Human-artificial intelligence interaction in gastrointestinal endoscopy
John R Campion,Donal B O'Connor,Conor Lahiff
Abstract The number and variety of applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy is growing rapidly.New technologies based on machine learning (ML) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are at various stages of development and deployment to assist patients and endoscopists in preparing for endoscopic procedures,in detection,diagnosis and classification of pathology during endoscopy and in confirmation of key performance indicators.Platforms based on ML and CNNs require regulatory approval as medical devices.Interactions between humans and the technologies we use are complex and are influenced by design,behavioural and psychological elements.Due to the substantial differences between AI and prior technologies,important differences may be expected in how we interact with advice from AI technologies.Human–AI interaction (HAII) may be optimised by developing AI algorithms to minimise false positives and designing platform interfaces to maximise usability.Human factors influencing HAII may include automation bias,alarm fatigue,algorithm aversion,learning effect and deskilling.Each of these areas merits further study in the specific setting of AI applications in GI endoscopy and professional societies should engage to ensure that sufficient emphasis is placed on human-centred design in development of new AI technologies.
Key Words: Artificial intelligence;Machine learning;Human factors;Computer-aided detection;Colonoscopy;Adenoma detection rate
INTRODUCTION
Artificial intelligence (AI) encompasses a wide variety of applications for sophisticated computer algorithms that use large volumes of data to perform tasks traditionally thought to require human intelligence[1].There is a growing list of current and proposed applications for AI in medicine,including direct patient interaction with AI chatbots to answer patient queries,analysis of a large amount of disparate data to predict disease diagnosis and course,and interpretation of images from radiological investigations[2-4].In gastroenterology,potential clinical applications span from use of domainspecific large-language models (LLMs) in the triage of specialist referrals to prediction of early-stage pancreatic cancer before it becomes overtly visible on imaging[5,6].
Following the development of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for computer-aided detection and diagnosis of pathology in the fields of radiology and dermatology,gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy became an area of early research into applications of CNNs in medicine[7-10].Among the most promising initial applications of AI in GI endoscopy were computer-aided detection (CADe) and computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) of premalignant polyps during colonoscopy using machine learning (ML) systems[11,12].These applications were prioritised in an effort to improve adenoma detection rate (ADR) and to differentiate premalignant polyps from those without malignant potential,with the attendant possibility of reducing incidence of colorectal cancer (CRC) and reducing costs and complications associated with unnecessary polypectomy[13,14].Additional applications have developed rapidly to include detection and diagnosis of other pathology in upper and lower GI endoscopy,capsule endoscopy and biliary endoscopy.There has also been initial exploratory use of LLMs to aid decision-making on management of early CRCs and patient-facing applications to determine adequacy of bowel preparation prior to colonoscopy[15-19].
While initial results on colorectal polyp CADe showed impressive improvements in key metrics of colonoscopy quality[20],some subsequent real-world studies showed more modest effects or even no effect,and noted an increased rate of unnecessary resection of non-neoplastic polyps[21-23].It is possible that factors involved in real-world human-AI interaction (HAII) are a driver of such differences between experimental and real-world results[24].
More than most other advances in medical science,successful implementation of AI platforms will depend not solely on the technical success and technical efficacy of the platform,but equally on the ability of the technology to interact with its human operators[25].There was early adoption of CADe technology in the field of breast radiology,based on experimental evidence of benefit[26].Analysis of real-world data from those systems later showed that early iterations contributed to greater resource utilisation due to false positives and increased additional radiological investigations[27].It is an important lesson for application of AI in GI endoscopy,that effectiveness of AI platforms and their impact on patient outcomes can only be properly assessed in real-world settings.Despite the high speed of progress in development and roll-out of new applications for AI in GI endoscopy,the real-world effects of AI on clinician decision-making remain underexplored[28].Multiple factors can affect HAII at each phase of the development and deployment of an AI platform(Figure 1).Areas of interest in the interaction between humans and AI in GI endoscopy,which will be explored in this review,include: (1) Human design choices in creation of AI platforms and their user interfaces;(2) Regulatory processes and interventions for new AI platforms;(3) Human factors influencing user interaction with AI platforms;and (4)Clinician and patient attitudes toward individual platforms and AI broadly.
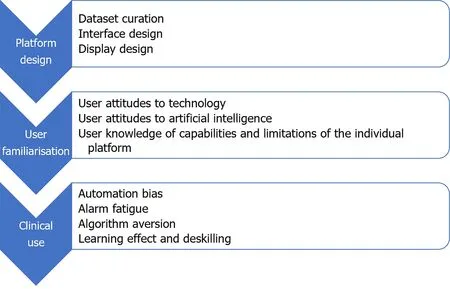
Figure 1 Major factors affecting human–artificial intelligence interaction in gastrointestinal endoscopy by phase of platform development and deployment.
FROM HUMAN–COMPUTER INTERACTION TO HUMAN–AI INTERACTION
Growth in use of information and computer technologies in the 1980s led to recognition of the importance of studying the relationship between humans and these new technologies[29].The field of human–computer interaction (HCI) sought to investigate social and psychological aspects of interactions that would influence the acceptability and utility of these new technologies[30].Humans interacted with early computers by inputting codeviakeyboard,but as humans’ methods of interacting with technology have become more sophisticated,the influences on and impact of HCI have also become more complex[31].Ease of use is recognised as an important driver of uptake of new technological products or platforms[32].
Psychological aspects of HCI were extensively explored in the pre-AI era.The ‘computers are social actors’ (CASA)theory held that,because psychological mechanisms evolve over centuries rather than decades,the human brain reflexively treats any entity with human-like abilities as human[29,33].Recent work has queried the durability of the CASA effect,and suggested that the human brain’s treatment of interactive technology as human may relate more to a technology’s relative novelty than to its existence[34].Whether human operators innately regard new technologies as tools or as other humans has significant ramifications for how the presence of AI may affect human performance.
A key question with regard to technological development in any sector is that of function allocationi.e.deciding which roles should be performed by the human and which by the technology.AI has led to a rapidly burgeoning cadre of tasks that can be performed by technology,with an ever-diminishing number of tasks the sole preserve of humans[29].Since the conception of AI,there has been disagreement between researchers on what the aim of AI should be;to replace human labour or to augment human performance.The prevailing view on this has changed from one position to the other frequently in the intervening period[35].At the current juncture,it appears that the decision will be made by the speed at which the technology can be developed,rather than by specific ethical considerations.A contrast between HCI and HAII is seen in the view by the former that computers and new technologies should be assistive,whereas the latter field recognises that AI has the possibility to replace human efforts entirely in some instances,so-called agential AI[36].
ALGORITHM DESIGN AND INTERFACE DESIGN
CADe and CADx platforms based on CNNs are created by training the programme on large volumes of datae.g.images and videos with a defined diagnosis,allowing the programme to learn patterns in the images that are suggestive of the presence of pathology or of the specific diagnosis of interest[37].Design of CADe and CADx systems requires the selection,curation and annotation of a large number of images of relevant pathology,to use as ‘ground truth’ for training and testing of the algorithm,while design of LLMs require large volumes of text data.Selection and curation of such image or text data represents the first point of contact between humans and the AI platform.There are several ways in which human decisions on training and design can influence the long-term operation of the AI platform.The functioning of the AI platform after its creation and the mechanism by which it arrives at its decisions are both opaque,with the processes being described as a ‘black box’[38].The possibility of building biases into the platform’s functioning makes selection of the best possible training database imperative,as unintended consequences of biased training data have been shown in other applications to have negative consequences on health outcomes for patients from minority groups[39].
Difficulties can arise due to a number of problems with the training dataset,giving rise to different types of selection bias.When a CADe algorithm is trained using images from prior colonoscopies,those images are typically compressed and altered in the process of saving them to a database.The compression may introduce artefact and alter the value of the image for the CNN’s learning.It may also cause changes to the image that are imperceptible to the human but integrated into the algorithm’s processing.Choosing images that are too idealised may lead the algorithm to be poor at detecting pathology that deviates from archetypal descriptions[40].There is also concern that if a CNN is trained on data that comes from homogenous Western populations in the most developed countries,this may weaken the algorithm’s ability to give appropriate advice in racially diverse groups[41].An unbalanced dataset with too many instances of pathology and not enough images without pathology may skew the algorithm causing decreased specificity.The larger the number of images used to train the algorithm,the better the system can be expected to perform[42].When the algorithm encounters,in real-world use,images outside what it encountered in the training set,it is more likely to flag those images as pathology[40].A novel methodology to train a CADe algorithm that involves training the platform by teaching it to read images in a similar fashion to an expert clinician,has recently been described[43].
Design of the user interface is an important factor in optimising CADe/CADx performance.Design features that minimise additional cognitive burden and make alarms and advice coherent can result in synergistic effects.Conversely,poorly-designed platforms may increase the risk of automation bias,discussed later[44].The effect of presenting,alongside a CADx bounding box,additional data regarding the algorithm’s confidence in the given diagnosis,may alter the endoscopist’s trust in the AI advice and influence their likelihood to endorse the same diagnosis[45,46].
REGULATION,SUPERVISION AND ACCOUNTABILITY
Precise definitions and classifications for medical device software and AI systems differ between jurisdictions but in general AI or ML-based tools or algorithms when used for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes,including applications for GI endoscopy,will meet the definition of a medical device and should be appropriately developed and evaluated before they are approved for clinical use in accordance with the relevant regional regulation[47].Similarly,clinical research including pilot studies to generate the clinical data required to validate and appraise novel and uncertified AI tools in endoscopy should be performed in accordance with applicable regulatory and ethical requirements.
To facilitate new and potentially beneficial advancements while protecting patients,regulation and scrutiny should be proportionate to the risk of the software and it is recognised that regulation of AI systems as medical devices is challenging and this is not unique to GI applications[48].The intended use of the AI and not simply the technology is a critical determinant of risk so for example CADx for malignancy diagnosis would generally fall into a higher risk category and require sufficient evidence and evaluation to support its use.Other important principles influencing risk evaluation include transparency,explainability,interpretability and control of bias.In CADe in GI endoscopy this includes the ability of the clinician user to detect erroneous output information compared to so called ‘Blackbox’algorithm-based interpretations.While many AI and ML applications have been approved,some experts have questioned the ability of currently emerging LLM products to meet these principles and GI clinicians must consider the evidence base and reliability of such devices for clinical practice use[49].Outside of basic regulation and licensing,clinicians and health systems trialling or implementing AI in GI endoscopy practice have a responsibility to ensure the applications(whether diagnostic or therapeutic) have a sufficient evidence base and the clinical data supporting algorithms for example is reliable and representative for the intended use patient population.
HUMAN FACTORS INFLUENCING USER INTERACTION WITH AI
Analysis of the interaction between humans and AI platforms in GI endoscopy can be informed by a human factors approach,examining how human work interacts with work systems[50].Human factors theories help to study and optimise components of work systems to allow human workers to get the most from the system[25].Human factors research also recognises that there are several cognitive biases that can affect human interaction with AI[51].Some of the cognitive biases that are most relevant to applications of AI in GI endoscopy are discussed below.
Automation bias
Automation bias refers to the human propensity to disengage cognitively from tasks that are assigned for execution or support by an external technology,usually resulting in decreased situational awareness[52].The potential for negative outcomes due to automation bias has been explored through a human factors paradigm in healthcare and other settings requiring high levels of accuracy[50,52].In the example of AI in GI endoscopy,automation bias may manifest as an overreliance on a CADe or CADx platform to rapidly detect and diagnose all pathology encountered during the endoscopic procedure[46].The use of automated decision support systems that are presumed to be highly accurate can lead to an over-reliance on the part of users,which may manifest as bias or as complacency.
Automation complacency may manifest with the endoscopist paying less attention to the presence of on-screen pathology during endoscopy,due to an assumption that the software will detect any pathology that appears[53].This reduced vigilance,whereby the user becomes dependent on the software to shoulder the detection burden,can result in reduced human detection of pathology[54,55].Second,the user can become progressively more confident in the AI platform’s performance,to the point where they over-rely on its advice against their own correct judgement[56,57].Studies of mammography and histology showed concerning over-reliance of clinicians on incorrect AI advice labelling cancers as benign[57].The complexity of verifying that the AI platform is performing appropriately impacts on the degree of automation bias that arises in a given task[44].In endoscopy,the ease of that verification task may vary depending on the endoscopist’s experience,where the complexity of verification is higher for non-expert endoscopists than for experts.
It is important that users of AI platforms are educated on the limitations of the individual platform.The latency of the systemi.e.the time difference between pathology appearing on-screen and recognition of the pathology by the computer system is typically as short as 0.2 s in the current generation of CADe platforms[37].The cumulative time taken for the platform to identify the pathology,activate the alarm and for the user to register the alarm may be significantly longer,however.
A related cognitive bias is anchoring bias,which posits that when presented with external advice,humans tend to adjust insufficiently from that advice toward their own opinion,in reaching their decision[58].It has been suggested that this insufficient adjustment is due to a trade-off between the accuracy required in the decision and the time required to fully consider the difference between the external advice and one’s own opinion[59].Taking longer to consider a decision may be an effective mitigation against anchoring bias[51].In real-time CADe-assisted endoscopy,however,the rapidity of decisions is an important factor in the efficiency of the procedure.
In CADx applications,the effect of AI may be synergistic for both expert and non-expert endoscopists[46].A study that reached this conclusion advised endoscopists to treat advice from CADx as that from a colleague,weighing it against how accurate it usually is compared to the endoscopist.A simple adjustment to reduce automation bias may involve decreasing the prominence of alarms on screen[60].More comprehensive strategies to mitigate automation bias could aim to decrease cognitive load on the endoscopist,instigate thorough training on use of the specific AI platform,address explainability and transparency of decision making and design adaptive user interfaces[44,52,61].
False positives and alarm fatigue
False positives are of significant interest in CADe,as they may negatively affect the efficiency and economy of endoscopic procedures[62].A false positive may prolong the procedure as the endoscopist reviews the highlighted area[63].It may also add to the cost of the procedure by increasing use of implementse.g.forceps/snares and raising the number of normal tissue samples submitted for processing and pathologic analysis[64].In colonoscopy,a CADe false positive may be caused by a normal colonic fold,other normal anatomy(e.g.the ileocaecal valve),a non-polypoid abnormalitye.g.a diverticulum,or luminal contents[63].In commercially-available CADe systems,false positives in colonoscopy may occur in a ratio to true positives as high as 25:1[63].
The incidence of false positives during colonoscopy has been reported to range from 0.071 to 27 alarms per colonoscopy,depending heavily on the definition used[11].Whereas some studies defined a false positive as any activation of a bounding box,others defined it as an activation that resulted in resection of normal tissue.Most studies examined the incidence of false positives only during withdrawal,as the CADe system was typically only active during withdrawal.In real world practice,however,the CADe platform is often active during both insertion and withdrawal,likely leading to more false positives than in the reported experimental studies.False positive alarms may be categorised according to the amount of time the endoscopist spends examining the area involved in the false positive alarm: mild (<1 s),moderate (1-3 s) or severe (>3 s)[63].While most false positives in the published studies did not result in additional examination time,the endoscopists involved in those studies were experts,so may have been more easily able to dismiss false alarms than non-expert endoscopists.
Alarm fatigue is a well-described phenomenon whereby the repetitive activation of visual or audio alarms causes diminished,delayed or absent response in the user over time[65].Alarms have the potential to add to cognitive burden on the endoscopist,increasing fatigue and negatively impacting performance[66].While the amount of time taken to examine the site of each false alarm is low in published studies,the effect of repeated activations (at a rate of 2.4 +/-1.2 false positive alarms per minute of withdrawal time) on endoscopist fatigue and possibly on algorithm aversion remains to be elucidated[63].
The frequency of alarms may be addressed by altering the confidence level of the CADei.e.decreasing the sensitivity of the platform,though this would need to be balanced against the resulting risks of decreased sensitivity.AI may also provide part of the solution for this problem,through development of CADe platforms with better accuracy and through filtering technology that uses generative learning to suppress false positives in real-world use[67].Another approach may be to increase the latency of output,so that activations of the bounding box of less than one second duration,which are almost always spurious,are suppressed and do not trigger an alarm.Alarm fatigue may also be reduced by minimising the alarm stimuluse.g.visual alarm without audio alarm,or altering the prominence or display of the bounding box.
Algorithm aversion
The ‘CASA’ phenomenon,discussed earlier,was a cornerstone of early HCI research.More recent research has shown that the way humans interact with technology is more nuanced than simply treating a new technology as they would another human.There are multiple influences on how humans interact with technology and how they use or discard advice given by technology,though the interaction of these factors is poorly understood[68,69].
Several studies have shown that a human user is likely to judge an AI algorithm more harshly for a mistake in advice than they would judge another human.This results in the user being substantially more likely to disregard the algorithm’s future advice,a phenomenon known as algorithm aversion[70].In contrast to automation bias,algorithm aversion suggests that once a human user notices the imperfect nature of the algorithm advising them,their adherence to the algorithm’s future suggestions decreases,causing under-reliance on the AI system[71].More recent work suggests that there are many factors affecting whether a user develops algorithm aversion,and durability of the phenomenon;these may include the individual endoscopist’s expertise,attitudes to AI and expectations of the system.Experts may be more likely to reduce their adherence to AI advice after a false alarm than non-experts,even when later advice is correct[72,73].
In the CADe setting,where the platform alerts for many more false positives than true positives,the impact of algorithm aversion may be important.A systematic review of the factors influencing algorithm aversion identified incorrect expectations of the algorithm,control of decision making and external incentives as significant contributors[55].With respect to AI in GI endoscopy,these factors may provide a framework for research on the human and AI platform variables that affect the propensity of a user to develop algorithm aversion.
Learning effect and deskilling
The effect of CADe and CADx platforms on an endoscopist’s learning and on their development of skills essential to performance of endoscopy is uncertain.Several studies have shown that CADe may improve a trainee’s ADR to close to that of an expert,providing additional safety and reducing the adenoma miss rate[74].It is not clear,however,whether this improved performance produces a persistent learning effect or whether it may bring about dependence of trainees on the CADe platform.There is some evidence that the ability of such platforms to draw a trainee endoscopist’s eye to a polyp and to give advice on the likely histologic type of the polyp may improve the trainee’s recognition and diagnosis of such lesions[46].
Evidence from non-endoscopic applications of AI show that the potential for non-expert clinicians and female clinicians to over-estimate the reliability of an AI platform raises concerns for poor training outcomes and for inequitable distribution of performance benefits[68].Interestingly,providing an explanation for its decision does not appear to improve the application of AI for training.In explainable AI platforms that showed the user how it had arrived at its advice,trainees were more likely to accept the advice,even when it was incorrect,than if no explanation was given,the so-called ‘white box paradox’[75].
Visual gaze pattern (VGP) is an important metric in vigilance tasks including detection of pathology during endoscopy,with substantial differences between VGPs of experts and those of non-experts[66,76-78].Analysis of the VGP of endoscopists with high ADRs showed a positive correlation with VGPs that tracked the periphery of the bowel wall and the periphery of the screen in a ‘bottom U’ configuration during colonoscopy[76,79].The repeated attraction of the endoscopist’s attention to a bounding box on screen may serve to embed alterations in the endoscopist’s VGP,which have been posited to have a negative effect on an endoscopist’s attainment of expertise in polyp detection in colonoscopy[80].In the eye-tracking experiment,endoscopists’ gaze patterns focused more on the centre of the screen when using CADe,reducing their likelihood of detecting pathology peripherally.
CLINICIAN AND PATIENT ATTITUDES TO AI
The quality of HAII depends to a significant degree on the attitudes of users and patients toward the technology.Levels of trust in technology generally,and in AI technologies specifically,are heterogenous across groups of clinicians and groups of patients[81].They depend on many factors including personal,professional,organisational and broader cultural considerations[82].Research and speculation on the role of AI platforms have occupied increasing amounts of space in the endoscopy literature.The promise of AI in revolutionising patient care and administrative burden have been much-vaunted in academic literature and in popular media,leading to high levels of awareness of AI among the general population,but low levels of knowledge on specific applications[83].
Knowledge of AI is seen to correlate with a positive perception of the benefits of AI,and perhaps an underestimation of its risks[84].Surveys of the attitudes of gastroenterologists and other endoscopists in the United States and the United Kingdom show a high degree of optimism on the potential role of AI to improve quality of care for patients[85].They also support development of guidelines for use of AI devices[86] and endorse concerns that CADe technology will create operator dependence on the technology[87].
Patient attitudes toward AI algorithms making decisions or offering advice appear more cautious[88].When used as a tool by their clinician,patients perceive benefit in AI in specific settings including cancer diagnosis and treatment planning[89].Patient attitudes to use of AI in GI endoscopy require further research.
CONCLUSION
In many of its current applications,AI marks a fundamental transition from technology as a tool to technology as a team member.Research is required to define what skills clinicians will need to optimally leverage AI technologies and to apply AI advice with adequate discrimination.It will then be necessary to decide how best to teach these skills from undergraduate to expert endoscopist level.
While there are regulatory pathways for appropriate trialling and development of AI software applications,guidance for clinical evidence requirements is lacking for medical AI software in general and not limited to software devices in GI endoscopy.Frameworks for design and reporting of trials involving AI are therefore to be welcomed[90].Uniform definitions of variables (e.g.false positive) are needed for research and reporting of real-world performance of AI platforms.Several professional societies have published opinions on priority areas for future research on AI in GI endoscopy[91,92].These opinions place a notable emphasis on technical outcomes,rather than on outcomes related to human interaction or patient-centred endpoints.It can be expected that priorities will need to be updated and redefined by professional societies frequently,as new technologies emerge.The medical community and professional societies should lead the way in defining the research agendas for AI platforms including the clinical evidence base required for their validation,adoption into clinical practice and continuous appraisal,while ensuring that patient priorities,human factors and real-world evidence are prioritised[93].
Priorities for research on HAII in GI endoscopy should include factors predicting individual clinician variations in utility of AI and the effect of AI use on trainees’ development of core competencies for endoscopy[94].A HAII focus in platform development may give rise to AI that learns how best to interact with each clinician based on their performance and use style,and adapts accordingly.Complementarity may be enhanced by prioritising study of human interaction with novel AI platforms that can perform tasks at which human clinicians are poore.g.measurement of polyps or other pathology,measurement/estimation of the percentage of the stomach/colon visualised during a colonoscopy[95].
HAII will be a key determinant of the success or failure of individual applications of AI.It is therefore essential to optimise interface elements,as clinician frustration with poorly-designed platforms now may have a negative impact on later engagement and uptake[96].The rapid development and implementation of AI platforms in GI endoscopy and elsewhere in medicine has been performed while studying mainly technical outcomes in idealised settings.This trend of adopting a technology-first approach expects clinicians and patients to adapt to the AI platforms,and risks taking insufficient account of human preferences and cognitive biases[50].Reorienting the focus toward development of humancentred AI and incorporating the study of human interaction at each stage of a new platform’s development,while aligning to appropriate regulation and governance,may allow creation of AI that is more user-friendly,more effective,safer and better value[90].
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Campion JR designed and drafted the original manuscript and reviewed all subsequent and final drafts;O'Connor DB drafted the manuscript and reviewed the draft and final manuscripts;Lahiff C designed and reviewed the original manuscript;all subsequent drafts,including the final draft.
Conflict-of-interest statement:Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.O'Connor DB is employed by the HPRA in Ireland,a government agency for medical device regulation in the EU and has no conflicts relevant to this article.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:Ireland
ORCID number:John R Campion 0000-0002-8722-6293.
S-Editor:Liu H
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Cai YX
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy2024年3期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy2024年3期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy的其它文章
- Anal pruritus: Don’t look away
- Tumor size discrepancy between endoscopic and pathological evaluations in colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection
- Impact of frailty on endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography outcomes in nonagenarians: A United States national experience
- Could near focus endoscopy,narrow-band imaging,and acetic acid improve the visualization of microscopic features of stomach mucosa?
- Using a novel hemostatic peptide solution to prevent bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection of a gastric tumor
