初中生学校恐惧心理及其影响因素研究
初中生学校恐惧心理及其影响因素研究
姚爱贞
(郑州大学教育系,河南郑州450001)
[摘要]采取分层抽样法抽取289名初中生,利用问卷调查法对其进行学校恐惧、自我效能感、应对方式、家庭关怀指数、社会支持等方面的调查。结果表明:(1)农村初中生学校恐惧得分显著高于城市初中生,初三学生学校恐惧得分显著高于初一学生;(2)自我效能感、指向问题的应对方式、成长度、社会支持、主观支持、客观支持及对支持的利用度对降低学校恐惧具有积极作用,指向情绪的应对方式对降低学校恐惧具有消极作用;(3)自我效能感、指向情绪的应对方式、成长度、适应度、对支持的利用程度对初中生学校恐惧心理具有较好的预测作用。
[关键词]初中生;学校恐惧;心理社会因素
[中图分类号]G844.1
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1674-3652(2015)02-0136-05
[收稿日期]2014-12-25
[作者简介]姚爱贞,女,河南巩义人。主要从事中小学职业发展与教育研究。
Abstract:Loyalty and piety have been playing an important role in carrying the social ethics in traditional Chinese moral culture. Since the imperial regime of Qin and Han dynasties was established,“loyalty”has become the basic principle of political moral. The combination of“piety”with“loyalty”leads to the interpretation of“be loyal to the emperor with the piety”and“serve the emperor with piety”. The moral propaganda of piety and loyalty as a unity and the identification on different social strata have become an influential cultural phenomenon in the history of Chinese ideology. In the mainstream ideology of traditional Chinese moral,“loyalty”plays a more important role. The so-called“be loyal to emperor with piety”and “seek loyalty from piety”are an embodiment of the special relations between“loyalty”and“piety”. There has been a new round of research upsurge of Chinese chieftain system and chieftain culture. In 2013, the research was mainly conducted in the following aspects: 1. research of the basic theory and methods for chieftain system study; 2. research of the classic works about Chinese chieftain system and culture; 3. research of Chinese chieftain system itself; 4. research of changing from chieftain to flowing officials; 5. research of chieftain culture; 6. research of application of the list of world heritage. These researches have not only laid solid academic foundations for the construction of chieftain study, but also provided possibility for the effective exploitation of chieftain culture. However, there still exist some deficiencies in terms of research perspective, discourse system, research contents and methods, document sorting, academic monographs, and team cooperation. This article mainly focuses on the last three aspects. Taking Yongshun ancient chieftain town as a case study, this article explores the protection of historical sites. The value of historical sites is mainly embodied in its relevance of physical space with history. The space of the ancient chieftain town is an emblem of the power relationship between chieftain and local masses, and between chieftain and central imperial court. Its continuation of history relies on the belief ritual and daily life of the local masses. Currently, with the protection of historical sites and planning of space display, the protection conception of outer planners is contradictory to the local residents’daily life and future development. The writer of this article holds that the view of dynamic protection by agglomerating local cultural identity should be the new direction for the protection of historical sites. A lot of bronze weapons were found to have been destroyed in the tombs in Ba and Chu areas during the period from Warring State to Western Han and Eastern Han Dynasties. This peculiar funeral custom was in fact the inheritance and continuation of the funeral custom of Central Plains during Western Zhou period. Apart from the primitive religious ideas about exorcism and counteracting evil force and the differences of weapon between human and ghosts, it was closely related to the change of social climate at that time. Situated in the remote southwest, Guizhou had not been well-known to the outsiders until Ming and Qing dynasties when, with the entrance of the central power, there were more and more scholars from outside, causing a surge of writing about social life in Guizhou. Some of the guest scholars left a lot of texts about Miao people’s living, food, clothes, rituals, and customs, displaying to the outside people the colorful life of Miao people. But the majority of descriptions are based only on the writers’life experience, with some imagined elements which deviate from the historical fact. Wulingshan area in southeast Chongqing is functionally established as limited and forbidden development area on the national level and ecological protection development area on Chongqing municipal level. As the limited and forbidden development area is a typical problem area, the promotion of functional area needs the nation to construct and improve special development policy which should focus on the following five aspects: central public financial policy, national ecological compensation policy, public service policy, new urbanization policy, and green ecological industrial policy. China’s international status has been one of the foci of history study. Based on the research achievements in the past 20 years, the writer of this article focuses on the analysis of the major views related to the field, and at the same time summarizes the causes for the changes of China’s international status during the war of resistance against Japanese, as well as the relationship between the changes and international order. On the basis of the researches of former scholars, the writer attempts to provide some suggestions for extending the research field. Of the linguistic characteristics of legal materials on bamboo slips in Qin and Han dynasties, abbreviation is remarkable. Through textual research, the writer of this article finds that“zhan wei cheng dan”is abbreviated from“zhan zuo zhi wei cheng dan”,“fa er yue”from“fa zi lao er ge yue”,“yuan”from“yue yuan”and“xia”from“qu xia”,“qu”is from“qu shu,“dian”from“li dian”,“lao”from“wu lao”and “mian lao”. The knowledge of these abbreviations will help us correctly understand the legal texts of Qin and Han dynasties and better know ancient China’s legal system. In the context of repeated review of classics, heterogeneity of Hibiscus Town is found to have overthrown the heroic tradition in the mainstream literary narration and created a weak and incompetent male world. Through bold and ethnic writing of female body, the novel expresses the rationality of personal desire concealed by the state discourse. While borrowing the mainstream narration mode, the novel makes use of a lot of local resources to form knowledge of locality with independent perspective. We may regard the novel as an important resource for constructing the current literary tradition. On January 17th, 2014, People’s Daily published a written conversation discussing the relationship between current literature and history. After that, Literary Review launched another written conversation on the second issue of 2014 on“literature cannot be devoid of history”. After analyzing some literary phenomena, the writer of this article holds that although literature is related to history, it cannot replace history and vice versa. Both Socrates and Plato were the founders and great achievers of ancient Greek philosophy, but they were quite different in their pursuit of social justice and goodness. From the perspective of ethics, the writers of this article focus on the differences in terms of background, contents, goal and influences of their ethical theories, so as to achieve a deeper understanding and cognition of their thoughts. The knowledge value, method value, thought value and humanity value in the socialist core value are the value soul of school curricula, the value standard for the development of school curricula, and conciseness of core concept and objection reconstruction; they are the value scale and method choice of content innovation organization of school curricula, and the spiritual pursuit of school curricular practictioners. They act on the curricular practice in every way and throughout the whole process. By the identification of curricular practioner with socialist core value, they are integrated into the value objective of school curricula.
一、问题的提出
良好的心理素质是中小学生素质教育中的重要组成部分。初中生正处于身心发展的加速期和过渡期,随着生理及心理的发育和发展、社会阅历及思维方式的扩展和变化,他们将面临学习、生活、人际交往、升学就业和自我意识等诸多方面的心理困惑及压力。张向葵(2001)指出,学校是初中生接触最多的场所,学校生活是否顺利对初中生的心理健康有直接的影响[1] [2]。国内外有关学校恐惧的研究大多集中于学龄儿童,有关初中生学校恐惧的研究不多。然而现实表明,初中生的学校恐惧已成为影响初中生学习及生活的重要因素,并给家长、学校及社会带来很大的困扰。
学校恐惧是青少年中常见的一种心理障碍,学校恐惧并不是一个专用的医学术语,有些人也称它为“学校拒斥”“学校恐怖”“惧学症”。综合他人的研究成果,我们将学校恐惧定义为:学生对学校产生厌恶倾向并伴有试图回避学校的行为。关于不同类别初中生学校恐惧差异的研究结果主要集中在以下几个方面:
第一,初中女生较之男生更容易产生学校恐惧倾向[3] [4]。
第二,农村初中生较之城市初中生更容易产生学校恐惧倾向[3]。
第三,关于初中生学校恐惧的年级差异,研究结论不尽相同[5] [6]。
已有研究表明,初中生的自我效能感、应对方式、家庭关怀度、社会支持均显著影响学校恐惧[7-14]。这里通过对初中生学校恐惧特点及心理社会影响因素的研究,希望为初中生心理健康教育提供借鉴。
二、研究过程
(一)研究对象
采取分层整群抽样法,于2014年在杭州市机场路中学发放150份问卷,回收有效问卷150份;在涪陵九中发放150份问卷,回收有效问卷139份。共回收有效问卷289份,其中,初中一年级学生92人,初中二年级学生108人,初中三年级学生89人;男生140人,女生149人;城市学生150人,农村学生139人。
(二)研究工具
自编初中生学校恐惧问卷。通过参阅大量有关焦虑、恐惧、学校恐惧、学校焦虑等文献,对30名初
中生及6名初中教师进行访问,并参照闫荣双对初中生学校恐惧的结构划分,将学校恐惧的内涵界定为“在学校情景中,学生感知到由学习压力、同伴交往、教育方法、校园暴力、学校纪律及教学设备等因素产生的威胁,从而诱发的情绪反应。”[15]围绕这一内涵界定,结合收集到的有关学校恐惧的具体内容,反复筛选,拟将20道具有代表性的题目作为学校恐惧的问卷项目。根据对学校恐惧的定义和部分心理学老师、研究生及初中老师的意见,最终拟定学校恐惧问卷由以下4方面构成,即对逃离学校环境的幻想、对学校压力的认知、对学校情境中易出现问题的担心和对学校人际关系的焦虑,最后形成包括4个项目的最终问卷,每个题目设置5个选项即“总是”“经常”“有时”“偶尔”“从不”,采用反向计分法。在问卷初步编制后,对100名初中生进行预测验,结果表明,克龙巴赫系数为0.701。
一般自我效能感量表(General Self-Efficacy Scale)。采取张建新和Schwarzer编制的一般自我效能感量表,共10个项目,采用李克特4级评分,此量表为单维量表,只统计总量表分。该量表的克龙巴赫系数为0.87,重测信度为0.83,折半信度为0.82。
中学生应对方式量表(Coping Style Scale For Secondary Student)。采取张作记编制的中学生应对方式量表,该量表有2个分量表即“指向问题的应对方式”与“指向情绪的应对方式”。该量表的克龙巴赫系数为0.92,重测信度为0.89,因素分析结果显示量表的结构效度较好。
家庭关怀度指数(Family APGAR Index)。采取Smilkstein医师设计的家庭关怀度指数量表,包括适应度(Adaptation)、合作度(Partnership)、成长度(Growth)、情感度(Affection)、亲密度(Resolve)等5个因子,共5个项目,采用3级评分。该量表的再测信度为0.8-0.83,且具有良好的预测效度。
社会支持评定量表(Social Support Rating Scale)。采取肖水源编制的社会支持评定量表,包括客观支持(共3个条目)、主观支持(共4个条目)和对社会支持的利用度(共3个条目)等3个因子。该问卷的克隆巴赫系数为0.90,重测信度为0.92,且具有较好的预测效度。
(三)研究过程及数据处理
以班级为单位进行团体施测,被试逐项填写,5份问卷一次性完成。利用SPSS19.0对数据进行t检验、单因素方差分析、相关分析及多层回归分析。
三、研究结果与分析
(一)初中生学校恐惧的基本情况
对初中生在学校恐惧问卷上的得分进行描述统计,采用独立样本t检验对初中生学校恐惧的性别、城乡差异进行比较,统计结果见表1。

表1 不同性别、来源初中生在学校恐惧问卷的得分情况(M±SD)
从表1可知,初中男生在学校恐惧问卷上得分略高于女生,但不具有统计学意义,说明男女生在学校恐惧问题上基本相同;农村初中生在学校恐惧问卷上得分显著高于城市初中生的得分。对初中各年级在学校恐惧问卷上的得分进行描述统计,并进行单因素方差分析,统计结果见表2。
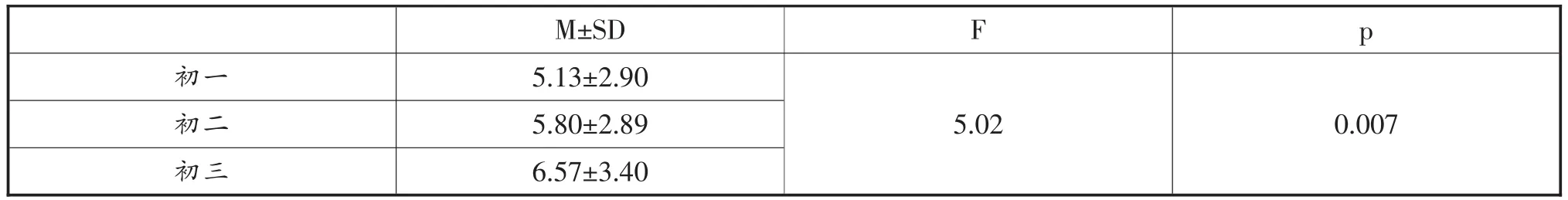
表2 不同年级初中生在学校恐惧问卷上的得分情况(M±SD)
从表2可知,不同年级在学校恐惧问卷上的得分差异非常显著,初三学生的学校恐惧得分最高,初二
次之,初一最低。采用LSD(即最小显著法)对不同年级学生在学校恐惧问卷上的得分进行事后检验,结果发现,初一与初三学生得分差异非常显著;初二与初三、初一与初二学生之间差异不显著。
(二)初中生学校恐惧与心理社会因素的相关分析
为考查学校恐惧与心理因素的关系,采用皮尔逊相关法对自我效能感、指向问题的应对方式、指向情绪的应对方式和学校恐惧两两之间分别计算相关系数,结果见表3。

表3 初中生学校恐惧与心理因素的相关系数(r)
从表3可知,学校恐惧与自我效能感、指向问题的应对方式呈显著负相关,与指向情绪的应对方式呈显著正相关,表明自我效能感、指向问题的应对方式对学校恐惧有积极作用,指向情绪的应对方式对学校恐惧有消极作用。
为考查学校恐惧与社会因素的关系,采用皮尔逊相关法对家庭关怀指数、适应度、合作度、成长度、情感度、亲密度、社会支持和学校恐惧两两之间分别计算相关系数,结果见表4。

表4 初中生学校恐惧与社会因素的相关系数(r)
从表4可知,学校恐惧与成长度、社会支持、主观支持、客观支持、对支持的利用度呈显著负相关,表明成长度、社会支持、主观支持、客观支持、对支持的利用度等对学校恐惧有积极作用;学校恐惧与合作度、情感度、亲密度、家庭关怀指数总分呈负相关,与适应度呈正相关,但均不具有统计学意义。
(三)心理社会影响因素对初中生学校恐惧的多元逐步回归分析
以学校恐惧总分为因变量,以自我效能感、指向问题的应对方式、指向情绪的应对方式、适应度、合作度、成长度、情感度、亲密度、主观支持、客观支持、对支持的利用度等因子为自变量进行多元逐步回归分析,结果发现有5个因子进入了回归方程(进入水平0.05,剔除水平0.10)。其回归方程的多元相关系数R=0.62,决定系数R2=0.38,调整后的R2=0.37,方差分析结果是F=34.85,P=0.000,说明此回归方程的有效性是较好的,具体结果见表5。
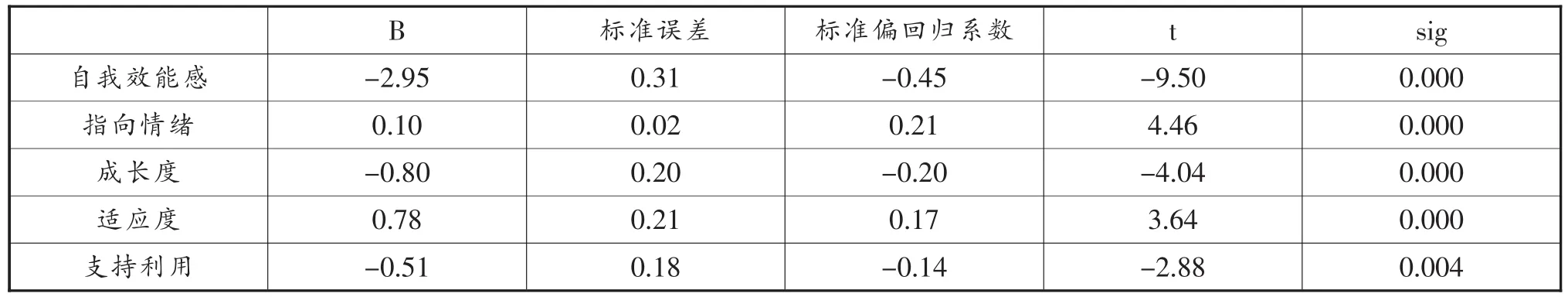
表5 心理社会影响因素对初中生学校恐惧的多元逐步回归分析
从表5可知,在进入回归方程的5个自变量中,自我效能感对学校恐惧的预测作用最大,指向情绪的应对方式对学校恐惧的预测作用最小。具体说来,自我效能感、成长度、对支持的利用程度对学校恐惧具有积极作用;指向情绪的应对方式、适应度对学校恐惧有消极作用。
四、讨论
(一)初中生学校恐惧的基本情况
在性别变量上,研究发现初中男生的学校恐惧略高于女生,但无显著性差异,研究结果与他人研究有出入。在青春期,女生发育比男生早,心智也更加成熟,这使得女生在面对学校问题上,和男生有一样的甚至有更为成熟灵活的处理能力,因而在面对学校问题时,女生的表现也不比男生差。
在城乡变量上,研究发现农村初中生的学校恐惧显著高于城市初中生,与他人研究结果一致。这可能与农村的生活环境、生活条件有关。心理健康教育、教学环境等教育因素也会影响初中生对学校的态度。近年来,农村校园安全隐患日益成为威胁农村初中生学习生活的一大因素。
在年级变量上,研究发现初三学生学校恐惧的得分显著高于初一学生。这可能是因为初三学生相比初一和初二学生,面临着升学压力。本研究于3月份进行,中考压力对初三学生的影响更是显而易见。
(二)影响初中生学校恐惧的心理社会因素
1.自我效能感。调查发现,初中生自我效能感与学校恐惧呈显著负相关,且自我效能感对学校恐惧有很好的预测作用,这说明初中生的自我效能感越高,学校恐惧水平则越低。根据班杜拉等人对自我效能感的定义,可以推断,自我效能感也会影响学生在学习上的努力程度和坚持性,影响学生在学校遇到困难时的态度,左右学生在学校的情绪。当学生确信自己有能力取得好成绩、有能力应付在学校出现的各种问题、有能力处理好同伴关系、有能力对自己的行为负责时,便能更好地融入学校环境。所以,要帮助初中生更好地适应学校生活,自我效能感的培养应成为学校及家庭教育的重要内容。
2.应对方式。调查发现,指向情绪的应对方式与学校恐惧呈显著正相关,且指向情绪的应对方式对学校恐惧具有很好的预测作用,说明当学生采取指向情绪的应对方式时,更容易产生学校恐惧。这与大多数研究结果一致。有研究表明,对初中生来说,当压力可控时,使用“以问题为焦点”的策略比较好,较少出现学校恐惧。学校是初中生经常接触且不可避免的场合,倘若采用指向情绪的应对方式,企图以忍耐、逃避、发泄情绪、幻想、否认等方式来应对学校恐惧,这显然是不可取的,且失败的应对结果又加剧了学生对学校的恐惧,形成恶性循环。
采取指向问题的应对方式与学校恐惧呈显著负相关,说明采取指向问题的应对方式,例如问题解决、寻求社会支持、积极的合理化解释等,将减轻学校恐惧对初中生的威胁。所以,应努力培养初中生形成以解决问题为主的应对方式。
3.家庭关怀。调查发现,家庭关怀指数中的4个因子(适应度、合作度、情感度、亲密度)与学校恐惧的相关不明显,与已有研究结论不一致。这可能暗示,进入中学阶段后,初中生与同伴及老师的交往比与父母的交往更密切,即使家庭给予再多的关怀,也是“远水解不了近渴”,故清除学校恐惧应更多地依赖个人的内部力量,如自我效能感、应对方式等。
成长度与学校恐惧呈显著负相关,且成长度对学校恐惧具有很好的预测作用。成长度指家庭成员在身心发展上得到其他成员支持与引导的程度。很明显,这个因子相比于其他的4个因子,强调对孩子提供实际的帮助和指导。正如前面所论述的那样,学校压力对初中生来说是长期存在且不可避免的一种困扰,因而,如果父母注意用现实经验指导孩子处理学习生活中的常见问题,教会技巧,而非纯说教式的教育,将有利于缓解学校恐惧的心理。
此外,适应度对学校恐惧起到显著的消极作用,这有悖于我们的常识经验,这一点有待后续研究的深入探讨。
4.社会支持。调查发现,学校恐惧与社会支持、主观支持、客观支持、对支持的利用度有非常显著的负相关关系,且“对支持的利用度”对学校恐惧具有较好的预测作用,说明初中生获得的社会支持越多,学校恐惧水平越低,这与大多数研究结果一致。个体良好的社会支持网络使其容易获得自尊和自我效能
感,从而抑制心理问题的产生,尤其是当个体面对学校压力时,社会支持一方面会降低个体对压力的感受程度,另一方面也为个体提供了问题解决的途径,从而弱化学校恐惧对初中生的影响。
对支持的利用度也在缓解学校恐惧方面发挥着重要作用,这就提示我们,个体对社会支持的利用存在差异,有的学生虽然拥有众多的社会支持资源,但却不善于发现这些资源,甚至拒绝别人的帮助,这肯定不利于学校恐惧问题的解决,所以应将“获得社会支持资源”与“善于利用社会资源”摆在同等重要的位置。
参考文献:
[1]张向葵.青少年心理问题研究——当代青少年心理问题反思与回应对策[M].长春:东北师范大学出版社,2001:212-219.
[2]秦晓霞,黄永进,丁宝坤.学校恐怖症的临床特点与心理社会因素分析[J].心理发展与教育,2003(3):11-13.
[3]钱昀,施慎逊,杜亚松.学校恐惧症的研究进展[J].上海精神医学,2005(2):112-114.
[4]朱月龙.青少年的6堂心理课[M].北京:海潮出版社,2006:33-35.
[5]马玉玲,柴寿文.抓住中学生心理发展的关键阶段,加强中学生心理健康教育[J].心理健康教育,1995(11):11-13.
[6]郑雪.中学生心理健康教育[M].广州:广东高等教育出版社,2004:278-287.
[7]谷丹.初中生父母教养方式、学业自我效能感与学业成绩的关系[D].东北师范大学,2010.
[8]谷崴.初中生师生关系、学业自我效能感与学业适应的关系[D].东北师范大学,2010.
[9]李婷婷.初中生学业归因、学业自我效能感与学习倦怠关系的研究[D].沈阳师范大学,2010.
[10]张文新.青少年发展心理学[M].济南:山东人民出版社,2002:17-25、506-507.
[11]陈树林,郑全全.中学生应激源、应对方式和情绪相关性研究[J].中国心理卫生杂志,2002(5):337-339.
[12]王晓琼.探讨初中生厌学的原因和对策[J].中国教师,2009(8):474.
[13]王军,李永超,伍毅.初中生焦虑情绪与家庭养育方式相关研究[J].中国临床心理学杂志,2006(2):98-99.
[14]叶曼.湖南省农村留守初中生心理健康状况及影响因素的研究[D].中南大学,2011.
[15]闫荣双.初中生学校恐惧的特点研究[D].山东师范大学,2004.
[责任编辑:庆来]
Piety with Loyalty vs. Loyalty with Piety: An Investigation of China’s Moral History
WANG Zi-jin
(School of Chinese Classics, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China)
Key words: loyalty; piety; piety with loyalty; loyalty with piety; political moral; social moral
A 2013-Annual Report of Researches in Chinese Chieftain System and Culture
China Chieftain System and Culture Research Team
(Yangtze Normal University, Chongqing 408100, China)
Key words: Chinese chieftain system; chieftain culture; researches; annual report
Space, Emblem and Protection of Historical Sites --A Case Study of Yongshun Ancient Chieftain Town
LI Ling-xia
(School of History and Cultural Study, Jishou University, Jishou, Hunan 416000, China)
Key words: space; emblem; cultural heritage; Yongshun ancient chieftain town
An Investigation and the Relevant Cognition of“Weaponry Destruction”in the Tombs of Ba and Chu Areas
ZHU Shi-xue
(Museum of Enshi Autonomous Prefecture, Enshi, Hubei 445000, China)
Key words: Ba people; weaponry destruction; investigation; cognition
Social Life of Miao People in the Perspective of Guest Scholars to Guizhou in Ming and Qing Dynasties
SUN Jing
(School of History and Political Science, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, Guizhou 550001, China)
Key words: Ming and Qing dynasties; Guizhou; guest scholars; Miao people; social life
Construction and Perfection of Development Policy in Forbidden Development Area --Based on the Investigation of Wulingshan Area in Southeast Chongqing
YAO Yuan-he
(Qianjiang Branch of CPC Chongqing Municipal Party School, Qianjiang, Chongqing 409000, China)
Key words: forbidden development area; strategy of major function-oriented region; policy construction and perfection
A Summary of the Researches of China’s International Status during the Anti-Japanese War
GENG Mi
(Chongqing Research Center for Anti-Japanese War in the Un-occupied Area, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715; School of Administration, Southwest University of Political Science and Law, Chongqing 401120, China)
Key words: the War of Resistance against Japanese; China’international status; review of the researches
Abbreviation of Legal Terms on the Bamboo Slips in Qin and Han Dynasties
ZHAO Jiu-xiang
(School of Liberal Arts, Yangtze Normal University, Chongqing 408100, China)
Key words: Bamboo slips in Qin and Han dynasties; legal terms; abbreviation
Yan Jun’s“Village Eclogue”--On the Writing of Gender and the Knowledge of Locality in Hibiscus Town
KANG Bin, TAN Mei
(School of Literature and Journalism, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610064; Chengdu Normal University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610106, China)
Key words: Hibiscus Town; gender; male image; rogue discourse; writing of female body; knowledge of locality
How Can Literature Be Devoid of History?
WEI Wei, MA Yue-yue
(Modern Chinese Poetry Research Institute, Chinese Literature Research Institute, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China)
Key words: literature; history; literature“devoid”of history
A Comparison of Socrates’and Plato’s Ethical Thought
LI Yin-bing, YANG Zheng-jun
(School of Political Science and Law, Yuxi Normal University, Yuxi, Yunnan 653100, China)
Key words: Socrates; Plato; ethical thought; comparison
Exploring the Integration of Socialist Core Value with School Curricula
JIN Yu-jun
(School of Marxism, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China)
Key words: socialist core value; school curricula; value identification
[英文编辑:曾文武]


