血清内NLR、PLR及RDW与慢性乙肝患者病情发展的相关性分析
马敏
[关键词] 慢性乙型肝炎;中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值;红细胞分布宽度;血小板与淋巴细胞比值
[中图分类号] R575 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)25-0017-03
Correlation analysis of serum NLR, PLR and RDW with disease development of chronic hepatitis B patients
MA Min
Department of Hepatitis, Xuzhou Infectious Disease Hospital in Jiangsu Province, Xuzhou 221100,China
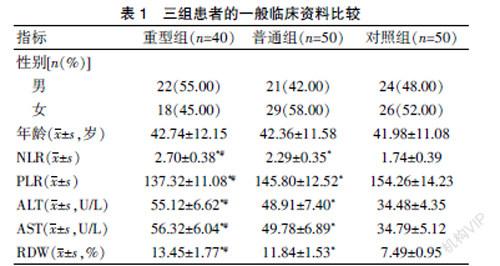
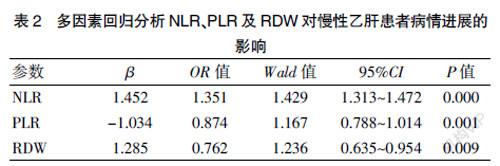
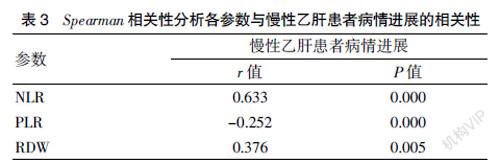
[Abstract] Objective To investigate and analyze the correlation between the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and red blood cell distribution width (RDW) in serum and disease progression in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Methods A total of 90 chronic hepatitis B patients who were treated in our hospital from January to November 2020 were selected and divided into 40 severe chronic hepatitis B patients (the severe group) and 50 chronic hepatitis B patients (the normal group) according to their disease progression. Another 50 healthy subjects (the control group) were selected during the same period. The general clinical data of the three groups were compared. Logistic regression analysis and Spearman correlation analysis were used to analyze the correlation between each factor and the disease progression of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Results Compared with the control group, NLR, RDW, AST and ALT in the severe group and the normal group were significantly increased, while PLR was significantly decreased, with statistically significant differences(P<0.05). Compared with the normal group, NLR, RDW, AST and ALT in the severe group were significantly increased, while PLR was significantly decreased, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). According to Logistic multivariate regression analysis, serum NLR, PLR and RDW were the risk factors of the disease progression of chronic hepatitis B patients (P<0.05). According to Spearman correlation results, NLR and RDW were significantly positively correlated with the disease progression of patients with chronic hepatitis B (r=0.633, 0.376), and PLR was significantly negatively correlated with the disease progression (r=-0.252). Conclusion Serum NLR, PLR and RDW are correlated with the disease progression of patients with chronic hepatitis B, which should be closely monitored in clinic.
[Key words] Chronic hepatitis B; Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; Red blood cell distribution width; Platelet-lymphocyte ratio
肝臟是人体最大的消化腺,一旦出现问题会给机体带来极大的不良影响,慢性乙肝是由乙型肝炎病毒感染诱发而来的,常迁延难愈而进一步发展为肝硬化、肝癌,预后较差。中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio,NLR)、血小板与淋巴细胞比值(Platelet-lymphocyte ratio,PLR)是反映慢性炎症状态及免疫防御功能的临床标志物,检测方便、重复性高,现已证实与多种肿瘤疾病的进展及预后相关,故而在临床上备受关注[1-2]。红细胞分布宽度(Red blood cell distributionwidth,RDW)可反映红细胞体积的变异程度,临床上最初用于鉴别诊断贫血,近年应用于肝肾功能不全、急性炎症、急慢性心力衰竭、肺动脉高压、高血压等相关疾病中[3-4],RDW与乙肝患者关联作用的机制可能是患者的肝功能损伤及炎症状态影响造血功能,从而导致血细胞成熟障碍、造血原料不足,以致不成熟的小体积红细胞进入血液,RDW增多。本研究考察血清内NLR、PLR及RDW与慢性乙肝患者病情发展的相关性,现报道如下。

