Existence of Approximate Solutions to Nonlinear Lorenz System under Caputo-Fabrizio Derivative
Khursheed J.Ansari,Mustafa Inc,K.H.Mahmoudand Eiman
1Department of Mathematics,College of Science,King Khalid University,Abha,61413,Saudi Arabia
2Department of Computer Engineering,Biruni University,Istanbul,34010,Turkey
3Department of Mathematics,Science Faculty,Firat University,Elazig,23119,Turkey
4Department of Medical Research,China Medical University,Taichung,40402,Taiwan
5Department of Physics,College of Khurma University College,Taif University,P.O.Box 11099,Taif,21944,Saudi Arabia
6Department of Mathematics,University of Malakand,Chakdara Dir(L),Khyber Pakhtunkhwa,18000,Pakistan
ABSTRACT In this article,we developed sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of an approximate solution to a nonlinear system of Lorenz equations under Caputo-Fabrizio fractional order derivative(CFFD).The required results about the existence and uniqueness of a solution are derived via the fixed point approach due to Banach and Krassnoselskii.Also,we enriched our work by establishing a stable result based on the Ulam-Hyers (U-H)concept.Also,the approximate solution is computed by using a hybrid method due to the Laplace transform and the Adomian decomposition method.We computed a few terms of the required solution through the mentioned method and presented some graphical presentation of the considered problem corresponding to various fractional orders.The results of the existence and uniqueness tests for the Lorenz system under CFFD have not been studied earlier.Also,the suggested method results for the proposed system under the mentioned derivative are new.Furthermore,the adopted technique has some useful features,such as the lack of prior discrimination required by wavelet methods.our proposed method does not depend on auxiliary parameters like the homotopy method,which controls the method.Our proposed method is rapidly convergent and,in most cases,it has been used as a powerful technique to compute approximate solutions for various nonlinear problems.
KEYWORDS Lorenz system;CFFD;fixed point approach;approximate solution
1 Introduction
Fractional calculus has gotten considerable attention in the last few decades.This is because of numerous applications in various fields of science and technology.Many real-world problems where hereditary properties and memory characteristics are involved can be comprehensively explained by using fractional calculus.For recent applications and interesting results,we refer to[1–4].Keeping in mind the valuable uses of the said area,scientists have given much attention to investigating fractional order differential equations (FDEs) from various aspects.They developed the existence theory of solutions very well.Also,a large number of articles have been framed about numerical analysis and optimization theory for the said area.Also,researchers have developed stability results for various problems of FDEs.For the aforesaid area,we refer to [5–8].Recently,various results related to fractional order chaotic systems have been investigated(see[9–12]).
In recent times,some new types of fractional differential operators have been introduced.The concerned definitions have been obtained,preserving the regular kernel instead of the singular one.In this regard,in 2015,Caputo et al.[4] introduced a new operator for fractional order derivatives,abbreviated here as CFFD.By using this new operator,researchers have developed numerous results,including existence theory and numerical solutions for various problems(see[13–16]).
Keeping the importance of FDEs in mind,various real-world problems have been investigated by using concepts of fractional calculus.Because fractional differential operators geometrically provide accumulation for a function,which includes its integer counter part as a special case.Also,in various cases,it has been found that fractional order derivative is more powerful than classical and describes the dynamics of various real world phenomena with more details(see[17–19]).Therefore,researchers have used FDEs in the study of dynamical problems of different natures.Among these real-world problems,Lorenz studied the Lorenz system first.The said problem has a chaotic solution for some parametric and initial values.
The said famous classical Lorenz system has been described in[20]given by
where the constantssigma,gammaandbare system parameters proportional to Prandtl,Rayleigh,and certain physical layer dimensions.The quantities involved are x,which is proportional to the rate of convection,y,which is proportional to the variation in horizontal temperature,and z,which is proportional to the variation in vertical temperature.The Lorenz system has many applications in simplified models for lasers,thermosyphon,brushers,DCmotors,electric circuits,chemical reactions,forward osmosis,etc.Due to the interesting behavior of the aforesaid model,the Lorenz system has been investigated by many researchers.
Keeping in mind the importance of the said model,it has never been investigated till now by using CFFD.
Instead of ordinary calculus fractions,order derivatives and integrals are more practical in nature and preserve a greater degree of freedom.Using this type of operator,additional short and longmemory terms are better explained.Because power law singular kernels are used in Caputo and Reimann-Liouville operators.in numerical discretization,it causes difficulties.Therefore,by using those differential operators which involve exponential type kernels,the descriptions of some problems are more easily understood.Therefore,in this regard,the first one,which is increasingly used as CFFD,The Lorenz model has been investigated under various fractional order concepts by using different techniques.In most cases,researchers have investigated the approximate solution of the Lorenz model by using differential transform techniques [21],the homotopy perturbation method[22],and the Adomian decomposition method[23],etc.Also,authors[24]have studied the fractional order Lorenz system by using the homotopy analysis method.Further authors [25] investigated the numerical-analytical solution of nonlinear fractional-order Lorenz’s system.But in all the mentioned studies,the existence theory of the fractional order Lorenz system has not been investigated.
Also,to the best of our knowledge,the Lorenz system under CFFD for semi-analytical solutions by using Laplace Adomian decomposition has never been investigated.Therefore,we update the model(1)under CFFD as given in(2)as
whereα∈(0,1]andCFDtdenoted CFFD,where we take values for the parameters asσ=10,b=8/3,γ=28.
It is a tedious job to deal with problems under the concept of fractional calculus for their exact or numerical solutions.Several algorithms,tools,and procedural theories have been established during the past few decades.A dynamical problem should be first treated for the criteria of its existence.Because,without knowing about its existence,we do not implement other techniques to compute numerical or semi-analytical results.For the existence theory,various tools have been developed.For instance,fixed point approaches,coincidence degree theories due to Mawhin and Schauder,etc.,have been used very well.The most powerful one is the use of the fixed point approach to investigate a dynamical problem whether it has a solution or not (see [6]).On the other hand,numerous tools,including perturbation and decomposition techniques,have been used to approximate solutions to various dynamical problems(for details,see[26–30]).The mentioned tools have been used in excessive numbers for classical fractional order problems.Also,those problems involving the CFFD have been treated by using the homotopy and decomposition methods in various articles;for instance,see a few as[31–37].
Inspired by the aforesaid work,we are going to derive some adequate results for the existence of approximate solutions to the nonlinear system given in(2)under CFFD.We apply some fixed point approaches due to Krassnoselskii and Banach to establish the existence theory for the solution of the intended problem.Some stability results are also provided here in this work by using the U-H concept.Also,some approximations for the solution are established via a hybrid method due to the Laplace transform and Adomian decomposition.We also present some graphical representations of Lorenz equations using computational software such as Matlab.
Our work is organized as: We first provide some literature and refer to it in Section 1.In the Section 2,we recollect some elementary results.In Section 3,we provide our first portion of the main results.In Section 5,stability results are developed.In Section 4,we provide general algorithms of analytical results.In Section 5,some graphical presentations are provided.Finally,we will give a brief conclusion.
2 Elementary Results
Definition 2.1.[4]Let h ∈H1(0,θ),θ >0,α∈(0,1),then the CFFD is recalled as
M(α)is called a normalization function which obeys M(1)=M(0)=1.Also if h is not in H1(0,θ),then we have
Definition 2.2.[4]For the function h,the Caputo-Fabrizio integral is define as
Lemma 2.1.[4]Let l ∈L[0,θ],forα∈(0,1],if right hand sides vanish at 0,then the solution of
can be calculated as
Definition 2.3.[4]The Laplace transform ofCFDtαh(t)with M(α)=1 is given as
Definition 2.4.Here we setI=[0,θ] and 0≤t≤θ <∞and define the Banach space asX=C([0,θ]×R,R)equipped with norm as
Theorem 2.5.[38]Let X be a Banach space andΩ:X→X be a contraction operator with constant 0≤K<1,thenΩhas a unique fixed point.
Theorem 2.6.[38]If U be a closed,bounded and convex subset of X,the equation S1(V)+S2(V)=V has at leat one fixed point,where S1,S2satisfy
1.S1(V)+S2(V)∈U for every V ∈U;
2.S1is contraction;
3.S2is continuous and compact.
Theorem 2.7.Inview of conditions x>0,y>0,z>0 at allt≥0,then the approximate solution of the model(2)satisfies x≥0,y≥0,z≥0,for allt>0.
Proof.Proof Keeping in mind the initial data of solution of the model(2),it is obvious that
therefore x≥0,y≥0,z≥0,for allt≥0.
3 Main Result for the Model(2)
This portion is devoted to the first part of our main results.Here we establish the existence criteria for our adopted model(2).We set the model(2)as
while f,g,h:I×R2→Rare continuous functions.Using Lemma 2.1 and applyingCFI tαon both sides of(4)and plugging values of initial conditions,one has
Further,we can write(5)as
where
We need the following hypothesis to be exist for onward analysis.
(A1)Subject constants Lψ >0,for every V,∈X,one has
(A2)For constantsCψ,Cψ >0 and Mψ >0,one has
|ψ(t,V(t))|≤Cψ|V|+Mψ.
Using(6)and(7),we define two operators as
Theorem 3.1.Thank to hypothesis(A1,A2)and continuity ofψ,integral Eq.(6)has at least one solution under the condition
Proof.Consider a closed bounded set as U={V ∈X:‖V‖∞≤ρ,ρ >0}of X,we have to derive that S1:U→U is contraction.Let V,∈U,we have
Hence S1is contraction.
For S2to be relatively compact,consider V ∈U,one has
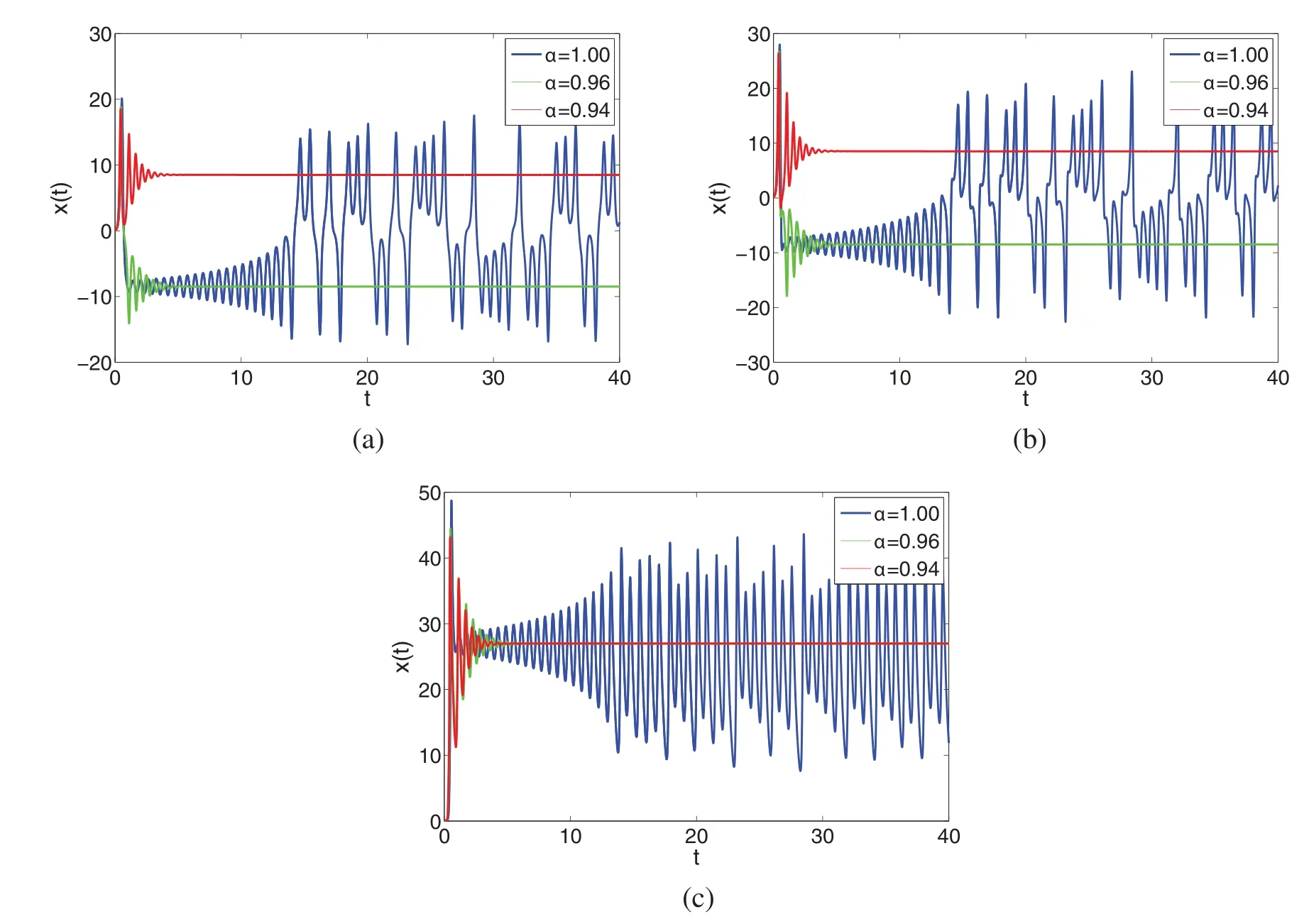
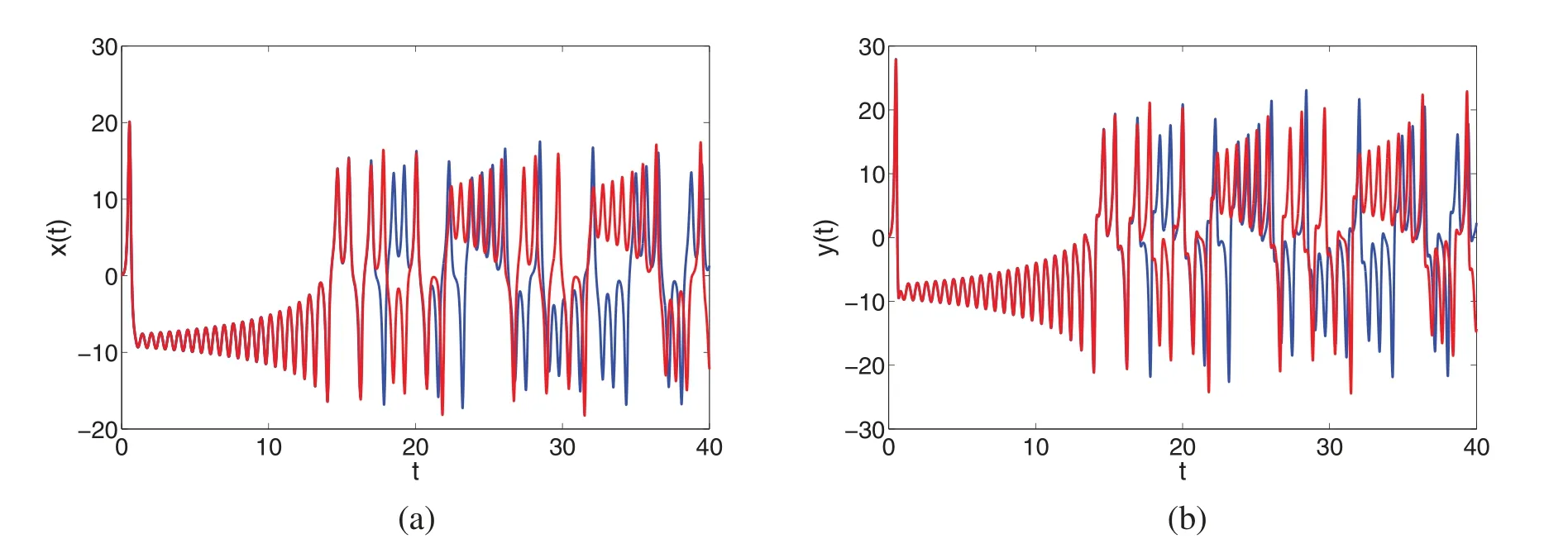
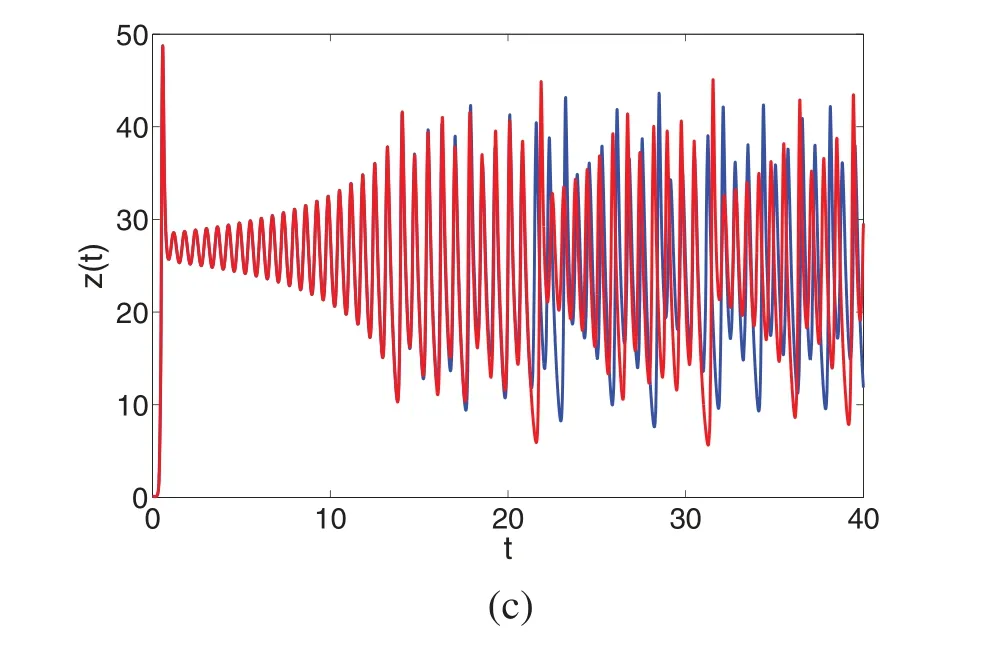
Hence (9) implies that S2is bounded.Alsoψis continuous so is S2.In same fashion,one can deduce that S2is equi-continues by takingt1 Since att2→t1,we observe that right side in(10)vanish.Also as S2is bounded and continuous operator overI.So ‖S2(V)(t2)−S2(V)(t1)‖∞→0,ast2→t1. Therefore S2is relatively compact as uniformly continuous.Thus the operator S2is completely continuous.Inview of Theorem 2.6,the problem(2)has atleast one solution. Theorem 3.2.Together with hypothesis(A1) and if the condition<1 holds,then the considered system(2)has a unique solution. Proof.Let defineΩ:X→X by As a result,Ωis contraction,and the proposed system(6)has a unique solution,implying that the Lorenz system(2)has a unique approximate solution. Here we recollect basic notions for U-H stability from[1,2,8,15] Definition 4.1.The integral Eq.(6)is U-H stable withδ >0 if for inequality we have at most one solutionand constantCψ,with Also the integral Eq.(6) is generalized U-H stable if there exists a nondecreasing mappingν:(0,1)→R+such that withν(0)=0. The given remark is needed. Remark 1.Letφbe a function independent of V ∈X and also vanishes at zero,such that 1.|φ(t)|≤δ,at every,t∈I; 2.CFDαtV(t)=ψ(t,V(t))+φ(t),at every,t∈I. Remark 2.Let the perturbed problem be described as Then the solution of(13)is computed as Hence using Remark 1,(14)yields where Theorem 4.2.Inview of hypothesis(A1)and using Remarks 1 and 2,the solution of the integral Eq.(2)is U-H stable if Moreover,the approximate solution of the model(2)is generalized U-H stable. Proof.Let V,∈X be any solution and at most one solution respectively of the problem(6),then one has From(16),upon simplification one has Thus(6)is U-H stable.Settingν(δ)=δ,then(17)yields Obviously in (18),we see thatν(0)=0.Hence we conclude that the model (2) is U-H and generalized U-H stable,respectively. We first develop a general algorithms for approximate solution to(2)as Using initial condition,(19)yields The solution we are computing can be expressed as Also,the nonlinear terms can be decomposed as Here few initial terms of Adomian polynomials are computed from(22)as n=0:P0(x,z)=x0z0, n=1:P1(x,z)=x1z0+x0z1, n=2:P2(x,z)=x2z0+x1z1+x2z0, n=3:P3(x,z)=x3z0+x2z1+x1z2+x0z3 and so on. Thus we calculate few terms(23)as n=0:Q0(x,y)=x0y0, n=1:Q1(x,y)=x1y0+x0y1, n=2:Q2(x,y)=x2y0+x1y1+x2y0, n=3:Q3(x,y)=x3y0+x2y1+x1y2+x0y3 and so on.Using(21),(22)and(23)in(20),we have Comparing terms on both sides of(24),we have Applying inverse Laplace transform to both sides of(25),the following result can be obtained Using D1=σ(y0−x0),D2=γx0−y0−x0z0,D3=−bz0+x0y0,then one has from(26),we have and so on.In this way the other terms are easy to compute.From(27),the approximate solution for each compartment of the model can be written as Theorem 5.1.[34]If X be the Banach spaces andΩ: X→X is a contraction operator,then for V,∈X,we have Using Banach theoremΩhas a unique fixed point V,withΩ(V)=V,where V=(x,y,z).The series given in(28),we can rewrite as Also V0=V0∈Uρ(V),with Uρ(V)=we have 1.Vn∈U ⊂X; 2.limn→∞Vn=V0. A phase portrait is a geometric description of a dynamical system’s paths in the phase plane.The collection of initial conditions is represented by a separate curve or point.Phase portraits are an immensely valuable tool in the study of dynamical systems.They are comprised of a structure of common state-space trajectories.This shows whether the selected parameter values have an attractor,repeller,or limit cycle.Phase portraits of a dynamical system can be used to study the directed characteristics of that system.In Fig.1,the phase portraits of the approximate solution given (28)are shown for the first five terms.Here we use values of parameters from[20]to present the obtained five-term solution graphically. Figure 1:The phase portraits presenting the dynamics of the attractor in the system(2)with different fractional orders A time series is a collection of data points that are indexed (listed or graphed)vs.timetin mathematics.It is a collection of points taken at evenly spaced intervals over a period of time.As a result,it is just a collection of discrete-time data.The time series includes sunspot counts and ocean tide heights,to name a few.Time series analysis depicts the behavior of state variables for each tiny value of time in the case of dynamical systems.Analyzing the time series data makes it simple to study the system’s stability and instability.In Fig.2,we show the behavior of x(t),y(t) and z(t) vs.timetwith various fractional orders using five terms of solution.Here we use values of parameters from[20]to present the obtained five-term solution graphically. When a system is chaotic in its nature,it shows sensitive dependence on initial conditions.A very small change results in a great change in the dynamics of the system when it has chaotic behavior.Therefore,we present the dependence of our considered system on initial conditions.In Figs.3a–3c,the sensitivity of x(t),y(t) and z(t) are presented.For the blue line in Fig.3,initial conditions are considered as[x0,y0,z0]=[0.1,0.1,0.1],while for the red line the initial conditions are considered as[x0,y0,z0]=[0.1,0.1,0.105].From the sensitivity of different state variables of the system(2),it is observed that the system highly depends upon initial conditions and is very sensitive.This proves the chaos in system(2).Here we use values of parameters from[20]to present the obtained five terms solution graphically. Figure 2:The dynamics of the state variables in the system(2)with different fractional orders vs.t Figure 3: (Continued) Figure 3:The sensitivity of the state variables in the system(2)towards initial conditions vs.t In the present work,we have derived some theoretical results based on some fixed point theorems due to Banach and Krassnoselskii for the existence and uniqueness of approximate solutions and their computation corresponding to the famous Lorenz nonlinear dynamical system.Sufficient conditions have been developed for the existence and uniqueness of solutions to the proposed model.Also,utilizing U-H and generalized U-H concepts,we have derived a few results for stability under some conditions for the considered system.Further,using a hybrid technique based on the Laplace transform and the Adomian decomposition method,we have also established an algorithm for approximate solutions.Some chaotic behaviors of the Lorenz system have been presented under the given fractional order by using five terms of approximate solution.Also,convergence and sensitivity of the model have been discussed.The proposed method has some features like being easy to implement,no need for prior discretization,and neither depends on auxiliary parameters like the homotopy analysis method.Also,the method is rapidly convergent in many cases.In future,we will investigate the aforesaid Lorenz model under piece-wise equations with fractional order derivative. Funding Statement: The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of Taif University Researchers Supporting Project No.(TURSP-2020/162),Taif University,Taif,Saudi Arabia.The authors extends their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through research groups program under Grant No.R.G.P.1/195/42. Conflicts of Interest:The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.4 Stability Results
5 Algorithms for Approximate Solution of the Model(2)
5.1 Some Graphical Investigation

5.2 Time Series Analysis
5.3 Sensitivity Towards Initial Conditions
6 Conclusion
 Computer Modeling In Engineering&Sciences2023年5期
Computer Modeling In Engineering&Sciences2023年5期
- Computer Modeling In Engineering&Sciences的其它文章
- Explicit Topology Optimization Design of Stiffened Plate Structures Based on the Moving Morphable Component(MMC)Method
- Towards a Unified Single Analysis Framework Embedded with Multiple Spatial and Time Discretized Methods for Linear Structural Dynamics
- Developments and Applications of Neutrosophic Theory in Civil Engineering Fields:A Review
- Surface Characteristics Measurement Using Computer Vision:A Review
- Recent Progress of Fabrication,Characterization,and Applications of Anodic Aluminum Oxide(AAO)Membrane:A Review
- Challenges and Limitations in Speech Recognition Technology:A Critical Review of Speech Signal Processing Algorithms,Tools and Systems
