MTBDRplus V2用于诊断涂阴疑似肺结核患者的效果评价
李强 包训迪 刘元 赵冰 欧喜超 赵雁林

MTBDRplus V2用于诊断涂阴疑似肺结核患者的效果评价
李强 包训迪 刘元 赵冰 欧喜超 赵雁林
目的 评价MTBDRplus V2线性探针技术(简称“MTBDRplus V2”)用于诊断涂阴疑似肺结核患者的检测效能。 方法 连续纳入2014年1—12月在安徽省胸科医院和西安市胸科医院就诊的涂阴疑似肺结核患者1973例,对其1973份痰标本同时开展MTBDRplus V2和MGIT 960快速液体培养(mycobacterial detection system,BACTECTMMGITTM960,简称“MGIT 960培养法”),对培养阳性鉴定为结核分枝杆菌复合群(Mycobacteriumtuberculosiscomplex,MTBC)的菌株,开展利福平和异烟肼药物敏感性试验(简称“药敏试验”),对两种方法耐药检测结果不一致样本进行耐药相关基因测序验证。采用SPSS 22.0软件进行统计学分析,两种方法对MTBC检出率的比较使用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。对利福平和异烟肼耐药基因检测的效能比较分析用敏感度、特异度进行效果评估。 结果 1973例涂阴疑似肺结核患者中,MTBDRplus V2和MGIT 960培养法对MTBC的检出率分别为27.67%(546/1973)和26.76%(528/1973),差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.05,P=0.974)。以MGIT 960培养法为标准,MTBDRplus V2检测痰标本中MTBC的敏感度和特异度分别为86.74%(458/528)和93.84%(1356/1445)。以MGIT 960药敏试验检测利福平和异烟肼耐药结果为标准,MTBDRplus V2检测利福平和异烟肼耐药性的敏感度分别为94.34%(50/53)和77.38%(65/84),特异度为96.62%(372/385)和98.02%(347/354)。结论 MTBDRplus V2可快速准确检测出涂阴疑似肺结核患者痰标本中的MTBC,并可同时检测利福平和异烟肼对MTBC的药物敏感性,其检测结果敏感度和特异度高,对于结核病防控有很好的应用价值。
结核, 肺; 分子探针技术; 分枝杆菌, 结核; 痰; 药物敏感性试验; 评价研究
结核病是严重危害公众健康的全球性公共卫生问题,每年数百万例感染患者,死亡患者在感染性疾病中居第二位[1]。中国是全球第三大结核病高负担国家,结核病发病患者始终居传染病前列[1]。2010年全国第五次结核病流行病学抽样调查结果显示,人群中活动性肺结核患病率没有明显下降,但涂阳患者比例大幅度下降[2]。由于缺乏有效的诊断涂阴结核病的病原学检测方法,使涂阴结核病特别是耐药结核病患者不能得到及时有效的诊断和治疗。
MTBDRplus V1(Hain Lifescience,德国)是一种可以通过反向探针杂交技术快速检测样本中结核分枝杆菌复合群(Mycobacteriumtuberculosiscomplex,MTBC),以及利福平和异烟肼耐药性的分子技术,报告时间短(6~8 h),近几年在全球范围已广泛应用[3-6],2008年被WHO推荐用于涂阳肺结核患者的耐药诊断[7]。与MTBDRplus V1相比,MTBDRplus V2(Hain Lifescience,德国)极大提高了检测样本中MTBC的敏感度,可直接对涂阴肺结核患者的痰标本进行病原学检测[8]。然而,目前国内尚没有关于MTBDRplus V2用于临床诊断的研究报道。本研究以涂阴疑似肺结核患者为研究对象,评价该技术用于诊断涂阴疑似肺结核患者的应用价值,为涂阴疑似肺结核患者的诊断提供科学依据。
材料和方法
一、患者来源
连续纳入2014年1—12月在安徽省胸科医院和西安市胸科医院就诊的胸部X线表现不典型、咳嗽咯痰>2周、有或无肺结核临床症状的连续3次痰涂片镜检抗酸杆菌阴性(简称“涂阴”)的疑似肺结核患者1973例(研究中使用临床剩余痰),其中安徽省胸科医院966例(份),西安市胸科医院1007例(份)。
二、实验室检测
1.痰标本处理:痰标本采用中和离心法去污染处理,按照实验室标准化流程[9],采用N-乙酰-L-半胱氨酸-NaOH (NALC-NaOH)消化液处理,消化后的菌液沉淀重悬于2 ml的磷酸盐缓冲液中,分装两份分别进行BACTEC MGIT 960快速液体培养(mycobacterial detection system,BACTECTMMGITTM960,简称“MGIT 960培养法”)和MTBDRplus V2线性探针技术(简称“MTBDRplus V2”)检测。
2. MGIT 960培养法和药物敏感性试验(简称“药敏试验”):加入0.5 ml处理后的痰标本至MGIT 960培养管(含0.8 ml OADC营养添加剂)中,对培养阳性鉴定为MTBC的菌株,严格按照操作手册将其加入含有利福平(1 μg/ml)和异烟肼(0.1 μg/ml)药物的培养管中,开展利福平和异烟肼的耐药检测。
3.MTBDRplus V2 检测:实验在4个独立房间进行,包括试剂准备间、模版制备区、扩增区和杂交区。实验操作严格按照MTBDRplus V2操作说明,取0.5 ml处理后的痰标本13 000×g离心5 min,弃上清,沉淀用100 μl分子级双蒸水悬浮,95 ℃水浴20 min提取核酸DNA备用;每个样本取5 μl核酸DNA加入含有35 μl AM-B和10 μl AM-A试剂的扩增体系中(Hain, MTBDRplus V2试剂盒),PCR扩增40个循环;取20 μl扩增产物经过化学变性、杂交孵育、洗涤、耦联和显色后,根据试纸条上的探针显色结果判定样本中是否含有MTBC及其对利福平和异烟肼的耐药性。
4.测序:对两种方法耐药检测结果不一致的样本进行耐药相关基因测序验证。采用16SrRNA基因测序进行结核分枝杆菌菌种鉴定,rpoB基因测序用于利福平耐药基因检测,katG和inhA用于异烟肼耐药基因检测。扩增产物由天一辉远生物技术有限公司进行单向测序,序列提交至美国国立生物技术信息中心(NCBI)网站(http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)做同源性比较或多序列比对,引物序列见表1。
三、统计学分析
采用SPSS 22.0软件进行统计学分析,对MTBC检出率的比较使用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。MGIT 960培养法和MTBDRplus V2对MTBC、利福平和异烟肼耐药基因检测效能的比较分析用敏感度、特异度进行效果评估。
结 果
一、两种方法对MTBC检出率的比较
MTBDRplus V2和MGIT 960培养法对MTBC检出率分别为27.67%(546/1973)和26.76%(528/1973),两种方法检出率差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.05,P=0.974)(表2)。
二、 两种方法对MTBC 检测效能的比较分析
以MGIT 960培养法为标准,MTBDRplus V2检测MTBC的敏感度和特异度分别为86.74%(458/528)和93.84%(1356/1445)(表3)。
三、两种方法对利福平耐药基因检测效能比较分析
以MGIT 960药敏试验检测利福平耐药结果为标准,MTBDRplus V2检测利福平耐药性的敏感度为94.34%(50/53),特异度为96.62%(372/385),不同研究现场数据差异不大(表4)。对利福平基因型和表型耐药结果不一致的16例样本进行rpoB基因测序,结果显示12例样本的测序结果与MTBDRplus V2检测结果一致,一致率为75.00%。

表1 耐药基因测序引物序列

表2 两家医院MTBDRplus V2和MGIT 960培养法对涂阴疑似肺结核患者MTBC检出率的比较
注a:培养阳性菌株进行测序鉴定

表3 两家医院MTBDRplus V2对MTBC检测的敏感度和特异度

表4 两家医院MTBDRplus V2进行利福平药物敏感性检测的敏感度和特异度
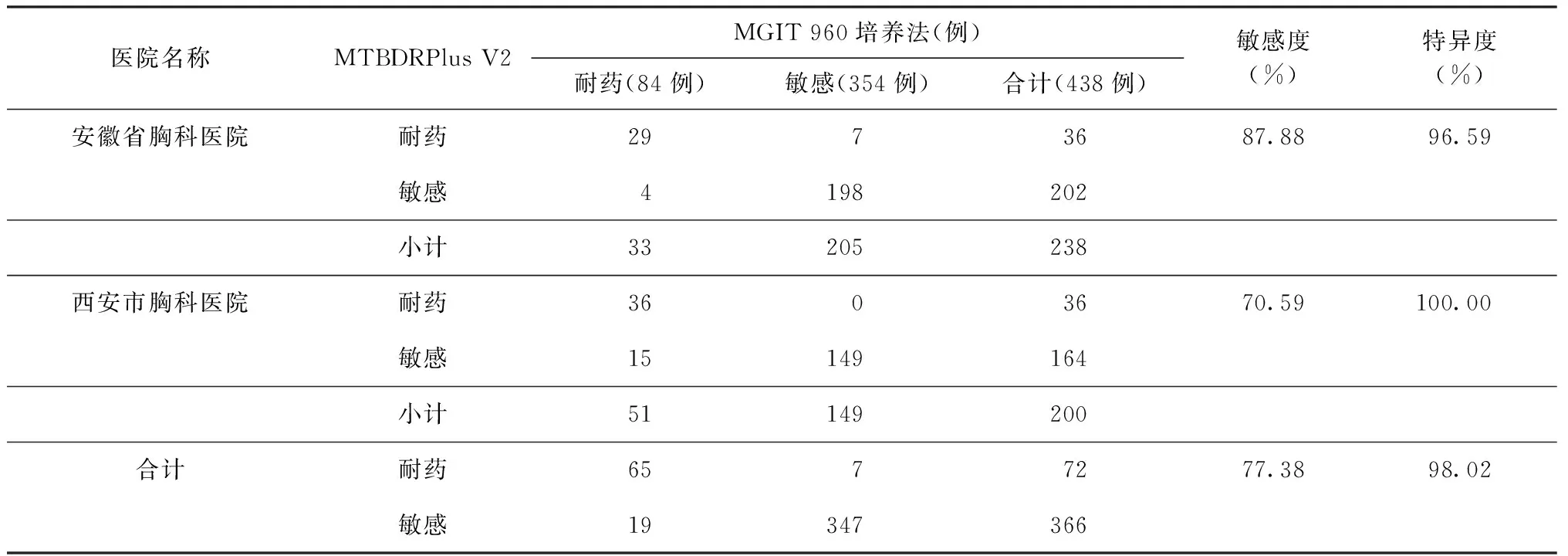
表5 两家医院采用MTBDRplus V2进行异烟肼药物敏感性检测的敏感度和特异度
四、两种方法对异烟肼耐药基因检测效能比较分析
以MGIT 960培养法检测异烟肼耐药结果为标准,MTBDRplus V2检测异烟肼的敏感度为77.38%(65/84),特异度为98.02%(347/354)(表5)。对异烟肼基因型和表型耐药结果不一致的26例样本进行katG和inhA基因测序,结果显示,23例样本的测序结果与MTBDRplus V2检测结果一致,一致率88.46%。
讨 论
本研究率先通过临床对照研究将有前景的MTBDRplus V2检测方法用于涂阴疑似肺结核疾病的诊断中,结果表明 1973例患者中,MTBDRplus V2对MTBC检出率为27.67%(546/1973),与MGIT 960培养法的检出率26.76%(548/1973)相比,差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.05,P=0.974),但MTBDRplus V2检测方法将报告时间从15 d缩短到了1 d[10],与本研究一致。此外,以MGIT 960培养法为标准,MTBDRplus V2检测MTBC的敏感度、特异度分别为86.74%(458/528)和 93.84%(1356/1445),说明其检测效能高。MTBDRplus V2在检测MTBC的同时还可以检测MTBC对利福平和异烟肼的耐药性。与MGIT 960药敏试验结果相比,MTBDRplus V2检测利福平耐药性的敏感度达到94.34%(50/53)以上,而国内研究报道,MTBDRplus V1检测利福平耐药性的敏感度仅88%[10]。对利福平基因型和表型耐药结果不一致患者样本进行利福平耐药相关基因(rpoB基因)耐药决定区的测序验证,MTBDRplus V2和测序结果一致率为75.00%(12/16),结果与国内相关研究报道相符[11],但低于国外文献报道[12],可能与不同国家流行菌株不同有关。
与MGIT 960药敏试验结果相比,MTBDRplus V2检测异烟肼耐药性的敏感度为77.38%(65/84),造成敏感度较低的原因,可能是由于其检测的耐药相关基因为katG和inhA基因,这2个基因与异烟肼耐药相关性一般为70%[13]。对异烟肼基因型和表型耐药结果不一致的患者样本进行异烟肼耐药相关基因(katG和inhA基因)耐药决定区的测序验证,88.46%(23/26)的患者样本的测序结果和MTBDRplus V2的检测结果一致。有研究报道oxyR-ahpC等基因与异烟肼耐药有一定相关性[14]。本研究中,MTBDRplus V2检测异烟肼耐药性的结果为“敏感”而MGIT 960培养法检测异烟肼耐药性的结果为“耐药”的19例样本中,测序结果均未发现katG和inhA存在突变。这一结果提示,MTBDRplus V2检测异烟肼耐药性的靶基因需要进一步完善。
综上所述,MTBDRplus V2检测MTBC的敏感度和特异度高、时间短,诊断涂阴疑似肺结核的可靠性强,同时可以准确检测利福平和异烟肼的耐药性,对指导涂阴疑似肺结核的防控具有重要意义。与其他分子检测技术如GeneXpert MTB/RIF和环介导等温扩增(loop-mediatedisothermal amplification,LAMP)等技术相比,MTBDRplus V2对实验室要求较高,需要具备有4个独立的检测区域,适合在地市级以上结核病诊疗机构的实验室开展。
志谢 安徽省胸科医院和西安市胸科医院的结核科医生对本研究做出了杰出贡献
[1] World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015.
[2] Wang L, Zhang H, Ruan Y, et al. Tuberculosis prevalence in China, 1990—2010; a longitudinal analysis of national survey data. Lancet, 2014,383(9934): 2057-2064.
[3] Lacoma A, Garcia-Sierra N, Prat C, et al. GenoType MTBDRplus assay for molecular detection of rifampicin and isoniazid resistance inMycobacteriumtuberculosisstrains and clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol, 2008, 46(11): 3660-3667.
[4] Bang D, Bengard Andersen A, Thomsen VO. Rapid genotypic detection of rifampicin- and isoniazid-resistantMycobacteriumtuberculosisdirectly in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol, 2006,44(7): 2605-2618.
[5] 李强,欧喜超,夏辉,等. Genotype MTBDRplus快速耐药诊断方法在地市级结核病医院应用的评估研究.中国预防医学杂志,2013,14(1):35-38.
[6] 陈琛,马远征.分子线性探针测定法在结核病诊断中的研究进展.中国防痨杂志, 2016,38(3): 218-221.
[7] World Health Organization. Policy statement: Molecular line probe assays for rapid screening of patients at risk of multidrug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). Geneva: World Health Organization, 2008.
[8] Crudu V, Stratan E, Romancenco E, et al. First evaluation of an improved assay for molecular genetic detection of tuberculosis as well as rifampin and isoniazid resistances. J Clin Microbiol, 2012, 50(4):1264-1269.
[9] Kent PT, Kubica GP. Public health mycobacteriology: a guide for the level Ⅲ laboratory. Atlanta GA:Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,1985.
[10] Li Q, Dong HY, Pang Y, et al. Multicenter evaluation of the molecular line probe assay for multidrug resistantMycobacteriumtuberculosisdetection in china. Biomed Environ Sci, 2015, 28(6): 464-467.
[11] Pang Y, Lu J, Wang Y, et al. Study of the rifampicin monoresistance mechanism inMycobacteriumtuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2013, 57(2): 893-900.
[12] Kumar P, Balooni V, Sharma BK, et al. High degree of multi-drug resistance and hetero-resistance in pulmonary TB patients from Punjab state of India. Tuberculosis(Edinb), 2014, 94(1): 73-80.
[13] Rufai SB, Kumar P, Singh A, et al. Comparison of Xpert MTB/RIF with line probe assay for detection of rifampin-monoresistantMycobacteriumtuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol, 2014, 52 (6): 1846-1852.
[14] Zhang Z, Lu J, liu M, et al. Genotyping and molecular chara-cteristics of multidrug-resistantMycobacteriumtuberculosisisolates from China. J Infect, 2015, 70(4): 335-345.
(本文编辑:孟莉 范永德)
A performance evaluation of MTBDRplus V2 for tuberculosis diagnosis in smear negative pulmonary tuberculosis suspects
LIQiang,BAOXun-di,LIUYuan,ZHAOBing,OUXi-chao,ZHAOYan-lin.
NationalTuberculosisReferenceLaboratory,NationalCenterforTuberculosisControlandPrevention,ChineseCenterforDiseaseControlandPrevention,Beijing102206,ChinaCorrespondingauthor:ZHAOYan-lin,Email:zhaoyanlin@chinatb.org
Objective To evaluate the performance of MTBDRplus version 2 (MTBDRplus V2) line probe assay for diagnosis of TB in the suspects with smear negative pulmonary tuberculosis. Methods The people who were clinically suspected to have smear negative pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) and detected in Anhui Chest Hospital and Xi’an Chest Hospital from January 2014 to December 2014 were consecutively enrolled into this study. A total of 1973 smear negative PTB suspects were enrolled and one sputum specimen was collected from each of them to conduct MTBDRplus V2 and BACTECTMMGITTM960 (MGIT 960) liquid culture, respectively. MGIT drug susceptibility testing (DST) for rifampin and isonozid was also performed once the liquid culture was positive andMycobacteriumtuberculosiscomplex (MTBC) was identified. Finally, the drug resistance related genes sequencing was performed for the samples with inconsistent results of drug resistance between MTBDRplus V2 and MGIT DST to confirm the drug resistance status. SPSS 22.0 was used for statistic analysis andχ2test was used to compare the detection rate of MTBC by using the two diagnostic methods. Statistical significance was defined asP<0.05. The sensitivity and specificity were applied to evaluate the performance of MTBDRplus V2 in the identification of MTBC and the detection of rifampincin and isonizid resistance. Results Among 1973 enrolled cases who were suspected to have smear negative PTB, the identification rate of MTBC by using MTBDRplus V2 and MGIT 960 were 27.67% (546/1973) and 26.76% (528/1973), respectively. The difference has no statistical significance (χ2=0.05,P=0.974). Compared with MGIT 960, the sensitivity and specificity of MTBDRplus V2 in the identification of MTBC was 86.74% (458/528) and 93.84% (1356/1445), respectively. Compared with MGIT DST,the sensitivity of MTBDRplus V2 in the detection of rifampicin and isonizid resistance was 94.34% (50/53) and 77.38% (65/84) respectively, and the specificity in the detection of rifampicin and isonizid resistance was 96.62% (372/385) and 98.02% (347/354), respectively. Conclusion MTBDRplus V2 is a rapid and reliable method in the diagnosis of MTBC among smear negative PTB suspects. At the same time, it also can tell us whether the patients diagnosed as having MTBC are susceptible to rifampin and isonizid or not, and both its sensitivity and specificity of drug resistance detection are high. Thus, this method has a good application value in the TB control and prevention.
Tuberculosis,pulmonary; Molecular line probe assay;Mycobacteriumtuberculosis; Sputum; Drug susceptibility testing; Evaluation studies
10.3969/j.issn.1000-6621.2016.07.006
“十二五”国家科技重大专项(2014ZX10003002)
102206 北京,中国疾病预防控制中心结核病预防控制中心 国家结核病参比实验室(李强、赵冰、欧喜超、赵雁林);安徽省胸科医院检验科(包训迪);西安市胸科医院检验科(刘元)
赵雁林,Email: zhaoyanlin@chinatb.org
2016-02-04)

