神经外科术后颞下颌功能紊乱临床分析
陈阳
神经外科术后颞下颌功能紊乱临床分析
陈阳
【摘要】目的回顾性分析研究神经外科术后颞下颌功能紊乱的发病情况、发病机制,探讨相关治疗效果。方法 本研究选择的对象为2010~2014年于我院神经外科经额颞行开颅手术患者,统计术后存在颞下颌功能紊乱发生情况。并以磁共振计算颞肌容积,分析颞下颌功能紊乱发生的原因。结果 行额颞去骨瓣减压患者,发生颞下颌功能紊乱的情况高于其它手术。检测颞肌容积(肌肉所占体积),发生颞下颌功能紊乱患者肌肉厚度均值低于5 mm,对照组高出3 mm,颞肌容积较对照组低52%。两组患者对照存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。结论 患者在手术前应对其进行综合考虑,以此来降低颞肌切断现象的发生率,并将颞肌进行复位。
【关键词】颞下颌关节障碍;神经外科手术;翼点入路手术;颞下颌关节脱位
作者单位: 430000武汉,长江航运总医院
Clinical Analysis of the Functional Disorders of the Temporomandibular Disorders in the Department of Neurosurgery
CHEN Yang, General Hospital of Yangtze River Shipping, Wuhan 430000, China
[Abstract]Objective Retrospectively analyzing the incidence and pathogenesis of Temporaromandibular Joint Disorders in department of neurosurgery after surgery, exploring the related therapeutic effect. Methods The patients of study are selected from 2010 to 2014 years in the Department of Neurosurgery of our hospital who underwent frontal temporal craniotomy, statistic the incidence of Temporomandibular Joint Disorders after operation. And by magnetic resonance calculating the temporal muscle volume, analysising the causes of temporomandibular dysfunction. Results Temporomandibular Joint Disorders occurred after the frontal temporal decompressive craniectomy, the situation is significantly higher than the other operation. The detection of temporal muscle volume(the volume of muscle), the occurrence of temporomandibular dysfunction in patients with muscle thickness lower than 5mm, the control group is higher than the 3mm, temporal muscle volume was lower than that in control group 52%. Two patients in the control group there were significant differences(P<0.05). Conclusion Preoperative patients with dealing with the comprehensive consideration, in order to reduce the incidence of temporalis cut off phenomenon, and will be reset by the temporal muscle.
[Key words]Temporomandibular joint disorders, Neurosurgery, Pterional keyhole craniotomy, Temporomandibular joint displacement
传统观念认为神经外科开颅手术后颞下颌关节紊乱(TMD)是的一种较少发生的并发症,发病率低于1%,好发于额颞开颅对颞肌及颞骨破坏较大的手术[1]。本研究通过严谨的临床观察,统计额颞开颅手术中,出现术后颞下颌关节(TMJ)咬合疼痛患者发生率为5%,远期出现颞下颌关节脱位患者约占2%,习惯性颞下颌关节脱位患者约为1%。对2010~2014年于我院就诊行开颅手术患者术后存在颞下颌功能紊乱患者180例。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
本研究选择的对象开颅手术后存在颞下颌功能紊乱患者180例,患者年龄4~75岁,平均年龄(50±4)岁。术后发生TMD时间1~2年。TMJ疼痛患者100例,TMJ脱位80例。选取经额颞开颅术后患者180例,均无TMD症状。其中对照组,年龄(60±10)岁,2组患者一般资料无显著性差异,因此可以进行比较。
1.2方法
颞肌容积对于颞肌功能的评判具有重要的价值。于MRI在检查颞肌厚度及分布面积,定义颞肌厚度×长度×高度/2=颞肌
容积(V)。颞肌范围在磁共振T1上取前至额颧突,上至顶结节,下至颧弓中点。取颞肌范围内的最厚层面为厚度。取额颧突到颧弓中点为长度。取颧弓中点到顶结节距离为高度。分别计算双侧V值,以及对照组V值,详见表1。
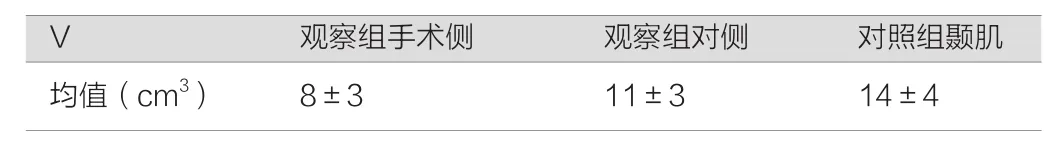
表1 对比两组患者的相关指标
1.3 统计学处理
数据处理软件包为SPSS 16.0,组间比较采用t值检验,计数资料比较采用χ2检验,P<0.05表示有显著性差异。
2 结果
发生TMD组,肌肉容积较对侧平均减少30%。较对照料组平均减少52%。对于额颞去骨瓣减压患者而言,产生下颌功能紊乱的发生率高于其他相关手术产生此现象的发生率。与此同时对患者的颞肌容积(肌肉所占体积)进行检测,产生颞下颌功能紊乱患者肌肉厚度的平均值<5 mm,和对照组相比,其肌肉厚度大于对照组患者,对比两组患者的颞肌容积,观察组低于对照组。两组患者通过对比,存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。
3 讨论
TMD是TMJ、咀嚼肌及周围相关结构表现的不同症状及体征的一个总称,临床表现主要包括关节区疼痛、关节杂音及功能障碍,伴或不伴有下颌骨运动受限,TMJ及相关肌肉触痛等[2]。根据我们的研究:咀嚼痛发生多在术后3个月以内,而下颌关节脱位随着时间的延长,发生概率在术后1年左右达到高峰。通过TMJ磁共振成像平扫发现,无论对照组还是观察组,都存在不同程度的TMJ骨质退化。其中髁突吸收率>32%。大于普通TMD患者髁突吸收率2.3%~26%。颞下颌关节活动异常导致了关节的退变,长期的关节退变,可能产生关节区疼痛及运动障碍等[3]。
作为神经外科医生,手术前将术后MTD作为一个考虑因素,手术时应尽可能的避免不必要的颞肌及颞骨损伤,减少不必要的颞肌切断,尽量将颞肌复位,保持肌肉适度的张力是防治颞肌萎缩的有效措施[4]。当MTD发生后,积极寻求口腔科医生指导治疗,部分病人症状能得到缓解。
综上所述,对经额颞行开颅手术患者而言,在手术前应对患者进行全方位的考虑,在对其进行手术时需要尽自身最大限度复位颞肌。
参考文献
[1]E L Zager,D A DelVecchio,S P, Bartlett. Temporal muscle microfixation in pterional craniotomies. Technical note[J]. Neurosurg,1993,79(6):946-947.
[2] De Santana Santos T,Albuquerque KM,Santos ME,et al. Survey on complications of orthognathic surgery among oral and maxillofacial surgeons[J].Craniofac Surg,2012,23(5):e423-e430.
[3] Yasuda CL,Costa AL,Franca M Jr,et al. Postcraniotomy temporalis muscle atrophy: a clinical, magnetic resonance imaging volumetry and electromyographic investigation[J]. Orofac pain,2010,24(4):391-397.
[4] 苏崇德,常鹏飞. 额颞开颅颞前叶切除术中颞肌处理的技术问题[J]. 中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2011,10(3):227-229.
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2015.25.055
【文章编号】1674-9308(2015)25-0082-02
【文献标识码】B
【中图分类号】R782.6+3

