裸鼠胰腺癌种植瘤乙醇瘤内注射的疗效观察
张文颖 吴洪玉 郭妍 龚艳芳 高军 金震东 李兆申
·论著·
裸鼠胰腺癌种植瘤乙醇瘤内注射的疗效观察
张文颖 吴洪玉 郭妍 龚艳芳 高军 金震东 李兆申
目的评价不同浓度乙醇瘤内注射对裸鼠胰腺癌种植瘤的疗效,为临床选择合适的乙醇浓度治疗胰腺癌提供实验依据。方法将人胰腺癌SW1990细胞接种于裸鼠皮下建立胰腺癌种植瘤模型。选取肿瘤大小相近的裸鼠48只,按随机表法随机分为20%、40%、60%、80%、95%乙醇注射组及注射生理盐水的对照组。治疗前后用游标卡尺测量肿瘤最长径(a)和最短径(b),计算肿瘤体积(TV)、相对肿瘤体积(RTV)和相对肿瘤体积增殖率(T/C)。治疗后第8天处死裸鼠,取肿瘤组织行病理组织学检查。结果20%乙醇注射组与对照组的RTV差异无统计学意义(P=0.212),40%、60%、80%、95%乙醇注射组的RTV均较对照组显著缩小(P值均<0.01),其中60%、80%、95%乙醇注射组的RTV<1,T/C<30%,且随着乙醇浓度的增加RTV及T/C值越小。80%和95%乙醇注射组的RTV值显著低于60%乙醇注射组(P值分别为0.003、0.009),而80%和95%乙醇注射组的RTV差异无统计学意义(P=0.819)。病理组织学检查显示对照组无肿瘤坏死,20%、40%乙醇注射组种植瘤内可见少量坏死, 60%、80%和95%乙醇注射组的种植瘤体内出现大面积凝固性坏死。结论选择80%乙醇瘤内注射治疗裸鼠皮下胰腺癌种植瘤是安全、有效的。
胰腺肿瘤; 乙醇; 超声检查,内镜; 注射,病灶内
胰腺癌是一种病情凶险、治愈率低、预后极差的消化道肿瘤。尽管吉西他滨已成为治疗晚期胰腺癌患者的一线化疗药物,一定程度上延长了患者的生存期,但其1年生存率仅为20%左右[1]。内镜超声(endoscopic ultrasound,EUS)作为一种成熟的内镜技术已广泛应用于胰腺疾病的诊断。随着凸面线阵型超声内镜的出现,EUS引导下的介入治疗也已逐步开展,包括放射性粒子植入、腹腔神经丛(节)阻滞及基因重组人溶瘤腺病毒植入等。超声引导下无水乙醇注射在肝、肾囊肿及原发性肝癌等治疗方面已取得较好的疗效。Matthes等[2]在EUS引导下对猪正常胰腺进行不同浓度的乙醇注射(0、20%、40%、60%、80%、100%),发现20%乙醇注射不能导致胰腺组织坏死,而40%及以上浓度可使胰腺组织发生坏死,并且坏死面积与乙醇浓度呈正相关。为此,本研究应用不同浓度乙醇注射于裸鼠胰腺癌种植瘤内,观察其疗效,为临床应用EUS引导下乙醇注射治疗胰腺癌提供实验依据。
材料与方法
一、裸鼠皮下种植性肿瘤模型建立及分组
BalB/c-nu裸小鼠4~6周龄,体重约18~20 g,购自中科院斯莱克动物中心,均获国家动物品系合格证。人胰腺癌细胞株SW1990 购自中科院上海细胞库,常规培养、传代。待细胞生长至70%~80%融合时,胰蛋白酶消化,制成细胞悬液。调整细胞密度至1×107个/ ml,取0.2 ml接种于裸鼠胸肋部皮下。以肿瘤体积长至100~300 mm3为成瘤标准,接种成功率为100%。给药前各组裸鼠饮食、行为均表现正常。
选取肿瘤大小相近的荷瘤裸鼠48只,按随机表法将其随机分为20%、40%、60%、80%、95%乙醇注射组及注射生理盐水的对照组,每组8只,采用单点注射。乙醇注射剂量参考肝脏肿瘤乙醇消融的回归方程[3],根据预实验结果进行修正,Y=2.885X/8=0.36X[Y为每次注射剂量(ml),X为肿瘤最大直径(cm)]。
二、方法
1.疗效判断:治疗前和治疗后第2、4、6、8天分别用游标卡尺测量肿瘤最长径(a)和最短径(b),同时称裸鼠的体重,计算肿瘤体积(tumor volume,TV)、相对肿瘤体积(relative tumor volume,RTV)及相对肿瘤增殖率T/C。TV =ab2/2,RTV=Vt/V0(V0为治疗前测量的肿瘤体积,Vt为t时间测量的肿瘤体积),T/C=RTV治疗组/RTV对照组×100%[4]。
2.种植瘤病理组织学检查:治疗后第8天将裸鼠全部处死,取肿瘤组织,常规染色,光镜下观察病理改变。
三、统计学处理
结 果
一、裸鼠存活情况
注射治疗后,60%、80%乙醇注射组裸鼠各死亡1只,95%乙醇注射组死亡2只,其余各组裸鼠均可耐受治疗。
二、疗效
60%、80%、95%乙醇注射组裸鼠皮下种植瘤组织在治疗后24 h即出现部分坏死。其中60%乙醇注射组在治疗后第4天有1只裸鼠的种植瘤组织完全坏死,80%乙醇注射组在治疗后第4天有4只裸鼠的种植瘤组织完全坏死,95%乙醇注射组在治疗后第4天有2只裸鼠的种植瘤组织完全坏死,第6天有1只裸鼠的种植瘤组织完全坏死(图1)。
20%乙醇注射组与对照组的RTV差异无统计学意义(P=0.212), 40%、60%、80%、95%乙醇注射组的RTV均较对照组明显缩小(P值均<0.01),其中60%、80%、95%乙醇注射组的RTV<1,T/C<30%,且随着乙醇浓度的增加RTV及T/C值越小。80%和95%乙醇注射组的RTV值显著低于60%乙醇注射组(P值分别为0.003、0.009),而80%和95%乙醇注射组的RTV差异无统计学意义(P=0.819,表1,图2)。
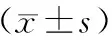
表1 不同浓度乙醇对裸鼠种植瘤的治疗效果
注:与对照组比较,aP<0.01;与60%乙醇注射组比较,bP<0.01
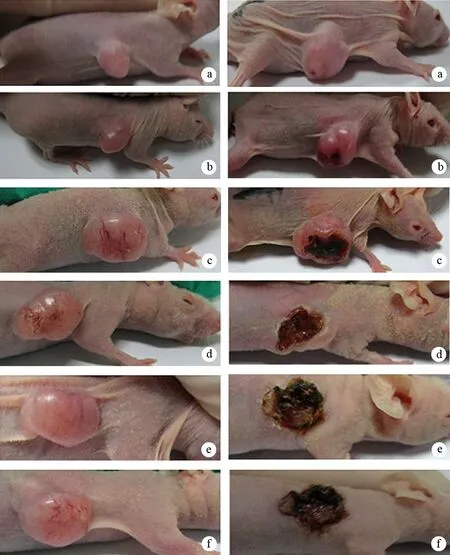
图1对照组(a)和20%(b)、40%(c)、60%(d)、80%(e)、95%(f)乙醇注射组治疗前(左)及治疗后1周(右)的大体标本
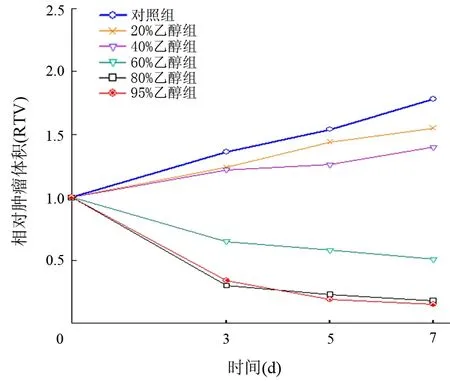
图2 对照组及各浓度乙醇注射组的RTV
三、种植瘤病理组织学改变
对照组未见肿瘤坏死,20%和40%乙醇组肿瘤瘤体内可见少量坏死,而60%、80%和95%乙醇组的瘤体内出现大面积凝固性坏死(图3)。
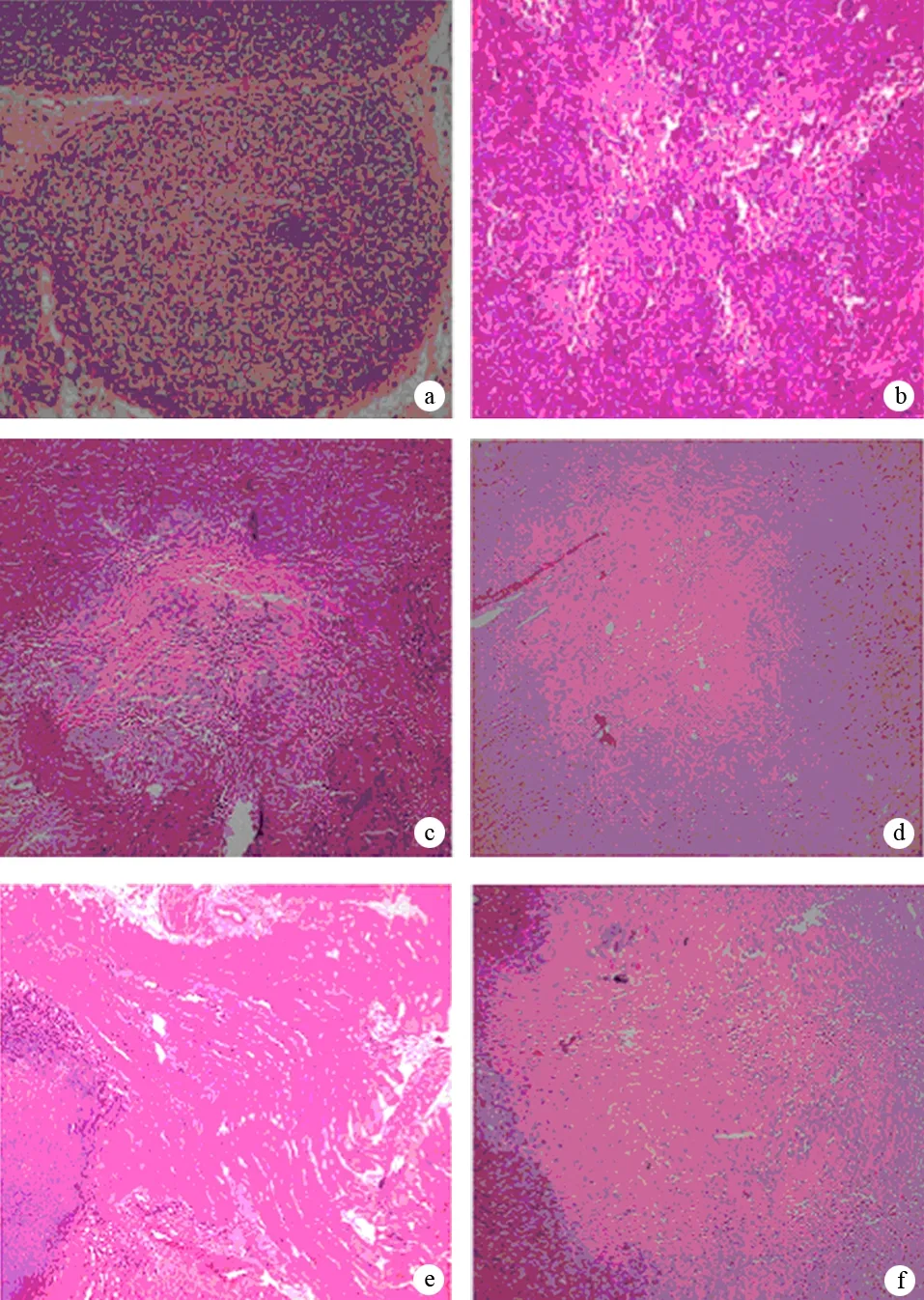
图3对照组(a)和20%(b)、40%(c)、60%(d)、80%(e)、95%(f)乙醇注射组治疗后1周种植瘤的病理改变(HE ×100)
讨 论
经皮乙醇消融在肝、肾囊肿及某些实体肿瘤如原发性肝癌、肾上腺肿瘤等方面治疗已取得较好的疗效[5-8]。但EUS引导下乙醇消融对胰腺癌治疗的报道较少。为了评价EUS引导下乙醇消融治疗胰腺癌的安全性,Aslanian等[9]在EUS引导下对猪的正常胰腺进行乙醇注射,结果发现,猪均可耐受乙醇,并无胰腺炎的发生,仅有轻度的淀粉酶升高,在胰腺注射部位可见炎细胞浸润、坏死和纤维化。2005年Gan等[10]报道,用EUS引导下细针瘤内注射乙醇治疗胰腺囊性肿瘤是安全可行的。Oh等[11-12]报道一项前瞻性研究,在EUS引导下行乙醇加紫杉醇注射治疗胰腺囊性肿瘤,结果完全缓解率达62%,仅1例并发轻度胰腺炎,1例并发脾静脉栓塞,是安全有效的治疗方法。Jürgensen等[13]报道1例EUS引导下给予95%乙醇8 ml注射治疗胰岛素瘤,治疗期间仅出现轻微的胰腺炎,3 d后恢复正常,治疗后患者低血糖症状明显改善,随访34个月,再次行EUS检查发现原发部位的肿块已消失。另外治疗1例胰腺内2个神经内分泌瘤,肿块大小分别是11 mm和7 mm,在EUS引导下给予40%乙醇2 ml注射治疗,随访18个月,患者血管活性肠肽及铬粒素A水平均恢复正常,MRI检查胰腺呈阴性[14]。
本研究结果显示,随着注射的乙醇浓度增加,裸鼠皮下胰腺癌种植瘤的坏死面积增大,瘤体积明显缩小。80%和95%乙醇注射组的疗效优于60%乙醇注射组,这2种浓度的疗效接近,但80%乙醇注射组死亡1只,95%乙醇注射组死亡2只,表明瘤内注射80%乙醇治疗裸鼠皮下胰腺癌种植瘤是较安全、有效的。
[1] Hochster HS, Haller DG, de Gramont A, et al. Consensus report of the international society of gastrointestinal oncology on therapeutic progress in advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer, 2006, 107: 676-685.
[2] Matthes K, Mino-Kenudson M, Sahani DV, et al. Concentration-dependent ablation of pancreatic tissue by EUS-guided ethanol injection. Gastrointest Endosc, 2007, 65: 272-277.
[3] Lin LW, Lin XY, He YM, et al. Experimental and clinical assessment of percutaneous hepatic quantified ethanol injection in treatment of hepatic carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol, 2004, 10: 3112-3117.
[4] Medioni J, Leuraud P, Delattre JY, et al. New criteria for analyzing the statistical relationships between biological parameters and therapeutic responses of xenografted tumor models. Contemp Clin Trials, 2012, 33: 178-183.
[5] Livraghi T, Bolondi L, Lazzaroni S, et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. A study on 207 patients. Cancer, 1992, 69: 925-929.
[6] Larssen TB, Jensen DK, Viste A, et al. Single-session alcohol sclerotherapy in symptomatic benign hepatic cysts. Long-term results. Acta Radiol, 1999, 40: 636-638.
[7] Omerovic S, Zerem E. Alcohol sclerotherapy in the treatment of symptomatic simple renal cysts. Bosn J Basic Med Sci, 2008, 8: 337-340.
[8] Xiao YY, Tian JL, Li JK, et al. CT-guided percutaneous chemical ablation of adrenal neoplasms. Am J Roentgenol, 2008, 190: 105-110.
[9] Aslanian H, Salem RR, Marginean C, et al. EUS-guided ethanol injection of normal porcine pancreas: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc, 2005, 62: 723-727.
[10] Gan SI, Thompson CC, Lauwers GY, et al. Ethanol lavage of pancreatic cystic lesions: initial pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc, 2005, 61: 746-752.
[11] Oh HC, Seo DW, Lee TY, et al. New treatment for cystic tumors of the pancreas: EUS-guided ethanol lavage with paclitaxel injection. Gastrointest Endosc, 2008, 67: 636-642.
[12] Oh HC, Seo DW, Song TJ, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided ethanol lavage with paclitaxel injection treats patients with pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology,2011, 140: 172-179.
[13] Jürgensen C, Schuppan D, Neser F, et al. EUS-guided alcohol ablation of an insulinoma. Gastrointest Endosc, 2006, 63: 1059-1062.
[14] Muscatiello N, Salcuni A, Macarini L, et al. Treatment of a pancreatic endocrine tumor by ethanol injection guided by endoscopic ultrasound. Endoscopy, 2008, 40: E258-E259.
Theeffectsofintra-tumoralinjectionofethanolonnudemicewithimplantedpancreaticcancer
ZHANGWen-ying,WUHong-yu,GUOYan,GONGYan-fang,GAOJun,JINZhen-dong,LIZhao-shen.
DepartmentofGastroenterology,ChanghaiHospital,SecondMilitaryMedicalUniversity,Shanghai200433,China
Correspondingauthor:JINZhen-dong,Email:zhendjin@126.com
ObjectiveTo study the efficacy of intra-tumoral injection of different concentrations of ethanol for nude mice with implanted pancreatic cancer and provide evidence for choosing appropriate concentration of ethanol for clinical treatment of pancreatic cancer.MethodsA subcutaneous xenograft mouse model of human pancreatic cancer SW1990 was established. Forty-eight nude mice with similar tumor size were randomly divided into 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 95% ethanol injection groups and saline injection group. The longest (a) and the shortest diameters (b) of tumor of nude mice were measured. Tumor volume (TV), relative tumor volume (RTV) and the relative rate of tumor proliferation (T/C%) were calculated. Eight days later the nude mice were sacrificed. The tumor tissue was harvested for pathologic examinations.ResultsRTV in 20% ethanol injection group was similar that of saline injection group (P=0.212). RTV in 40%, 60%, 80% and 95% ethanol injection groups were significantly lower than that in saline injection group (P<0.01). RTV was less than 1 and T/C% was less than 30% in 60%, 80% and 95% ethanol injection groups. The values of RTV and T/C% decreased with the increase of ethanol concentration. RTV in 80% and 95% ethanol injection groups were significantly lower than that of 60% ethanol injection group (P=0.003 andP=0.009). RTV was similar in 80% and 95% ethanol injection groups (P=0.819). The pathologic examinations showed no tumor necrosis in saline injection group, while small amounts of necrosis in implanted pancreatic cancer was observed in 20% and 40% ethanol injection groups, while a large area of coagulation necrosis could be found in 60%, 80% and 95% ethanol injection groups.ConclusionsIntra-tumoral injection of 80% ethanol is feasible therapy method for nude mice with human pancreatic cancer xenografts.
Pancreatic neoplasms; Ethanol; Ultrasonography, endoscopic; Injections, intralesional
2013-01-11)
(本文编辑:屠振兴)
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2013.03.012
上海市科学技术委员会(11D21921605)
200433 上海,第二军医大学长海医院消化内科
金震东,Email:zhendjin@126. com

