抗生素耐药基因突变与儿童幽门螺杆菌感染治疗效果关系的研究
陈彭亮 刘旻 李桢 邹姒妮 张勇

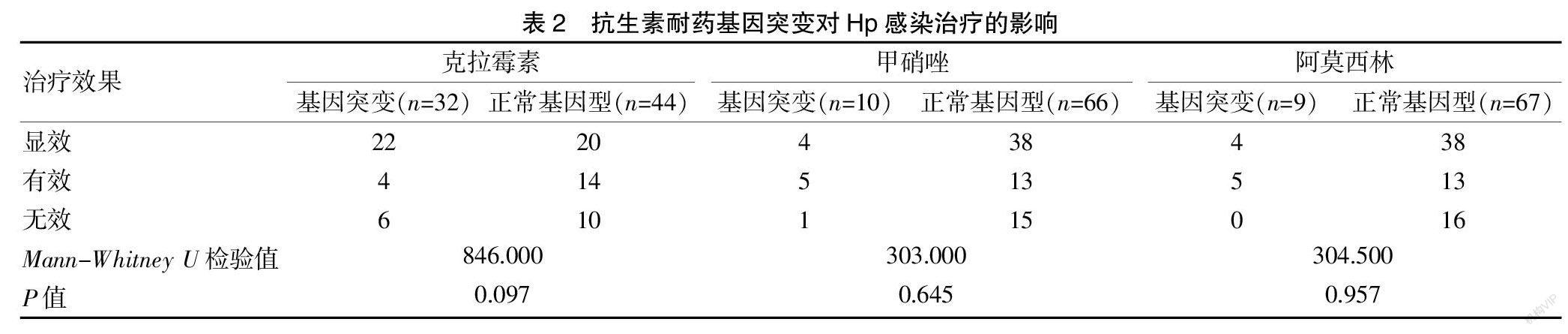
[摘要] 目的 分析克拉霉素、甲硝唑、阿莫西林等耐藥基因突变对幽门螺杆菌(Hp)感染患儿治疗根除情况的影响。 方法 选取东莞市妇幼保健院(以下简称“我院”)2019年12月至2021年1月确诊为Hp感染患儿76例,所有患儿均接受14 d标准三联疗法进行治疗,测定Hp分离菌株对克拉霉素、甲硝唑及阿莫西林耐药基因的突变情况,并分析其对抗幽门螺杆菌感染治疗的影响。 结果 Hp感染患儿根除情况:显效42例(55.3%),有效18例(23.6%),总有效率为78.9%;无效16例(21.1%);Hp感染患儿根除治疗疗效的性别差异:男性患儿中显效21例(56.8%),有效6例(16.2%),无效10例(27.0%);女性患儿中显效21例(53.8%),有效12例(30.8%),无效6例(15.4%),Hp感染患儿的治疗疗效在性别上比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);抗生素耐药基因突变对Hp感染根除治疗疗效的影响:克拉霉素、甲硝唑耐药基因突变对Hp感染患儿治疗疗效的影响比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),阿莫西林耐药基因突变对Hp感染患儿治疗疗效的影响比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 该地区治疗Hp感染患儿可优先考虑阿莫西林。
[关键词] 幽门螺杆菌;阿莫西林;甲硝唑;克拉霉素;标准三联疗法
[中图分类号] R725.1;R515 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)24-0014-04
Study on relationship between antibiotic resistance gene mutation and therapeutic effect of Helicobacter pylori infection in children
CHEN Pengliang LIU Min LI Zhen ZOU Sini ZHANG Yong
Department of Pediatrics,Dongguan Maternal and Child Health Hospital in Guangdong Province,Dongguan 523000,China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the effect of clarithromycin (CLA),metronidazole,amoxicillin and other drug-resistant gene mutations on the treatment and eradication of Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection in children. Methods A total of 76 children with Hp infection who were diagnosed in Dongguan Maternal and Child Health Hospital (hereinafter referred to as "our hospital") from December 2019 to January 2021 were selected. All the children were given 14-day standard triple therapy. The mutation of the resistance genes of Hp isolates to CLA,metronidazole and amoxicillin were determined,and its effect on the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection was analyzed. Results The eradication of Hp infection in children: 42 patients were excellent,with an excellent rate of 55.3%; 18 patients were effective, with an effective rate of 23.6% and the total effective rate of 78.9%; 16 patients were ineffective,with an ineffective rate of 21.1%. The gender differences in the curative effect of eradication therapy in children with Hp infection: 21 patients (56.8%) were excellent,and 6 patients (16.2%) were effective, and 10 patients (27.0%) were ineffective in male children; 21 patients (53.8%) were excellent,and 12 patients (30.8%) were effective,and 6 patients (15.4%) were ineffective in female chidren; no statistically significant differences were observed in the treatment curative effect of the children with Hp infection (P>0.05). Effects of antibiotic resistance gene mutation on the curative effect of Hp infection eradication: no statistically significant differences were observed in the effects of CLA and metronidazole resistance gene mutations on the curative effect of children with Hp infection (P>0.05), and a statistically significant different was observed in the curative effect of amoxicillin resistance gene mutation on the curative effect of children with Hp infection (P<0.05). Conclusion Amoxicillin may be a priority in the treatment of children with HP infection in this region.

