Therapeutic effects of salidroside vs pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate against severe acute pancreatitis in rats
QIAN Jing,WANG Xiaohong,WEI Benzhong,ZHOU Guoxiong,ZHU Shunxing,LIU Chun
QIAN Jing,Department of General Surgery,Yizheng Hospital of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Group,Yizheng 211900,China
WANG Xiaohong,Department of Gastroenterology,Yizheng Hospital of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Group,Yizheng 211900,China
WEI Benzhong,Department of Anesthesiology,Yizheng Hospital of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Group,Yizheng 211900,China
ZHOU Guoxiong,Department of Gastroenterology,Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University,Nantong 226001,China
ZHU Shunxing,LIU Chun,Department of Laboratory Animal Center,Nantong University,Nantong 226001,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the therapeutic effectiveness of salidroside (Sal) and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC)against severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) in a rat model.METHODS: Rat models of SAP were established by retrograde infusion of sodium taurocholate solution.SAP rats were randomly divided into 6 groups: SAP 3 h group,SAP 24 h group,low-dose Sal treatment group (Sal L+S),middle-dose Sal treatment group (Sal M+S),high-dose Sal treatment group (Sal H+S) and PDTC treatment group (PDTC+S).The serum amylase,tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α),interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-10(IL-10) levels were determined by optical turbidimetry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.The expression of Beclin-1,microtubule-associated protein light chain 3Ⅱ(LC3 Ⅱ),lysosome associated membrane protein 2(LAMP2),interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 1(IRAK1),inhibitor α of nuclear transcription factor-κB(IκBα),nuclear transcription factor-κB 65 (p65) in the pancreas tissues were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot,while the p-IκBα and p-p65 levels were detected by Western blot.Pathological changes of the pancreas and all the other indexes were observed at 3 and 24 h after operation.RESULTS: The serum IL-10 level,IκBα and LAMP2 levels in Sal M+S,Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups were higher than those in SAP 24 h group,while all the other indexes in these three groups were all lower significantly than those in SAP 24 h group.There was no significant difference in all indexes between Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups.CONCLUSION: High-dose Sal has an effectively therapeutic effect on SAP in rats,which was similar to PDTC.
Keywords: rhodioloside;pyrrolidines;ethylenebis (dithiocarbamates);pancreatitis;autophagy;NF-kappa B;signal transduction
1.INTRODUCTION
Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) is a commonly encountered clinically emergency that is characterized by sudden onset and rapid progression,accompanied with systemic inflammation response syndrome and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome,causing a mortality of 20%-30% and incurring heavy burdens on both families and society.1Therefore,it is particularly important and urgent to explore the pathogenesis of SAP and find effectively therapeutic drugs.The development and progression of acute pancreatitis (AP) involves activation of trypsinogen,impaired autophagy and uncontrolled inflammatory responses.The severity of AP is depended on inflammatory responses and trypsin activation.Impaired autophagy may promote the activation of trypsinogen and inflammatory responses in pancreatic acinar cells.2
Salidroside (Sal),also known as 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl-β-D-glucoside,is a natural antioxidant extracted from the root of Rhodiola rosea L.Sal shows anti-fatigue,anti-hypoxia,anti-osteoarthritis,anti-diabetes,anticancer and anti-apoptosis activities.In addition,it can modulate immunity,and protect the heart,liver,kidney,skin,lung,brain and nervous system against damages.3-16Sal is safe and reliable for clinical use due to low toxicity and few adverse effects.17,18Previous studies have shown that Sal has a therapeutic effect against various inflammatory diseases.19-24The mechanism may be through regulation of cellular autophagy and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway.We therefore postulated that Sal might also be effective for the treatment of SAP.
Few studies have reported the clinical use of Sal for SAP treatment.In this study,we first established rat SAP models to observe the therapeutic effect of Sal on SAP,and further explored the probable mechanisms,hoping that the obtained results could provide a reliable experimental basis for the clinical use of Sal in the treatment of SAP.
2.METHODS
2.1.Ethical declarations
The research protocol was approved by the Yizheng Hospital of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Group Institutional Review Board (No.2019-04-26).Animal experiment procedures were in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals(Eighth Edition,2011,published by The National Academies Press,2101 Constitution Ave.NW,Washington,DC 20055,USA).
2.2.Preparation of Sal and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate(PDTC) injection
Sal injection was prepared with 20 mg Sal (National Institutes for Food and Drug Control,Beijing,China)dissolved in 10 mL double distilled water at a concentration of 2 mg/mL.PDTC injection was prepared with 1 g PDTC (Sigma-Aldrich,MO,USA) dissolved in 50 mL double distilled water at a concentration of 20 mg/mL.
2.3.Rat models of SAP
Specific pathogen free (SPF)-grade healthy male Sprague-Dawley rats (10-12 weeks;250-260 g) were raised in the Animal Experimental Center of Nantong University School of Medicine (Certificate of quality No.SYXK [SU] 2017-0046) with 12 h light/dark cycles and free access to standard laboratory feed and water.Rat models of SAP were established by retrograde infusion of sodium taurocholate solution as described by Wanget al.25,26Briefly,rat was starved for 12 h with free access to water and anesthesized by 2% sodium pentobarbital(0.25 mL/100g,i.p.).After laparotomy,freshly prepared 3.5% sodium taurocholate solution (Sigma-Aldrich,MO,USA;0.1 mL/100 g) was retrogradely infused into the biliopancreatic duct at a rate of 0.1 mL/min.Sham operation (SO) group rats received equivalent volume of normal saline (NS) solution.The incision was closed with continuous 3-0-silk suture.
2.4.Experimental procedures
Eighty rats were randomly divided into 8 groups by random number table method: SO 3 h,SO 24 h,SAP 3 h,SAP 24 h,Sal L+S,Sal M+S,Sal H+S and PDTC +S groups.Each group included 10 rats.Rats in Sal L +S,Sal M+S and Sal H+S groups received low-dose(5 mg/kg),middle-dose (10 mg/kg) or high-dose (20 mg/kg)Sal (i.p.) at 3 h after successful modeling.Rats in PDTC+S group received PDTC (100 mg/kg,i.p.) at 3 h after successful modeling.Rats in SAP 24 h group received NS (i.p.) at 3 h after successful modeling,and rats in SAP 3 h group were sacrificed at 3 h after successful modeling.Rats in SO 24 h group received NS(i.p.) at 3 h after sham operation,and rats in SO 3 h group were sacrificed at 3 h after sham operation.Mortality of the experimental rats was calculated at 3 and 24 h in all 8 groups.Three or 24 h later,rats were sacrificed,and blood and tissue samples were harvested.
2.5.Histological examination
Pancreas tissues were harvested from each group and fixed in 4% formaldehyde,embedded in paraffin,and cut into 4-μm thick sections.The sections were subjected to routine hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and observed under a light microscope (Olympus Optical Ltd.,Tokyo,Japan) at 200× magnification.Edema,inflammation,glandular cell necrosis (each 0-4 points) and hemorrhage(0-1 point) of the pancreatic tissues were scored by 2 independent pathologists who were blind to this experiment according to Schmidt’s severity score standard of pancreas.27The mean score of 10 visual fields of one pathological section was regarded as the pathological score.
For transmission electron microscopy,the pancreas tissues were fixed in 2% glutaraldehyde for 24 h,stained with acetic acid dioxygen oil and lead citrate,and finally observed under a transmission electron microscopy(JEM-1230;JEOL Ltd.,Tokyo,Japan).
2.6.Analysis of amylase,tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α,interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10
Serum amylase level was measured by optical turbidimetry (VITROS 250 automatic biochemical analyzer,Johnson &Johnson,NJ,USA),and the levels of serum TNF-α,IL-1β and IL-10 were measured by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits(Wuhan Xinqidi Biological Technology Co.,Ltd.,Wuhan,China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.7.Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction(qRT-PCR) analysis
Total RNA was extracted from pancreas tissues using Trizol RNA extraction reagent (Life Technologies,CA,USA) and reverse-transcribed into cDNA with PCR Master Mix kit (Toyobo Co.,Ltd.,Osaka,Japan).qRTPCR was performed using SYBR Green Premix Ex Taq in a Mastercycler ep realplex instrument (Eppendorf AG.,Leipzig,Germany),with cDNA as template and primers in Table 1.The PCR protocol was as follows:predenaturation for 20 min at 95 ℃ followed by denaturation for 30 s at 95 ℃,annealing for 30 s at 55 ℃,and extension for 40 s at 72 ℃ for 40 cycles.The mRNA levels of Beclin-1,LC3Ⅱ,LAMP2,IRAK1,IκBα,p65 were normalized to GAPDH and calculated using 2-ΔΔCtmethod.
2.8.Western blot analysis
Proteins were extracted from pancreas tissues and evaluated by the Bradford method using bovine serum albumin as a standard.The protein sample (40 μg) was electrophoresed in 8% sodium dodecylsulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes.The membranes were blocked with non-fat milk for 2 h at room temperature and then incubated with the following primary antibodies: rabbit monoclonal anti-rat Beclin-1 antibody (1∶3000),LC3Ⅱantibody (1∶2000),LAMP2 antibody (1∶500),IRAK1 antibody (1∶1500),p-IκBα antibody (1∶500),IκBα antibody (1∶1500),p-p65 antibody (1∶2000),p65 antibody (1∶1000) and GAPDH antibody (1∶2000)overnight at 4 ℃.Rabbit monoclonal anti-rat Beclin-1 antibody,LC3II antibody,LAMP2 antibody,IRAK1 antibody,p-IκBα antibody,IκBα antibody,p-p65 antibody,p65 antibody and GAPDH antibody were purchased from Abcam,Cambridge,UK.The membranes were washed with TBST,incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (1∶5000,Pierce Biotechnology,Rockford,USA) at room temperature for 1 h,and developed with ECL reagent (Millipore Corporation,Billerica,USA).Images were captured using lightsensitive imaging films (Kodak,Rochester,USA).The protein bands were quantitated using Quantity One 4.5.0 software (Bio-Rad Laboratories,Hercules,USA).GAPDH served as the internal reference.
2.9.Statistical Methods
All data were analyzed using SAS (vers 8.2,SAS Institute,Chicago,IL,USA) software.Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (x±s).Nor mal data were analyzed by analysis of variance.Pairwise comparison was performed by Kruskal-Wallis H test and multiple comparison was performed by Mann-Whitney U test.Difference in mortality between two groups was assessed by exact test.P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.RESULTS
3.1.Sal is unable to reduce the mortality of SAP rats
The mortality at 3 h and 24 h was 0% (0/10) and 40%(4/10) in SAP group respectively.All animals in SO group survived at 3 h and 24 h.However,after indicated treatment,the mortality was 0% (0/10) and 40% (4/10)in Sal L+S group,0% (0/10) and 30% (3/10) in Sal M+S group,0% (0/10) and 20% (2/10) in Sal H+S group,and 0% (0/10) and 20% (2/10) in PDTC+S group,respectively.No significant difference was observed in mortality at 24 h between SAP,Sal L+S,Sal M+S,Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups (P> 0.05).
3.2.Sal and PDTC treatment mitigate SAP
In SO groups,no significant pathological changes were observed.Mild interstitial edema or neutrophil infiltration was occasionally observed (Figure 1A,1B).Gross edema in acinus,sublobular hemorrhage,neutrophil infiltration and parenchymal necrosis were observed at 3 h after SAP.In addition,saponified spots were observed in the pancreas and peripancreatic tissues(Figure 1C).While at 24 h after SAP,the acinus disappeared,and massive fat and parenchymal necrosis,interstitial edema,hemorrhage,inflammatory infiltration,cell lysis,hemorrhage,necrosis and lobular outline damages were enhanced along with time.Additionally,there were more saponified spots in the peripancreatic epiploon and peritoneum (Figure 1D).The pathological changes in Sal M+S,Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups were less severe than those in SAP 24 h group (Figure 1E-1H).Pathological scores for pancreas tissues and the serum amylase level in SAP group were significantly higher than those in SO group at 3 and 24 h (P< 0.01),suggesting the success in establishment of SAP rat model.In Sal M+S,Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups,thepancreas pathological scores and serum amylase levels were significantly lower than those in SAP group (P<0.01),suggesting that treatment with Sal and PDTC alleviated SAP injury.No significant difference was observed in the serum amylase level in Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups (P> 0.05) (Table 2).

Table 1 Primers for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
In addition,the serum levels of TNF-α,IL-1β and IL-10 were also detected.The levels of TNF-α and IL-1β were increased after SAP,and later decreased upon Sal or PDTC treatment (P< 0.01 or < 0.05).The level of IL-10 was declined after SAP,while raised upon Sal or PDTC treatment (P< 0.01 or < 0.05).There was no significant difference between the Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups(P> 0.05).These results indicate that inflammation during SAP was attenuated by Sal and PDTC treatment(Table 3).
3.3.Abnormal autophagy of pancreatic acinar cells in SAP is mitigated by Sal and PDTC treatment
In SAP group,more autophagosomes and autophagolysosomes in pancreatic acinar cells were observed.Mitochondrial swelling was also observed at 3 h after SAP (Figure 2A).More autophagosomes and autophagolysosomes,mitochondrial swelling,acinar nucleus chromatin margination and nuclear condensation and dissolution were observed at 24 h after SAP (Figure 2B).In Sal M+S,Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups,the numbers of autophagosomes and autophagolysosomes was less than those in SAP group (Figure 2E-2H).
In SAP group,the levels Beclin-1 and LC3II were higher,while the level of LAMP2 was lower than those in SO group at 3 h and 24 h,at both mRNA and protein levels(P< 0.01),suggesting that abnormal autophagy of pancreatic acinar cells was involved in the progression of SAP.After treatment with Sal or PDTC,the raised levels of Beclin-1 and LC3II were declined,while the decreased LAMP2 level was increased (P< 0.01).There was no significant difference between the Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups (P> 0.05).It is indicated that treatment with Sal or PDTC inhibited the abnormal autophagy of pancreatic acinar cells during SAP (Table 4,Figure 3B-3D,see Supplementary Table 1 for details).

Figure 1 Pathological changes of the pancreas detected by HE staining (×200)
Table 2 Comparison of pancreas pathological scores and serum amylase level in 8 groups ()
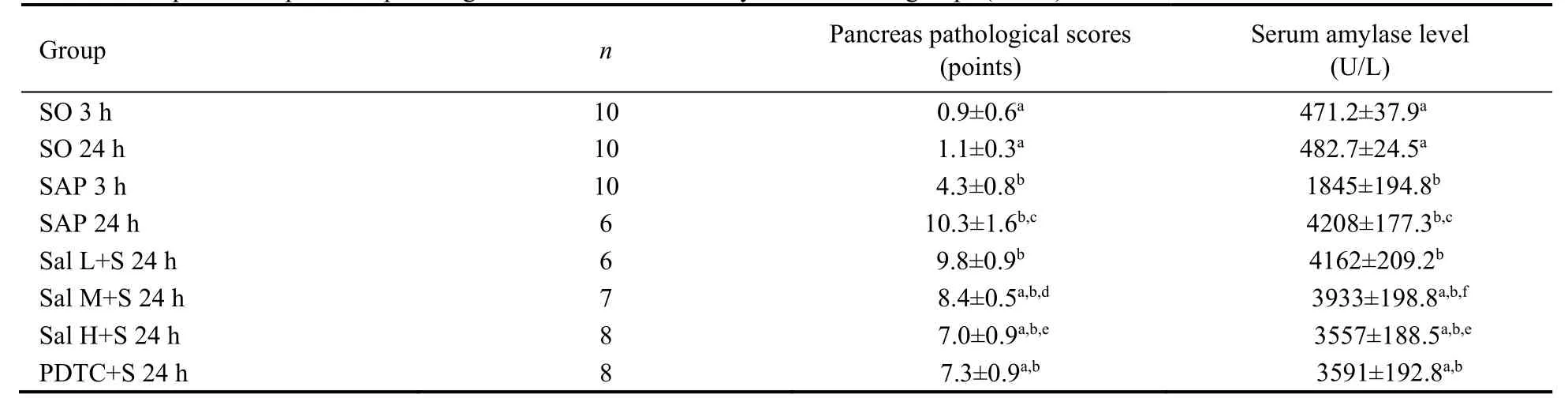
Table 2 Comparison of pancreas pathological scores and serum amylase level in 8 groups ()
Notes: SAP group: the rats were treated with 0.1 mL/min speed uniformly retrograde infusion of a freshly prepared 3.5% sodium taurocholate solution (0.1 mL/100 g) into the biliopancreatic duct after laparotomy.SO group: the rats were treated with an equivalent volume of normal saline solution as the 3.5% sodium taurocholate solution in the SAP group.Sal L+S group: SAP rats were treated with low-dose (5 mg/kg) Sal;Sal M+S group: SAP rats were treated with middle-dose (10 mg/kg) Sal;Sal H+S group: SAP rats were treated with high-dose (20 mg/kg)Sal;PDTC+S group: SAP rats were treated with PDTC (100 mg/kg).SO: sham operation;Sal: salidroside;PDTC: pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate;SAP: severe acute pancreatitis.aP < 0.01 vs SAP group at the same time point;bP < 0.01 vs SO group at the same time point;cP < 0.01 24 h vs 3 h in SAP group;dP < 0.01,fP < 0.05 Sal L+S 24 h group vs Sal M+S 24 h group;eP < 0.01 Sal M+S 24 h group vs Sal H+S 24 h group.

Table 3 Comparison of serum TNF-α,IL-1 β and IL-10 contents in 8 groups (x ± s)

Figure 2 Performance of the pancreas by TEM (×2000)
3.4.Sal and PDTC inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway in SAP
After SAP,the levels of IRAK1 and p65 were increased at both mRNA and protein level,while the level of IκBα was decreased with increased phosphorylation levels of IκBα and p65.Additionally,in Sal M+S,Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups,the levels of IRAK1 and p65 were decreased,while the level of IκBα was increased with decreased phosphorylation levels of IκBα and p65 upon treatment with Sal and PDTC (P< 0.05 or < 0.01).There was no significant difference between the Sal H+S and PDTC+S groups (P> 0.05).It is suggested that Sal and PDTC inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway which is activated during SAP.(Table 5,Figure 3E-3H,see Supplementary Table 2 for details;Figure 3I-3K,see Supplementary Table 3 for details)
Table 4 Comparison of Beclin-1 mRNA-GAPDH ratio,LC3II mRNA-GAPDH ratio and LAMP2 mRNA-GAPDH ratio in the pancreas tissue in 8 groups ()
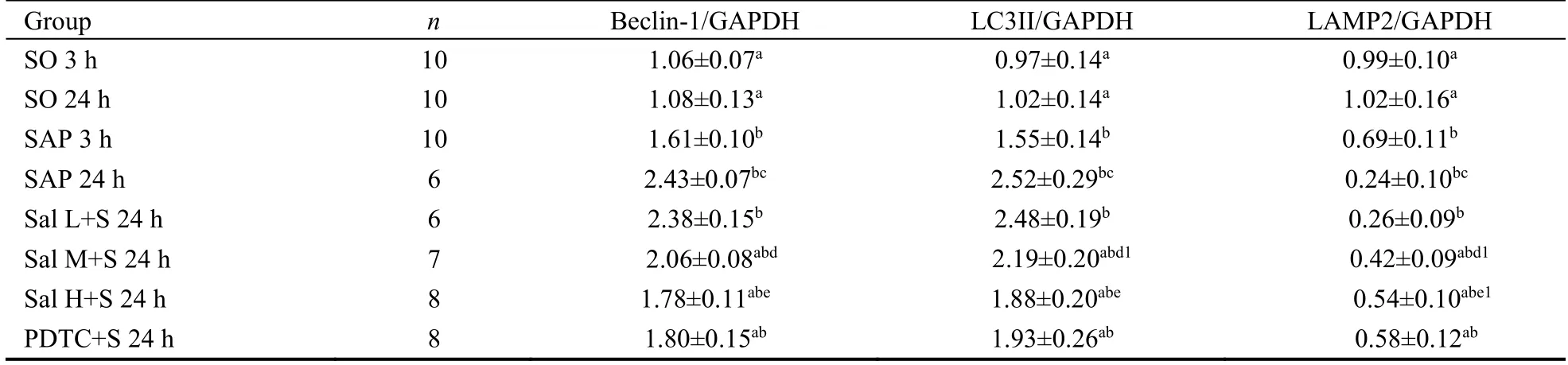
Table 4 Comparison of Beclin-1 mRNA-GAPDH ratio,LC3II mRNA-GAPDH ratio and LAMP2 mRNA-GAPDH ratio in the pancreas tissue in 8 groups ()
Notes: SAP group: the rats were treated with 0.1 mL/min speed uniformly retrograde infusion of a freshly prepared 3.5% sodium taurocholate solution (0.1 mL/100 g) into the biliopancreatic duct after laparotomy.SO group: the rats were treated with an equivalent volume of normal saline solution as the 3.5% sodium taurocholate solution in the SAP group.Sal L+S group: SAP rats were treated with low-dose (5 mg/kg)Sal;Sal M+S group: SAP rats were treated with middle-dose (10 mg/kg) Sal;Sal H+S group: SAP rats were treated with high-dose (20 mg/kg) Sal;PDTC+S group: SAP rats were treated with PDTC (100 mg/kg).SO: sham operation;Sal: salidroside;PDTC: pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate;SAP: severe acute pancreatitis.aP < 0.01 vs SAP group at the same time point;bP < 0.01 vs SO group at the same time point;cP < 0.01 24 h vs 3 h in SAP group;dP < 0.01,d1P < 0.05 Sal L+S 24 h group vs Sal M+S 24 h group;eP < 0.01,e1P < 0.05 Sal M+S 24 h group vs Sal H+S 24 h group.
Table 5 Comparison of IRAK1 mRNA-GAPDH ratio,IκBα mRNA-GAPDH ratio,and p65 mRNA-GAPDH ratio in the pancreas tissue in 8 groups ()

Table 5 Comparison of IRAK1 mRNA-GAPDH ratio,IκBα mRNA-GAPDH ratio,and p65 mRNA-GAPDH ratio in the pancreas tissue in 8 groups ()
Notes: SAP group: the rats were treated with 0.1 mL/min speed uniformly retrograde infusion of a freshly prepared 3.5% sodium taurocholate solution (0.1 mL/100 g) into the biliopancreatic duct after laparotomy.SO group: the rats were treated with an equivalent volume of normal saline solution as the 3.5% sodium taurocholate solution in the SAP group.Sal L+S group: SAP rats were treated with low-dose (5 mg/kg)Sal;Sal M+S group: SAP rats were treated with middle-dose (10 mg/kg) Sal;Sal H+S group: SAP rats were treated with high-dose(20 mg/kg) Sal;PDTC+S group: SAP rats were treated with PDTC (100 mg/kg).IRAK1: interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 1;GAPDH:glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase;IκBα: inhibitor α of nuclear transcription factor-κB;p65: nuclear transcription factor-κB 65;SO:sham operation;Sal: salidroside;PDTC: pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate;SAP: severe acute pancreatitis.aP< 0.01 vs SO group at the same time point;bP< 0.01,b1P< 0.05 vs SAP group at the same time point;cP< 0.01 24 h vs 3 h in SAP group;dP< 0.01,d1P< 0.05 Sal L+S 24 h group vs Sal M+S 24 h group;eP< 0.01,e1P< 0.05 Sal M+S 24 h group vs Sal H+S 24 h group.
4.DISCUSSION
Inflammatory response is an important feature during AP development,which to some extent determines the severity of AP.Damages to pancreatic cells induce the release of a variety of inflammatory factors,which in turn induce infiltration of inflammatory cells and cascade effects,resulting in necrosis of pancreatic acinar cells.Sal is one of the important active ingredients in Rhodiola rosea,a traditional Tibetan medicine in China.Pretreatment with Sal inhibits the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase,reduces nitrosoanion,nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation,represses the activation of NF-κB signal,and further improves the renal function of rats with kidney ischemia reperfusion injury.28Sal shows no obvious maternal toxicity,embryotoxicity and teratogenicity at the dose tested,but had a mild effect on ossification delay in fetal rats.17,18In the present study,we explored the effects of Sal in SAP.Treatment withSal mitigated histopathological changes during SAP and reduced the release of inflammatory cytokines,indicating a therapeutic effect of Sal on SAP.
Autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved process.Immune signaling cascade is regulated by autophagy,and the homeostasis recovery after strong immune responses also depends on autophagy.Autophagy can promote or reduce inflammation by regulating clearance,antigen presentation,and innate and adaptive immune responses.29When autophagy is impaired,inflammatory corpuscles cannot be removed in time.The excessive accumulation of inflammatory corpuscles leads to upregulation of IL-1β,which further aggravates the impaired autophagy and promotes the activation of trypsinogen,thus aggravating AP.30Autophagy is involved in the pathogenesis of AP.Activation of autophagy related gene (ATG) 5 and knockout of ATG 7 decrease the number of vacuoles in the acinus,and lowered the activation of zymogen in mice.31Deletion of the autophagy-associated gene LAMP2 in acinar cells leads to impaired autophagy,pancreatic trypsinogen activation,acinar cell degeneration and inflammatory response,which further aggravate AP.32Wan et al showed that regulation of autophagy could reverse the progression of SAP in mice induced by L-arginine or caerulein plus lipopolysaccharide (LPS).33In addition,the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA)reduces inflammation by regulating the NF-κB signaling and caspase-1/IL-1β pathways,which further mitigates organ damages.In the present study,abnormal autophagy of pancreatic acinar cells during SAP was found,and the increased autophagosomes and autophagolysosomes during SAP were decreased upon treatment with Sal,indicating that Sal may inhibit the activation of autophagy during SAP.LC3Ⅱ,a marker on autophagosomes,and Beclin-1 which is required for the initiation of autophagasome formation,are regarded as markers of autophagy.To some extent,these two markers can reflect the number of autophagosomes.Upon treatment with Sal and PDTC,the increased LC3Ⅱand Beclin-1 were decreased,confirming that Sal and PDTC inhibit the abnormal autophagy activation during SAP.Through modulating autophagy,Sal could also inhibit neurotoxicity during cerebral hypoxiasodium nitroprusside,35and protect hepatic ischemiareperfusion injury.36
NF-κB signal is an important signaling pathway involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses.37Studies have shown that the NF-κB signal is involved in the development and progression of SAP.Inhibition of NFκB signal effectively protects against SAP.38Yanget al39found that NF-κB suppression attenuated the severity of APviaautophagy inhibition.Therefore,we speculated that NF-κB inhibition is able to inhibit the autophagy of pancreatic acinar cells,thus mitigating AP.In this study,we found that the NF-κB signal was associated with the progression of SAP.Treatment with Sal and PDTC inhibited the activation of NF-κB signal,thus performing a protective effect against SAP.Through repressing the activity of NF-κB,Sal also alleviates allergic airway inflammation and LPS-induced acute lung injury.40,41In conclusion,Sal and PDTC exert their therapeutic effects against SAP through reducing autophagy in pancreatic acinar cells via inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway.The therapeutic efficacy of high dose Sal is comparable to that of PDTC.Sal may be superior to PDTC due to a lower price,more convenient administration,more extensive pharmacological actions,and fewer adverse effects.
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2022年1期
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2022年1期
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Flavonoids from traditional Chinese herbs for diabetes in rats: a network Meta-analysis
- In-vitro and in-vivo pharmacological screening of Iris albicans
- Detailed approach toward the anti-hyperglycemic potential of Sterculia diversifolia G.Don against alloxan-induced in vivo hyperglycemia model
- Efficacy of Bushen Culuan decoction (补肾促卵方) on ovarian follicle and follicular granulosa cells in mice with premature ovarian insufficiency induced by tripterygium wilfordii polyglycoside
- Efficacy of Wumei Baijiang prescription (乌梅败酱方) on regulatory T cells/ helper T cells Immune balance in mice with ulcerative colitis
- Shenweifang-containing serum inhibits transforming growth factorβ1-induced myofibroblast differentiation in normal rat kidney interstitial fibroblast cells
