尿血管紧张素原在CRRT治疗急性肾损伤中的预测作用
赵娜 邱国萍 赵云艽


[关键词] 尿血管紧张素原;持续血液滤过;急性肾损伤;肾小球滤过率;尿蛋白
[中图分类号] R446.1 [文獻标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)19-0053-03
The predictive role of urinary angiotensinogen in CRRT treatment of acute kidney injury
ZHAO Na QIU Guoping ZHAO Yunjiao
Department of Nephrology, Jiujiang NO.1 People's Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Jiujiang 332000, China
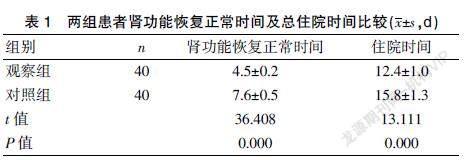
[Abstract] Objective To explore the predictive role of urinary angiotensinogen in CRRT treatment of acute kidney injury. Methods A total of 80 patients with acute renal function injury who underwent continuous hemofiltration treatment in our hospital from November 2017 to April 2019 were selected and divided into two groups according to whether the level of urinary angiotensinogen was abnormal at the time of enrollment. The level of urinary angiotensinogen in the observation group was elevated, and the level of urinary angiotensinogen in the control group was normal. The clinical data of all enrolled patients were collected, mainly including gender, age, course of disease, glomerular filtration rate, urine protein, urea nitrogen, blood creatinine and blood uric acid levels at enrollment, etc. The time for kidney function to return to normal and total hospital stay, the glomerular filtration rate and urine protein levels of the two groups before and after CRRT intervention were compared. The correlation between urinary angiotensinogen and renal function-related indicators during treatment were analyzed. Results The time for kidney function to return to normal and hospital stay in the observation group were significantly shorter than those in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the glomerular filtration rate and urine protein level between the two groups before the intervention(P>0.05). The glomerular filtration rate in the observation group after the intervention were significantly higher than that before the intervention and in the control group after the intervention, and the urine protein level in the obervation group was lower than that before the intervention and in the control group after the intervention. The differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). Urinary angiotensinogen level was positively correlated with the renal function-related indexes of patients during treatment, such as urea nitrogen, creatinine and blood uric acid level, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion In patients with acute kidney injury, those with elevated levels of urinary angiotensinogen are more severely ill, have a longer hospital stay, and are related to the recovery of renal function.

