Treatment and exploration of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine for hypertension
Introduction
With the social transformation and economic development, the prevalence of hypertension and its complications, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, has been increasing.It has become the primary problem in preventing and treating chronic diseases in the world.China released “China Hypertension Survey” included 451,755 people over the age of 18 from 31 provinces.The results showed that the prevalence rate of hypertension among adults over 18 years old was 23.2%, and the number of patients was 245 million; the prevalence rate of high-normal blood pressure was 41.3%, and the number of patients was 435 million; the awareness rate and treatment rate of hypertension and control rates were 46.9%, 40.7% and 15.3%,respectively.The increasing prevalence of hypertension and the low control rate of hypertension year by year reflect the seriousness of the situation of hypertension prevention and control.Hypertension is a common clinical cardiovascular disease that seriously endangers human health, with elevated systemic arterial pressure as the main sign.Vital organs lead to multi-system lesions or dysfunctions and become the fuse of many diseases, with high morbidity and mortality rates, bringing physical and mental extremes to patients [1, 2].Currently, the prevalence of hypertension in China is as high as 27.9%, and the number of deaths related to hypertension is about 2 million every year [3].Therefore, hypertension has received significant attention from society.Hypertensive patients need to take drugs for a long time.Diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors,calcium ion antagonists,etc.,are commonly used in clinical practice.However, these drugs have many contraindications and adverse reactions, such as irritating dry cough and hyperkalemia.Sexual dysfunction, deterioration of renal function, etc., seriously affect patients’ quality of life, reducing medication compliance,resulting in an unstable antihypertensive effect [4, 5].Traditional Chinese medicine has long-term practicality in the treatment of hypertension.It can achieve good clinical efficacy and reduce the risk of dementia in hypertensive patients [6].It also shows certain advantages in the treatment of hypertension complications.This article reviews the definition, pathogenesis, diagnostic criteria,current drug treatment, and benefits of traditional Chinese medicine to clarify the specific advantages and characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of hypertension to guide the integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine treatment of hypertension and improve hypertension cure rate.
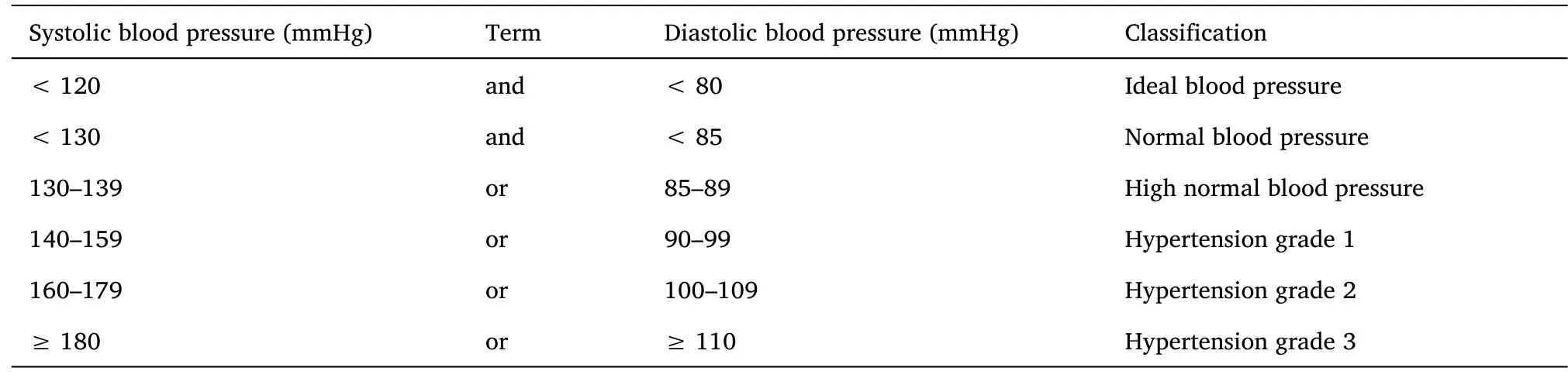
Diagnostic criteria for hypertension
The 1999 World Health Organization/International Hypertension(WHO/ISH) League guidelines for the prevention and treatment of hypertension also defined blood pressure higher than 140/90 mmHg as hypertension [7].In 2003, the first European guidelines for the prevention and treatment of hypertension also included 140/90 mmHg as the diagnostic criteria for hypertension [8].With a further understanding of the harm of elevated blood pressure, systolic blood pressure of 120-139 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure of 80-89 mmHg was first defined as prehypertension in JNC in 2003[9].At the American Heart Association Annual Meeting on November 13, 2017,the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA) and other organizations jointly issued guidelines for the prevention, detection, evaluation and management of hypertension in adults in the United States (The new guidelines for hypertension in the United States), the new guidelines changed the definition of hypertension from the original blood pressure ≥140/90 mmHg to blood pressure ≥130/80 mmHg for the first time.This change has caused widespread concern and controversy at home and abroad [10].The revision of the diagnostic criteria for the new guidelines for hypertension in the United States is mainly based on two studies.(1) Observational studies: a meta-analysis of 61 prospective studies showed that cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease risk in people with blood pressure ≥115/75 mmHg increased with increasing blood pressure.This study suggests that every 20 mmHg increase in systolic blood pressure,or every 10 mmHg increase in diastolic blood pressure, doubles the risk of stroke, ischemic heart disease, and vascular disease-related death [11].Also cited in the observational study was our team’s study, a meta-analysis of prehypertension that found people with a blood pressure of 130-139/85-89 mmHg had a higher incidence of total heart disease compared with those with blood pressure less than 120/80 mmHg.The risk of vascular(CVD)events was 1.56 times,including 1.95 times the risk of stroke and 1.99 times the risk of myocardial infarction[12].(2) Intervention studies: the clinically instructive SPRINT study was cited, which suggested that compared with the population with blood pressure controlled at 140 mmHg, the incidence of CVD events and all-cause mortality were reduced by 25% in the population whose blood pressure was controlled at 120 mmHg.[13].Multicenter randomized clinical trials have stronger support.The results of the above studies suggest that the hypertensive population with blood pressure ≥ 140/90 mmHg has a significantly increased risk of developing CVD, and the population with blood pressure 130-139/80-89 mmHg also has an increased risk of developing CVD.These findings provide evidence for the revision of hypertension diagnostic criteria and blood pressure target values in the American Hypertension Guidelines.However, considering the current situation of hypertension prevention and treatment in China,the main problem in China is to speed up the improvement of the hypertension control rate with blood pressure <140/90 mmHg as the blood pressure-lowering standard to reduce the number of hypertension complications in my country.Based on combining the actual situation in China and fully analyzing the relevant evidence at home and abroad, the expert group proposed that the diagnostic criteria for hypertension in China still use the criteria of systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg.Blood pressure control targets were systolic blood pressure <140 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg.Among them, the controversy of the new US hypertension guidelines is how to define and treat people with blood pressure values of 130-139/80-89 mmHgAmong them, the controversy over the new guidelines for hypertension in the United States lies in how to define and treat people with blood pressure values of 130-139/80-89 mmHg.Although Chinese experts have not changed the diagnostic criteria of blood pressure, the CVD risk of these people cannot be ignored, and a new classification should be adopted.The specific criteria for the diagnosis of hypertension are shown in Table 1.
Open the door, the back door of their sweet home, the warmth of a corner in a disorderly manner, the table three seasons, women are always hard to manage with. Men very satisfied with this life, he will open the door in the woman after 10 minutes back in time.
Clinical research on the etiology of hypertension
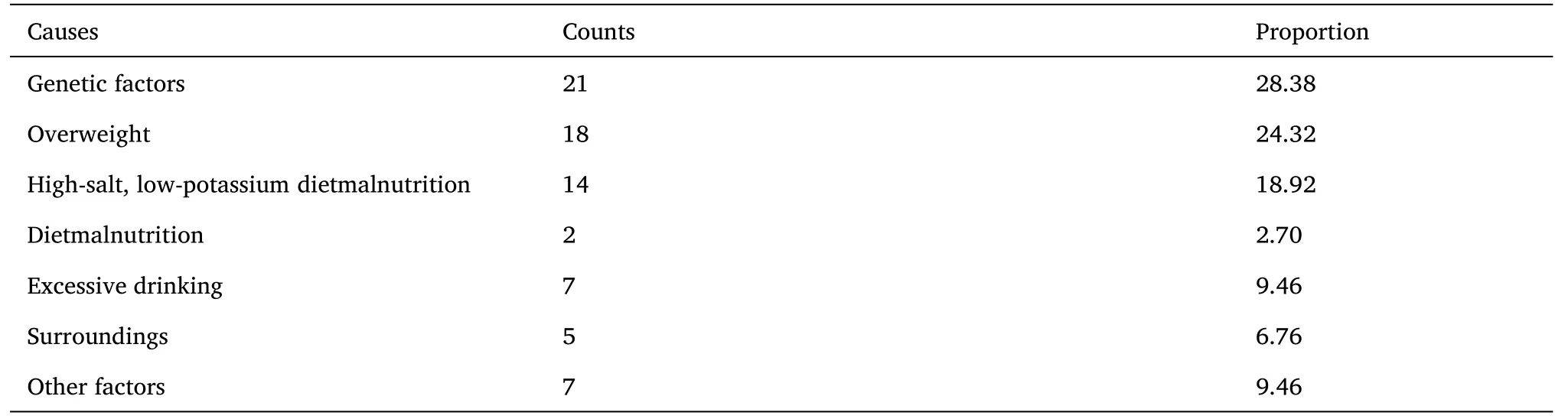
By observing and comparing the etiological analysis of primary hypertension in 120 hypertensive patients, Jilin Central Hospital found that among the 120 hypertensive patients, 74 were primary hypertension,accounting for 61.67%; 46 patients with blood pressure,accounting for 38.33%.The main causes of essential hypertension are genetic factors and overweight.The proportion of genetic factors and overweight is higher than that of high-salt, low-potassium diet,malnutrition, excessive drinking, and the environment.The main causes of hypertension in patients with essential hypertension are sleep apnea syndrome and primary aldosteronism.The proportion of sleep apnea syndrome and primary aldosteronism is higher than that of renal parenchymal hypertension.Anxiety,hyperthyroidism,and the proportion of the detailed etiology analysis as shown in Table 2,Table 3, and Figures 1, 2, 3.
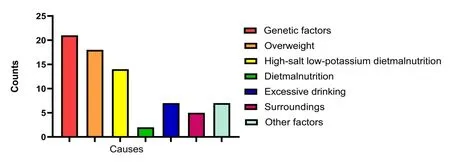
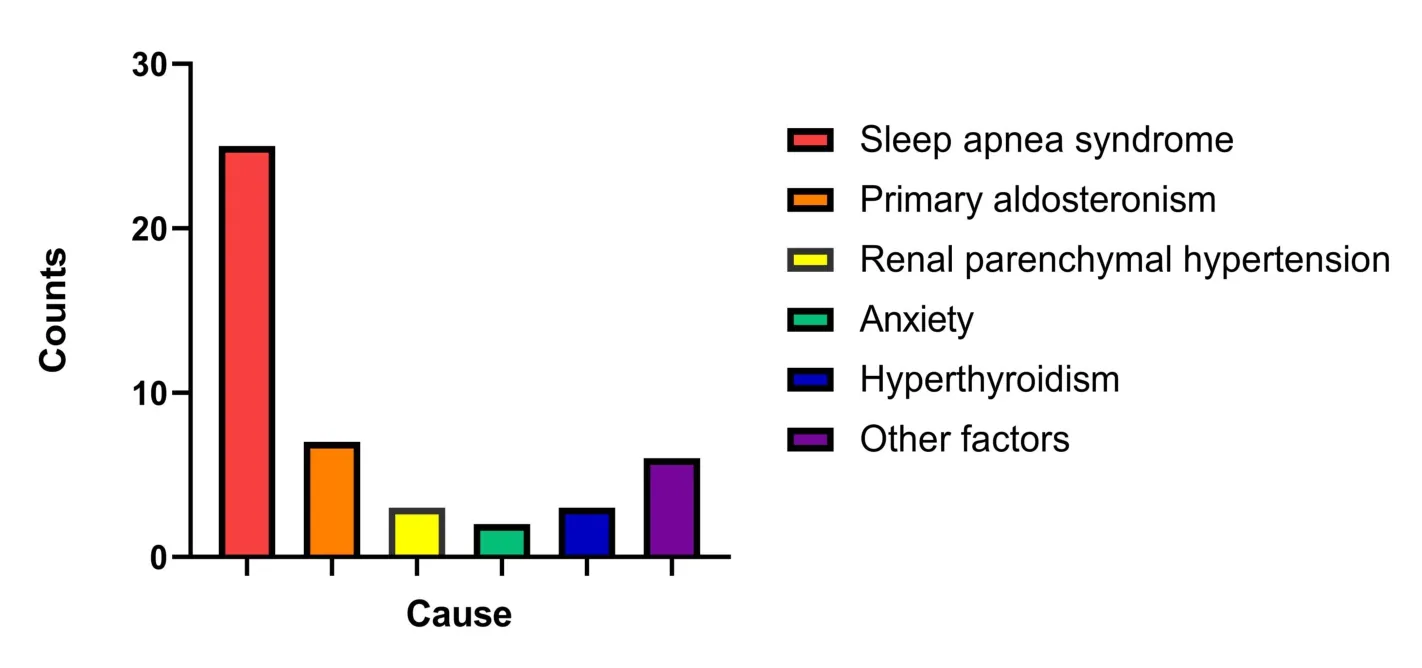

Pathogenesis of hypertension
The pathogenesis of hypertension is generally believed to be related to endothelial injury, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, vascular wall thickening, lumen stenosis, and vascular remodeling caused by matrix deposition.According to the different regulatory mechanisms,the regulation of hypertension is divided into neural rule, kidney regulation, hormone regulation, vascular regulation, and insulin resistance regulation (Figure 4).Vascular tension and blood pressurechanges are controlled by vascular autoregulation.Endothelial cells sense blood shear force and release vasodilator factors such as nitric oxide (NO), which are essential in regulating blood pressure.The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system participates in the occurrence and development of hypertension by promoting the release of vasoconstrictor factors such as NO from endothelial cells, changing vasoconstriction.Ortega et al.studied the pathogenesis of hypertension in African American population [14].They found that hypertension is directly related to obesity, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and salt intake.Studies on the peripheral outline of hypertensive animals have found that macrophage polarization can stimulate the nervous and immune system through inflammatory cytokines to increase blood pressure and participate in hypertension.At the same time, angiotensin can promote the differentiation of M2 macrophages,further promoting the occurrence of hypertension [15].Sodium, potassium, calcium and other cations are involved in the body’s heart beating,neurotransmitter synthesis and release, blood coagulation and other physiological activities.Abnormal ion channels can lead to an abnormal discharge of sympathetic nerves, resulting in hypertension.The kidneys play an essential role in maintaining the body’s balance of sodium and potassium ions.Modern diets rich in sodium ions and deficient in potassium ions lead to an imbalance in the intake of sodium and potassium ions by the body, which in turn leads to oxidative stress and tubulointerstitial inflammation.Relevant animal experiments have shown that angiotensin-induced oxidative stress in the kidney and cardiovascular system is an essential mechanism for the pathogenesis of hypertension, and the increase in arterial pressure mediated by high sodium ion levels caused by high salt intake may be salt-sensitive.In the etiology of hypertension, based on epigenetic studies, it was found that in the pathological process of hypertension,the DNA sequence did not change, but the expression traits changed.MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate the levels of angiotensin II, participate in the phenotypic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells, and affect endothelial cells [16-19].Cell function and other aspects are essential in blood pressure regulation [20].

The pathogenesis of hypertension is generally believed to be related to endothelial injury, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation,vascular wall thickening, lumen stenosis, and vascular remodeling caused by matrix deposition.According to different regulatory mechanisms, the regulation of hypertension can be divided into neuromodulation, renal regulation, hormone regulation, vascular regulation and insulin resistance regulation.The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system promotes the release of vasoconstrictor factors such as NO from vascular endothelial cells.Angiotensin can promote the differentiation of M2 macrophages and further promote the occurrence of hypertension.Abnormal ion channels can cause abnormal firing of the sympathetic nerves, leading to high blood pressure.The kidneys play an important role in maintaining the body’s balance of sodium and potassium ions.The elevation of arterial pressure mediated by high sodium ion levels caused by high salt intake may be salt-sensitive.MicroRNAs(miRNAs)regulate the levels of angiotensin II and are essential for blood pressure regulation.
Western medicine treatment of hypertension
So there was no one left belonging to the house but the landlord s daughter, who was a good, well-meaning girl, and had taken no part in all the evil doings
Chinese medicine treatment of hypertension
Traditional Chinese medicine monomers commonly used in the treatment of hypertension
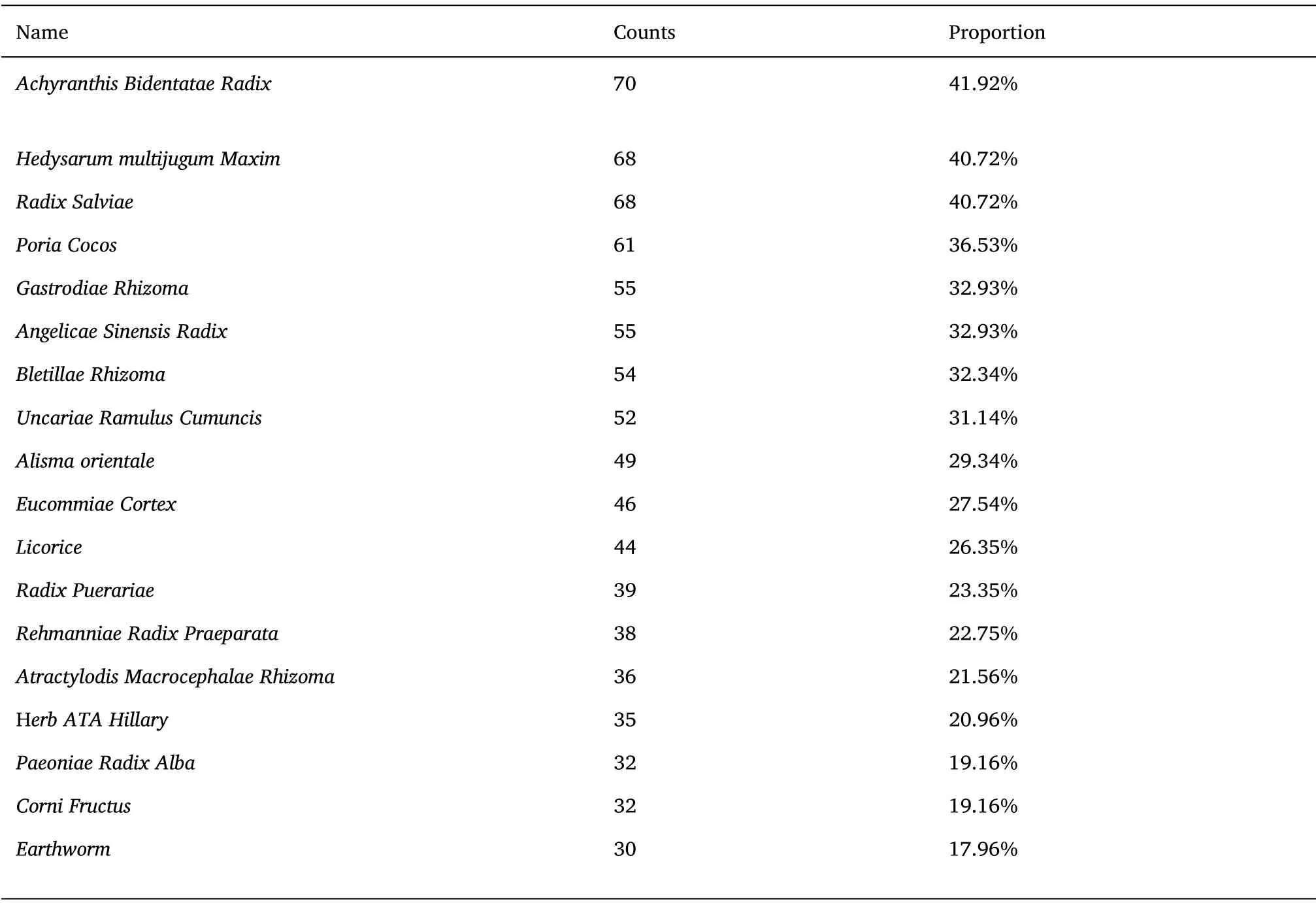
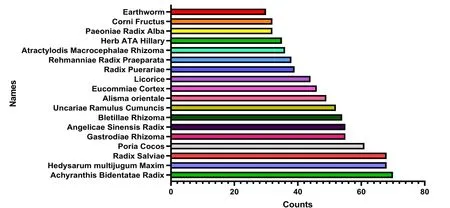
Previously published literature was retrieved by searching CNKI,Wanfang Database, VIP database and PubMed medical literature database.The search terms were hypertension in the elderly and isolated systolic hypertension.The titles, keywords and abstracts contained traditional Chinese medicine, traditional Chinese and western medicine, traditional Chinese and western medicine,prescriptions and compound prescriptions.The frequency of use of high-frequency traditional Chinese medicine.The total frequency of traditional Chinese medicine is 1,762 times, and the frequency of occurrence is ≥30 times.There are 18 high-frequency medicines in total.The results of frequency analysis showed that the commonly used drugs for hypertension were
,
,
,
,
, etc.The results are shown in Table 4 and Figure 5.
Traditional Chinese medicine compounds commonly used to treat hypertension
“I can see myself, I can see myself,” said the narcissus. “Oh, how sweet is my perfume! Up in a little room with a bow window, stands a little dancing girl, half undressed; she stands sometimes on one leg, and sometimes on both, and looks as if she would tread the whole world under her feet. She is nothing but a delusion31. She is pouring water out of a tea-pot on a piece of stuff which she holds in her hand; it is her bodice. ‘Cleanliness is a good thing,’ she says. Her white dress hangs on a peg32; it has also been washed in the tea-pot, and dried on the roof. She puts it on, and ties a saffron-colored handkerchief round her neck, which makes the dress look whiter. See how she stretches out her legs, as if she were showing off on a stem. I can see myself, I can see myself.”
Currently, commonly used drugs for hypertension in clinics mainly include calcium channel blockers (CCB), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI), and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI), thiazide diuretics and β-blockers and other 6 categories [5].Calcium channel blockers mainly include dihydropyridine CCBs and non-dihydropyridine CCBs,which can reduce blood pressure by blocking calcium channels on vascular smooth muscle cells to dilate blood vessels.Both ACEI and ARB act on the renin-angiotensin system to exert antihypertensive effects.ACEI can reduce blood pressure by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme, inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, and inhibiting the degradation of kininase.ARB exerts its antihypertensive effect by blocking the binding of angiotensin II to its receptor.Thiazide diuretics mainly include hydrochlorothiazide and indapamide.Thiazide diuretics mainly exert antihypertensive effects through diuresis, sodium excretion, and volume load reduction.Beta-blockers exert their antihypertensive effects by inhibiting sympathetic nerve activity,slowing heart rate, and inhibiting myocardial contractility.ARNI was used in the early treatment of heart failure; in addition to the role of ARB, it also has the role of an enkephalinase inhibitor, which can increase the levels of natriuretic peptide bradykinin and other endogenous vasoactive peptides to play a role in reducing blood pressure[21].A clinical study of 38 patients with severe hypertension(office systolic blood pressure 180 to 220 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure 110 to 120 mm Hg) found reduced sacubitril and valsartan 200 mg once daily office systolic blood pressure during the first week.18.7 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure decreased by 10.3 mm Hg, and after 4 weeks of follow-up, in the absence of other drugs, the systolic and diastolic blood pressure in the office decreased by 23.1/14.0 mmHg, respectively.A multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled study [22] compared sacubitril-valsartan 200 mg QD with olmesartan 20 mg QD and reduced systolic blood pressure by 3.7 mmHg.In an Asian population study, sacubitril-valsartan 200 mg QD has a stronger antihypertensive effect than olmesartan 20 mg QD[23].In another study, compared with olmesartan, sacubitril and valsartan reduced, and the left ventricular mass index increased more significantly at week 12,and the left ventricular mass index decreased further after follow-up to 52 weeks[24].In patients with salt-sensitive hypertension, sacubitril-valsartan 400 mg QD compared with valsartan 320 mg QD, sacubitril-valsartan has more advantages in-office blood pressure and ambulatory blood pressure control and can be significantly reduced N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide(NT-proBNP) [25].In terms of reducing diastolic blood pressure,sacubitril-valsartan,compared with valsartan(200 mg vs 160 mg,400 mg vs 320 mg), sacubitril-valsartan reduced diastolic blood pressure more significantly [26].The 2018 guidelines for the prevention and treatment of hypertension in China recommend that all 5 types of drugs can be used as initial and maintenance drugs.The guidelines for drug treatment of hypertension in adults issued by WHO recommend that any one of thiazide diuretics, ACEI, ARB, and long-acting dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers can be used as first-line drugs, but β-blockers are not recommended.Guidelines vary on whether beta-blockers can be used as first-line drugs.US guidelines recommend against recommending beta-blockers as first-line drugs in patients without heart failure and coronary artery disease [27].European procedures and Chinese guidelines point out that β-blockers can be used as first-line drugs, mainly based on the fact that, in general,5 types of drugs are used as the initial treatment plan,and the incidence of major cardiovascular events and mortality are similar[28].In the 2020 ISH Hypertension Guidelines, indications with beta-blocker indications, such as heart failure, angina, myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, pregnancy or planning to become pregnant, may be used at any stage of hypertension treatment.
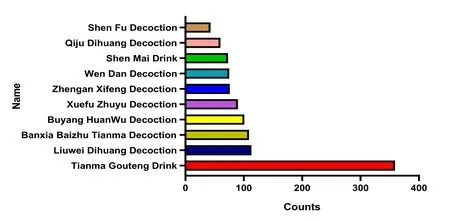
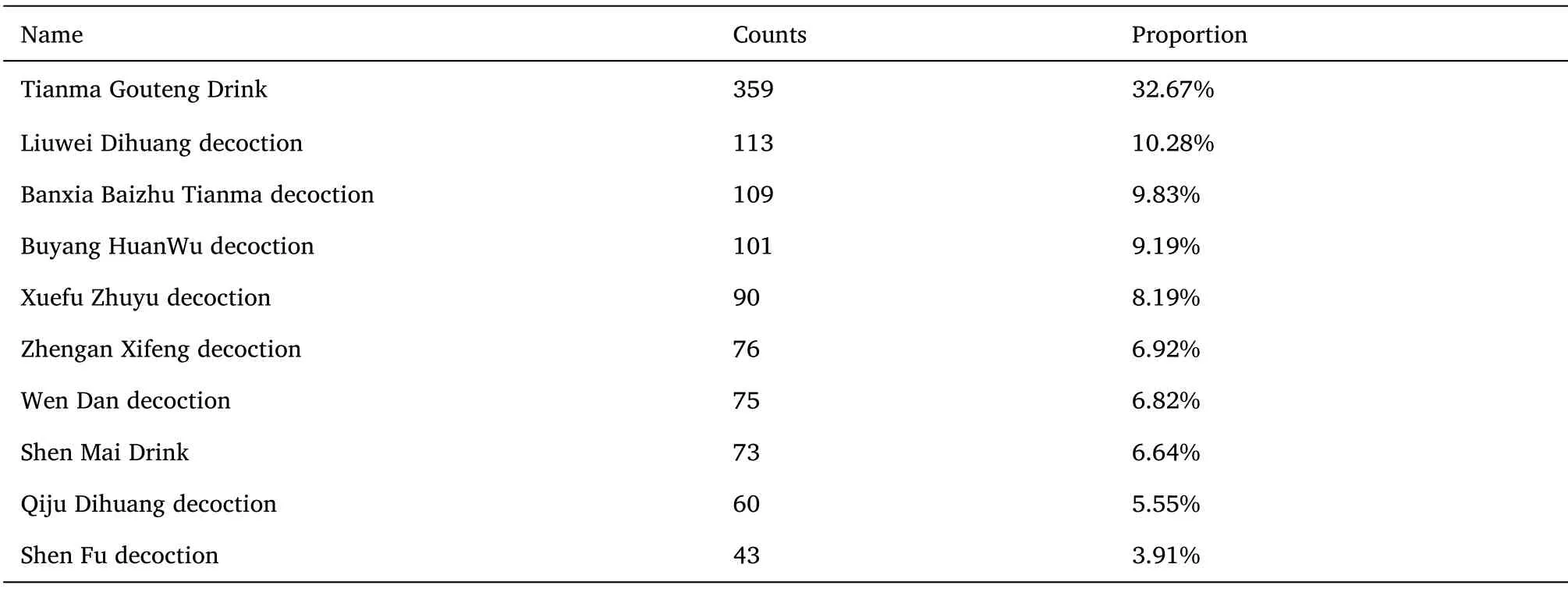
Retrieve hypertension-related literature in the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database, use proprietary text tools to extract information,and explore the classification of TCM syndromes of hypertension and the use of clinical prescriptions through literature analysis.The results showed that the top 10 common prescriptions for the treatment of hypertension were Tianma Gauteng Drink, Liuwei Dihuang decoction,Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction, Buyang Huanwu decoction, Xuefu Zhuyu decoction, Zhengan Xifeng decoction, Wen Dan decoction,Shen Mai Drink,Qiju Dihuang decoction,Shen Fu decoction he results are shown in Table 5 and Figure 6.Blood-activating and stasis-removing prescriptions commonly used in the clinical treatment of hypertension, including
g,
12 g,
12 g,
12 g,
60 g,
10 g,
12 g,
12 g,
6 g.Tianma Gouteng soup (
15 g,
15 g,
15 g,
10 g,
10 g, Chinese yam 10 g,
15 g,
20 g,
12 g,
15 g,
15 g, etc.Traditional Chinese medicine foot bath combined with acupuncture to treat patients with hypertension.Method:acupuncture treatment main points: “Baihui” “Hegu”, “Quchi” “Sanyinjiao”“Taichong” auxiliary points: “Shenshu” “Liver” “Yu”, “Xinshu”“Fengchi” “Shenmen” “Neiguan” “Taixi” (These acupoints are the tender points corresponding to various acupoints in traditional Chinese medicine.Acupoint massage generally has the functions of relaxing meridians and activating collaterals, softening tendons and relieving pain, removing blood stasis and stopping bleeding,promoting the circulation of Qi and blood,and adjusting the functions of viscera) once a day, 10 days as a course of treatment; at the same time, give Chinese medicine foot bath treatment (Ten merits 20 g,summer 10 g of subtilis, 10 g of gentian, 10 g of aloe, 10 g of
,10 g of
, 10 g of fried
, 10 g of Treats, 10 g of Coleus,and 10 g of
,once a day, 1 h each time.
Discussion
With the continuous development of the condition of patients with hypertension, ischemic lesions of the heart, brain, kidney and other important organs can be caused in the middle and late stages.Some studies have found that traditional Chinese medicine has a certain preventive effect on the reversal of certain target organ damage and complications.Practice has shown that, whether it is traditional Chinese medicine alone, combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine, different surgical methods combined with traditional Chinese medicine, or traditional Chinese medicine combined with acupuncture, foot bathing and sticking therapy for the treatment of hypertension and its complications, it is still the current state of hypertension and its complications.The effective method of treatment has obvious advantages compared with simple western medicine.Traditional Chinese medicine can improve blood circulation, lower lipids, resist atherosclerosis, improve insulin resistance, and improve or eliminate clinical symptoms.Combining different methods and methods can enhance the sensitivity of the patient’s body to antihypertensive drugs, reduce the damage of target organs, and has obvious effects.From the perspective of long-term efficacy, traditional Chinese medicine can make up for the shortcomings of western medicine in the above aspects,but it also has shortcomings such as slow onset of action, inconvenient medication,and lack of clinical efficacy evaluation system.Therefore, it is necessary to study effective, quick-acting and safe TCM antihypertensive methods and drugs in order to give full play to the characteristics and advantages of TCM in the prevention and treatment of hypertension.
At present, there is no evident and effective cure for hypertension.There is contention among a hundred schools of thought in traditional Chinese medicine.There is no standardized scientific research, and many classic and proven prescriptions cannot reach a consensus,which limits the development of traditional Chinese medicine in modern times.At this stage, traditional Chinese and Western medicines play a positive role in preventing and treating refractory hypertension.However, the focus is still on the prescribed medication in traditional Western medicine guidelines, but with the development of the times, people’s awareness has also improved.The proportion of traditional Chinese medicine is also becoming more and more critical.
The internal and external treatment methods of traditional Chinese medicine are also more and more recognized by people.Traditional Chinese medicine can often achieve unexpected results for many problems that cannot be solved by Western medicine, and traditional Chinese medicine still has excellent upside.TCM has a long history and has accumulated rich experience in the treatment of hypertension.We can give full play to the advantages of TCM, formulate individualized treatment plans, assist conventional Western medicine treatment, improve clinical symptoms of the disease, and improve patients’ quality of life.It provides patients with the most optimal treatment plan, and traditional Chinese medicine is cheap, has few adverse reactions, and has high safety.It is worthy of clinical use and promotion by medical workers.
1.Lu B,Zhou XJ,Fu DY,et al.Characteristics of TCM syndromes of abdominal obesity and hypertension and their correlation with target organ damage.
.2017;15(1):1-5.(Chinese)https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&d bname=CJFDLAST2017&filename=ZYYY201701001&uniplatf orm=NZKPT&v=cVJNB71r9R8ufWDkdreqlaLEEmuMzQuTwK_snRx4HZlAjdF2ClKnojxZ1_f55Lhg
2.Zhang W, Zhang S, Deng Y, et.al.Trial of intensive blood-pressure control in older patients with hypertension.
.2021;385(14):1268-1279.https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2111437
3.McLaughlin VV, Channick R, De Marco T, et al.Results of an expert consensus survey on the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension with oral prostacyclin pathway agents.
.2020;157(4):955-965.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2019.10.043
4.Wang SY.Analysis of common adverse drug reactions and rational drug use in patients with hypertension.
.2018;18(11):115.(Chinese)https://doi.org/10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2018.11.082
5.Gebreyohannes EA, Bhagavathula AS, Abebe TB, Tefera YG,Abegaz TM.Adverse effects and non-adherence to antihypertensive medications in University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital.
.2019;25:1.https://doi.org/10.1186/s40885-018-0104-6
6.Chen KH, Yeh MH, Livneh H, et al.Association of traditional Chinese medicine therapy and the risk of dementia in patients with hypertension: a nationwide population-based cohort study.
.2017;17(1):178.https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-017-1677-4
7.Travis WD, Garg K, Franklin WA, et al.Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma: the clinical importance and research relevance of the 2004 World Health Organization pathologic criteria.
.2006;1(9 Suppl): S13-9.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17409995/
8.Baruch L.Hypertension and the elderly: more than just blood pressure control.
(
).2004;6(5):249-255.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-6175.2004.03307.x
9.Singh V, Christiana J, Frishman WH.How to use calcium antagonists in hypertension: putting the JNC-VI guidelines into practice.Joint National Committee for the prevention,detection,evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure.
.1999;58(4):579-587.https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199958040-00001
10.Carey RM,Wright JT Jr,Taler SJ,Whelton PK.Guideline-driven management of hypertension: an evidence-based update.
.2021;128(7):827-846.https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.121.318083
11.Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R,Prospective Studies Collaboration.Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies.
.2002;360(9349):1903-1913.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(02)11911-8
12.Bellamy L, Casas JP, Hingorani AD, Williams DJ.Pre-eclampsia and risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer in later life:systematic review and meta-analysis.
.2007;335(7627):974.https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39335.385301.be
13.Ruiz-Hurtado G, Banegas JR, Sarafidis PA, Volpe M, Williams B,Ruilope LM.Has the SPRINT trial introduced a new blood-pressure goal in hypertension?
.2017;14(9):560-566.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2017.74
14.Ortega LM, Sedki E, Nayer A.Hypertension in the African American population: a succinct look at its epidemiology,pathogenesis, and therapy.
.2015;35(2):139-145.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nefro.2015.05.014
15.Yang HX, Jing C, Liu R, Wang BZ.Research progress on the pathogenesis of hypertension.
.2019;25(22):4483-4487.(Chinese)https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&d bname=CJFDLAST2019&filename=YXZS201922024&uniplatf orm=NZKPT&v=19lQY4BzrUqdkOqi7T451sDIPOmzyuwexoyq hELXsIfL22pyRMNERw6Zku-yZvm5
16.Adrogué HJ, Madias NE.Sodium surfeit and potassium deficit:keys to the pathogenesis of hypertension.
.2014;8(3):203-213.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jash.2013.09.003
17.Sprenkle NT, Sims SG, Sánchez CL, Meares GP.Endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in the central nervous system.
.2017;12(1):42.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0183-y
18.Vaziri ND,Rodríguez-Iturbe B.Mechanisms of disease:oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of hypertension.
.2006;2(10):582-593.https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpneph0283
19.Hirooka Y, Sagara Y, Kishi T, Sunagawa K.Oxidative stress and central cardiovascular regulation.-Pathogenesis of hypertension and therapeutic aspects-.
.2010;74(5):827-835.https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.cj-10-0153
20.Gjorgjieva M,Sobolewski C,Dolicka D,Correia de Sousa M,Foti M.miRNAs and NAFLD: from pathophysiology to therapy.
.2019;68(11):2065-2079.https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2018-318146
21.Seferovic JP, Claggett B, Seidelmann SB, et al.Effect of sacubitril/valsartan versus enalapril on glycaemic control in patients with heart failure and diabetes:a post-hoc analysis from the PARADIGM-HF trial.
.2017;5(5):333-340.https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(17)30087-6
22.Williams B, Cockcroft JR, Kario K, et al.Effects of sacubitril/valsartan versus olmesartan on central hemodynamics in the elderly with systolic hypertension: the PARAMETER study.
.2017;69(3):411-420.https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.116.08556
23.Huo Y, Li W, Webb R, Zhao L, Wang Q, Guo W.Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan compared with olmesartan in Asian patients with essential hypertension: a randomized,double-blind, 8-week study.
(
).2019;21(1):67-76.https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.13437
24.Schmieder RE, Wagner F, Mayr M, et al.The effect of sacubitril/valsartan compared to olmesartan on cardiovascular remodelling in subjects with essential hypertension: the results of a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study.
.2017;38(44):3308-3317.https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx525
25.Wang TD, Tan RS, Lee HY, et al.Effects of sacubitril/valsartan(LCZ696) on natriuresis, diuresis, blood pressures, and NT-proBNP in salt-sensitive hypertension.
.2017;69(1):32-41.https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.116.08484
26.Ruilope LM,Dukat A,Böhm M,Lacourcière Y,Gong J,Lefkowitz MP.Blood-pressure reduction with LCZ696, a novel dual-acting inhibitor of the angiotensin II receptor and neprilysin: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, active comparator study.
.2010;375(9722):1255-1266.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(09)61966-8
27.Ambrosy AP, Braunwald E, Morrow DA, et al.Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibition based on history of heart failure and use of renin-angiotensin system antagonists.
.2020;76(9):1034-1048.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2020.06.073
28.2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension.
(
).2019;72(2):160.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rec.2018.12.004
