Acupuncture and Related Therapies for Hyperlipidemia:A Network Meta-Analysis
WANG Xue-Song,WANG Yue-Shen,LI Jia-Jia,YU Chao-Chao,WU Miao,KONG Li-Hong*
a.Hubei University of Chinese Medicine,Wuhan,Hubei 430061,China
b.Preventive Treatment of Acupuncture and Moxibustion of Hubei Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center,Wuhan,Hubei 430061,China
c.Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital,Shenzhen,Guangzhou 518033,China
d.Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Wuhan,Hubei 430061,China
e.Hubei Province Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Wuhan,Hubei 430074,China
ABSTRACT Objective To compare and rank the clinical effects of different acupuncture and related therapies on hyperlipidemia patients.Methods We used network meta-analysis (NMA) to evaluate direct and indirect effects in studies of acupuncture and related therapies for hyperlipidemia.Databases PubMed,EMBASE,Cochrane Library,the China Biology Medicine (CBM),the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI),Wanfang Data and the Chinese Scientific Journal Database (VIP) were searched to collect randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of acupuncture and related therapies in the treatment of hyperlipidemia.The data were analyzed using Stata 15.0 and WinBUGS 1.4.3 software after two researchers independently screened the literature,extracted the data,and assessed the risk of bias in the included studies.Results We analyzed a total of 36 eligible studies that included 3 124 patients,involving 12 types of acupuncture and related therapies and comprehensive therapies.The results of the NMA showed that:for the total cholesterol (TC),acupoint catgut embedding (ACE),simple acupuncture (ACU),acupoint injection(AI),electroacupuncture (EA),western medicine of statins (WM),and combination of acupuncture and related therapies(combined therapies) were all more effective than placebo(P <0.05).For triacylglycerol (TG),ACU,E A,warming acupuncture (WA),WM and combined therapies were better than placebo(P <0.05),while WA was better than Chinese herb (CH)(P <0.05).For low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C),combined therapies were more effective than lifestyle modification (LM) (P <0.05).For high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C),auricular acupoint stimulation ( AAS),ACE,ACU,AI,CH,EA,LM,moxibustion (MOX),WM,combined therapies and placebo were all worse than WA (P <0.05),while WM and combined therapies were better than ACU (P <0.05).Combined ranking results suggest that ACU and combined therapies may be the optimal intervention.Conclusions The efficacy of all kinds of acupuncture-related therapies in patients with hyperlipidemia is better than lifestyle changes.However,for different outcome indicators,all kinds of acupuncture-related therapies have their advantages and disadvantages,and comprehensive ranking results suggest that ACU and combined therapies may be the optimal intervention.
Keywords Acupuncture Hyperlipidemia Network meta-analysis Total cholesterol (TC)Triacylglycerol (TG)Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C)
1 Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is a disorder of lipid metabolism characterized by an increase in triacylglycerol (TG),total cholesterol (TC),low-density lipoprotein cholesterol(LDL-C),a decrease in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in the peripheral blood,and is associated with hypertension,diabetes,and obesity as major vascular risk factors[1,2].The incidence of hyperlipidemia is increasing yearly with the improvement of people’s living standards and lifestyle changes.According to the 2016 guidelines for the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in adults in China,the prevalence of dyslipidemia among adults in China is as high as 40.4%,a substantial increase from 2002[3],and the proportion of children and adolescents with hypercholesterolemia in China is also significantly higher[4].This suggests that the burden of dyslipidemia and related diseases in China will continue to increase in the future[5].Hyperlipidemia is closely related to the occurrence of coronary heart disease and stroke,and may induce Alzheimer's disease (AD),vascular dementia (VD) and Parkinson's disease (PD)[6,7].At present,statins,betablockers and other lipid-lowering drugs are mainly used in clinical practice,which have some efficacy but may cause adverse effects such as liver damage,rhabdomyolysis,neoplasia and diabetes[8].Because of the complex etiology of hyperlipidemia,it is closely related to the environment and genetics,but its mechanism has not been fully elucidated.As the most representative non-pharmacological therapy in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM),acupuncture is a treatment method with the potential for development.In recent years,an increasing number of studies have been conducted on the use of acupuncture to treat hyperlipidemia patients.Previous meta-analysis have found that for hyperlipidemia patients,acupuncture[9-11],auricular acupuncture[12]and herbal medicine[13]may be more advantageous and safer than western medicine[9,10].However,owing to the wide variety of acupuncture and the different focus on efficacy,there is still a lack of direct comparative studies between different acupuncture-related therapies.In this study,the network meta-analysis (NMA) method was used to evaluate the effects of various acupuncture-related therapies in hyperlipidemia patients,which is expected to provide evidence-based medicine selected from the best combination of options.
2 Methods
This study was conducted following the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and metaanalyses for network meta-analysis (PRISMA-NMA)[14]checklist and reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis of acupuncture[15].
2.1 Search strategies
Our literature search was performed from database establishment until April 1st,2020,including three English databases:PubMed,EMBASE,Cochrane Library,and four Chinese databases:the China Biology Medicine (CBM),the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI),Wanfang Data and the Chinese Scientific Journal Database (VIP).The search was conducted using a combination of medical subject headings (MeSH) terms and free words.In addition,the references included in the medical literature were retrospectively supplemented to obtain the associated references.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
The published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of acupuncture-related therapies for the treatment of primary hyperlipidemia,regardless of age and sex.Clear diagnostic criteria were required to confirm the diagnosis of primary hyperlipidemia.Interventions in the treatment group included various types of acupuncture-related therapies,including simple acupuncture (ACU),electroacupuncture (EA),warm acupuncture (WA),auricular acupoint stimulation(AAS),acupoint injection (AI),acupoint catgut embedding (ACE),or a combination of acupuncture and drugs;the control group is statin lipid-lowering western medicine,or placebo,or comparison between various acupuncture-related therapies.The results of the report are required to include at least one of the following outcome indicators:TC,TG,LDL-C and HDL-C.The language of the publication was limited to Chinese or English.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
(1) Research on self-controlled or other non-RCTs;(2) research with unclear diagnostic criteria;(3) research on subjects belonging to secondary hyperlipidemia (such as obesity,diabetes,among others);(4) pre-clinical studies,systematic reviews,case reports,meta-analysis;(5) the report did not have clear original data,and contacting the author was unsuccessful;(6) there was no acupuncture-related therapy or other forms of acupuncture (such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation or transcranial magnetic stimulation);(7) repeated research or research report results are the same.
2.4 Literature screening and data extraction
Two researchers independently conducted the literature screen,data extraction and cross-check.In any case of disagreement,they would discuss reaching a consensus or the third researcher would assist in the final determination.A unified data extraction table was used for data extraction,which included general information of the included literature:(1) the name of the first author,journal name,publication year,and so on;(2) baseline data of the subjects included in the literature:interventions,the sample size of each group,and subjects’ age;(3) intervention methods:type of intervention,treatment frequency and treatment period;(4) risk bias-related factors:random method,allocation hiding,blinding;and (5) outcome indicators before and after treatment data.
2.5 Risk assessment of bias in inclusion studies
Two researchers evaluated the included studies in accordance with the bias risk assessment tool recommended in the Cochrane Handbook 5.1[16,17].
2.6 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Stata 15.0 and WinBUGS 1.4.3 software[18-20].TC,TG,LDL-C and HDL-C are numerical variables,and the difference before and after treatment is used as the effect size.In some trials,the change between baseline and after treatment failed to show,and the missing data were estimated using the following formula[17].
First,Stata 15.0 was used to draw an NMA evidence relationship diagram (metan,network metaanalysis,metareg packages),if the literature is threearm or more,it is split and reconstituted into all paired two-arm tests[21].Second,WinBUGS 1.4.3 was run to set the number of iterations to 50 000 for NMA;95% confidence interval (95% CI) of inconsistency factors (IF) was used to judge the consistency of the closed-loop.If the IF with 95% CI contains 0,it means that the direct and indirect evidence is consistent;otherwise,it means that there is a higher possibility of inconsistency[22].Third,the Stata 15.0 program was applied to create funnel plots to determine whether there was evidence of small sample effects in the included studies[23].Last,the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) was generated using Stata 15.0 to show the SUCRA scores for all interventions,with higher SUCRA scores implying higher treatment class[24].
3 Results
3.1 Study search and description
A total of 2 098 relevant studies were obtained from the literature search.36 RCTs containing 3 124 patients with primary hyperlipidemia were included in the final screening,including 34 in Chinese and two in English.The literature screening process and results are shown in Figure1.A total of 12 interventions including ACU,EA,ACE,AI,WA,AAS,moxibustion (MOX),Chinese herb (CH),lifestyle modification (LM),combination of acupuncture and related therapies (combined therapies),western medicine of statins (WM),and placebo acupuncture/blank control (placebo) were involved in the study.There were two four-arm trials,one three-arm trial,and all others were two-arm trials in the study.The characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table1 and Table2.
3.2 Quality assessment of included studies
Our two researchers evaluated the included studies in accordance with the bias risk assessment tool recommended in Cochrane Handbook 5.1,including random sequence generation,allocation concealment,blinding of participants and personnel,blinding of outcome assessment,incomplete outcome data,selective reporting and other biases.Because of the particularity of the acupuncture operation,it is impossible to be blinded to the participants and personnel.The results of the risk evaluation are shown in Figure2.
3.3 Network meta-analysis results for four outcomes
3.3.1 Network evidence plotTC,TG,LDL-C and HDL-C were all centered on western medicine,with a star structure of 12 intervention nodes.TC formed a total of 15 closed loops,TG formed a total of 14 closed loops,LDL-C formed a total of 13 closed loops,and HDL-C formed a total of seven closed loops.The network evidence diagram is shown in Figure3.
3.3.2 Inconsistency testThe results of the inconsistency test are shown in Figure4.TC involved 15 closed loops,wherein among the nine closed loops’95% CI for IF contained 0,showing no significant inconsistency,while the other six closed loops’ 95%CI for IF did not contain 0,with minimum values of 2.12,1.21,0.89,0.86,0.41 and 0.01,and the inconsistency was statistically significant.TG involved 14 closed loops,wherein among the 10 closed loops’95% CI for IF contained 0,showing no significant inconsistency,while the other four closed loops’ 95%CI for IF did not contain 0,with minimum values of 2.12,1.73,1.60 and 1.62,and the inconsistency was statistically significant.
LDL-C involved 13 closed loops,wherein among the 10 closed loops’ 95% CI for IF contained 0,showing no significant inconsistency,while the other three closed loops’ 95% CI for IF did not contain 0,withminimum values of 4.36,0.10 and 0.54,and the inconsistency was statistically significant.HDL-C involved 12 closed loops,wherein among the seven closed loops’ 95% CI for IF contained 0,showing no significant inconsistency,while the other five closed loops’ 95% CI for IF did not contain 0,with minimum values of 10.65,10.90,2.08,2.39 and 0.58,and the inconsistency was statistically significant.
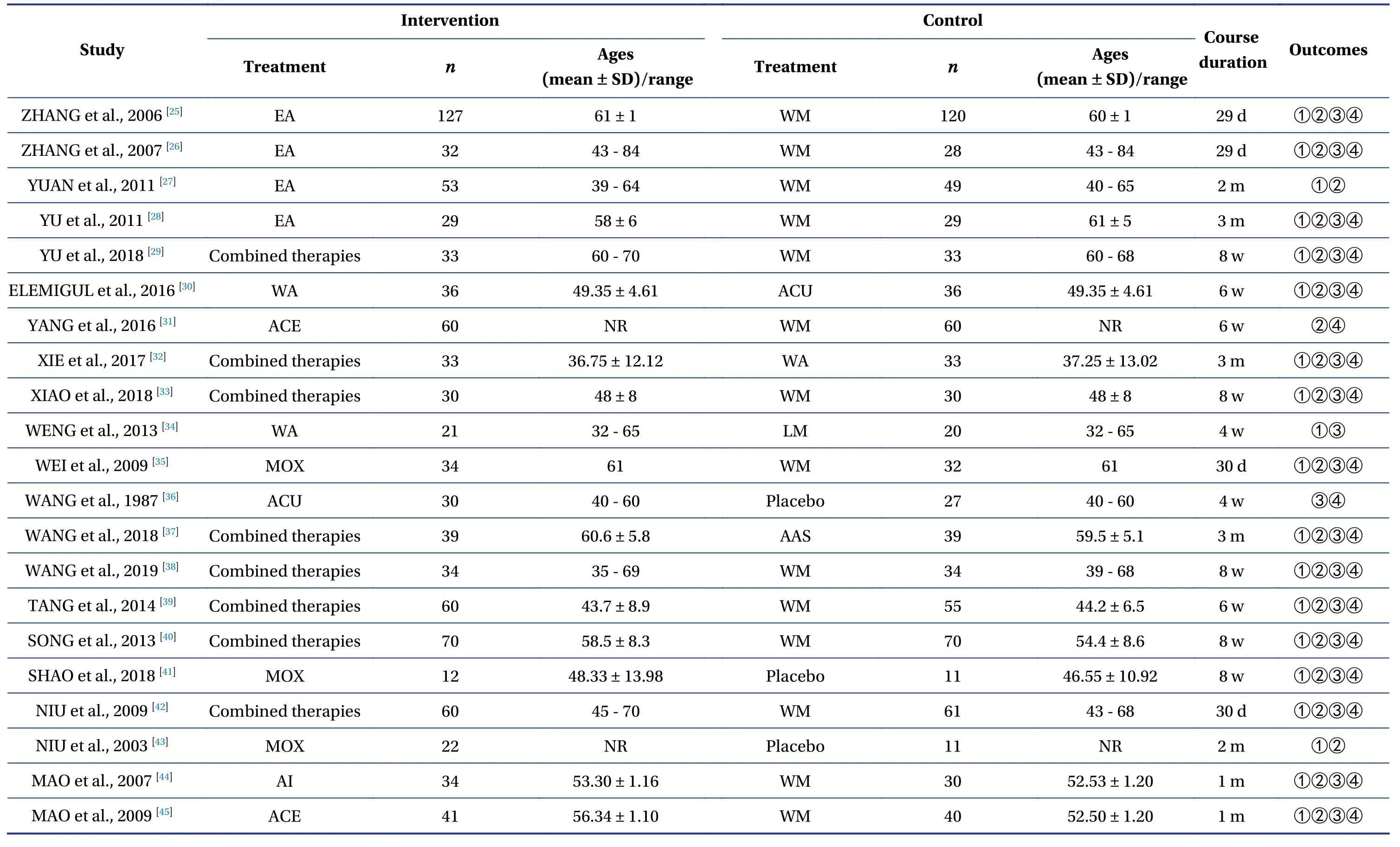
Table1 Basic characteristics of the included studies

Table1 Continued
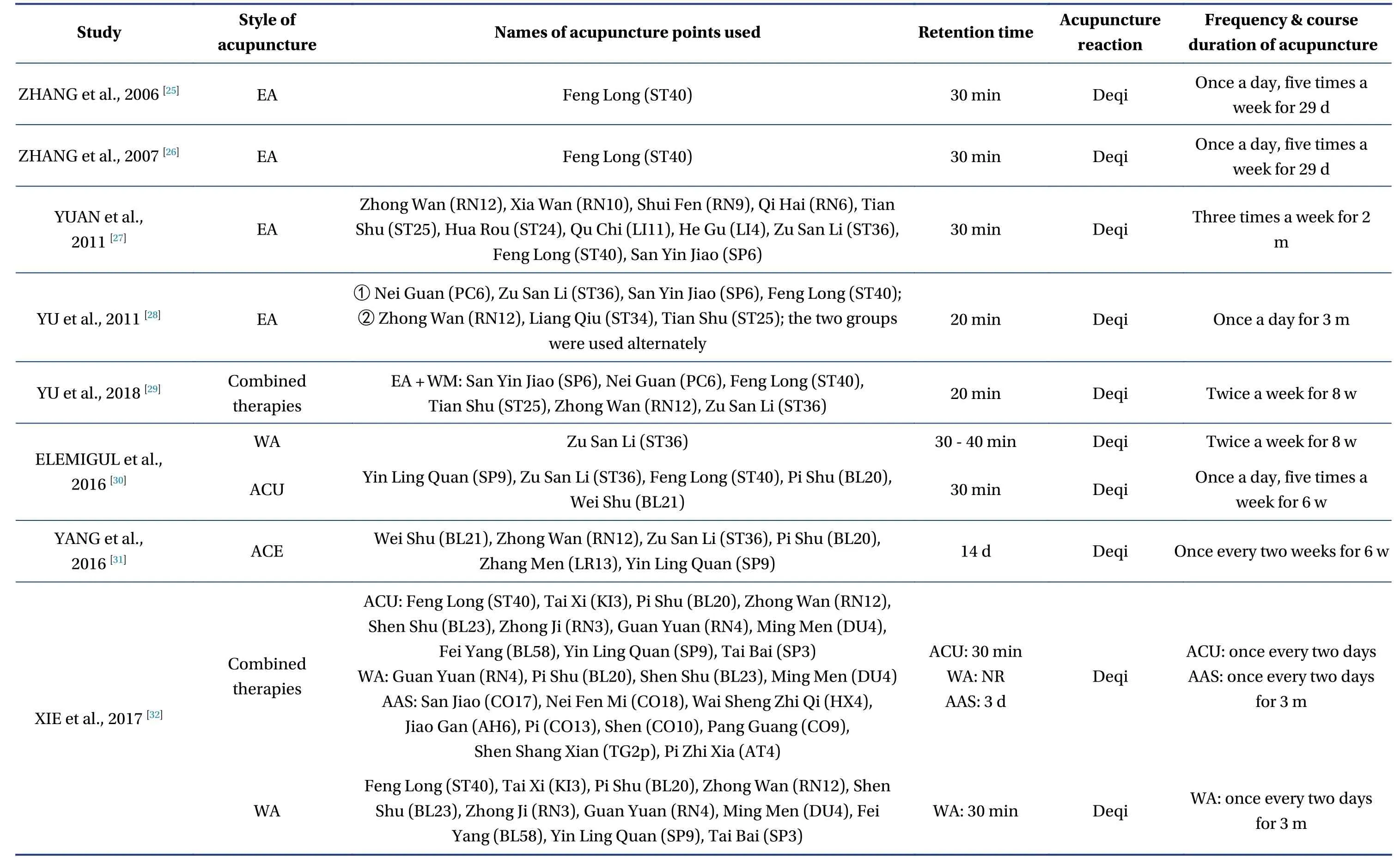
Table2 Descriptions of the included acupuncture and related therapies
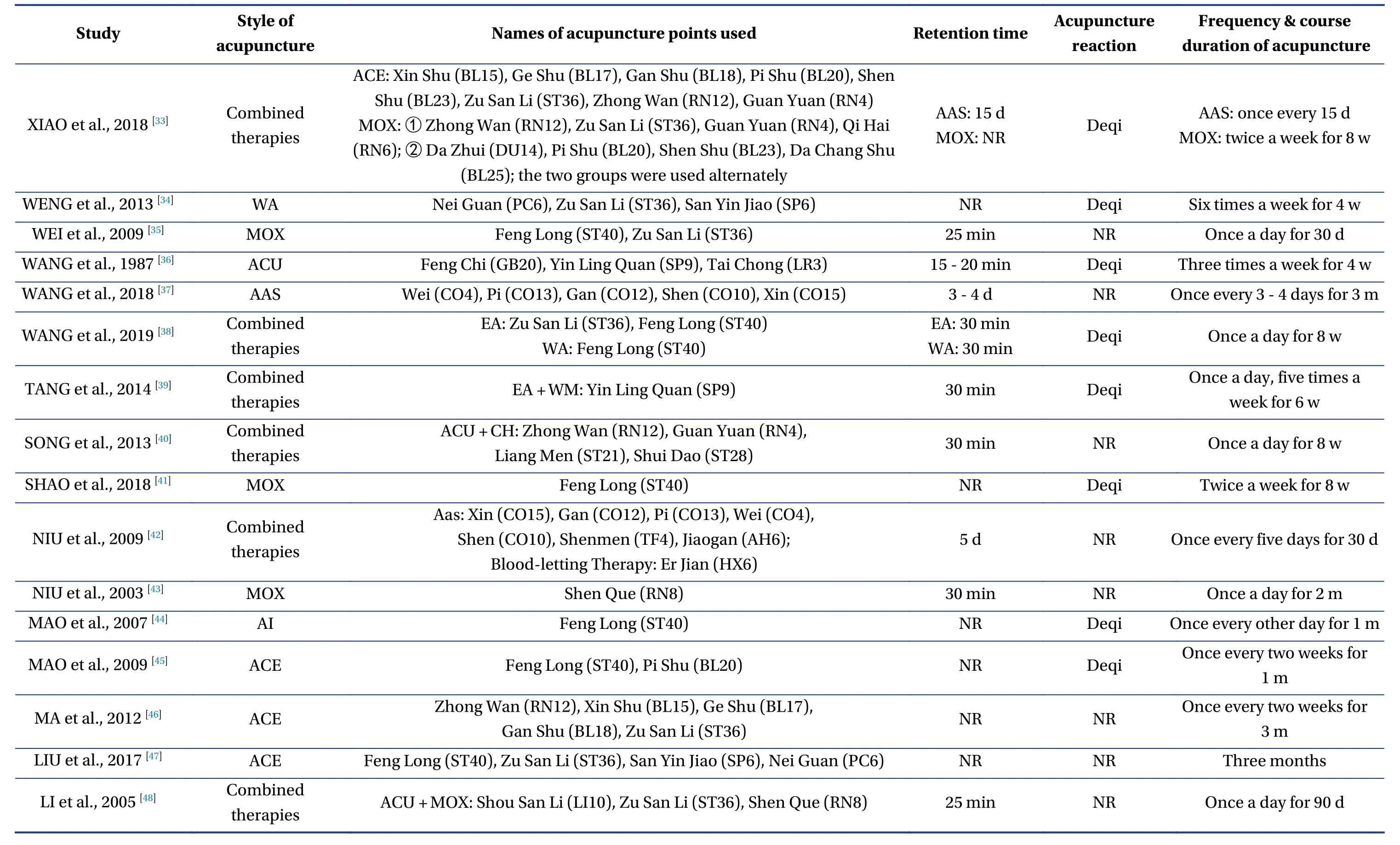
Table2 Continued
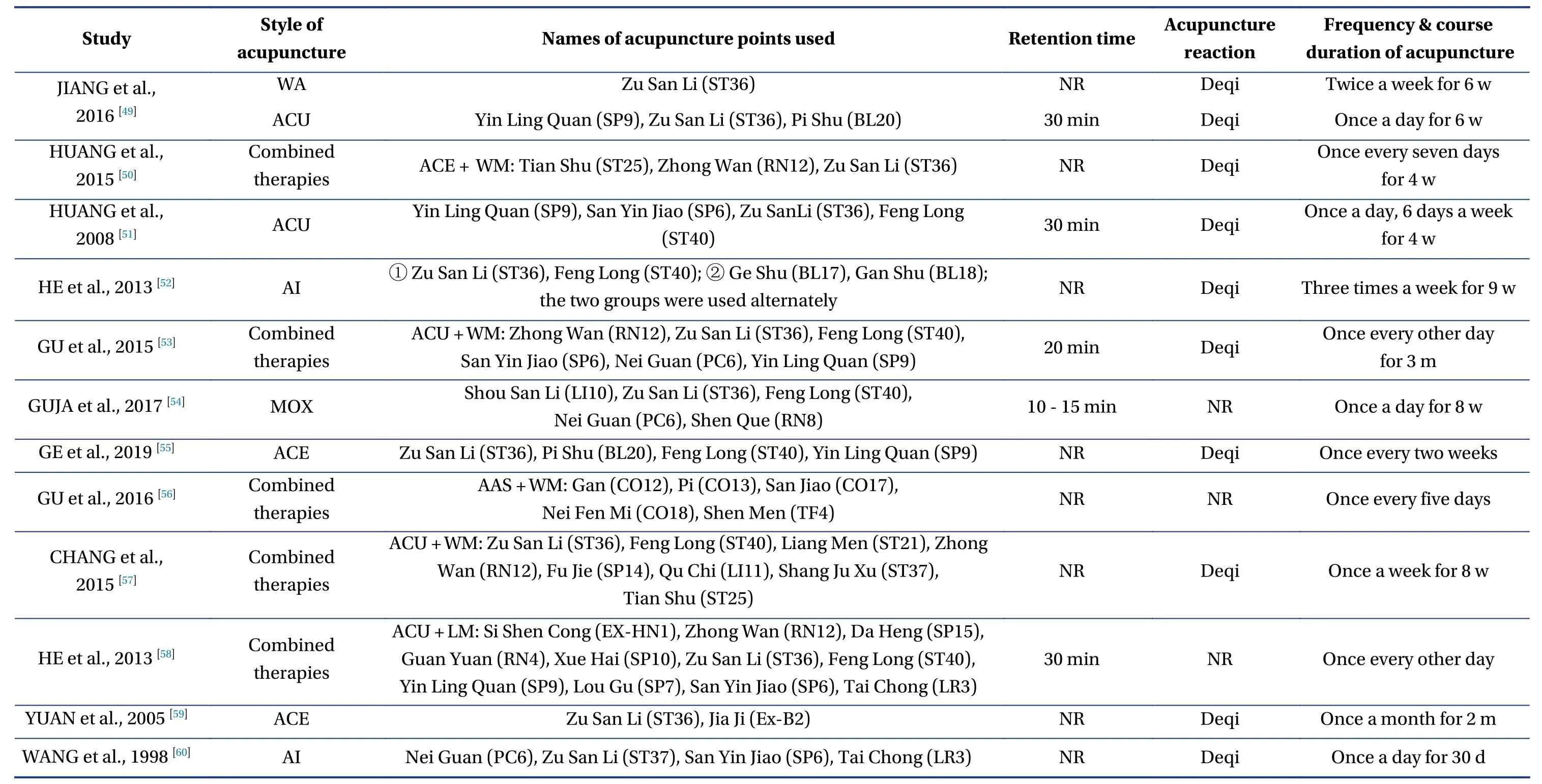
Table2 Continued
3.3.3 Small sample testThe small sample test results are shown in Figure5.The funnel diagrams of TC,TG,LDL-C and HDL-C are roughly symmetrical,but studies that fall outside the funnel diagram (13,13,13 and 7,respectively) indicate that there is evidence of a small sample effect in the research network.
3.3.4 Network meta-analysisAs shown in Table3 and 4,a total of 34 studies reported TC.The results of the NMA showed that compared with placebo,ACE[standard mean difference (SMD):− 1.97,95% CI:(− 3.31,− 0.66)],ACU [SMD:− 2.53,95% CI:(− 4.55,− 0.67)],AI [SMD:− 1.88,95% CI:(− 3.57,− 0.26)],EA[SMD:− 2.13,95% CI:(− 3.72,− 0.57)],WM [SMD:− 1.89,95% CI:(− 3.17,− 0.67)],and combined therapies [SMD:− 2.39,95% CI:(− 3.65,− 1.17)] had better effect in reducing TC.There were 34 studies that reported TG,wherein when compared with placebo,ACU [SMD:− 1.85,95% CI:(− 3.43,− 0.36)],EA [SMD:− 1.26,95% CI:(− 2.57,− 0.03)],WA [SMD:− 2.01,95% CI:(− 3.65,− 0.50)],WM [SMD:− 1.08,95% CI:(− 2.11,− 0.10)],and combined therapies [SMD:− 1.28,95% CI:(− 2.33,− 0.29)] had better effect in reducing TG,while WA [SMD:1.64,95% CI:(0.12,3.23)] was more effective than CH.
There were 30 studies that reported LDL-C,in which the results showed that combined therapies[SMD:0.90,95% CI:(0.11,1.67)] was more effective than LM.There were 31 studies that reported HDL-C,in which the results showed that WA had better effect than AAS [SMD:− 3.29,95% CI:(− 5.37,− 1.11)],ACE[SMD:− 2.85,95% CI:(− 4.41,− 1.27)],ACU [SMD:− 1.57,95% CI:(− 2.87,− 0.25)],AI [SMD:− 2.75,95%CI:(− 4.36,− 1.08)],CH [SMD:− 2.74,95% CI:(− 4.66,− 0.83)],EA [SMD:− 2.83,95% CI:(− 4.39,− 1.18)],LM[SMD:− 3.00,95% CI:(− 4.69,− 1.25)],MOX [SMD:− 2.77,95% CI:(− 4.36,− 1.11)],WM [SMD:2.81,95%CI:(1.46,4.12)],combined therapies [SMD:2.88,95%CI:(1.55,4.16)],and placebo [SMD:2.59,95% CI:(1.02,4.08)] in enhancing HDL level,while WM[SMD:1.24,95% CI:(0.06,2.43)] and combined therapies [SMD:1.31,95% CI:(0.10,2.56)] were more effective than ACU.
3.3.5 RankingWith WM as a control,the SUCRA of the different treatments are shown in Figure6.The ranking results for the different outcome indicators were different.For TC,the top three interventions were combined therapies (80.9%),EA (76.2%) and ACU (72.1%).For TG,the top three interventions were ACU (91.2%),WA (84.9%) and combined therapies (77.2%).For LDL-C,the top three interventions were combined therapies (87.2%),WM(70.6%) and CH (63.5%),respectively.For HDL-C,the top three interventions were WA (99.7%),ACU(86.1%) and WM (59.1%).Overall,compared with western medicine,ACU and combination therapy show certain advantages and may be the optimal intervention.
4 Discussion
With the improvement of people's living standards and changes in lifestyles,hyperlipidemia has become an important public health problem,and its incidence has increased significantly in all age groups[61].Acupuncture,as a characteristic therapy of TCM,has a good effect on many diseases which can be used as a safe and effective complementary alternative therapy for hyperlipidemia,considering the safety and no side effect characteristics of acupuncture operation.It is necessary to scientifically evaluate the curative effect of acupuncture on hyperlipidemia to evaluate the curative effect-cost relationship of acupuncture to select the best acupuncture methods or combination of treatments that can better reduce the economic burden of patients.This study uses NMA to compensate for the lack of direct data.Indirect data are used to compare the efficacy of different acupuncture-related therapies in hyperlipidemia treatment,which provides some evidencebased medical indication of the clinical efficacy of acupuncture-related therapies for hyperlipidemia.
The levels of TC,TG,LDL-C and HDL-C in patients with hyperlipidemia were evaluated treated using 12 acupuncture-related therapies.The results showed that the most frequently used acupuncture intervention was ACE,followed by ACU and EA.For TC,ACE,ACU,AI,EA,WM and combined therapies were more effective than placebo.For TG,ACU,EA,WA,WM and combined therapies were more effective than placebo,while WA was more effective thanCH.For LDL-C,combined therapies were more effective than LM.For HDL-C,WA was more effective than AAS,ACE,ACU,AI,CH,EA,LM,MOX,WM,combined therapies and placebo,while WM and combined therapies were more effective than ACU.There were some differences in the ranking results of the four outcome indicators.According to the results,ACU and combined therapies showed some advantages and may be the best interventions.A total of 16 studies reported adverse reactions,and overall,the adverse reaction rate of acupuncture-related therapies was significantly lower than that of western medicine,indicating that acupuncture-related therapies were safer.Modern studies have shown that acupuncture has antioxidant and protective effects on the arterial wall and myocardium,which may be the mechanism of acupuncture-related therapy in the treatment of hyperlipidemia[62].

Table3 Network meta-analysis results for TC and TG
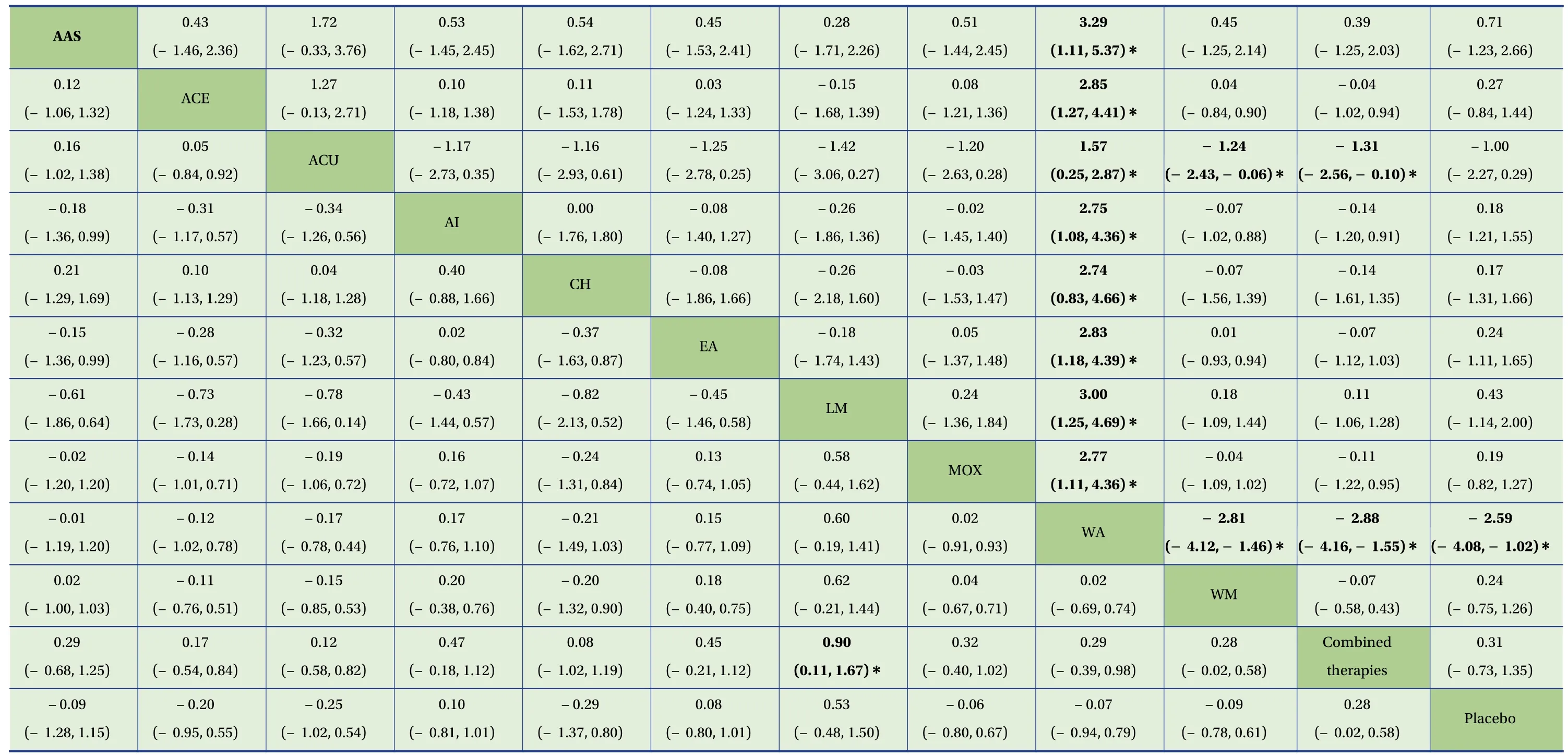
Table4 Network meta-analysis results for LDL-C and HDL-C
However,there are still some limitations in this study.First,NMA is an extension of pairwise metaanalysis that can indirectly compare the efficacy of three or more interventions.We analyzed the clinical efficacy of 11 interventions compared with statin lipidlowering drugs in the treatment of patients with primary hyperlipidemia,and solved the problem of lack of direct comparison of clinical research data.However,NMA is based on the assumption of homogeneity,and there are differences in clinical factors affecting the results among the included studies,such as patients,interventions,and control implementations,which may directly affect the reliability of the NMA.Second,when the different outcome indicators were assessed and ranked by the NMA,it was possible that the same intervention might show different efficiency in different outcome indicators,which may reduce the level of clinical evidence.According to the different clinical symptoms,hyperlipidemia is mainly divided into three categories:hypercholesterolemia,hypertriglyceridemia and mixed hyperlipidemia.According to the results of this study,higher treatment levels of intervention measures are recommended for patients with different categories of hyperlipidemia to achieve better clinical efficacy.Third,we only selected statin lipid-lowering drugs as western medicine controls,and other lipid-lowering drugs should be further elaborated in future studies.Fourth,the quality of the final included literature is low,and the risk of bias assessment results are mostly unclear.Future studies should be designed and conducted in strict accordance with RCTs and reported with the consolidated standards of reporting trials(CONSORT) to ensure the quality of the literature.Fifth,since the included articles were all short-term efficacy observations,the obtained results only represent the assessment of the short-term efficacy of acupuncture on hyperlipidemia,while the long-term efficacy needs to be studied further.Sixth,there are few studies on direct comparison between different acupuncture-related therapies which should be conducted in future studies to better evaluate the differences and advantages of different acupuncture therapies.
Acknowledgements
We thank for the funding support from the “Qihuang”Project on the Inheritance and Innovation of Traditional Chinese Medicine funded by National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No.284,2018).
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Digital Chinese Medicine2020年4期
Digital Chinese Medicine2020年4期
- Digital Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Yi Qi Jie Du Formula and Salinomycin Combination Treatment Mediates Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Stem Cell Proliferation,Migration and Apoptosis via CD44/Ras Signaling Pathway
- Physical Therapy Modalities of Western Medicine and Traditional Chinese Medicine for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
- Identification of Potential Flavonoid Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease 6YNQ:A Molecular Docking Study
- Network Biological Modeling:A Novel Approach to Interpret the Traditional Chinese Medicine Theory of Exterior-Interior Correlation Between the Lung and Large Intestine
- Fabrication of A Folic Acid-Modified Arsenic Trioxide Prodrug Liposome and Assessment of its Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Activity
- Silkworm Extract Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Protects Pancreatic β-cell Functions in Rats
