A heteropolysaccharide from Rhodiola rosea L.: preparation,purification and anti-tumor activities in H22-bearing mice
Yaru Wu,Qing Wang,Huiping Liu*,Lulu Niu,Mengyu Li,Qi Jia
State Key Laboratory of Food Nutrition and Safety,Key Laboratory of Food Nutrition and Safety,Ministry of Education of China,College of Food Science and Engineering,Tianjin University of Science and Technology,Tianjin 300457,China
Keywords:Polysaccharide Antitumor activity Rhodiola rosea L.Structure analysis
ABSTRACT Numerous polysaccharides isolated from plants have been used to augment traditional drugs in the treatment of cancer.I n order to explore the influence to hepatocellular carcinoma,a novel cold water-soluble polysaccharide was separated from Rhodiola rosea L.root (RLP) and then its structure and anti-cancer activities were tested.The chemical compositions and high performance gel permeation chromatography(HPGPC) results indicated that RLP was an acid heteropolysaccharide with the molecular weight of about 1.15×106 Da.Furthermore,ion chromatography (IC),Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and nuclear magnetic resoance (NMR) further indicated that RLP was main composed of →2,4)-α-Rha(1→,→5)-α-L-Araf-(1→,α-D-Glu,→6)-β-D-Galp-(1→,β-D-Man and →4)-α-GalpA-(1→.In vivo antitumor activities of RLP were carried out by using H22 tumor-bearing mice model.The results shown that RLP (100 and 300 mg/kg) could inhibit tumor growth of H22 cells from 23.59% to 45.52% and protect thymuses and spleen without damage.In addition,according to cell cycle,AV-FITC/PI and JC-1,RLP could induce dose-dependent apoptosis of H22 cells via S phase arrested which was through a mitochondrial related pathway.Our data indicated that RLP has a broader application prospect in anti-tumor preparations.
1.Introduction
RhodiolaroseaL.which belongs to the plant family crassulaceae is a perennial herb and mainly grows in the harsh alpine environment of Tibet.The root ofRhodiolaroseaL.known as “golden root” is a traditional medicinal and edible plant which is used to soak in water.And then,multiple active ingredients are isolated from that such as polysaccharide,salidroside,tyrosol,flavones,and so on [1,2].Among them,polysaccharide is one of main active ingredients,which has the effects of antioxidant,immune regulation,antiinflammatory and anti-diabetic [3].Furthermore,many researchers have shown that natural polysaccharides have an inhibitory effect on the proliferation of various tumor cells.Therefore,recent work have focus on the extraction of the functional component from medicinal and edible plants.In recent years,the anti-tumor researches of salidroside have achieved relatively mature results [4,5].However,there are few researchers about the mechanism of large molecular weightRhodiolaroseaL.polysaccharide (RRP) which is isolated by traditional technology.Thus,it is particularly necessary to research the polysaccharide further because it can effectively promote the development of auxiliary therapy in anti-tumor drugs.
The study of RRP structure was mainly focused on relatively small molecular weight components.Cheng et al.[6]isolated and purified the RRP by using traditional crafts (80 °C) and DEAE-52.And then,the molecular weight of RRP was calculated as 11.82 kDa by HPLC.More importantly,it was concluded that the RRP was consist of rhamnose,arabinose,xylose,mannose,glucose,galactose and galacturonic acid (1:2.71:0.16:0.21:0.11:0.58:0.14).Meanwhile,Xu et al.[7]improved the method of purification and got the RRP1 and RRP2 by using DEAE-52 and Sephadex G-100.Furthermore,the molecular weight of RRP1 and RRP2 was 5.5 kDa and 425.7 kDa.The structural information of RRP1 and RRP2 was then further confirmed by periodate oxidation,smith degradation,methylation analysis and NMR,and the results shown that RRP1 and RRP2 had a pyranose ring and uronic acid.More specifically,in RRP1,arabinose and glucose were connected by 1→3,and then mannose,rhamnose and galactose were mainly connected by 1→2,6,1→6,1→2 and 1→4.In RRP2,The association between rhamnose,glucose and galactose was 1→3,and between mannose and arabinose was 1→2,1→6 or 1→4.
Regarding to the anti-tumor activity of RRP,the tissue and immune factors of mice have been studied extensively.However,further exploration of its mechanisms has been neglected.Cai et al.[8]purificated the polysaccharide (RRP-ws) and then established an S-180 sarcoma mice model to explore the immune regulation and antitumor activity of RRP-ws on sarcoma mice.The results shown that RRP-ws had a direct toxic effect on S-180 cellsinvitro.Invivo,RRP-ws could inhibit growing of tumor cells while increasing index of spleen/thymus.In addition,RRP-ws also increased the production of interleukin-2 (IL-2),tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interferon-γ(IFN-γ) in serum and the ratio ofin peripheral blood T lymphocytes.Many studies [9-11]have demonstrated that many cancers were caused by infection,chronic irritation,and inflammation,which might play a key role in the treatment of cancer.Pu et al.[12]suggested thatRhodiolaroseaL.might affect tumor cells through two pathways,which were direct inhibition and inflammatory regulation.Besides,non-coding RNA fusions became the target ofRhodiola roseaL.for the treatment of cancer [13].
In addition,RRP has many other activities.The results (Cheng et al.) [6]shown that the intake of RRP could improve the influence of growth performance and nonspecific immunity on red swamp crayfishProcambarusclarkia.Meanwhile,it could enhance resistance to infection byA.hydrophilaand exhibit high hypolipidaemic activities [14,15].Yang et al.[16]studied the protective effect of freeze-thawed RRP on boar sperm.Xu et al.[7]studied its antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities,and then the unique advantages of RRP were appeared according to these researches.
Hepatocellular caicinoma is the most common primary liver cancer,which is one of the most common fatal malignancies [17].Currently,treatment is still limited to the poor prognosis and severe toxic side effect [18].According to the isolated methods of RRP,high-temperature was convenient.While the extraction of long-term high-temperature would accelerate the degradation of polysaccharides and lead to changes in higher-level structures,which will affect the biological activities closely related to their structures [19,20].The low temperature extraction process was relatively complicated and timeconsumed,while it could be mildly and maintain biological activities.Furthermore,few reports have been published on the low-temperature extraction of water-soluble RRP and their anti-tumor activity,which were closely related to their structural characteristics.In order to find natural products against liver cancer,it was necessary to understand its plant polysaccharide composition and its anti-tumor potential.
In this work,a cold water-soluble and acidic polysaccharide,RLP,was isolated and purified from the root ofRhodiolaroseaL.Moreover,its anti-tumor activities and possible mechanism of the RLP were against tumor in H22 tumor-bearing mice were also studiedInvivo.This study provides comprehensive utilization ofRhodiola roseaL.and new ideas for the future research for the source of new natural anti-tumor drugs.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and reagent
The roots ofRhodiolaroseaL.were purchased from locial medical market (Xizang,China),which grown in the high mountain.T-series dextran (T-10,T-40,T-70,T-110,T-500,and T-2000),Propidium iodine (PI),and RIPA lysis buffer were purchased from Solarbio Co.(Beijing,China).Sephadex-G 200 were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co.(St.Louis,MO,USA).Test kits for bicinchoninic acid (BCA) were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing,China).Cell cycle and apoptosis detection kit,Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis detection kit were purchased from Beyotime Biotechnology (Shanghai,China).
2.2 Isolation and purification of the Rhodiola rosea L. polysaccharide
The dried roots ofRhodiolaroseaL.were smashed into powder and passed through a 80 mesh sieve.The preparedRhodiolaroseaL.powder (50 g) were immersed in 30 times (m/V) ultrapure water and placed at 4 °C for three times (12 h each time).The mixed liquid was centrifuged (4 000 ×g,15 min) and then collect the supernatant.Next,it was frozen and thawed repeatedly to make the volume 1/3 of the original volume,following precipitated by anhydrous ethanol(95%) to 50% .Finally,after incubating at 4 °C overnight,the crudeRhodiolaroseaL.polysaccharide were obtained by centrifuging(8 000 ×g,10 min).
The crude polysaccharide re-dissolved in distilled water and deproteinated by Sevag (n-butanol and chloroform 1:4,V/V).After protein were removed,the mixture was dialyzed (mw100 kDa) with distilled water for 72 h and lyophilized.The gained polysaccharide(20 mg/L) were further purified by Sephadex G-200 (16 mm ×40 cm).The column was eluted with ultrapure water at 0.1 mL/min,with 1 mL each tube.After measuring the carbohydrate content by the phenol-sulfuric acid method,the main fraction was collected and confirmed by high performance gel permeation chromatography(HPGPC).The pure polysaccharide,named as RLP,was obtained after lyophilization.
2.3 Characterization of RLP
2.3.1 Chemicalcompositionanalysis
The total carbohydrate content of RLP was tested by phenolsulfuric acid method using galactose as standard.The protein content was measured by using the Bradford method.The total uronic acid was measured by usingm-hydroxydiphenyl method.
2.3.2 Molecularweightanalysis
The molecular weight of RLP was measured by HPGPC,a TSK-gel G4000PWxl column (7.8 mm × 300 mm) and a refractive index detector (RID).The mobile phase was ultrapure water at 0.6 mL/min and then the RLP (20 µL,1 mg/mL) was injected and eluted under the same conditions with the column temperature at 30 °C.In order to calculate the molecular weight of RLP,a series of T-series dextran’s (T-10,T-40,T-70,T-110,T-500 and T-2000) were selected to establish the standard curve.
2.3.3 UV-visibleandFT-IRspectroscopyanalysis
The RLP (1 mg/mL) was dissolved with distilled water and the ultraviolet spectrum scanning was performed in the range of 190 nm to 500 nm.
The RLP (1 mg) and dried KBr powder (150 mg) were mixed fully and tableted.The mixed sample was measured by using FT-IR spectrometer ((Bruker VECTOR-22,Karlsruhe,Germany) at the range of 4 000-400 cm-1.
2.3.4 Monosaccharidecompositionanalysis
The RLP (5 mg) and the 1 mL trifluoroacetic acid (TFA,2.0 mol/L)were added into oil bath tube.Then the mixture was oiled by oil bath under 110 °C for 3 h.After that,the degraded sample was blown by N2until dried.Next,in order to remove the TFA,the methanol was added three times.Finally,the hydrolysates were dissolved with ultrapure water and adjusted to the final concentration of 10 mg/L for ion chromatography (IC) (Dionex ICS2500,Thermo,USA) analysis.D-glucose,D-galactose,L-rhamnose,D-xylose,D-mannose,andD-arabinose,D-glucuronic acid andD-galacturonic acid were used as standard up to 10 mg/L.
2.3.5 NMRanalysis
The sample was dissolved with D2O for 2 h and freeze dried for three times.The RLP (50 mg) was dissolved into D2O (0.5 mL) fully and transferred into NMR tube.The1H,13C,COSY,HSQC spectra were measured at room temperature on a Bruker Advance III 400M spectrometer (400 MHz;Bruker Co.,German) [21].
2.4 Animals and animal experiments
Female mice (8 weeks old,weighting (20 ± 2) g) were purchased from the Department of Experimental Animal,Academy of Military Medical Science,Beijing,China.All the mice were under barrier conditions in the Center of Experimental Animals at Tianjin University of Science and Technology.All mice were feed food and water freedom under temperature of (24 ± 1) °C,(50 ± 10)% relative humidity with a 12/12 h light/dark cycle.
After adapting for a week,all mice were divided into five groups(10 mice/group) named as blank group,model group,low and high dose group,and fluorouracil (5-fu) group.The mice of blank group and model group were administered 0.2 mL water once each day.And the mice of low and high dose group were administered by RLP (0.2 mL) with 100 or 300 mg/kg weight every day.After two weeks,the pre-cultured H22 cells (2 × 106cell/mice) were injected into the right armpit of the mice expect the blank group to establish the H22 model [20].Furthermore,the mice of blank,model and RLP group were administered continuously as above while the 5-Fu group(20 mg/kg) were intraperitoneally injected.All groups of mice were oral administrated for another 15 days.At the end of the experiment,all mice were weighed and collected blood from eyeball.Finally,each group of mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation and dissected out the tumor issues immediately.
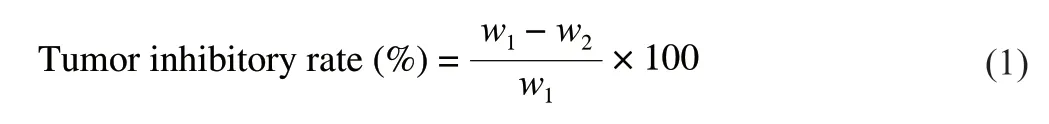
Wherew1represents the average tumor weight of the model group,w2represents the tumor weight of the RLP groups.
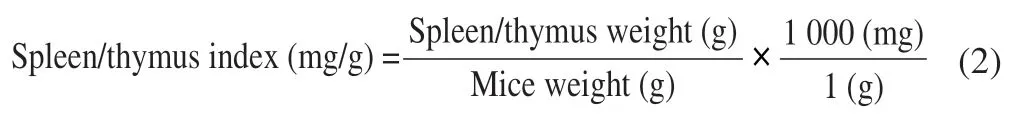
2.5 Blood routine examination
Two hundred microliter blood of each mouse was quickly mixed with anticoagulant (K2EDTA,7.5 μL),and then the sample was detected by XFA-6130 automatic blood analyzer after mixing gently.
2.6 Cell cycle analysis
Tumor issues (0.2 g) were polished by using saline (0.9%) to obtain the cell suspension,next washed with saline for three times.Then the cell suspension was added into the cold 70% ethanol to fixed over 18 h.At the end of fixing,the cell suspension was centrifuged(1 000 ×g,10 min) and washed by using saline for three times to remove ethanol.The mixture (500 µL) of RNase and PI were added into the cell precipitation in dark under 4 °C.After passing cell sieve,the cell cycle was analyzed by using flow cytometer (Becton Dicknson,USA).
2.7 Annexin V-FITC/PI staining assay
Tumor issues (0.2 g) were polished under low temperature by using PBS to obtain the cell suspension.After centrifuging(1 000 ×g,10 min),the 1 × binding buffer (100 μL) were added into the cell precipitation.Next the AV-FITC (5 μL) was added into the cell suspension.Then mixing them,in dark,PI (5-10 μL) was added and then incubated for 15 min.The mixture was made up to 500 μL and detected by flow cytomenter in 1 h.
2.8 Mitochondrial membrane potential detection
The mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) was detected by using the fluorescent probe JC-1.The method of obtaining the cell suspension was the same as above.After that,the cell suspension was treated by the JC-1 working solution according to the assay kit(JC-1) instruction (Solarbio Beijing,China).The ΔΨmwas detected by flow cytomenter.
2.9 Statistical analysis
Experimental data were presented as mean ± standard deviation and an inter-group test was used.The statistical analysis was made by SPSS 19.0 (SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).Significant differences and standard deviation were established through analysis of variance(ANOVA).*P<0.05 was considered as significant,and**P<0.01 was considered as extremely significant.
3.Results and discussion
3.1 Purification and physicochemical properties of RLP
In this study,the crude cold water-soluble polysaccharide was obtained fromRhodiolaroseaL.root (cRLP) after alcohol precipitating (4 °C) and deproteinizing.The yield of cRLP was 2.58% (m/m).The cRLP was then purified by Sephadex G-200,resulted in a final yield of (21.32 ± 0.46)% based on dried cRLP powder.
The results of chemical compositions shown that RLP was consist of total sugar (92.35 ± 0.21)% and uronic acid (27.68 ± 0.45)% which indicated that the RLP was acid polysaccharide.The result of acid polysaccharide was consistent with the research of Xu et al.[7].As shown in the Fig.1A,there were no significant peak in 260 nm and 280 nm in the UV-visible spectrum which indicated that RLP had no nucleic acid and protein [31].
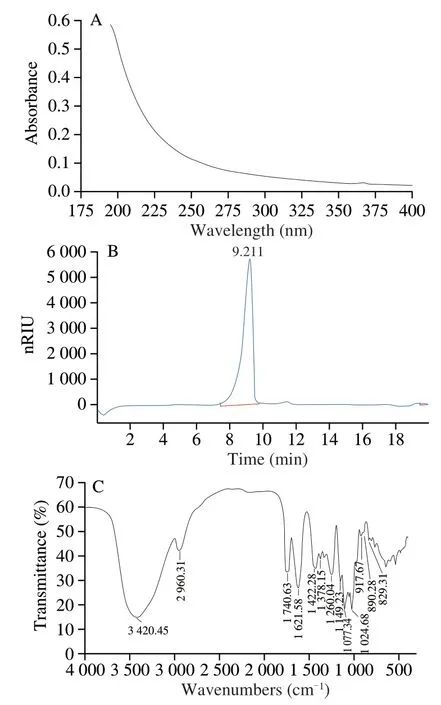
Fig.1 Purification,composition of RLP was carried out by various instruments(A) UV-visible spectrum;(B) HPGPC chromatogram;(C) FT-IR spectrum.
3.2 Primary structure of RLP
3.2.1 HPGPCandFT-IRresults
HPGPC was an effective method to measure the molecular weight of polysaccharide.The HPGPC spectrum of RLP (Fig.1B) shown that RLP was homogeneous polysaccharide.The average molecular weight of RLP was calculated to 1.15 × 106Da by a calibration with standard regression lgmw=-0.352T+9.334 (R2=0.996 6).
The functional groups of RLP could be defined by FT-IR analysis.As shown in the Fig.1C,there was a strong major absorption peak at 3 420.45 cm−1,which revealed the O-H stretching vibrations.And the C-H variable angle vibration were relatively weak at 2 960.31 cm−1and 1 422.28 cm−1.The absorption band at 1 621.58 cm−1and 1 740.63 cm−1were resulted from the presence of C=O and COOH.Furthermore,the absorption band at 1 260.04 cm−1and 1 378.15 cm-1indicated the bending of C-H and C-O bond of carbohyydrates.It was reported that the several bands (1 200-1 000 cm−1) were characteristic for C-O and C-C stretching vibration [23].In addition,the three band at 1 149.23,1 077.34 and 1 024.68 cm−1were due to the pyranose which represented galactose,mannose and glucose [24].The absorption peaks at 917.67 cm−1and 890.28 cm−1proved that there were bothα-configuration andβ-configuration in RLP [25].The characteristic absorption peaks at 890.28 cm−1and 829.31 cm−1further indicated that RLP contained mannose and galactopyranose.Peaks at 1 625.11 cm−1and 1 743.09 cm−1were from the carboxyl and ester carbonyl,respectively.The degree of esterification (DE) value was estimated at 19% according to the equationA1743.09/(A1743.09+A1625.11)(whereAreferred to the peak area),which indicated that RLP was a low methoxylated pectin.Singthong et al.[26]established calibration curve and obtained the DE value according to titrimetric method.Compared with this method and FT-IR,they confirmed that FT-IR was a reliable method for determining the DE value of pectins and there was no significant difference.
3.2.2 Monosaccharidecompositionanalysis
As shown in Fig.2,the sugar composition and molar ratio of RLP were identified and shown by IC analysis that RLP was mainly consist of Rhamnose (Rha),Arabinose (Ara),Galactose (Gal),Glucose (Glu),Xylose (Xyl),Mannose (Man),Galacturonic acid in a molar ratio of 1:3.33:2.87:5.62:0.49:0.32:4.50,which suggested that the RLP was an acidic polysaccharide.The results of confirming uronic acid were consistent with the method bym-hydroxydiphenyl.At the same time,according to monosaccharide composition,the results also confirmed the difference of RLP compared with others [7],which could further confirm the novelty of RLP.
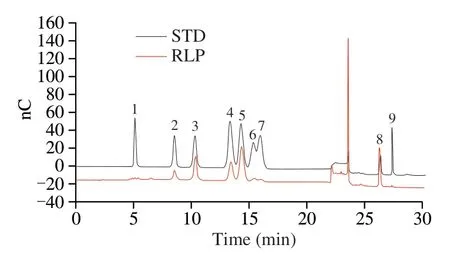
Fig.2 Ion chromatogram of standard monosaccharide (above) and RLP monosaccharide (below): (1) Fucose (Fuc);(2) Rhamnose (Rha);(3) Arabinose(Ara);(4) Galactose (Gal);(5) Glucose (Glu);(6) Xylose (Xyl);(7) Mannose(Man);(8) Galacturonic acid (GalA);(9) Glucuronic acid (GluA).
3.2.3 NMRofRLP
The NMR spectra of1H and13C of RLP were presented in Figs.3A and B.As shown in Fig.3A,in the1H spectrum of RLP,the proton signals almost all appeared in the narrow range ofδ3.56-5.38,which was a typical polysaccharide signal.Generally,then proton signalδ>4.9 wasα-configuration whileβ-configuration in range ofδ4.3-4.9.And according to FT-IR,ion chromatography and previous research,we could infer that the proton H-1 signals atδ5.36,5.26 and 5.19 proved the presence ofα-D-Glu,α-D-Gal andα-L-Araf(residue A) residues The presence ofα-D-Glu,α-D-Gal andα-L-Araf(residue A) residues could be inferred from the proton H-1 signal atδ5.36,5.26 and 5.19 [27-29].In addition,the signal atδ4.60,4.40-4.42,and 4.34 was assigned toβ-D-Gal (residue B),β-D-Man andβ-D-Xyl [30,31].And the proton signal peak atδ1.37 in the high field indicated the presence of Rha (residue C).It could be seen from the Fig.3B that there was an obvious absorption peak at low fieldδ170.70,which indicated that RLP contained uronic acid.Accordingly,in the anomeric carbon region,the faint signals atδ100 and 100.46 indicated the presence ofβ-D-Man andβ-DXyl [29]which was consistent with the result of monosaccharide analysis.And then,the anomeric carbon C-1 signals ofδ107.18/5.36 andδ107.75/5.26 suggested the presence ofα-D-Glu andα-L-Araf[31].The signal atδ107.40/4.60 indicated the presence of →6)-β-D-Galp-(1→,which suggested that there had a substituent on C-4 and the chemical shift would move to low field.The signal absorption peak in the high field region ofδ16.86 was the Rhamnose,which further confirmed the result of1H [33,34].As shown in Fig.3C,the chemical shifts of cross absorption peaks H-2/H-1,H-2/H-3,H-4/H-3,H-4/H-5 in arabinose were atδ4.11/5.19,4.11/3.96,4.24/3.96,4.24/3.82.Subsequently,the C-1,C-2,C-3,C-4,C-5 signals from Fig.3D of arabinose were identified atδ107.75,84.03,85.3,79.3,83.42,which indicated the existences of 1→5 glycosidic linkages in arabinose [35].Combined with COSY and HSQC,the chemical shifts of C-1/H-1,C-2/H-2,C-3/H-3,C-4/H-4,C-5/H-5,C-6/H-6 in galactose were atδ107.40/4.58,71.24/3.69,74.97/3.91,77.16/4.08,72.32/3.58,63.92/3.96,and the linkages was 1→6,which was consistent with 1D NMR and previous researchers.And in rhamnose,the chemical shifts H-2/H-1,H-2/H-3,H-4/H-3,H-4/H-5 were atδ4.09/5.21,4.09/3.92,3.80/3.92,3.80/3.78,1.31/3.78,which indicated the linkages of →2,4)-α-Rha (1→ according to the previous studies [36].The other chemical shifts of monosaccharide were difficult to obtain because of its big molecular weight and the more structure analysis needed to be explored further.
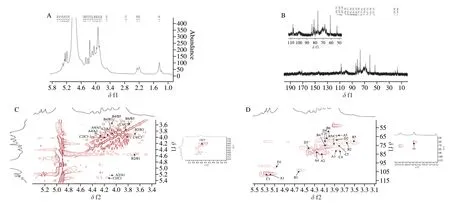
Fig.3 The 1D and 2D NMR spectrum of RLP.(A)1H spectrum;(B) 13C spectrum;(C) COSY spectrum;(D) HSQC spectrum.
Many studies have indicated that the linkages of (1→6)-β-DGalpandα-D-Glu might be the basis reason for immune activity [37].In addition,compared with the study of literature [8],the presence of →5)-α-L-Araf-(1→ of RLP might be the main structure basis to improve biological activities,which was the unique linkages of RLP under low temperature conditions.
3.3 Antitumor effect on H22-bearing mice
3.3.1 Effect of RLP on transplanted cell growth
As shown in Table 2,at the beginning of experiment,the weight of mice was maintained at about 25 g,and there was no significant difference between the dose group.The final body masss of groups apart from 5-Fu were increased.Especially,the reason why final weight of model group increased significantly was the infinite proliferation of H22 cells.In contrast,the average weight in RLP groups were obviously descended compared to model group(P<0.05),which indicated that RLP treatment exhibited the tumor inhibitory effect and few negative impacts.Additionally,compared to the blank group,the mice in RLP groups had normal body mass,healthy appetite and shiny hair.Meanwhile,significant anorexia,lethargy,and thinning hair were observed about mice in the 5-Fu group.And the body mass in 5-Fu group were significant lower compared to model group (P<0.01),indicating that 5-Fu had toxic and side effect while inhibiting tumor cells.
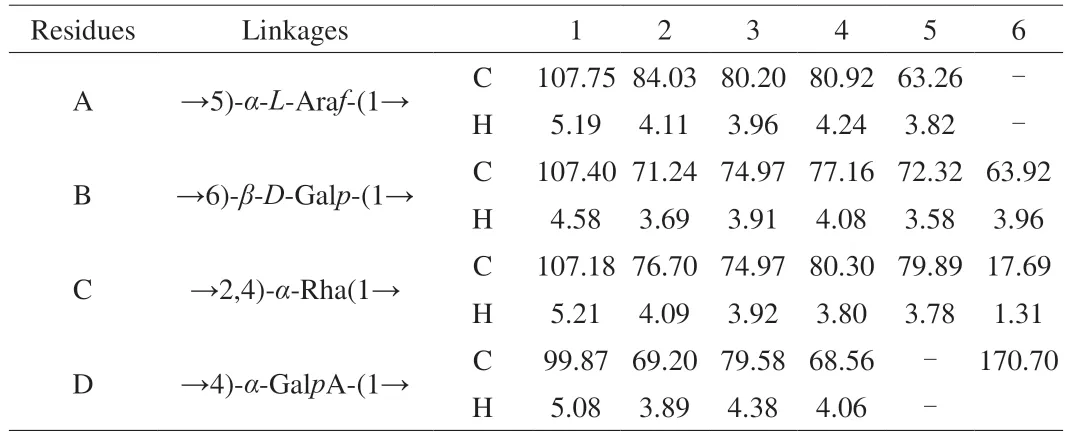
Table 1 Assignments of 1H and 13C NMR spectra for RLP.
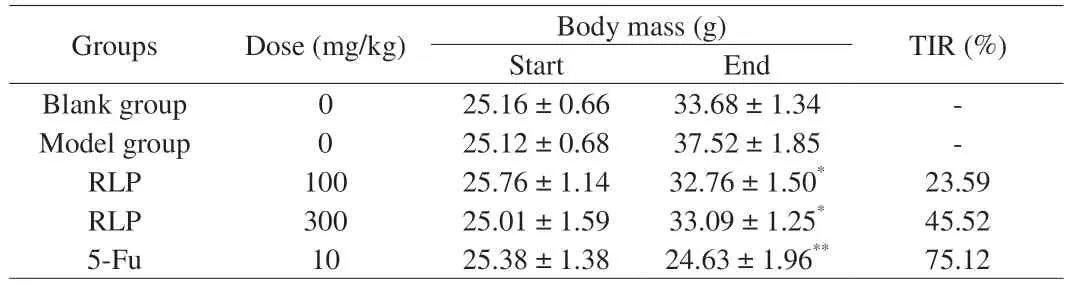
Table 2 Effect of RLP on body mass,number,and tumor rate of mice.
Under normal physiological conditions,the weight and function of immune organs were related to the number of immune cells [38].Therefore,being important immune organs of the body,the thymus and spleen could be used to obtain organ index and assess the strength of the body’s immune function to a certain extent [39].Many studies have found that the atrophy of thymus and splenomegaly were often accompanied by developing of tumors cells [40].To further obtain the inhibitory activity of RLP,the average weight,volume of tumor,the index of spleen,and thymus were noted.It was shown in Fig.4A and B that the average weight and volume of tumor in model group were significant higher compared to RLP dose groups.And the antitumor effect of high dose group (300 mg/kg) was superior to low dose group(100 mg/kg),with the tumor inhibition ratio of 45.52% and 23.59%,which suggested that RLP oral administration could effectively suppress the growth of H22 cell in a dose-dependent manner.Similarly,the literature [8]found a water-soluble polysaccharide fromRhodiola rosea,which could significantly inhibitory the growth of S-180 cells with inhibition ratio of 37.61% .And then,the index of spleen and thymus of H22 mice in different groups were show in Fig.4C.The results shown that the thymus index of the mice in the model group was significantly reduced compared to blank group(P<0.05),while the spleen index was significantly increased(P<0.05),which indicated that the attack of tumor cells severely could damage the thymus and spleen of the tumor-bearing mice.Compared with the model group,the thymus and spleen indexes of H22 mice treated with RLP were significantly improved (P<0.05) with a dose correlation,which indicated that RLP oral administration could effectively protect the immune organs of mice from attacking of H22 cells [41].
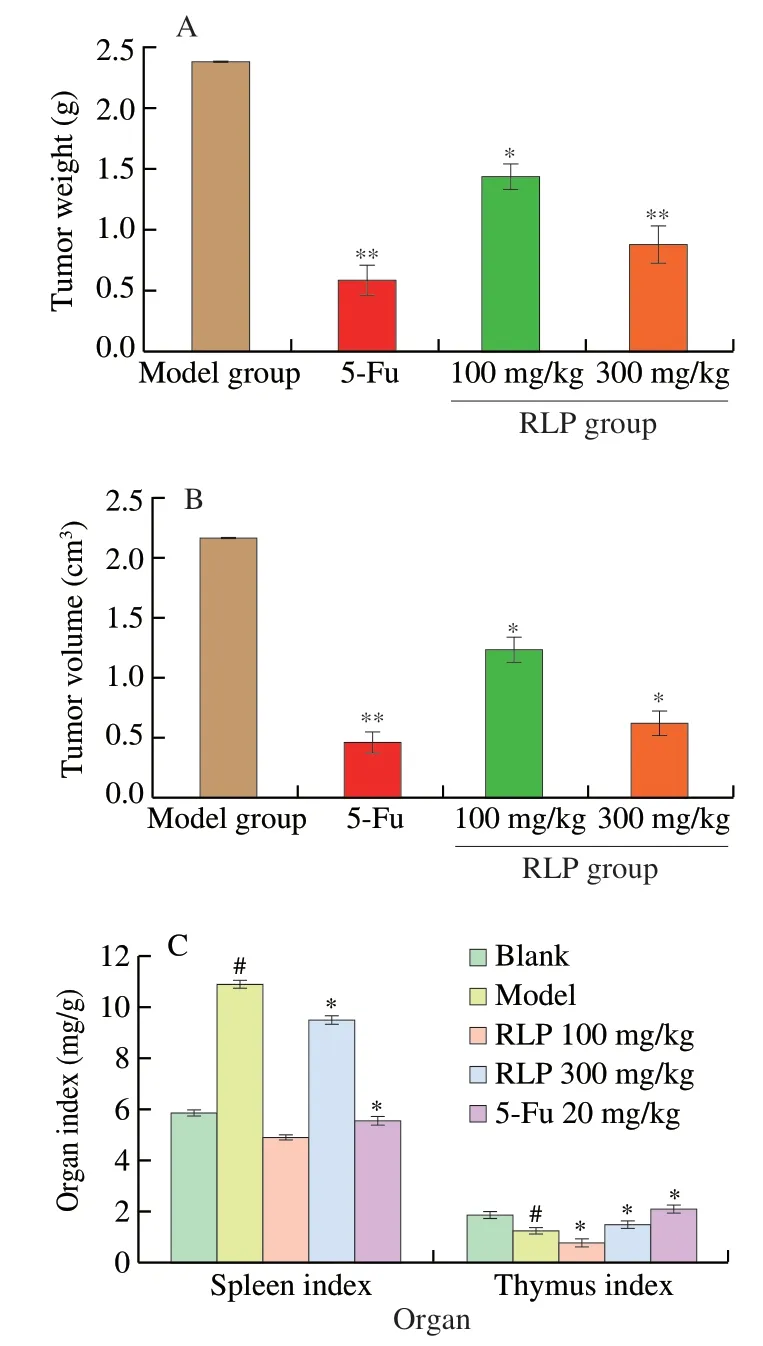
Fig.4 The antitumor effect of RLP on H22 bearing mice.(A) The effect of RLP on weight of tumor at different dose groups;(B) The effect of RLP on volume of tumor at different dose groups;(C) Effects of RLP on spleen index and thymus index.* P <0.05 indicated significant from model group;** P <0.01 indicated extremely significant from model group.# P <0.05 indicated significant from blank group.
Being a conventional chemotherapeutic drug,5-Fu was widely used in clinical H22 treatment and had obvious present inhibitory activities with sorafenib.Our results also shown that the immune organ index of H22 tumor-bearing mice treated with 5-Fu was significantly lower than that of blank group with inhibition ratio of 75.12% (P<0.05),which further illustrated the toxic side effects of 5-Fu on the body’s immune system.In contrast,this study has shown that RLP treatment had no toxic side effect and could inhibitory the growth of tumor cells.
3.3.2 Blood routine examination
The occurrence and development of tumors were not only caused lesions in tissues and organs,but also caused changes in blood components.The blood routine test results of each group of mice were shown in Table 3.Compared with the blank group,the Leucocytes and Platelets in the model group increased significantly (P<0.05),while Erythrocytes and Hemoglobin were all reduced (P<0.05),which indicated that the normal growth and proliferation of H22 cells could cause inflammation,anemia and immunosuppression in tumorbearing mice.Each examination in 5-Fu group were all lower than that in model group (P<0.05),which fully verified the serious side effects of 5-Fu on the body.While compared with model group,each examination has been greatly improved after treating RLP,especially closed to the normal index (RLP,300 mg/kg).The results suggested that RLP could maintain the examination at normal levels and alleviate the additional damage caused by tumor cells so that it could prevent immune dysfunction in tumor-bearing mice and inhibit the malignant proliferation of H22 cells effectively.
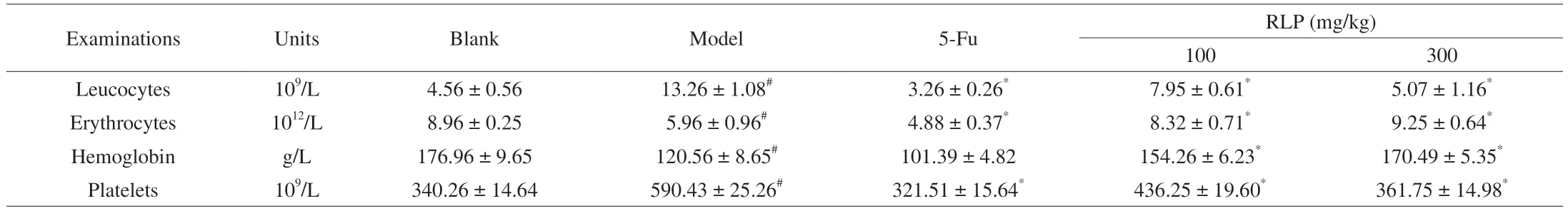
Table 3 Blood routine examination of H22 mice.
3.3.3 Cell cycle assay
The cell cycle arrest could affect tumor growth and induce apoptosis of tumor cell.Many studies have shown that many antitumor drugs can block the cell cycle at a specific site and thus induce apoptosis [13].Cell cycle was composed of G0/G1,S and G2/M,which defined on the DNA content of cell.From the Fig.5,a dose-dependent decrease was also observed in G1/G0 phase from 51.55% (model group) to 45.63% (RLP,100 mg/kg),41.45% (RLP,300 mg/kg) and 36.90% (5-Fu group) as well as in G2/M phase (from 17.23% to 6.06%).The reduction of synthesized RNA and ribosomes in G1/G0 indicated that RLP could induce the disruption of preparing substance and energy [42].More importantly,the RLP treatment could result in accumulation of cells proportion in S phase with a significantly increase from 39.2% (RLP,100 mg/kg) to 52.65% (RLP,300 mg/kg),which suggested that the cell cycle arrest could cause by disruption of DNA replication after RLP treatment [18,43].These results indicated that RLP could induce tumor cell apoptosis by blocking solid tumor cells in S phase and the synthesis of energy and substances,thereby achieving the purpose of inhibiting tumor growth.
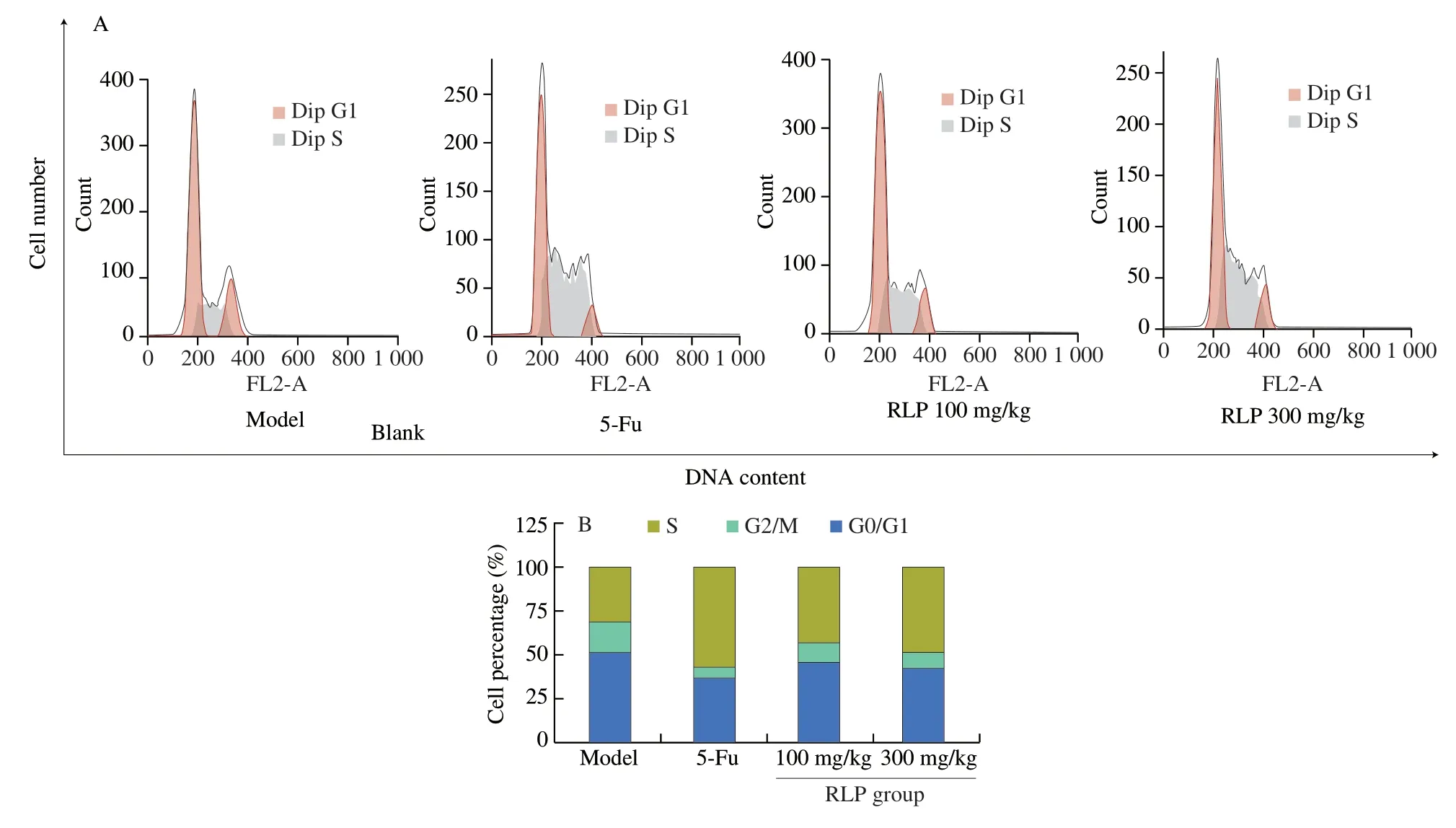
Fig.5 (A) Effect of RLP on cell cycle and apoptotic rates of the tumor in mice;(B) Bar graph of cell population about G0/G1,S,G2/M.
3.3.4 Cell apoptosis assay by Annexin V-FITC/PI
In the process of inducing apoptosis,the phosphatidylserine (PS)of tumor cells will transfer from the inner surface to outside of the plasma membrane.Annexin V,as a Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding protein,was found to have high affinity with PS and could be combined with propidium iodide (PI) to distinguish normal cells,apoptotic cells,and necrotic cells [44].In order to confirm the above cell morphological results,Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining was further used to detect the apoptosis-inducing effect of RLP [45].As shown in Fig.6,with the increasing of RLP dose,the proportion of living cells (Annexin V-/PI-) decreased from 96.6% to 71.7%,31.2% and 26.3%,respectively.In addition,the total apoptosis rate of tumor cells (including early and late apoptosis) increased significantly from 2.36% to 57.90% (P<0.01).And after treating RLP,the proportion of early apoptosis cells (Annexin V+/PI-) increased from 2.25% (model group) to 15.4% (RLP,300 mg/kg),as well as the proportion of late apoptosis cells (Annexin V+/PI+) from 0.12% (model group) to 42.4% (RLP,300 mg/kg),which shown a dose-dependent manner [47].These data further confirmed that RLP could induce apoptosis on H22 tumor cells and further caused changes in apoptosis morphology,which was consistent with the results of TIR and cell cycle.
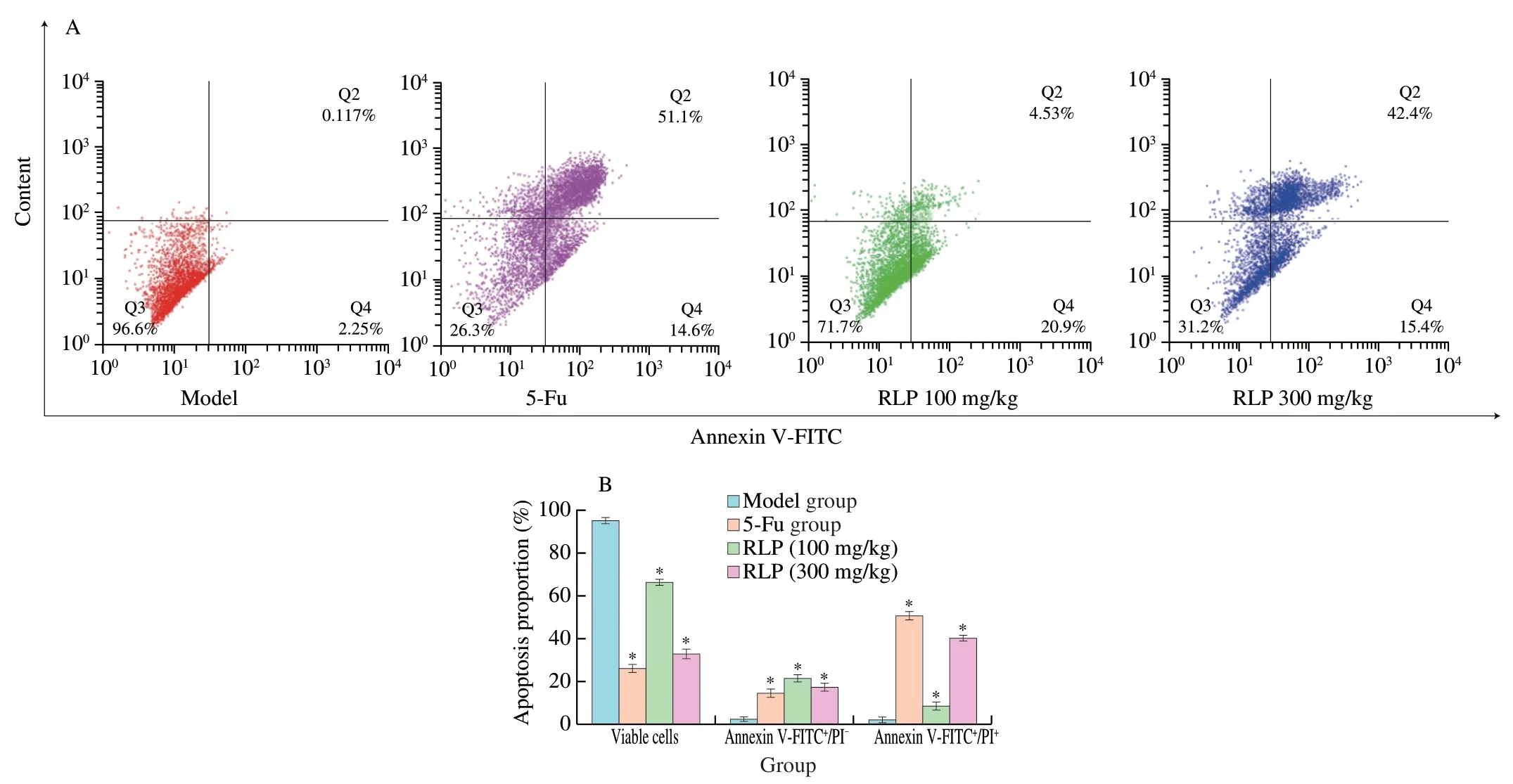
Fig.6 (A) The distribution effect of RLP on viable cells,apoptotic cells,and death cells of tumor issues in different groups;(B) Bar chart of apoptosis percentage.* P <0.05 compared to model group.
3.3.5 Mitochondrial membrane potential detection
As an important organelle of multicellular organisms,mitochondria play an important role in the signal cascade of apoptosis [17].More and more evidence has shown that the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential might lead to mitochondrial dysfunction,which was essential in the process of apoptosis induced by polysaccharide [46].As shown in Fig.7,the mitochondrial membrane potential decreased in a dose-dependent manner after treating with different concentrations of RLP,from 84.6% (model group) to 68.87% (RLP,100 mg/kg) and 42.26% (RLP,300 mg/kg).In addition,the ΔΨmin 5-Fu was significantly lower compared to the model group.According to the results,it could be concluded that RLP might induce apoptosis of H22 tumor-bearing mice cells through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway [47].
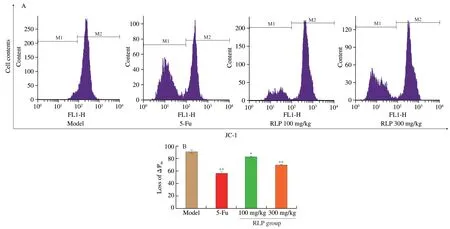
Fig.7 (A) Histograms of the Rh123-stained tumor issue by flow cytometry;(B) Representative bar graph of the mitochondrial membrane potential changes in H22 cells.
4.Conclusions
In this work,a novel cold water-soluble polysaccharide was isolated and purified fromRhodiolaroseaL.root (RLP).Furthermore,its structure and anti-cancer activitiesInvivowere further researched.In addition,the structure of RLP was tested by using HPGPC,FT-IR,IC,NMR,and SEM.More importantly,the growth of tumor cells and immune organs were observed in H22-bearing mice after administration of RLP,and then the cell cycle and apoptosis were detected by AV-FITC/PI and JC-1.The key findings of this study could be summarized as follows:
(I) RLP was an acid heteropolysaccharide with the molecular weight of about 1.15 × 106Da.
(II) RLP was composed of Rha,Ara,Gal,Glu,Xyl,Man,GalA in a molar ratio of 1:3.33:2.87:5.62:0.49:0.32:4.50.
(III) RLP was a pyranose containingα-andβ-configuration,which was consist of→2,4)-α-Rha(1→,→5)-α-L-Araf-(1→,α-D-Glu,→6)-β-D-Galp-(1→,β-D-Man and →4)-α-GalpA-(1→.
(IV) RLP could reduce the damage of cancer for spleen and thymus and inhibit the growth of H22 cells (45.52%).
(V) RLP might destroyed mitochondrial membrane potential and induced tumor cells apoptosisinvivovia mitochondrial pathway
The data indicated that RLP had potential in the treatment of liver cancer,and it provided new ideas for finding natural functional anticancer ingredients and preparations.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31801568);the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City of China (18JCQNJC79300);the Science and Technology Major Special Projects and Engineering of Tianjin City(17ZXYENC00010);the Science and Technology Project of Gaoyou City,Jiangsu Province (GY201812).
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- Colloidal nanoparticles prepared from zein and casein:interactions,characterizations and emerging food applications
- Biological factors controlling starch digestibility in human digestive system
- Preparation methods,biological activities,and potential applications of marine algae oligosaccharides: a review
- Development of hyaluronic acid-based edible film for alleviating dry mouth
- Mushroom β-glucan and polyphenol formulations as natural immunity boosters and balancers: nature of the application
- Preparation of multicore millimeter-sized spherical alginate capsules to specifically and sustainedly release fish oil

