Mechanism of action of verbascoside in mice with Parkinson's disease based on molecular docking, molecular dynamics and in vivo experiments
ADILAI Aibibuli, KELIBINUER Saidierding, LU Ran-ran, YANG Xin-ling
The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 841100, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the improving effect of verbascoside on Parkinson's disease (PD) model mice and to clarify the possible mechanism.Methods: 60 C57BL/6 male mice were randomly divided into normal group, model group, low, middle and high dose groups (30,60 and 120 mg/kg, respectively).After a week of adaptive culture, except for the blank group, the subacute model of PD was established by intraperitoneal injection of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1 (MPTP)in each group for 5 consecutive days.After a week of adaptive culture, except for the blank group, the subacute model of PD was established by intraperitoneal injection of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1 (MPTP) in each group for 5 consecutive days.The establishment of the model, the drug group was intragastrically administered continuously for 7 d, and the mice in the normal group were injected with the same amount of saline.The behavioral changes of mice were observed by open field test, pole climbing test and grip test; the morphology, apoptosis and Nissl bodies of substantia nigra neurons were observed by HE staining and Nissl staining;the ultrastructural changes of neurons were observed by transmission electron microscope;the positive expressions of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), α-synuclein (α-Syn) and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) were detected by immunohistochemistry.The protein levels of TH, α-Syn,TLR4, NF- κB and P-NF-κB in substantia nigra of mice were detected by Western blot,and the levels of inflammatory factors IL-1 β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF- α)in serum were detected by Elisa.Molecular docking was used to verify the binding ability of verbascoside to TLR4/NF- κB signal pathway and related factors, and molecular dynamics was used to verify the binding mode and stability of verbascoside with compounds.Results:compared with the normal group, the total walking distance, average speed, free activity time,pole climbing time and forelimb grip in the model group were significantly longer than those in the normal group (P < 0.05).The ultrastructural changes of neurons, nuclear lysis, deformation and mitochondrial damage were observed under transmission electron microscope, and the number and morphological changes of HE staining substantia nigra neurons were decreased(P < 0.05).Nissl staining showed that the number of Nissl positive cells decreased (P < 0.05), the positive expression of TH decreased and the positive expression of α-syn and TLR4 increased (P < 0.05).Western blotting showed that the expression of TH protein decreased, the expression of α-syn, TLR4, NF- κ B p65 protein increased (P < 0.05), and the expression of IL-1 β, IL-6 and TNF-α in serum increased significantly (P < 0.05).Compared with the model group, the activity ability of mice in the treatment group was significantly improved (P< 0.05), the morphology of neurons gradually recovered and the number of neurons increased (P< 0.05).The number of Nissl positive cells increased (P < 0.05).The expression of TH protein increased, while the expression of α-syn, TLR4, NF- κ Bp65 protein decreased (P < 0.05),and the expression of IL-1 β, IL-6, TNF- α in serum decreased significantly (P < 0.05).The results of molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation show that the combination of mulberry glycoside with the compound is good and the property is stable.Conclusion:verbascoside has protective effect on PD mice, and its mechanism may be related to TLR4/NFκ B pathway, and then regulate neuroimmunity.
1.Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common progressive neurodegenerative disease associated with aging.Data show that more than 7 million people worldwide are affected, estimated to reach more than 12 million by 2040[1].PD is characterized by selective loss of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of substantia nigra and abnormal accumulation of α-synuclein(α-Syn) to form cytoplasmic inclusion bodies.The clinical manifestations are characterized by motor disorders such as tremor,stiffness, slowness of movement, postural and gait instability[2].Although the exact cause of PD is not clear, more and more studies have shown that inflammation can induce and / or aggravate PD symptoms[3].Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear transcription factor kappaB (NF-κB) is an important inflammatory signaling pathway that plays an important role in degenerative neurological diseases such as PD by regulating the body’s immune response and regulating cell apoptosis[4].Therefore, clarifying the relationship between the occurrence and development of neuroinflammation and PD and taking effective measures can help to improve PD.
Modern pharmacological research shows that many Chinese herbal medicines and extracts with anti-inflammatory and antineuroinflammation properties have also been proven to be beneficial in the treatment of PD[5].Cistanche deserticola is a valuable traditional Chinese medicine growing in desert and extremely arid areas.it has the functions of tonifying kidney and strengthening yang, moistening intestines and laxative, improving immunity, and even has been given the reputation of “desert ginseng”[6].Domestic and foreign scholars have found that Cistanche deserticola plays an increasingly important role in the prevention and treatment of neurological diseases, with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor and cognitive function improvement effects[7], Verbascoside(VB) is A phenylethanol glycoside plant compound extracted from Cistanche deserticola, its specific pharmacological mechanism in PD has not been fully elucidated.In this study, the PD mouse model was established by intraperitoneal injection of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1(1-methyl-4-phenyl-1) (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1-methy4-phenyl-3-tetrahydropyridine hydrochloride), in order to study the protective effect of VB on PD model mice and its mechanism.
2.Materials and Methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Animals
60 SPF grade C57BL/6 male mice, aged 8 to 10 weeks, weighing(20 ±2) g, were purchased from Sibef Biotechnology Co., Ltd.Laboratory animal license number: SCXK (Beijing) 2019-0010.All the mice kept the temperature of the feeding room at (22.4±2.6) ℃, ate and drank freely, and alternated light and dark for 12 h.The research procedure has been approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Xinjiang Medical University (IACUC-20230217-46) and given humane care according to the 3R principle used by experimental animals.
2.1.2 Reagents
VB (batch number 61276-17-3, Chengdu Ruifensi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); MPTP (batch number 23007-85-4, MCE company);TLR4 antibody (batch number 66350-1-Ig, Protentech company);NF-κ B p65 antibody, P-NF-κ B p65 antibody, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) antibody (batch numbers 4242S, 3033S, 58844S,Cell Signaling Technology) α- Syn antibodies, GAPDH antibodies(batch numbers ab51253, ab181602, Abcam company); HRP labeled sheep anti-rabbit second antibody (batch no.S0001Graver Affinity Co., Ltd.), HRP labeled sheep anti-mouse second antibody(batch No.SA00001-1 Proteintech Co., Ltd.); ELisa kit for enzymelinked immunosorbent assay of interleukin-1 β (IL-1 β), IL-6(interleukin-6,IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (batch number JL18442-96T, JL20268-96T, JL10484-96T, Jianglai biology).
2.1.3 Instrument
Open field experimental analysis system (Shanghai Jisun Software Technology Co., Ltd.); Mouse gripper (Huaibei 900 Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.); positive microscope (Japan Nikon instrument Co., Ltd.); Transmission electron microscope (Japan HITACHI Co., Ltd.); protein electrophoresis instrument, chemiluminescence analyzer (Beijing Liuyi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Animal modeling,grouping and drug administration
60 male C57/BL mice were randomly divided into normal group,model group and different dose groups of VB.According to the previous literature report[8, 9], VB group was divided into low,middle and high dose groups (30,60 and 120mg/kg respectively)with 12 rats in each group.After 1 week of adaptive feeding, the normal group was given the same volume of normal saline, and the other groups were intraperitoneally injected with MPTP (30mg/kg) for 5 days to establish PD subacute model, and the treatment group was given continuous administration for 7 days.After the last administration, the mice in each group were subjected to open field test, pole climbing test and grip test, and then were killed under anesthesia.
2.2.2 Draw materials
Intraperitoneal injection of 1% pentobarbital sodium (50 mg/kg) anaesthetized, half fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, the rest collected serum and isolated midbrain substantia nigra on ice and placed in cryopreservation tube.
2.3 Animal behavior analysis
2.3.1 Open field test
Open field experiment is a commonly used sensory exercise test,which is used to evaluate the movement activities of rodents and the ability to explore new environments.Sixteen squares with the same size are formed at the bottom of the activity box with the size of 50×30×20cm.Put the mouse on the corner of the box facing the wall,and record its motor function within 3 min with video equipment.After each test, thoroughly disinfect and clean the instrument to avoid odor influence.
2.3.2 Pole climbing test
This experiment is a special test to evaluate the motor coordination ability of mice.The pole-climbing equipment consists of a rod with a high 50 cm and a diameter of 1cm, and a ball with a diameter of 2 cm on the top of the rod for placing mice.Place each mouse on top of the pole, face up, and observe the time it takes for the mouse to get from the top to the bottom of the pole.Each group was tested for 3 times, and the 1min recovery time was averaged each time.
2.3.3 Grip test
In the grip test, the neuromuscular strength of mice was evaluated by a gripper.Place each mouse on the metal grid of the gripper,and when both front claws firmly grasp it, the experimenter gently pulls the tail in the other direction, and the force sensor records the maximum grip.Each mouse was tested for 3 times and the average value was taken.
2.4 Transmission electron microscope
Remove the substantia nigra of the midbrain, fix it with 2.5%glutaraldehyde for 24 h, rinse with 0.1 m phosphoric acid, fix it with 1% Osmic acid for 2 h, and rinse again with 0.1 m phosphoric acid for three times.Then dehydrated, fixed, sliced, stained with lead citrate and observed by transmission electron microscope.
2.5 Nissl staining
The prepared brain tissue sections were dewaxed and dehydrated in turn.Put the slices in toluidine blue solution, infect 30min in a thermostat at 50-60 ℃, rinse slightly with distilled water, rapidly differentiate with 95% alcohol, dehydrate with anhydrous ethanol,transparent xylene, resin seal, air dry, microscopic examination.
2.6 HE staining
The cut slices were dewaxed and dehydrated, the slices were placed in hematoxylin solution 8 min, washed away hematoxylin hydrochloric acid alcohol differentiation, moved into eosin solution to dye 2 min, rinsed with running water, dehydrated and sealed.
2.7 Immunohistochemical method
The prepared brain tissue sections were dewaxed and dehydrated.Brain tissue sections were placed in antigen repair solution, and 5 min was repaired by high pressure antigen.When the temperature dropped to room temperature, PBS was used to rinse for three times,then hydrogen peroxide blocker was added, and PBS was washed for 15 min at room temperature, and one antibody was added to incubate at 4 ℃ overnight.After rinsing for three times, the goat anti-rabbit IgG polymer was added and incubated at room temperature for 1 h.PBS rinse with DAB chromogenic solution for three times, rinse 5min with tap water after optimal color reaction under microscope,add hematoxylin to re-dye 3 min, rinse with tap water, dehydration,resin seal to dry, microscopic examination.
2.8 Western blot
The nigra tissues of mice in each group were ground into powder and added with appropriate amount of RIPA lysate.After BCA protein was quantified, SDS--PAGE gel electrophoresis was performed and the membrane was transferred.After sealing at room temperature for 2 h, one antibody was added to 1V1 000 and overnight at 4 ℃.Rinse with TBST for three times, add second antibody and incubate at room temperature for 2 h.After washing with BST for 3 times, color development, exposure and imaging are performed.
2.9 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay(Elisa)
The blood 1.5 mL of mice in each group was centrifuged for 10 min at 4 ℃ and 3 000 r/min, and then the blood was stored at-20 ℃.The levels of IL-1 β, IL-6 and TNF- α inflammatory factors were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (Elisa) kit.All operations are carried out in strict accordance with the instructions of the kit.
2.10 Molecular docking
Search and download the 3D structure of TLR4, NK- κ B,IL-1 β, IL-6 and TNF-α from RCSBPDB (http://www.rcsb.org) database) and download the 3D structure of VB from ZINC database.The protein receptor is dehydrated, hydrogenated and minimized by AutoDockTool software.AutodockVina is used for molecular docking and the results are calculated.The binding energy is less than-5kJ/mol indicating that the receptor has a certain binding activity with the compound.The lower the binding energy is, the more stable the docking effect is.The results were visualized by PyMOL software.
2.11 Molecular dynamics
In this molecular dynamics simulation, the Gromacs2022.3 version was used to simulate the receptor protein with the lowest binding energy to the ligand.The simulation conditions were carried out at static temperature 300 K and atmospheric pressure (1 Bar).The force field was Amber99sb-ildn, the solvent was water molecule(Tip3p water model), and the total charge of the simulation system was neutralized by adding appropriate amount of Na+ions.The molecular dynamics simulation system first minimizes the energy by the steepest descent method, and then performs 100 000-step isothermal isobaric ensemble (NVT) equilibrium and isothermal isobaric ensemble (NPT) equilibrium with a duration of 100 ps.Finally, the free molecular dynamics simulation is run, which has a total of 5 000 000 steps and a total time of 100ns.After the completion of the simulation, the trajectory was analyzed, and the root mean square deviation (RMSD) of each amino acid trajectory was calculated.
2.12 Statistical processing
The data were analyzed by SPSS27.0 software, and the measurement data were expressed by x variables±s.LSD-t test was used for comparison between the two groups, and t ‘test was used for variance.
3.Results
3.1 Effects on the behavior of mice in each group
3.1.1 Open field test
Compared with the mice in the normal group, the total distance walked by the mice in the model group was significantly shortened,the average speed decreased, and the free activity time was less(P<0.05, P<0.01); compared with the model group, the mice in the VB medium and The total distance traveled and walking speed of mice in the high-dose group were significantly extended, and the free activity time of mice in the low-, medium-, and high-dose groups of VB was significantly increased.(P<0.05, P<0.01).(Table 1, Figure 1)
Tab 1 Comparison of the results of open field test in each group of mice(n=12, ±s)

Tab 1 Comparison of the results of open field test in each group of mice(n=12, ±s)
Note: compared with the normal control group,*P<0.05,**P<0.01; compared with the model control group,#P<0.05,##P<0.01, the same below
Free activity time (s)Normal group 1250.1±296.5 7.0±1.7 170.9±5.4 Model group 869.9±298.1** 4.8±1.7** 157.3±15.3*Low dose group 971.7±186.2 5.4±1.0 170.8±5.9#Middle dose group 1178.1±243.8# 6.5±1.4# 171.6±5.4##high dose group 1237.7±226.2## 6.9±1.3## 174.3±2.5##F 5.218 5.447 8.047 P 0.001 <0.001 <0.001 Group Total distance (cm) Average speed(cm/s)
3.1.2 Pole climbing test
Compared with the normal group, the coordination of limbs in the model group became worse and the total pole climbing time was significantly longer in the model group, while the total pole climbing time in the middle and high dose groups of VB was significantly shorter than that in the model group.(P < 0.05, P < 0.01) (Table 2)
3.1.3 Grip test
Compared with the normal group, the coordination of limbs in the model group became worse and the total pole climbing time was significantly longer in the model group, while the total pole climbing time in the middle and high dose groups of VB was significantly shorter than that in the model group.(P< 0.05,P< 0.01) (Table 2)
3.2 Effects on ultrastructural changes of substantia nigra neurons in mice in each group
Transmission electron microscope showed that in the normal group,the substantia nigra neurons had large cell body, rich cytoplasm,intact nuclear membrane, obvious nucleolus, uniform distribution of chromatin, normal mitochondrial morphology and oval shape,while in the model group, the neuron cell morphology changed, the nucleolus decomposed, the structure was blurred, the mitochondria swelled and degenerated, the mitochondrial crest disappeared,and vacuolar changes appeared.After administration, the structure of neurons gradually recovered, the nucleolus was obvious, the abnormal chromatin in the nucleus decreased, and the morphology of mitochondria was improved.(Figure 2)
Tab 2 Comparison of the results of pole climbing test and grip test in each group of mice(n=12, ±s)
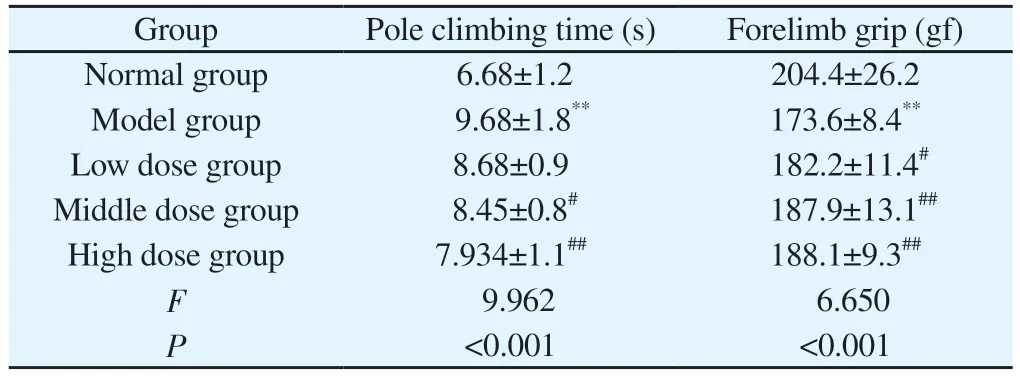
Tab 2 Comparison of the results of pole climbing test and grip test in each group of mice(n=12, ±s)
Group Pole climbing time (s) Forelimb grip (gf)Normal group 6.68±1.2 204.4±26.2 Model group 9.68±1.8** 173.6±8.4**Low dose group 8.68±0.9 182.2±11.4#Middle dose group 8.45±0.8# 187.9±13.1##High dose group 7.934±1.1## 188.1±9.3##F 9.962 6.650 P<0.001 <0.001
3.3 Results of HE staining and Nissl staining in substantia nigra of mice in each group
As shown in the picture, the structure of substantia nigra neurons in the normal group was intact, the morphological structure of the cells was normal, the edge of the nucleus was clear, and the Nissl body was blue.Compared with the normal group, the number of neurons in the model group decreased and the cell morphology and structure changed.the number of Nissl positive cells decreased (P< 0.05).After VB treatment, the morphology and structure of neurons in the middle and high dose groups were significantly better than those in the model group, the number of neurons and Nissl positive cells increased (P < 0.05, P < 0.01).(Table 3, figure 3)
Tab 3 Results of the number of substantia nigra neurons and Nissl positive cells in each group(n=3, ±s)

Tab 3 Results of the number of substantia nigra neurons and Nissl positive cells in each group(n=3, ±s)
Group Number of neurons Nissl body positive cell Normal group 73.67±13.50 39.67±8.88 Model group 39.33±6.03* 15.00±3.00*Low dose group 48.67±3.79 21.33±2.52 Middle dose group 60.67±4.51## 26.00±2.65##High dose group 65.33±3.79## 35.67±4.51##F 10.379 12.188 P 0.001 <0.001
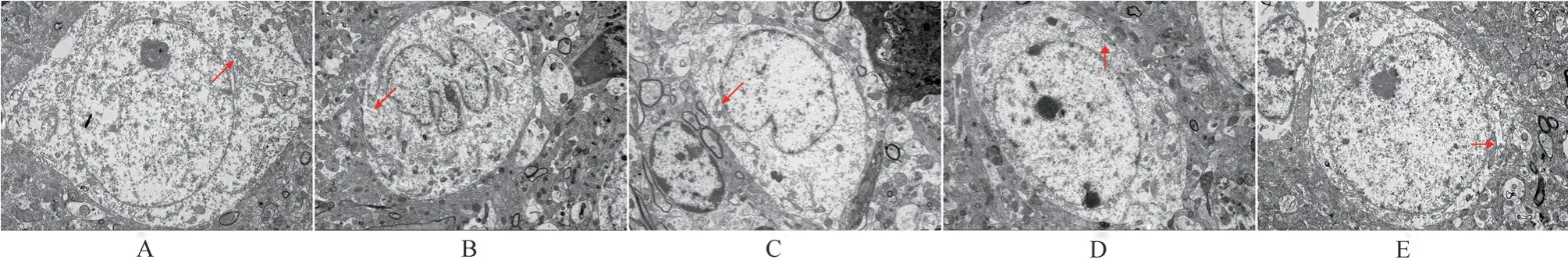
Fig 2 Ultrastructure of substantia nigra neurons in each group (6 000×)
3.4 Immunohistochemical results of TH, α-Syn and TLR4 in substantia nigra of mice
Compared with the normal group, the level of TH protein in the substantia nigra of the model group decreased and the levels of α-Syn and TLR4 increased (P < 0.05), compared with the model group,the positive expression of TH in the substantia nigra of mice in the low, middle and high dose groups of VB increased, and the positive expression of α-Syn and TLR4 decreased in the middle and high dose groups of VB.(Table 4, figure 4)
3.5 Expression of TH, α-Syn, TLR4, NF-κB p65 and P NF-κB p65 proteins in substantia nigra of mice
Compared with the normal group, the expression of TH protein in the model group decreased, while the expression of α-Syn, TLR4 and NF-κB increased significantly in the middle and high dose groups of VB, while the expression of TLR4, NF-κB decreased in the middle and high dose groups of VB, and the protein level of NFκB p65 decreased significantly in the low, middle and high dose groups of VB (P < 0.05).(Table 5, figure 5)
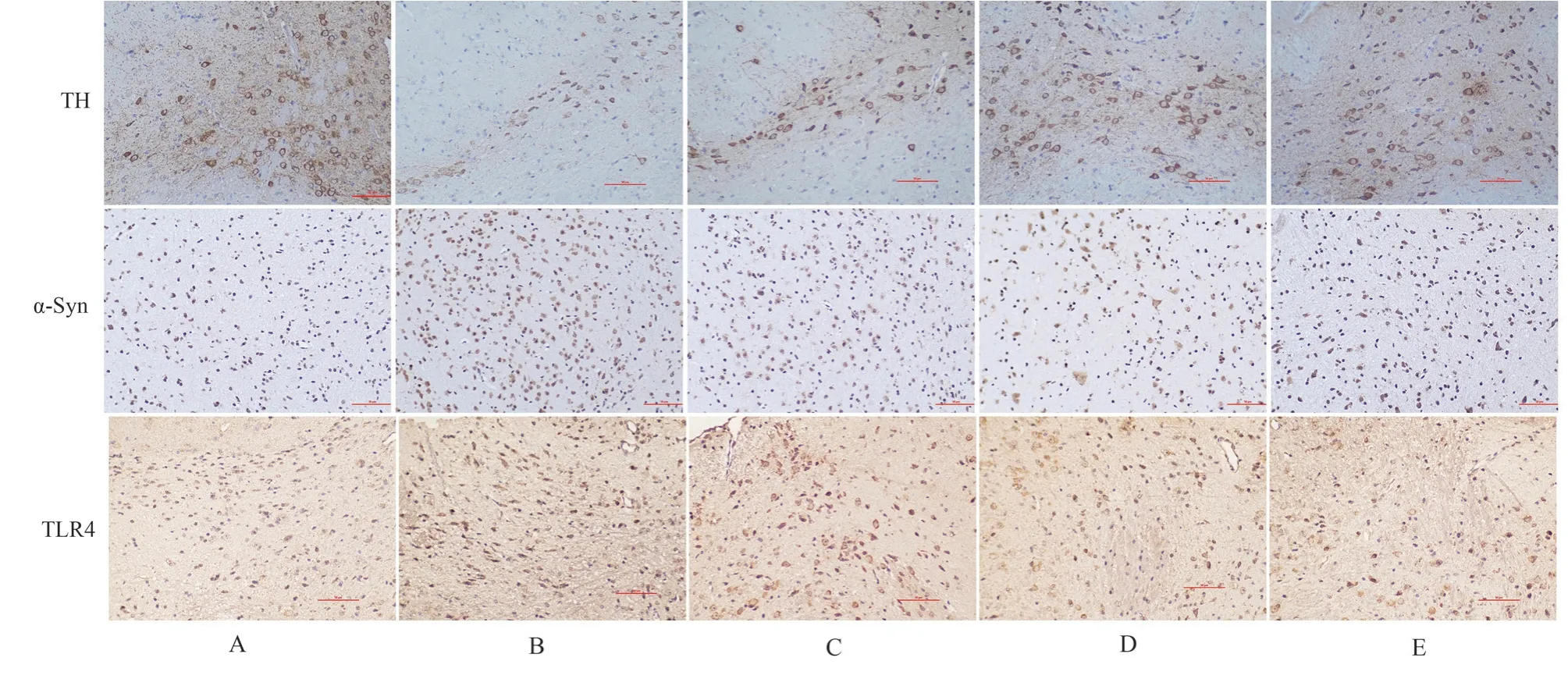
Fig 4 Positive expression of TH, α-Syn and TLR4 in substantia nigra of mice in each group (200 ×)
Tab 4 Comparison of positive expressions of TH, α-Sy and TLR4 in substantia nigra of mice in each group(n=4,±s)

Tab 4 Comparison of positive expressions of TH, α-Sy and TLR4 in substantia nigra of mice in each group(n=4,±s)
Group TH α-Syn TLR4 Normal group 0.378±0.021 0.183±0.040 0.217±0.015 Model group 0.195±0.031** 0.263±0.028* 0.347±0.015**Low dose group p 0.265±0.042# 0.225±0.026 0.320±0.010 Middle dose grou 0.323±.056## 0.220±0.014# 0.287±0.021#High dose group 0.335±0.053## 0.193±0.022## 0.263±0.015##F 11.000 5.209 30.878 P<0.001 0.008 <0.001
3.6 Effect on inflammatory factors in mice
Compared with the normal group, the serum levels of IL-1 β, IL-6 and TNF-α in the model group increased significantly (P < 0 01),and the contents of IL-1 β, IL-6 and TNF-α decreased significantly in different dose groups of VB (P < 0 05, P < 0 01).
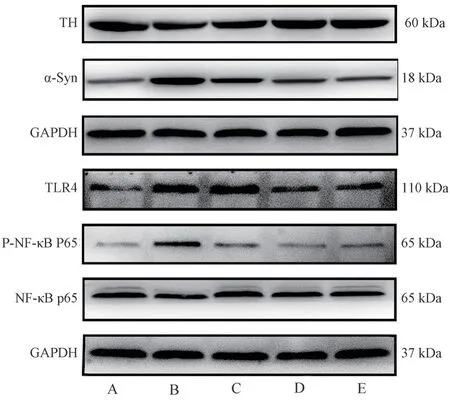
Fig 5 Expression of TH, α-Syn, TLR4, NF-κB p65 and P-NF-κB p65 proteins in substantia nigra of mice in each group.
Tab 5 Expression level of TH, α-Syn, TLR4, NF- κ B p65 in substantia nigra of mice in each group(n=4,±s)

Tab 5 Expression level of TH, α-Syn, TLR4, NF- κ B p65 in substantia nigra of mice in each group(n=4,±s)
Group TH/GAPDH α-Syn/GAPDH TLR4/GAPDH P-p65/p65 Normal group 1.15±0.11 0.47±0.09 0.67±0.14 0.60±0.15 Model group 0.79±0.08** 1.36±0.11** 1.11±0.05** 1.01±0.09**Low dose group 0.89±0.10 0.83±0.18 1.09±0.12 0.75±0.19#Middle dose group 0.99±0.12# 0.60±0.14# 0.93±0.13# 0.67±0.14##High dose group 1.03±0.10## 0.54±0.08# 0.69±0.06## 0.61±0.04##F 9.381 25.338 16.584 6.569 P<0.001 <0.001 <0.001 0.003
3.7 Molecular docking
The results of molecular docking show that the binding energies of VB to TLR4, NF-κB, IL-1 β, IL-6 and TNF-α are all less than-5 kJ/mol, which are-24.35 kJ/mol, -21.92 kJ/mol, -28.12 kJ/mol,-18.91 kJ/mol and-22.18 kJ/mol, respectively.The hydrogen bond structure is stable, indicating that VB has a good binding ability to the core target, thus playing an anti-inflammatory role.Use PyMOL to visualize some of the docking results, as shown in figure 6.
Tab 6 Levels of IL-1 β,IL-6 and TNF-αin serum of mice in each group (n=3,pg/mL, ±s)

Tab 6 Levels of IL-1 β,IL-6 and TNF-αin serum of mice in each group (n=3,pg/mL, ±s)
Group IL-1β IL-6 TNF-α Normal group 6.899±1.273 28.397±1.165 37.777±2.662 Model group 23.556±2.809** 37.003±1.726** 56.241±3.875**Low dose group 15.865±1.578# 35.245±1.462 49.486±3.354 Middle dose group 12.634±0.987## 32.530±0.923## 43.764±3.289#high dose group 10.065±.1.710## 30.909±.1.086## 39.741±2.819##F 38.290 20.543 16.336 P<0.001 <0.001 <0.001
3.8 Molecular dynamics
In order to clarify the interaction mode between VB and proteins and factors at the molecular level, molecular dynamics simulations were carried out.RSMD represents the distance between different structures and the same atom, and the RSMD of proteins and small molecules can reveal the position change between the conformation and the initial conformation during the simulation process.The lower RSMD value indicates the high stability of the protein, while the larger RSMD indicates that the structural conformational change of the skeleton occurs in the simulation time, and the general change range is less than 1 means that it is stable.In the initial stage of the simulation (0-6000ps), the conformation changes to some extent,but after 6000ps, the RMSD curve tends to be stable and the protein conformation is gradually stable.In particular, the RMSD fluctuation of TLR4 and TNF-α is slightly larger than that of other proteins.(Figure 7)

Fig 6 Results of docking of mulberry glycoside with TLR4, NF- κ B, IL-1 β, IL-6 and TNF-α molecules

Fig 7 RMSD values for molecular dynamics simulations of VB with proteins
4.Discussion
PD is a complex neurodegenerative disease.The main neuropathological feature is the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra compact, accompanied by the accumulation of misfolded α-syn to form Lewy bodies[10].Although the etiology of PD is unclear, strong evidence from clinical and epidemiological studies suggests that neuroinflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of PD[11].At present, drug therapy is mainly used to improve symptoms and slow down the progress of the disease, these treatments can not completely cure the disease, the urgent need to identify effective PD treatment drugs has become an important challenge.Cistanche deserticola is one of the valuable herbs in traditional Chinese medicine.In recent years,Cistanche deserticola and its extract have shown extensive and complex neuropharmacological activities against nervous system diseases[12, 13].VB is one of the main effective components of Cistanche deserticola.More and more studies have found that it has strong immune regulation and anti-inflammatory ability against various diseases, such as septic myocarditis[14], proctitis[15],Neuroinflammation after cerebral hemorrhage[16] etc.However, there are no relevant reports on whether VB can improve PD symptoms by regulating neuroinflammation.Therefore, this study further explores this.
Inflammatory responses are usually related to the activation of different receptors.TLR4 is a pattern recognition receptor, a type I transmembrane glycoprotein, which is expressed in immunerelated cells and various cells of the nervous system.TLR4 may be an important immune receptor in PD[16, 17].A survey of human postmortem brains analyzed through transcriptomic data showed that TLR4 expression was higher in different brain regions of PD patients, with the most obvious upregulation in the substantia nigra and putamen[18], Increased ,TLR4 has also been observed in the blood of PD patients[19].The TLR4 signaling pathway is complex and involves a variety of molecules.The first one is the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, which is involved in immune and inflammatory responses.NF-κB is a transcription factor required for the expression of many inflammatory mediator genes and can regulate IL-1β and TNF-α.release of inflammatory factors[20].Studies have shown that misfolded α-Syn participates in the imbalance of TLR4-mediated signal pathway in microglia, which eventually activates NF-κB,triggering the production and release of TNF-α and IL-6[21].TH is a rate-limiting enzyme involved in dopamine biosynthesis.TLR4 deficiency can increase the expression of TH protein, reduce the number of α-Syn positive neurons, regulate the activation of NFkappa B, and reduce the release of inflammatory factor IL-1β, thus reducing neuroinflammation[22].
In this study, the mouse PD model was established by intraperitoneal injection of MPTP.The results of open field test, pole climbing test and grip test showed that VB could reduce the motor symptoms of PD mice and increase the ability of limb movement and coordination.Transmission electron microscope showed that VB restored the dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra damaged by MPTP, and the structure of organelles such as nucleus and mitochondria were clear.The results of HE staining and Nissl staining showed that VB could restore the morphological structure of dopaminergic neurons, increase the number of Nissl positive cells,and protect dopaminergic neurons.In order to further study whether VB is affected by TLR4/NF- κ B signal pathway, the expression of α-Syn, TLR4 and PmurNF-κ Bp65 in substantia nigra of PD mice was significantly increased, while the expression of TH was decreased.After treatment with VB, the protein expression of α-Syn, TLR4 and PmurNF-κ Bp65 decreased significantly, while the expression of TH protein increased.The inflammatory factors IL-1 β, IL-6 and TNF- α in the serum of mice were detected by Elisa.The results showed that VB reduced the levels of IL-1 β,IL-6 and TNF-α in the serum of PD mice, thus alleviating the neuroinflammation.The molecular docking technique was used to verify the binding energy between VB and key targets.The binding energies of VB to TLR4, NF-κ B, IL-1 β, IL-6 and IL-1 were all less than-5 kJ/mol, indicating that it had good binding activity.Through molecular dynamics simulation of docking process, it was found that the protein complex fluctuated to some extent in the early stage, but then tended to be stable, in which TLR4 and TNFα fluctuated greatly, which may be related to the specific structure of the protein, which explained the relationship between VB and protein from the molecular level.
To sum up, VB has a protective effect on PD mice, reducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors and reducing inflammation,and its mechanism may be related to the inhibition of TLR4/NF-κ B pathway.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年24期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年24期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Meta-analysis of the impact of hyperuricemia on contrast agent-related acute kidney injury after percutaneous coronary intervention
- Research progress on the drug action and resistance mechanism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Macrophage-derived exosomes mediate mir-222 targeting Caspase-10 to promote glioma proliferation
- Mechanism of Sanshi decoction inhibits macrophage pyroptosis by inhibiting BRD4/NF-κB/ NLRP3 pathway in the treatment of gouty arthritis
- Effects of female body mass index on embryo development and ART outcomes
- Prediction of potential targets and molecular mechanisms of Tripterygium hypoglaucum for oral lichen planus based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
