利用ITS基因研究徐闻滨珊瑚的系统发生关系
李文娟, 刘楚吾, 刘 丽, 廖宝林
(1. 广东海洋大学 水产学院 , 南海水产经济动物增养殖广东省普通高校重点实验室, 广东 湛江 524025;2. 徐闻珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区, 广东 湛江 524100)
利用ITS基因研究徐闻滨珊瑚的系统发生关系
李文娟1, 刘楚吾1, 刘 丽1, 廖宝林2
(1. 广东海洋大学 水产学院 , 南海水产经济动物增养殖广东省普通高校重点实验室, 广东 湛江 524025;2. 徐闻珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区, 广东 湛江 524100)
分别研究了徐闻3种滨珊瑚的ITS1和ITS2基因的碱基组成和G+C含量, 并和已上传至Genbank上的其他9种滨珊瑚的ITS序列进行比较, 研究了徐闻3种滨珊瑚的系统发生关系。序列分析结果显示, 3种滨珊瑚的ITS1的长度为205 bp~209 bp, G+C含量为37.6%~45.5%, ITS2的长度为192 bp~226 bp,G+C含量为45.1%~50.7%, 利用MEGA4.1软件计算滨珊瑚属基于ITS1和ITS2基因的平均遗传距离分别为0.097和0.200。基于ITS1和ITS2的NJ系统进化树都显示出, 灰黑滨珊瑚位于进化树的基部,是原始的类群, 普格滨珊瑚是进化类群, 澄黄滨珊瑚是过渡类群。
滨珊瑚; ITS基因; 系统发生关系
滨珊瑚属(Porites link)属刺细胞动物门(Cnidaria), 六放珊瑚亚纲(Anthozoa), 石珊瑚目(Scleractinia), 滨珊瑚科(Poritidae Gray)。滨珊瑚属的珊瑚都是群体, 主要由外触手芽形成群体, 珊瑚群体小, 珊瑚之间有少量的共骨紧密相连[1]。滨珊瑚在生长的时候, 骨骼中的碳酸钙在积聚时会因环境的影响而有不同的密度, 因此滨珊瑚属可提供关于过去的气候资料[2], 全球气候变化使滨珊瑚面临严峻的考验, 珊瑚礁白化的加剧迫使人们研究它们的系统发育关系。传统的石珊瑚分类依据于骨骼, 但是由于石珊瑚具有形态可塑性, 传统的分类方法具有一定的局限性, 往往存在同种异名的现象, 例如在香港海域找到的澄黄滨珊瑚和团块滨珊瑚[1]就曾被认为是同一种。
ITS(Internal Transcribed Spacer)基因, 即内转录间隔区, 由于所受的选择压力较小、DNA碱基替换速率较快, 加上较大的拷贝数、适中的长度和快速的同步化等特点, 变异速度较快, 可以提供丰富的变异位点和信息位点[3], 所以经常被用于低等真核生物, 研究属水平种间关系。在石珊瑚中, 除了鹿角珊瑚, 都可以用 ITS基因研究种间的系统发生关系[4], Sanchez 等[5]、McFadden 等[6-8]、Forsman 等[9]分别用 ITS基因研究八放珊瑚和石珊瑚的系统发生关系, 本文以滨珊瑚属的普哥滨珊瑚(Porites pukoensi), 灰黑滨珊瑚(Porites nigrescens)和澄黄滨珊瑚(Porites lutea)为研究对象, 研究徐闻3种滨珊瑚的系统发生关系, 以确定徐闻3种滨珊瑚种间关系。通过PCR扩增获得ITS序列, 利用MEGA4.1软件对所得 ITS序列进行比较分析, 邻近法(NJ )构建滨珊瑚属的系统发育树。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 实验样本
3种滨珊瑚样品采自广东省徐闻珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区, 纯酒精固定, -20℃保存备用。
1.1.2 试剂
dNTPs; PCR 缓冲液; Taq酶均购自 Takara 公司(大连), 引物由上海生工工程技术服务有限公司合成。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 基因组DNA的制备
参照卢圣栋[10]的方法提取基因组 DNA, 4℃低温保存备用。
1.2.2 目的片段的PCR扩增和序列测定
所用的引物为六放珊瑚 ITS基因通用引物[11],PCR反应体系是25 µL, 内含 10×Buffer(含 mg2+)2.5 μL, dNTPs 2 μL,引物各 1 μL, rTaqDNA 聚合酶 2.5 U,总DNA约100 ng。扩增条件为: 95℃预变性4 min,94℃变性30 s, 50℃退火30 s, 72℃延伸2 min, 循环4次, 然后94℃变性30 s, 56 ℃ 3 0 s, 72℃延伸2 min, 30个循环, 最后72℃总延伸10 min。1%琼脂糖电泳检测, PCR产物直接由北京六合华大基因科技股份有限公司进行双向测序。
1.2.3 数据分析
采用 MEGA 4.1(molecular evolution genetic analysis, Version 4.1)邻近法(NJ ) Bootstrap重复检测2000次构建基于滨珊瑚的ITS1和ITS2基因的系统发育树,空位(gap)始终作为缺失状态, 并计算滨珊瑚属种间的遗传距离。
2 结果
2.1 基于 ITS1基因的滨珊瑚属种间遗传距离分析和聚类分析
通过Krima2-Paramenter模式计算得到遗传距离矩阵(表1), 用采用MEGA4.1软件包对测序的3种滨珊瑚ITS1与GenBank的其他9种滨珊瑚ITS1进行对位排序后做NJ聚类分析, 用kimura双参数法计算上述12种滨珊瑚个体之间的遗传距离, 其中滨珊瑚各种ITS1基因之间遗传距离为0.011~0.231, 它们的平均遗传距离是0.097。NJ聚类树上分为3支, 徐闻3种滨珊瑚分别位于进化树的不同分支上, 基于ITS1基因研究徐闻 3种滨珊瑚系统关系时, 灰黑滨珊瑚处于底部原始的位置, 较其他 2种珊瑚亲缘关系较远, 澄黄珊瑚是过渡种, 普格滨珊瑚处于进化树的上端(图1)。
2.2 基于ITS2基因的滨珊瑚种间遗传距离分析和聚类分析
对测序3种滨珊瑚的ITS2基因与GenBank的其他9种滨珊瑚ITS2进行对位排序后做NJ聚类分析,用kimura双参数法计算上述12种滨珊瑚之间的遗传距离(表 2)。ITS2基因的遗传距离为 0~0.489, 平均遗传距离是0.200。基于ITS2基因的NJ树显示徐闻的 3种滨珊瑚分别位于树的两大分支上, 灰黑滨珊瑚单独作为一支位于进化树的基部, 澄黄滨珊瑚处于过渡位置, 普格滨珊瑚处于系统进化树的大分支上, 并且与柱状滨珊瑚和扁缩滨珊瑚聚为一支(图 2)。
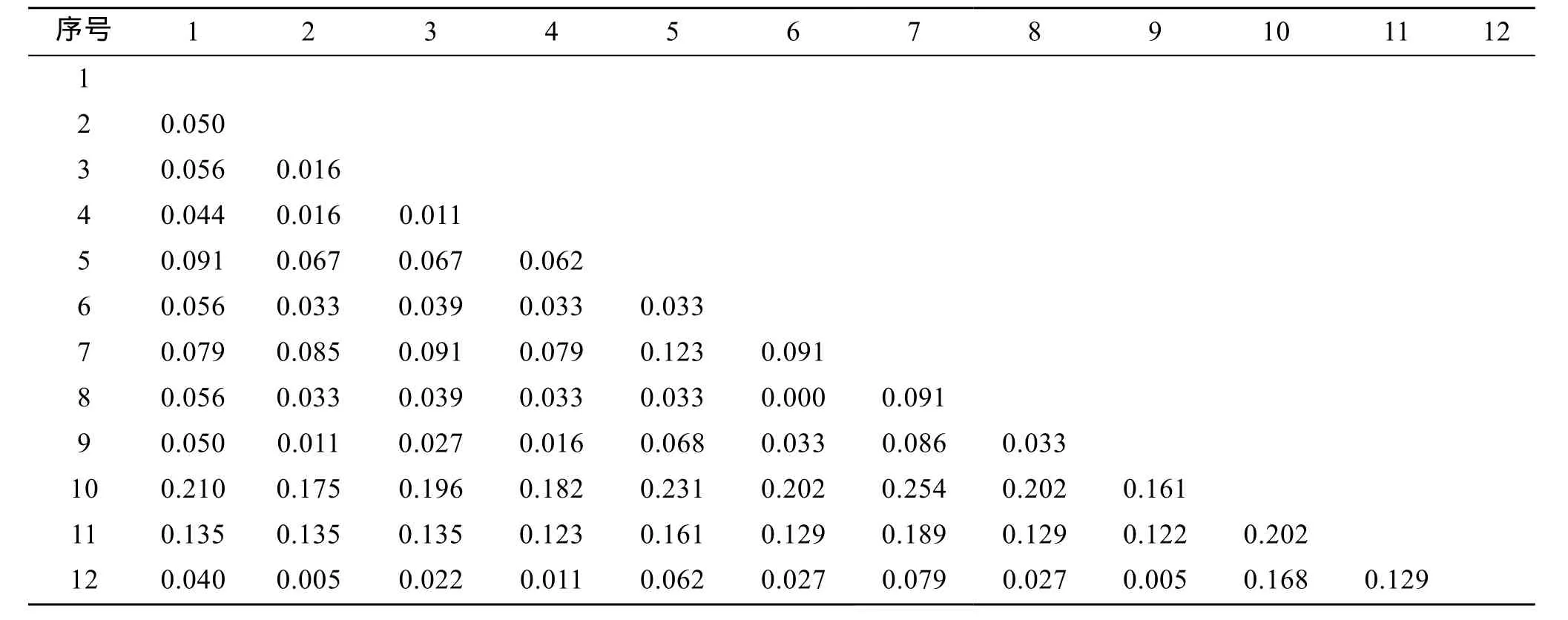
表1 基于ITS1基因的滨珊瑚属种间遗传距离Tab. 1 Genetic distance among Porites Link according to ITS1 gene
3 讨论
随着环境的变化, 滨珊瑚已经成为徐闻珊瑚礁国家级保护区内的一大优势种, 明确滨珊瑚属内各种间的遗传关系和分类地位对于研究整个珊瑚礁生态是举足轻重的。本研究分别用 ITS1和ITS2基因研究了徐闻3种滨珊瑚属的系统发生关系。
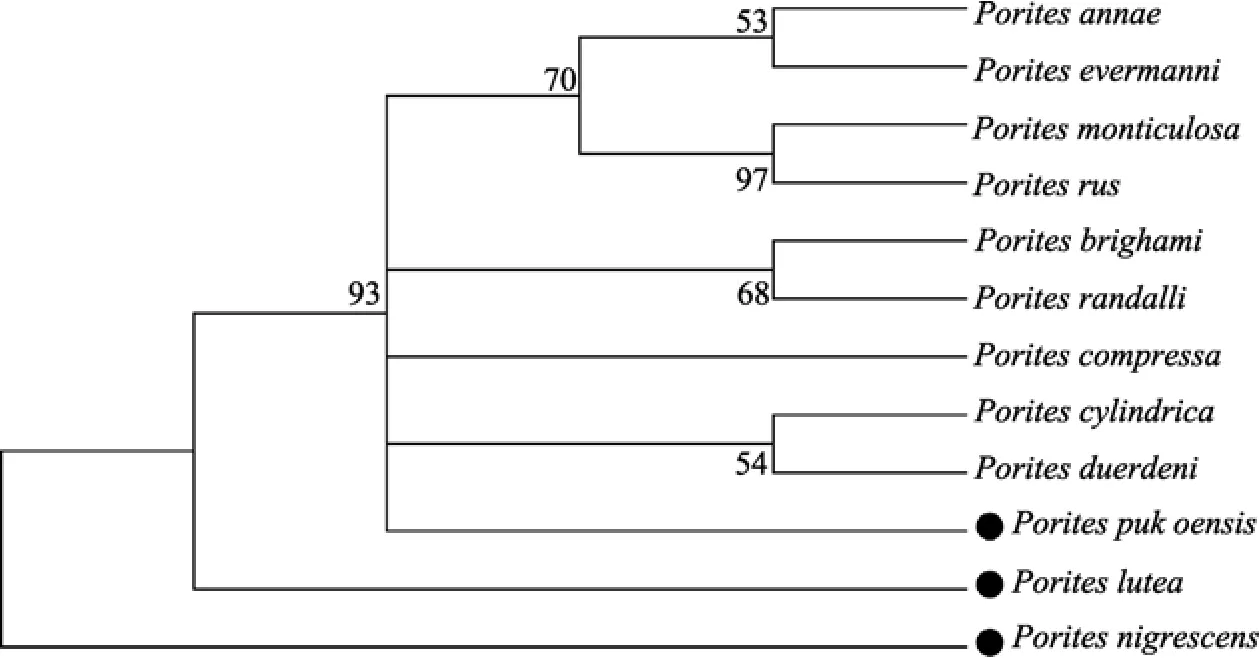
图1 基于Kimura双参数模型用检测到的滨珊瑚ITS1序列构建的NJ树Fig. 1 Neighbor-joining tree topology constructed on Kimura two-parameter distance matrix using ITS1 entire region in Porites Link
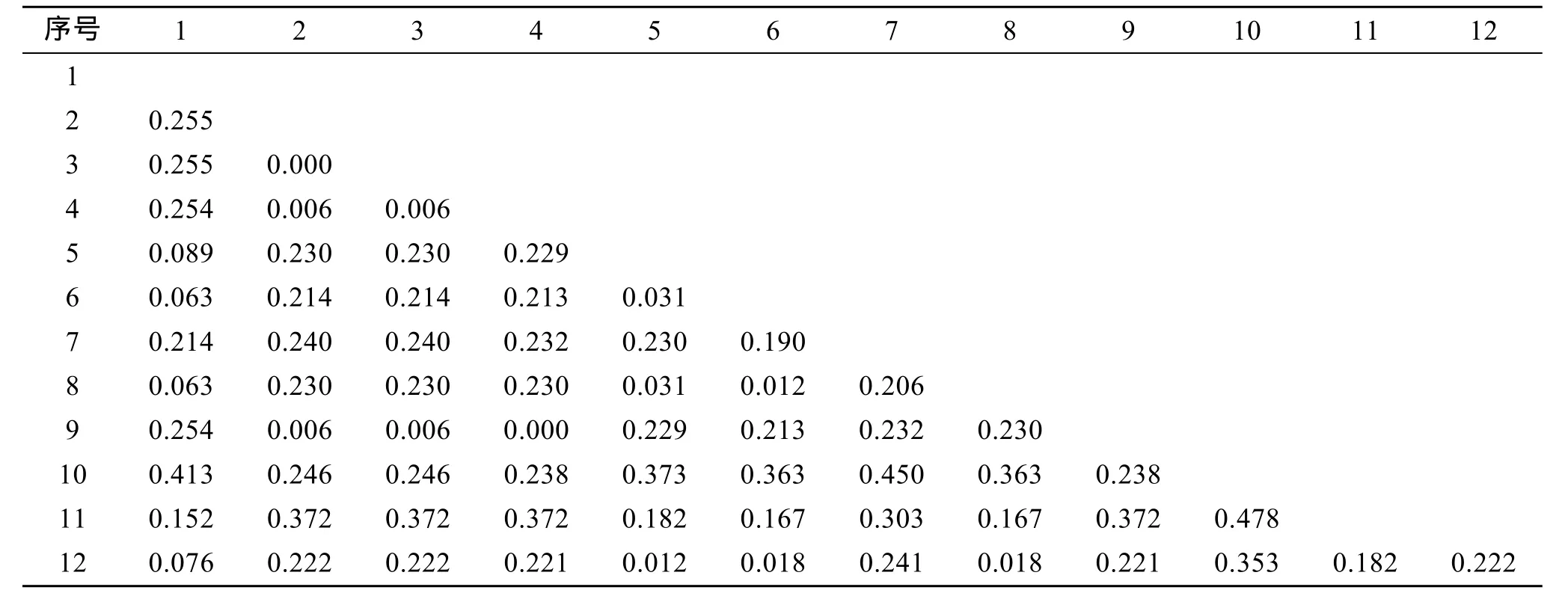
表2 基于ITS2基因的滨珊瑚属种间遗传距离Tab. 2 Genetic distance among Porites Link according to ITS2 gene
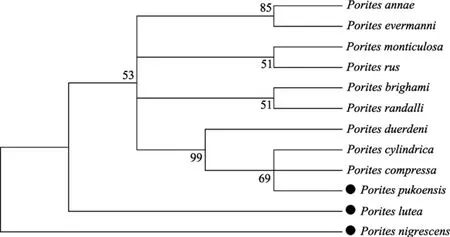
图2 基于Kimura双参数模型用检测到的滨珊瑚ITS2序列构建的NJ树Fig. 2 Neighbor-joining tree topology constructed on Kimura two-parameter distance matrix using ITS2 entire region in Porites Link
Nu-Wei[12]和 Chen[13]分别利用 ITS基因研究了鹿角珊瑚属的系统发生关系, 认为ITS1基因不能用于种间或者种群间的系统进化分析, 而采用ITS2基因研究了鹿角珊瑚属的系统发生。ITS2已经广泛应用于植物[14-15]、动物[16]、真菌[17-18]的分类研究中。本实验研究结果显示基于ITS1得到的系统进化树和基于ITS2的系统进化树一致, 能够反映出滨珊瑚各种之间的亲缘关系和系统进化关系。全球珊瑚的分布有太平洋-印度洋区系以及大西洋-加勒比海区系,无论基于 ITS1还是基于 ITS2基因的研究结果都表明, 这两个区系的珊瑚在基因距离上不存在明显差异。从得到进化树上来看, 太平洋-印度洋区系的疣滨珊瑚(Porites annae)和大西洋-加勒比海区系的Porites evermanni位于进化树的一支上, 太平洋-印度洋区系火焰滨珊瑚和大西洋-加勒比海区系Porites rus Porites monticulosa也始终位于进化树的一支上。
滨珊瑚的形态受环境影响较大, 同种珊瑚在不同的环境下, 骨骼的发育会发生很大的变化[19-21],依据于形态的滨珊瑚的分类存在着很大的不足。在形态学上, 滨珊瑚的群体形状, 有块状和分枝状的。在形态进化上认为分枝状的要比块状的复杂。在用ITS2基因分析滨珊瑚属时, 块状的扁缩滨珊瑚(Porites compressa)没有和其他的块状滨珊瑚聚在一支, 而是和群体分枝状的滨珊瑚聚在一起。Verril将Porites monticulosa和Porites rus和滨珊瑚科的另一个单种属Stylaraea作为滨珊瑚属的一个亚属[22], 而本文分别用ITS1和ITS2研究了Porites monticulosa和 Porites rus的分类地位, Porites monticulosa和Porites rus始终聚在一起, 表示这两个种在滨珊瑚属中亲缘关系较近, 遗传距离计算结果表明 Porites monticulosa和Porites annae的遗传距离只有0.033,Porites rus和 Porites annae的的遗传距离也只有0.033, 所以, Porites monticulosa和 Porites rus还不足以作为滨珊瑚的一个亚属。
[1] 中国科学院中国动物志编辑委员会中国动物志[M].北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 127.
[2] 苏瑞侠, 孙东怀. 南海北部滨珊瑚生长的影响因素[J].地理学报, 2003, 5: 442-451.
[3] 牛宪立, 姬可平, 吴群, 等. rDNA ITS 区序列分子标记技术在植物学研究中的应用[J]. 生物信息学, 2009,4: 269-271.
[4] Catalina A, Juan A S. Phylogenetic hypotheses of gorgoniid octocorals according to ITS2 and their predicted RNA secondary structures[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2007, 43: 774-786.
[5] Sanchez J A, McFadden C S, France S C, et al. Molecular phylogenetic analyses of shallow-water Caribbean octocorals[J]. Mar Biol, 2003, 142: 975-987.
[6] McFadden C S, France S C, Sanchez J A, et al. A molecular phylogenetic analysis of the Octocorallia (Coelenterata:Anthozoa)based on mitochondrial proteincoding sequences (ND2, msh1)[J]. Mol Phylogenet Evo,2006, 41: 513-527.
[7] McFadden C S, Donahue R, Hadland B K, et al. A molecular phylogenetic analysis of reproducti-ve trait evolution in the soft coral genus Alcyonium[J]. Evolution, 2001, 55: 54-67.
[8] McFadden C S,Tullis L D, Hutchinson M B, et al.Variation in coding(NADH dehydrogenase subunits 2,3,and6) and noncoding intergenic spacer regions of the mitochondrial genome in Octocorallia(Cnidaria: Anthozoa)[J]. Mar Biotechnol, 2004, 16: 516-526.
[9] Forsman Z, Hunter C, Fox G, et al. Is the ITS region the solution to the “species problem” in corals? Intragenomic variation and alignment permutation in Porites,Siderastrea and outgroup taxa[J]. Proc Coral Reef, 2006,1: 14-23.
[10] 卢圣栋. 现代分子生物学实验技术[M]. 北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社, 1999: 61.
[11] Odorico D M, Miller D J.Variation in the ribosomal internal transcribed spacers and 5.8S rDNA among five species of Acropora(Cnidaria;Scleractinia):patterns of variation consistent with reticulate evolution[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 1997, 14: 465-473.
[12] Nu-wei V, Carden C W. Analyses of the ribosomal internal transcribed spacers and the 5.8S gene indicata that extremely high rDNA heterogeneity is a unique feature in scleractinian coral genus Acropora (Scleractinian Acroporidae)[J]. Zoological Studies, 2006,45(3): 404-418.
[13] Chen C A, Chang C C, Wei N V, et al. Secondary structure and phylogenetic utility of the ribosmal internal transcribed spacer2(ITS2)in scleractinian corals[J]. Zool Stud, 2004, 43: 759-771.
[14] Alvarez I, Wendel J F. Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference[J]. Mol Phylogenet Evol 2003, 29(3): 417-434.
[15] 王东, 白雁, 陈志江. 不同产地山药 rDNA ITS 序列的比较[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2007, 18(1): 54-55.
[16] 周开亚. 两栖爬行动物的分子系统发生[J]. 动物学研究, 2001, 22(5): 397-405.
[17] Hibbett D S. Ribosomal RNA and fungal systematics[J].Trans Mycol Soc Jpn, 1992, 33: 533-556.
[18] 王国芬, 代 鹏. 海南省蕉褐缘灰斑病菌的鉴定及ITS 序列分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 2006, 27(4):46-50.
[19] Todd P. Morphological plasticity in scleractinian corals[J]. Biol Rev, 2008, 83: 315-337.
[20] Fukami H, Budd A F, Paulay G, et al. Conventional taxonomy obscures deep divergence between Pacific and Atlantic corals[J]. Nature, 2004, 427: 832-832.[21] Veron J E N. Corals of the World Volume 3[M]. Australia: Australian Institute of Marine Science, 2000.
[22] Verrill A E. List of the polyps and corals sent by the Museum of Comparative Zoölogy to other institutions in exchange, with annotations[J]. Bull of the Mus of Comp Zoölogy at Har-vard College,1864, 1: 29-60.
Phylogeny analysis of Porites link in Xuwen using its gene
LI Wen-juan1, LIU Chu-wu1, LIU Li1, LIAO Bao-lin2
(1. Fisheries College, Guangdong Ocean University, Key Laboratory of Aquaculture in South China Sea for Aquatic Economic Animal, Regular High Education Institution of Guangdong Province, Zhanjiang 524025,China; 2. Xuwen National Coral Reef Nature Reserve, Zhanjiang 524100, China)
Nov.,11, 2011
porites; ITS genes; phylogeny
The obtained ITS (internal transcribed spacer) sequences of 3 species in Porites by PCR technique were analyzed by MEGA4.1 software to get base composition, G+C content and phylogenetic relationship with ITS gene of other 9 species uploaded to Genbank, The results showed that the ranges of ITS1 and ITS2 of the tested 3 species were 205~209 bp and 197~226 bp, and the ranges of G+C content of ITS1 and ITS2 were 37.6%~45.5% and 45.1%~50.7%. The average genetic distance based on ITS1 and ITS2 were 0.097 and 0.200 respectively .The NJ-based phylogenetic tree based both ITS1 and ITS2 shows that Porites nigrescens at the base of evolutionary tree,is a primitive group, Porites pukoensis is an evolutionary group and Porites lutea is a transitional group.
Q959
A
1000-3096(2012)07-0056-05
2011-11-11;
2012-01-22
广东省海洋渔业科技推广专项(A200908F01); 国家海洋公益性行业科研专项(201105012)
李文娟(1986-), 女, 安徽亳州人, 硕士研究生, 研究方向:海洋水产动物发育生物学, E-mail: liwenjuan8551@163.com; 刘丽, 通信作者, 副教授, 主要从事水产经济动物发育生物学研究, E-mail:zjouliuli@163.com
(本文编辑:梁德海)

