前馈控制在外科持续腹腔冲洗安全管理中的应用[J].中华护理杂志,2016,51(3):280-283.
[7]吴云华,周桂容.反馈控制在护理文书持续质量改进中的作用[J].护理研究,2010,24(28):2603-2604.
[8]李正英,王梅,魏红艳,等.前馈控制对骨科手术患者消毒供应中心相关医院感染的影响[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2017,27(13):3110-3113.
[9]李家增,贺石林,王鸿利.临床血栓病学[M].上海:上海交通大学出版社,2014:368.
[10]高玲,胡珊珊,王莹莹.静脉留置针常见并发症预防及护理[J].中华全科医学,2015,13(3):490-491,511.
[11]万丽.婴幼儿外周静脉留置针穿刺置管方法的研究进展[J].护士进修杂志,2016,31(9):784-786.
[12]陈月香,朱俊清,彭晓红,等.小儿外周静脉留置针成功留置时间与拔管原因分析[J].安徽医学,2016,37(7):907-909.
[13] Chau C T,Prielipp R C.Prevention of Thrombophlebitis in Peripheral Intravenous Catheters:The Butterfly Effect[J].Anesth Analg,2018,127:1287-1288.
[14]王磊.小儿应用静脉留置针致静脉炎的危险因素分析及相关防治对策[J].中国社区医师,2015,31(7):144-145.
[15] Goodhead A.Clinical efficacy of comfeel plus transparent dressing[J].British Journal of Nursing (Mark Allen Publishing),2002,11(4):284.
[16]杨洋,王欣然,寇京莉.重点环节干预在降低留置针堵管发生率中应用的效果评价[J].中国护理管理,2015,15(9):1122-1124.
[17]耿少英,赵改婷,高荣花,等.静脉留置针封管频次与静脉炎关系的实验研究[J].护理学杂志,2006,21(13):1-3.
(收稿日期:2020-02-13) (本文编辑:马竹君)

