基于高频旋转电压注入的永磁同步电机无位置传感器矢量控制
张伯泽, 阮 毅
(上海大学,上海 200072)
基于高频旋转电压注入的永磁同步电机无位置传感器矢量控制
张伯泽, 阮 毅
(上海大学,上海 200072)
对基于高频旋转电压注入的内置式永磁同步电机(IPMSM)无位置传感器矢量控制策略进行了研究。向IPMSM注入高频旋转电压矢量,应用IPMSM的高频模型,推导出高频电流响应。提出了一种高频电流信号提取方案,从高频电流响应中估算出IPMSM的位置。提出的控制策略可以实现IPMSM从极低速0.5Hz到高速的宽范围工作。大量的仿真结果表明: 提出的控制策略有良好的动态响应和稳态响应,位置和转速估算有较高的精度,系统有较强的鲁棒性,IPMSM在极低速下运行良好。
内置式永磁同步电机; 高频旋转电压注入; 矢量控制; 无位置传感器控制
0 引 言
永磁同步电机因其体积小、重量轻、响应快、损耗小、功率密度大和效率高等优点获得了广泛应用[1-2]。通常情况下,对永磁同步电机转速和转矩的精确控制,是用位置或速度传感器实现的。然而,位置和速度传感器的安装需要额外的空间,且有位置或速度传感器的系统成本高、可靠性低、不易维护。
为了替代位置和速度传感器,提出了各种控制策略,总体上可分为两大类: 基波模型法[3-8]和高频信号注入法[9-17]。基波模型法直接或间接地从反电动势中提取位置信号,实施起来简单。但是基波模型法对电机的参数变化敏感;在低速和零速时,反电动势很小甚至为零、难以提取,此时该类方法不能正常工作。高频信号注入法在电机出线端注入高频电压(或电流)信号,通过检测产生的高频电流(或电压)响应来获得转子位置信息。高频信号注入法能够解决永磁同步电机低速和零速下的转子位置估算,对电机的参数变化不敏感,鲁棒性好。近年来出现了人工智能法[18-19],这类方法硬件复杂、实现困难,目前多停留在理论研究阶段。
本文向内置式永磁同步电机(Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor, IPMSM)注入高频旋转电压矢量,应用IPMSM的高频模型,推导出高频电流响应,提出一种新型高频电流信号提取方案和位置估算策略,准确地跟踪转子永磁体的位置,实现了IPMSM的无位置传感器控制[20]。本文建立了仿真模型,对所提出的控制策略进行了验证。大量的仿真结果表明: 本文提出的控制策略具有良好的动态响应和稳态响应,估算的位置和转速有较高的精度,系统有较强的鲁棒性,IPMSM在极低速0.5Hz下运行良好。
1 高频旋转电压注入下的IPMSM数学模型
在同步旋转d、q坐标系中,IPMSM的数学模型为
(1)
忽略电阻压降及反电动势,则IPMSM的高频模型变为
(2)
用Park反变换,可将上述d、q坐标系中的IPMSM高频数学模型变换为静止α-β坐标系中的高频数学模型:

(3)
式中:L——平均电感,L=(Lsd+Lsq)/2; ΔL——半差电感,ΔL=(Lsq-Lsd)/2。
2 基于高频旋转电压注入的IPMSM无位置传感器矢量控制策略
在静止α、β坐标系中注入高频旋转电压矢量为
usαβc=ucjωct
(4)
式中:uc——注入高频旋转电压的幅值;ωc——高频旋转电压的角频率。
向IPMSM注入高频旋转电压矢量后,产生的高频电流响应为
isαβc=Icpej(ωct-π/2)+Icnej(2θr-ωct+π/2)
(5)
其中:

(6)

(7)
从高频电流响应中可见,其包含两个分量: 正序分量和负序分量。正序分量中不包含位置信息,只有负序分量中含有位置信息。如何将IPMSM的位置信息从负序高频电流分量中提取出来,便成为进一步研究的核心。
本文先用带通滤波器(BPF)将低频和其他频率的高频信号滤除,获得高频旋转电压注入下产生的高频电流响应。之后,用ej(-ωct+π/2)乘以这个高频电流矢量,将正序高频电流分量转变为直流分量,用BPF将此直流分量滤除,得到含有位置信息的负序高频电流分量。
提取负序高频电流分量后,用外差算法解调出IPMSM的转子位置,转子位置的估算表达式如式(8)所示:


(8)

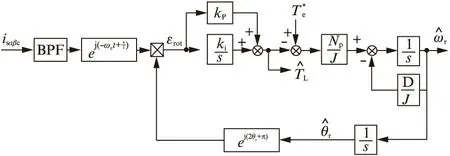
图1 基于高频旋转电压注入的IPMSM位置估算原理图
3 仿真研究
对基于高频旋转电压注入的IPMSM无位置传感器矢量控制系统进行了仿真验证,注入高频旋转电压的幅值为10V,频率为1000Hz。IPMSM的参数如表1所示。电机运行速度范围从极低速30r/min(对应0.5Hz)到高速3600r/min,仿真结果如图2~图13所示。

表1 IPMSM的参数

图2 α轴负序高频电流响应波形(30r/min)

图3 β轴负序高频电流响应波形(30r/min)

图4 转子速度的实际值(30r/min)

图5 转子速度的估算值(30r/min)

图6 转子速度的实际值与估算值之差(30r/min)
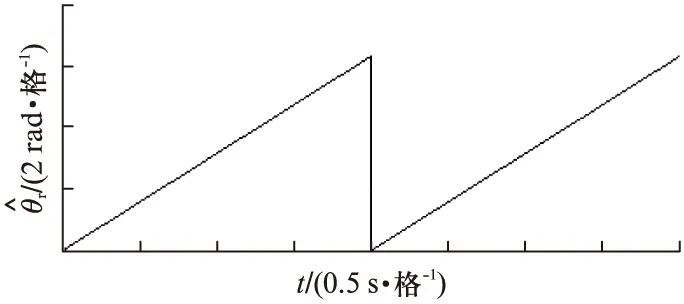
图7 转子位置的估算值(30r/min)

图8 α轴负序高频电流响应波形(3600r/min)
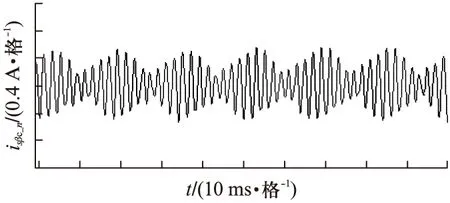
图9 β轴负序高频电流响应波形(3600r/min)
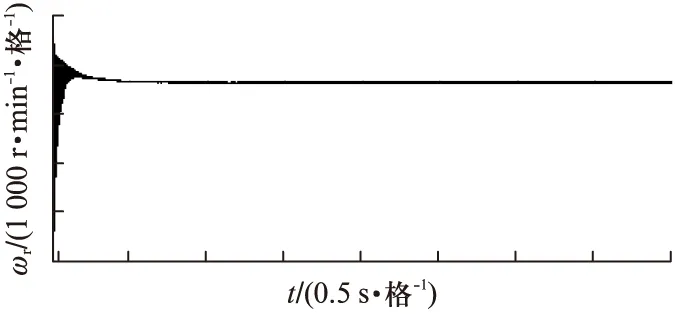
图10 转子速度的实际值(3600r/min)

图11 转子速度的估算值(3600r/min)

图12 转子速度的实际值与估算值之差波形(3600r/min)
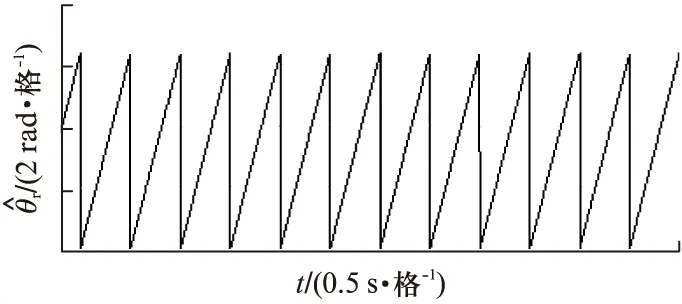
图13 转子位置的估算值(3600r/min)
从波形可以看出,基于高频旋转电压注入的IPMSM无位置传感器矢量控制策略具有良好的动态响应和稳态响应,在极低速30r/min下运行良好,转速估算在稳态时具有较高的精度。
4 结 语
本文向IPMSM注入高频旋转电压矢量,应用IPMSM的高频模型,推导出高频电流响应。本文提出了一种新型高频电流控制信号提取方法和位置估算策略,从高频电流响应中提取位置信息,实现了对IPMSM转子位置和转速的估算。对所提出的控制策略进行了验证,仿真结果表明: 本文提出的控制策略有良好的动态响应和稳态响应,估算的位置和转速有较高的精度,系统有较强的鲁棒性,IPMSM在极低速下运行良好。
[1] 张伯泽,阮毅.内置式永磁同步电机最大转矩电流比控制研究[J].电机与控制应用,2015,42(2): 13-15.
[2] 崔俊国,肖文生,喻高远,等.潜油永磁同步电机国内外研究进展[J].电机与控制应用,2015,42(3): 7-12.
[3] BOLOGNANI S, TUNIANA L, ZIGLIOTTO M. Extended kalman filter tuning in sensorless PMSM drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2003,39(6): 1741-1747.
[4] HAN Y S, CHOI J S, KIM Y S. Sensorless PMSM drive with a sliding mode control based adaptive speed and stator resistance estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2000,36(5): 3588-3591.
[5] SHINNAKA S. New sensorless vector control using minimum-order flux state observer in a stationary reference frame for permanent magnet synchronous motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2006,53(2): 388-398.
[6] JONES J A, LANG J H. A state observer for the permanent-magnet synchronous motor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1989,36(3): 374-382.
[7] LI C, ELBULUK M. A sliding mode observer for sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motors[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Chicago, 2001: 1273-1278.
[8] 黄雷,赵光宙,年珩.基于扩展反电动势估算的内插式永磁同步电机无传感器控制[J].中国电机工程学报,2007,27(9): 59-63.
[9] CORLEY M J, LORENZ R D. Rotor position and velocity estimation for a salient-pole permanent magnet synchronous machine at standstill and high speeds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 1998,34(4): 784-789.
[10] JANG J H, HA J I. Analysis of permanent-magnet machine for sensorless control based on high-frequency signal injection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2004,40(6): 1595-1604.
[11] KIM H, HUH K K, LORENZ R D, et al. A novel method for initial rotor position estimation for IPM synchronous machine drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2004,40(5): 1369-1378.
[12] JEONG Y S, LORENZ R D, JAHNS T M, et al. Initial rotor position estimation of an interior permanent-magnet synchronous machine using carrier-frequency injection methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2005,41(1): 38-45.
[13] LORENZ R D. Practical issues of and research opportunities when implementing zero speed sensorless control[C]∥Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems,Shenyang, China, 2001: 1-10.
[14] 刘毅,贺益康,秦峰,等.基于转子凸极跟踪的无位置传感器永磁同步电机矢量控制研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2005,25(17): 121-126.
[15] 秦峰,贺益康,刘毅,等.两种高频信号注入法的无传感器运行研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2005,25(5): 116-121.
[16] KIM H, LORENZ R D. Carrier signal injection based sensorless control methods for IPM synchronous machine drives[C]∥Proceedings of the 39thIAS Annual Meeting, 2004: 977-984.
[17] PIIPPO A, SALOMAKI J, LUOMI J. Signal injection in sensorless PMSM drives equipped with inverter output filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2008,44(5): 1614-1620.
[18] 李鸿儒,顾树生.基于神经网络的PMSM速度和位置自适应观测器的设计[J].中国电机工程学报,2002,22(12): 32-35.
[19] LI H R, WANG J H, GU S S, et al. A neural-network-based adaptive estimator of rotor position and speed for permanent magnet synchronous motor[C]∥IEEE ICEMS, 2001: 735-738.
[20] 张海燕,刘军,兖涛,等.永磁同步电机在全速范围内的无位置传感器矢量控制[J].电机与控制应用,2014,41(7): 1-5.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Sensorless Vector Control Based on High Frequency Rotating Voltage Injection
ZHANGBoze,RUANYi
(Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China)
The interior permanent magnet synchronous motor(IPMSM) sensorless vector control based on high frequency rotating voltage injection was investigated. By injecting high frequency rotating voltage vector into IPMSM and use IPMSM high frequency mathematical model, the high frequency current response was deduced. One strategy to extract the high frequency current was presented. Then the IPMSM rotor position was estimated from the high frequency current response. By using the control strategy, the IPMSM could work well in the wide speed range from very low speed value 0.5Hz to high speed value. A lot of simulation results verified the proposed control strategy has excellent dynamic and static responses,the estimated position and speed has good precisions and the system was robust, the IPMSM could work well in very low speed value.
interior permanent magnet synchronous motor(IPMSM); high frequency voltage injection; vector control; sensorless control
张伯泽(1976—),男,博士研究生,研究方向为电力电子与电力传动。 阮 毅(1955—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为电力电子与电力传动。
TM 351
A
1673-6540(2016)07-0012-04
2015-11-16

