交叉引物等温扩增检测霍乱弧菌方法的建立
张霞,高琳,王淞,赵良娟,郑文杰,王硕
(1.天津科技大学食品工程与生物技术学院,天津300457;2.天津出入境检验检疫局,天津300461)
交叉引物等温扩增检测霍乱弧菌方法的建立
张霞1,2,高琳2,王淞2,赵良娟2,郑文杰2,王硕1,*
(1.天津科技大学食品工程与生物技术学院,天津300457;2.天津出入境检验检疫局,天津300461)
建立食品中全血清型霍乱弧菌的交叉引物等温扩增检测方法。针对霍乱弧菌设计特异性引物及探针,建立交叉引物等温扩增法,利用免疫金标试纸条对结果进行检测。用57株霍乱弧菌及相近株细菌进行特异性试验;通过定量DNA、纯菌液计数、样品中添菌检测及与环介导等温扩增方法进行灵敏度验证及比较工作。结果表明,建立方法具有较好特异性;DNA检测灵敏度为79.28 fg/test,增菌液检测灵敏度为4.2×102CFU/mL,当每25克样品中有5.6 CFU菌时经增菌步骤后即可检出。建立的交叉引物恒温检测方法可作为食品中霍乱弧菌快速初筛检测方法使用,较环介导等温扩增方法灵敏且易于操作。
交叉引物等温扩增技术;霍乱弧菌;检测
人类在饮食过程中,由于食用污染霍乱弧菌(Vibrio cholera)的食物,导致胃肠道紊乱,产生明显的腹泻、呕吐等临床症状。通常人们认为O1与O139血清型的霍乱弧菌容易导致霍乱疾病的流行,而非O1和非O139的霍乱弧菌是普遍存在于河流、水域的正常菌群,不具有致病性,称为非致病性霍乱弧菌[1]。但是,在近十几年的研究中发现,非致病性霍乱弧菌也可导致胃肠炎、败血症及脑膜炎等疾病[2-3]。因此,针对食品中霍乱弧菌的检测不应仅局限于对O1和O139等致病性霍乱弧菌,还应包括非致病性霍乱弧菌,即对于全血清型霍乱弧菌进行检测成为保障食品安全的必然。
目前对于霍乱弧菌的检测主要有常规生化培养法、PCR方法、实时荧光PCR方法[4-8]及LAMP方法[9]等;常规生化培养方法作为检测用金标准,检测流程在3 d以上,可以对全血清型霍乱弧菌进行检测;目前分子生物学检测方法主要针对mshA、RTX及ctxA等基因[10-12]进行O1群及O139群霍乱弧菌检测,还鲜见检测全血清型霍乱弧菌方法报道。
本研究旨在应用新型交叉引物等温扩增技术[13]建立全血清型霍乱弧菌检测方法,不依赖PCR、荧光PCR等昂贵仪器,避免LAMP方法结果检测需要电泳使用EB危害、PCR产物污染等问题,将分子生物学检测推广至基层实验室或经济不发达地区。
1材料与仪器
1.1主要材料与试剂
dNTPs:Fermentas;10×Bst buffer:New England Biolabs;Bst DNA polymerase large fragment:New England Biolabs;MgSO4、betaine:Sigma;核酸快速检测试纸条:杭州优思达公司;DNA ladder II:北京天为时代科技有限公司;琼脂糖:promega公司;10×loading buffer:大连宝生物工程公司;5×TBE:大连宝生物工程公司。
菌株采用16株霍乱弧菌,其中5株O1群、1株O139群,10非O1和非O139,来源于临床分离2株、食品中分离10株;17株其他弧菌,24株食品中常见致病菌,详见表1。
1.2主要仪器与设备
PCR仪:Biometra;离心机:Eppendorf,5417R;DNA/RNA/蛋白分析仪:BHIMUZDA,Bio Specmini;电泳仪:Hoefer,PS3000,American;凝胶成像仪:Bio-Rad,Italy。
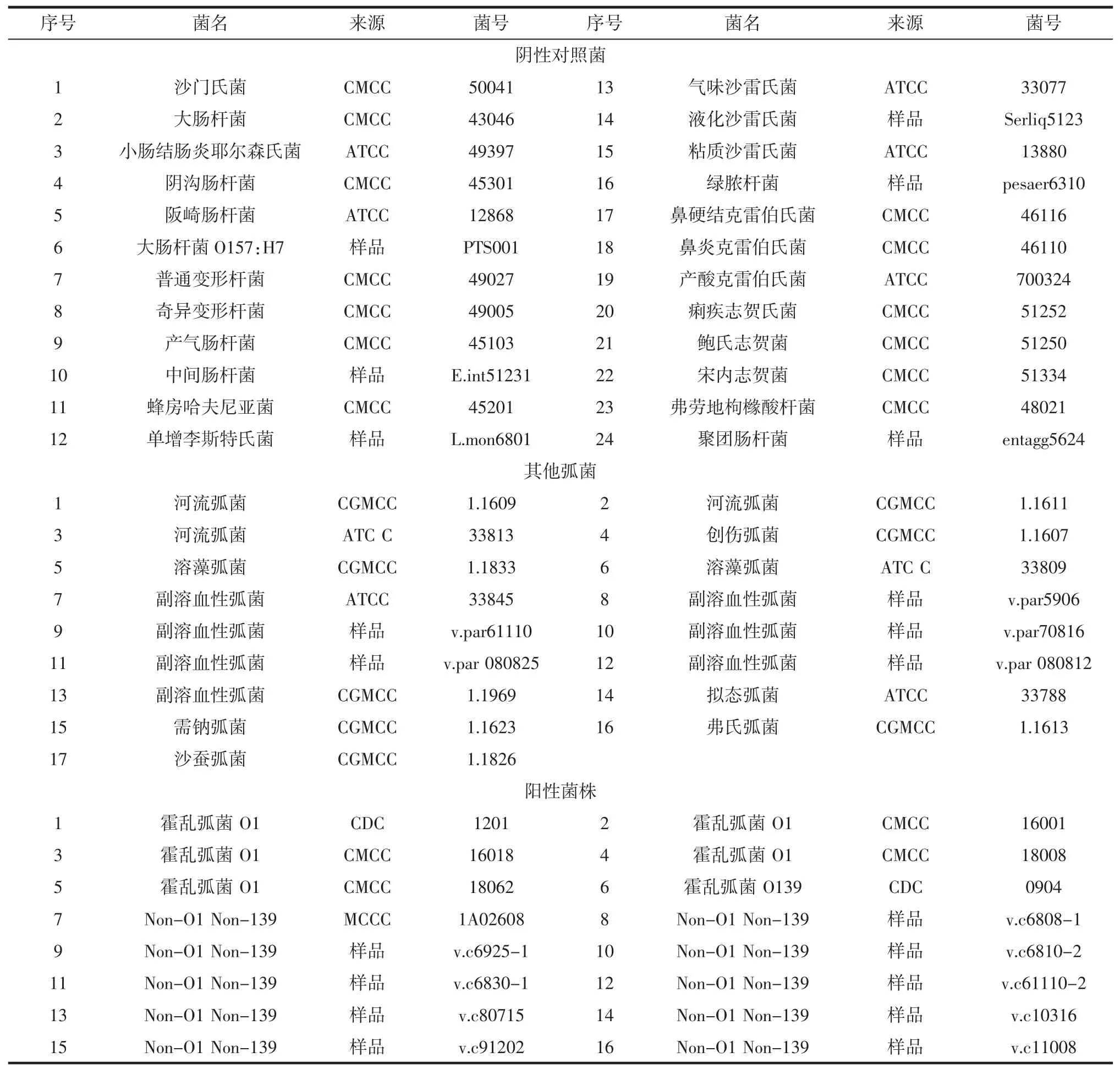
表1 试验菌株Table 1Bacterial strains for detection
1.3方法
1.3.1引物及探针的设计
利用霍乱弧菌toxR基因序列(GenBank CP001233)[14-15]设计特异性引物及探针见表2。参照已发表的LAMP方法[16]设计引物,序列见表2。
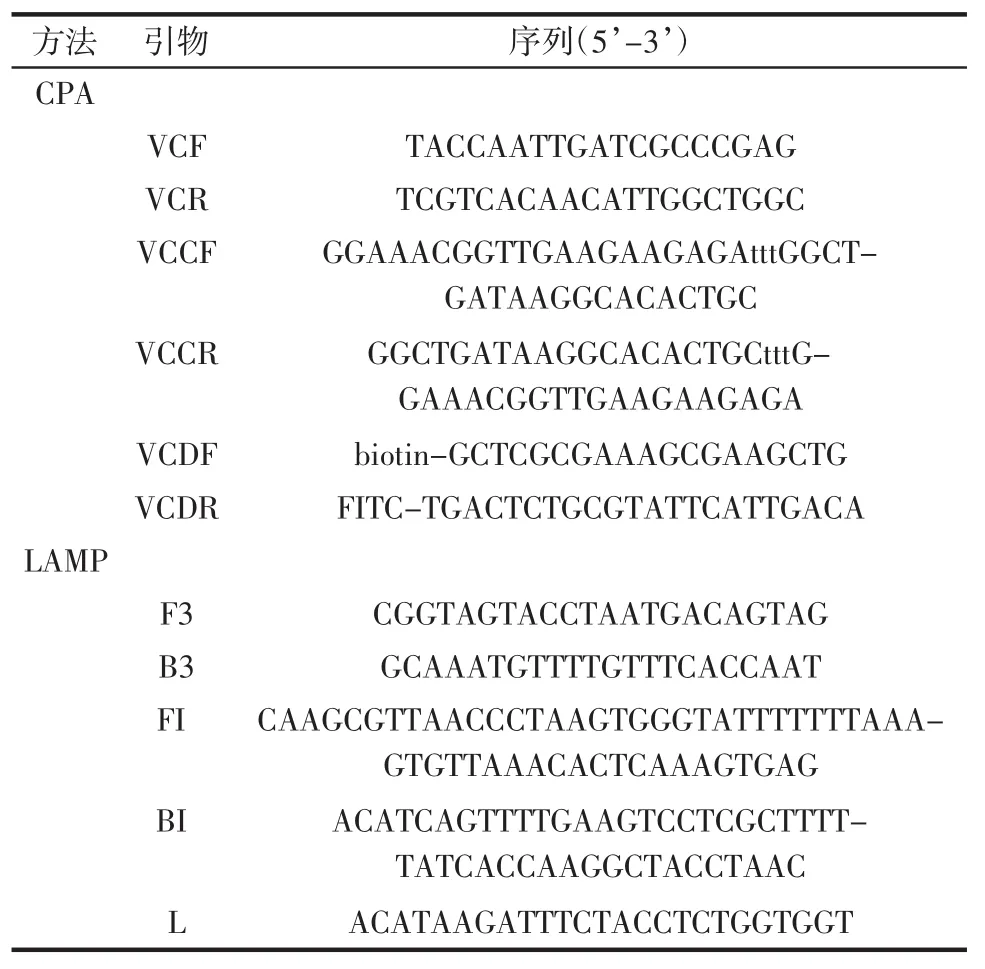
表2 检测霍乱弧菌引物序列Table 2 Primers and probe used for the detection of V.cholera
1.3.2反应体系和反应条件
1.3.2.1交叉引物等温扩增方法
反应体系50 μL,各试剂浓度为:10×ThermoPol buffer 5 μL,10 mmol/L dNTP 2 μL,100 mmol/L MgSO42 μL,5 mol/L betaine 5 μL,8 U/μL Bst DNA酶2.5 μL,2 μmol/L VCF及VCR各1 μL,20 μmol/L VCCF及VCCR各2 μL,20 μmol/L VCDF及VCDR各2 μL,1 μL模板,22.5 μL水。
反应条件:60℃反应60 min。
1.3.2.2环介导等温扩增方法
反应体系50 μL,各试剂浓度为:浓度50 μmol/L的FI及BI引物各1.6 μL,10 μmol/L的F3及B3引物1 μL,50 μmol/L的L引物0.8 μL,10 mmol/L dNTP 2 μL,100 mmol/L MgSO43 μL,5 mol/L betaine 4 μL,8 U/μL Bst DNA酶2 μL,10×ThermoPol buffer 5 μL,1 μL模板,水补足至50 μL。
反应条件:60℃反应75 min。
1.3.3特异性试验
对表1中菌株核酸样本进行试验,以证明交叉引物等温扩增检测方法是否具有通用性及特异性。
1.3.4灵敏度试验
霍乱弧菌CDC1201、CDC0904及MCCC1A02608为试验菌株,37℃培养16 h,取1 mL用于细菌基因组提取,利用DNA/RNA/蛋白分析仪检测进行DNA定量。对培养的纯菌液计数后10倍稀释,按照CPA及LAMP反应体系进行试验。
1.3.5样品添菌检测
取经证实不含霍乱弧菌的鱼糜样品A、B在增菌前分别添加101CFU/25g,100CFU/25g霍乱弧菌MCCC1A02608菌液1 mL,混匀1 min,加入225 mL碱性胨水(APW)37℃培养24 h,取1 mL样品增菌液按照本研究方法进行检测,未添加菌的样品A、B作为空白对照,同时做细菌计数。
2结果与分析
2.1特异性试验
图1是交叉引物等温扩增方法部分霍乱弧菌检测结果。

图1 霍乱弧菌交叉引物等温扩增特异性检测Fig.1Specificity of detecting V.cholera
56株实验菌株,其中16株霍乱弧菌检测全部为阳性,其余17株其他弧菌及24株阴性相关菌检测为阴性,说明交叉引物等温扩增结合免疫金标试纸条检测方法特异性良好,而且对于霍乱弧菌全血清型具有很好的通用性。
2.2检测灵敏度
2.2.1DNA检测
利用紫外分光光度计检测CDC1201,CDC0904 and MCCC1A02608的OD 260/280在1.83-1.982,说明DNA质量好,可以进行分子生物学检测,DNA浓度分别为79.28、74.02、67.39 μg/mL,10倍梯度稀释至10-8,按照2种等温扩增反应体系进行试验,重复3次,结果见表3。
说明交叉引物等温扩增方法DNA检测灵敏度高于环介导等温扩方法,交叉引物在79 fg/test时,检测全部为阳性,环介导3个检测出现1个阳性。
2.2.2纯菌液检测
霍乱弧菌试验菌株过夜培养后菌液浓度分别为CDC1201(4.2×108CFU/mL)、CDC0904(8.7×107CFU/mL)、MCCC1A02608(6.7×107CFU/mL),用PBS对菌液进行10倍梯度稀释至100CFU/mL数量级,各取1 mL提取DNA做实验模板,两种等温扩增方法结果见表4。
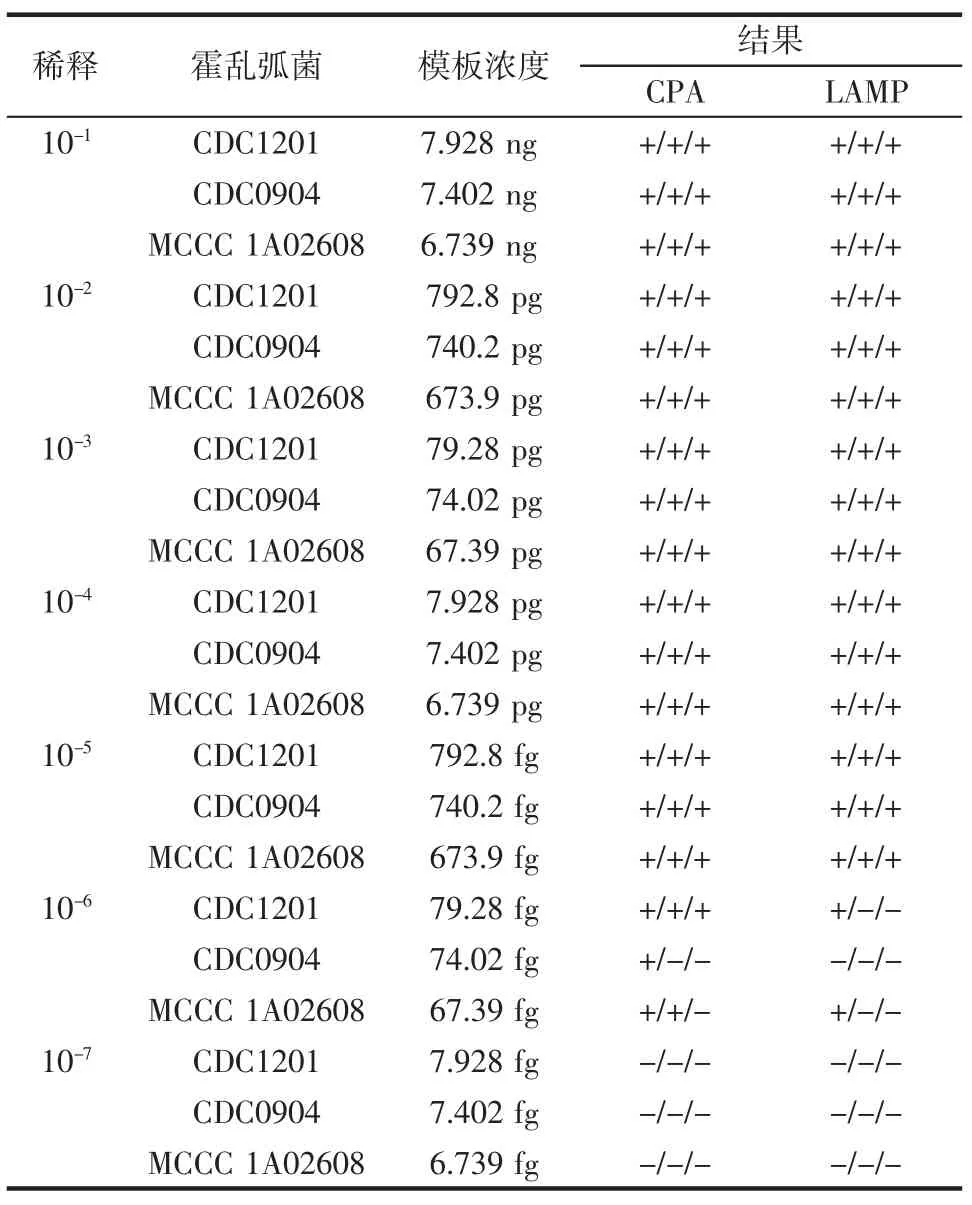
表3 霍乱弧菌DNA灵敏度试验结果Table 3Sensitivity of detecting V.cholerae genomic DNA
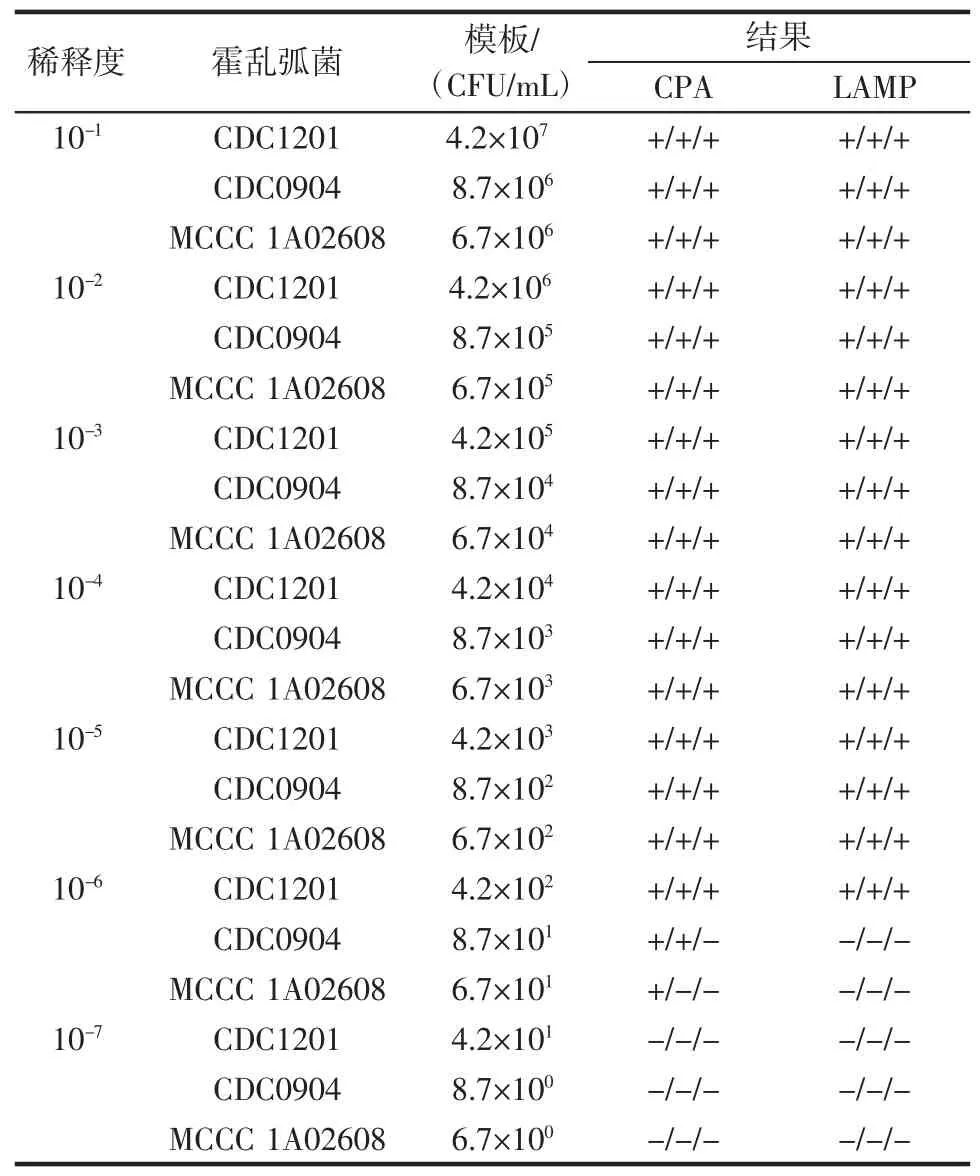
表4 霍乱弧菌菌液灵敏度试验结果Table 4Sensitivity of detecting V.cholerae in pure cultures
其灵敏度稳定达到102CFU/mL,在101CFU/mL数量级时,CPA方法可以检出,但LAMP方法检测全部为阴性。
2.3样品添菌实验
对鱼糜空白样品细菌计数,即样品本底杂菌数为7.2×102CFU/g,向样品中添菌量为5.6及56 CFU/25 g,两种方法均可检出,说明经增菌后的检测灵敏度二者一致,在有其他干扰菌的情况下均可以达到100CFU/ 25 g的检测低限。
3结论
霍乱弧菌作为人类食源性致病菌其致病性及检测方法早已引起各国学者的重视,对非致病性霍乱弧菌在近年来发展迅速,研究发现非致病性霍乱弧菌也导致人类疾病,推测可能与有关毒力因子有关,如毒素协同调节菌毛(TCP)[17],毒力调节基因toxR,细胞毒素因子[18]溶血素(Hly A)[19]等,其中ToxR在所有的非致病性霍乱弧菌中被发现,其与霍乱毒素A基因的调节有关[20-21],因此本研究以toxR为靶基因检测全血清型霍乱弧菌,经特异性试验结果表明,以该基因为目的片段检测霍乱弧菌具有良好的特异性及通用性。
随着等温扩增技术的发展,解决了分子生物学快速检测方法对仪器的依赖,将其应用推广到一个新的高度。通过研究发现,由于引物设计原理的不同,交叉引物等温扩增方法实际检测灵敏度要略高于环介导等温扩增方法,但是由于样品增菌后目标菌浓度一般可达到104CFU/mL左右,二者添菌试验检测灵敏度一致,由于方法操作简便,不需要特殊设备,均可应用于基层实验室检测以及样品的快速筛选检测。但是本研究交叉引物等温扩增结合免疫金标试纸条检测方法的建立,解决了环介导等温扩增方法检测结果的缺陷,避免电泳时PCR产物的二次污染和EB对人体的危害,同时克服了观察沉淀或颜色变化造成的不客观性,在结果观察方面明显优于环介导等温扩增方法,所以本研究建立的霍乱弧菌检测方法具有较强的推广效应。
[1]Ottaviani D,Leoni F,Rocchegiani E,et al.Prevalence and virulence properties of non-O1 non-O139 Vibrio cholera strains from seafood and clinical samples collected in Italy[J].Int J Food Microbiol,2009,132:47-53
[2]Matte G R,Matte M H,Rivera I G,et al.Distribution of potentially pathogenic vibrios in oysters from a tropical region[J].J Food Prot,1994,57:870-873
[3]Morris J G,Takeda T,Tall B D,et al.Experimental non-O1 group Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in humans[J].J Clin Invest,1990,85: 697-705
[4]Chakraborty S,Khanam J,Takeda Y,et al.Application of PCR for detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 in water samples during an outbreak of cholera[J].Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg,1999,93:527-538
[5]Gubala A J,Proll D F.Molecular-Beacon Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for Detection of Vibrio cholerae[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2006,72:6424-6428
[6]Lyon W J.TaqMan PCR for Detection of Vibrio cholerae O1,O139,Non-O1,and Non-O139 in Pure Cultures,Raw Oysters,and Synthetic Seawater[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2001,67:4685-4693
[7]Singh D V,Isac S R,Colwell R R.Development of a Hexaplex PCR Assay for Rapid Detection of Virulence and Regulatory Genes in Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus[J].J Clin Microbiol,2002,40: 4321-4324
[8]Fykse E M,Nilsen T,Nielsen A D,et al.Real-time PCR and NASBA for rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio cholerae in ballast water[J].Mar Pollut Bull,2012,64:200-206
[9]Yamazaki W.Sensitive and rapid detection of cholera toxin-producing Vibrio cholerae using a loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Methods Mol Biol,2011,739:13-22
[10]Thattiyaphong A,Okada K,Khangrang S,et al.Development of a 5-minute rapid test for detecting Vibrio cholerae O139[J].Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health,2013,44:448-555
[11]DePaola A,Hwang G C.Effect of dilution,incubation time,and temperature of enrichment on cultural and PCR detection of Vibrio cholerae obtained from the oyster Crassostrea virginica[J].Mol Cell Probes,1995,9:75-81
[12]Fields PI,Popovic T,Wachsmuth K,et al.Use of polymerase chain reaction for detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 strains from the Latin American cholera epidemic[J].J Clin Microbiol,1992,30: 2118-2121
[13]Fang R,Li X,Hu L,et al.Cross-priming amplification for rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum specimens[J].J Clin Microbiol,2009,47:845-847
[14]Waldor M K,Mekalanos J J.ToxR regulates virulence gene expression in non-O1 strains of Vibrio choleraethat cause epidemic cholera[J].Infect Immun,1994,62:72-78
[15]Kumar R,Lalitha K V.Prevalence and molecular characterization of Vibrio cholerae O1,non-O1 and non-O139 in tropical seafood in Cochin India[J].Foodborne Pathog Dis,2013,10:278-283
[16]Srisuk C,Chaivisuthangkura P,Rukpratanporn S,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio cholerae by loop-mediated isothermal amplification targeted to the gene of outer membrane protein ompW[J].Lett Appl Microbiol,2010,50:36-42
[17]Sarkar A,Nandy R K,Nair G B,et al.Vibriopathogenicity island and cholera toxin genetic element-associated virulence genes and their expression in non O1 non O139 strains ofVibrio cholerae[J]. Infect Immun,2002,70:4735-4742
[18]Saka HA,Bidinost C,Sola C,et al.Vibrio is essential for high enterotoxicity and apoptosis induction produced by a colera toxin gene-negative V.choleraeenon-O1,non-O139 strain[J].Microb Pathog,2008,44:118-128
[19]Dutta D,Chowdhury G,Pazhani G P,et al.Vibrio cholerae non-O1,non-O139 serogroups and cholera-like diarrhea,Kolkata,India[J]. Emerg Infect Dis,2013,19:464-467
[20]Preeprem S,Mittraparp-arthorn P,Bhoopong P,et al.Isolation and characterization of Vibrio cholerae isolates from seafood in Hat Yai City,Songkhla,Thailand[J].FoodbornePathogDis,2014,11:881-886
[21]Rajpara N,Vinothkumar K,Mohanty P,et al.Synergistic effect of various virulence factors leading to high toxicity of environmental V. cholerae non-O1/non-O139 isolates lacking ctx gene:comparative study with clinical strains[J].PLoS One,2013,8:1-10
Detection of Vibrio cholera by Lsothermal Cross-priming Amplification
ZHANG Xia1,2,GAO Lin2,WANG Song2,ZHAO Liang-juan2,ZHENG Wen-jie2,WANG Shuo1,*
(1.College of Food Engineering and Biotechnology,Tianjin University of Science&Technology,Tianjin,300457,China;2.Tianjin Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau,Tianjin 300461,China)
To develop a cross-priming amplification(CPA)method for the detection of all serotypes of V. cholera on food.Specific primers and probe were designed,we developed cross-primer isothermal amplification method,using the immuno-gold standard test strip to test results.The specificity of the method was evaluated by 57 different bacterial strains.The sensitivity of the method was evaluated by testing the quantitative DNA,pure bacteria counted and the sample of adding V.cholera comparing with the loop-mediated isothermal amplification(LAMP)method.All of the V.cholera strains showed positive results,and 41 other types of bacteria gave negative results.The limit of detection of the CPA method was 79.28 fg of genomic DNA,4.2×102CFU/mL for bacteria in pure culture,and 5.6 CFU per 25 g of sample with pre-enrichment.This method showed a higher sensitivity than the LAMP method did and was more convenient to perform.These results indicate that the CPA method can be used for the rapid preliminary screening of V.cholera.
cross prime isothermal amplification;Vibrio cholera;detection
10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2015.17.028
2015-07-21
质检总局科研专项《食源性致病菌恒温扩增结合免疫金标检测技术的研究》资助(2011IK241)
张霞(1975—),女(汉),高级工程师,硕士研究生,研究方向:食品安全检测。
王硕(1969—),男,教授,研究方向:食品安全检测。

