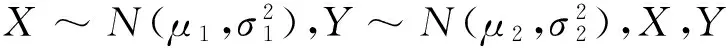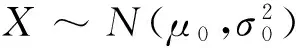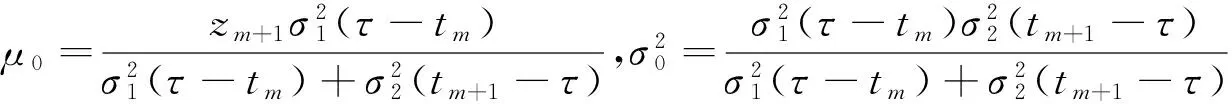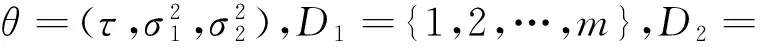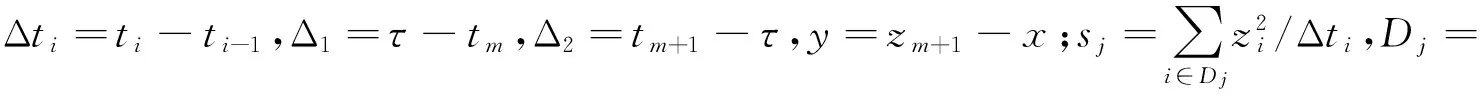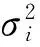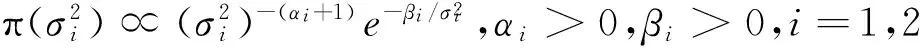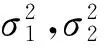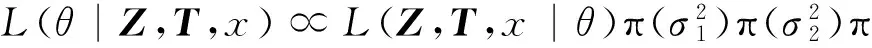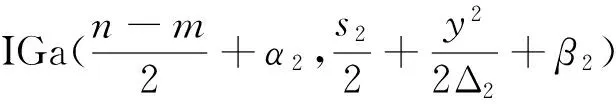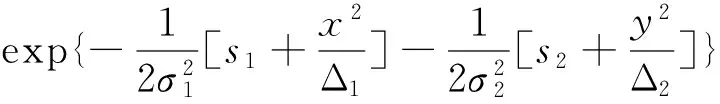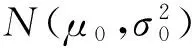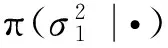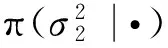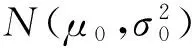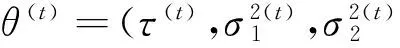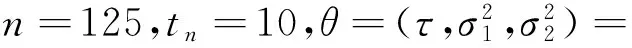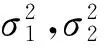维纳过程单变点模型的贝叶斯参数估计
何朝兵
(安阳师范学院数学与统计学院,中国 安阳 455000)
维纳过程单变点模型的贝叶斯参数估计
何朝兵
(安阳师范学院数学与统计学院,中国 安阳455000)
摘要通过引入潜在变量,利用正态分布的重要性质得到了维纳过程单变点模型比较简单的似然函数.结合Metropolis-Hastings算法对参数进行Gibbs抽样,基于Gibbs样本对参数进行估计.随机模拟的结果表明估计的精度较高.
关键词潜在变量;可加性;满条件分布;Gibbs抽样;Metropolis-Hastings算法
变点问题成为近年来比较热的研究方向,它在经济、质量控制和医学等领域应用广泛[1-5].变点分析方法主要有非参数方法、最小二乘法和贝叶斯方法等.而随着统计计算技术的发展,贝叶斯变点分析方法越来越受到人们的欢迎,而复杂性的计算是贝叶斯方法的难点.贝叶斯计算方法中的Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) 方法是最近发展起来的一种简单有效的计算方法.MCMC方法中的Gibbs抽样和Metropolis-Hastings算法使变点分析变得非常方便[6-9].Gibbs抽样可以简化变点问题,例如,未知参数的满条件分布可转化为无变点的后验分布,变点的满条件分布可转化为分布参数已知的后验分布.维纳过程是具有平稳独立增量的二阶矩过程,是一种特殊的扩散过程,它在纯数学、应用数学、经济学与物理学中都有重要应用.维纳过程不只是布朗运动的数学模型,在应用数学中,维纳过程可以描述高斯白噪声的积分形式;在电子工程中,维纳过程是建立噪音的数学模型的重要部分;控制论中,维纳过程可以用来表示不可知因素.对扩散过程变点模型的研究较多[10-13],虽然维纳过程是特殊的扩散过程,但对维纳过程变点模型的研究却较少[14-15],并且这些文献都是基于随机微分方程的求解来进行参数估计,计算比较繁琐,但基于似然函数并且利用MCMC方法研究此模型还不多见.
本文主要利用MCMC方法研究维纳过程单变点模型的参数估计问题.通过添加潜在变量得到了比较简单的似然函数,结合Metropolis-Hastings算法对参数进行Gibbs抽样,基于Gibbs样本对参数进行估计.随机模拟的结果表明估计的精度较高.
1维纳过程单变点模型
定义1随机过程W(t)如果满足:
1)W(0)=0,具有独立增量;
2)对任意s,t>0,W(s+t)-W(s)服从正态分布N(0,σ2t),σ>0,则称W(t)为以σ2为参数的维纳过程.
当维纳过程的参数σ2在某个时刻改变时,有如下定义.
定义2随机过程W(t)如果满足:
1)W(0)=0,具有独立增量,

(1)

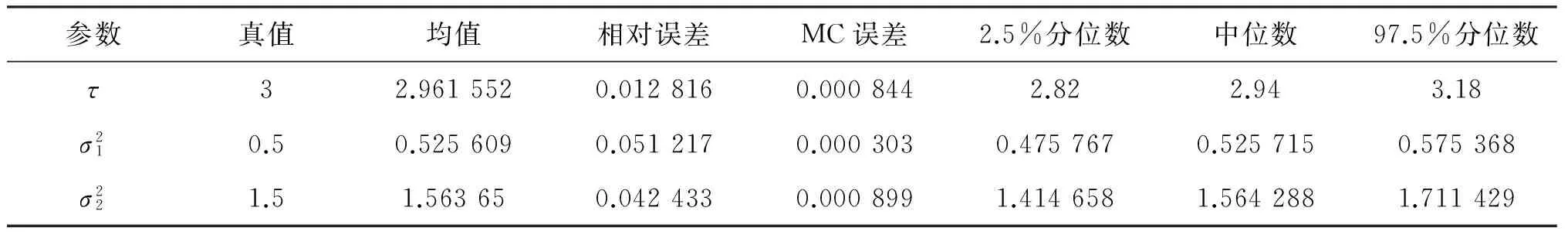
在n个时刻t1 W(ti)-W(ti-1)=zi,t0=0,i=1,2,…,n. 假设已知在观察时间区域(0,tn]内有一个变点,即0<τ τ∈(tm,tm+1],0≤m≤n-1,实际上m是τ的函数. 由式(1)知 由正态分布的可加性得 W(tm+1)-W(tm)的观察值为zm+1. 下面介绍概率论中一个很重要的结果,即下面的引理1. 当m=0时,D1=∅, 当m=n-1时,D2=∅.记x为X的取值,添加潜在变量后的似然函数为 2模型的贝叶斯估计 下面给出参数的先验分布. 1) 取τ的先验分布为均匀分布,即π(τ)∝1,0<τ 下面介绍MCMC方法的具体步骤. 3随机模拟 下面进行随机模拟试验. 表1 各参数的贝叶斯估计 图1 τ的Gibbs抽样迭代 图2 τ的两条迭代链 Fig.1 Gibbs sampling iterations of τ Fig.2 Two iterative chains of τ 参考文献: [1]PAGE E S. Continuous inspection schemes[J]. Biometrika, 1954,41(1):100-115. [2]CHERNOFF H, ZACKS S. Estimating the current mean of a normal distribution which is subjected to changes in time[J]. Ann Math Stat, 1964,35(3):999-1018. [3]CSÖRGÖ M, HORVTH L. Limit theorems in change-point analysis[M]. New York: Wiley, 1997. [4]PERREAULT L, BERNIER J, BOBÉE B,etal. Bayesian change-point analysis in hydrometeorological time series. Part 1. The normal model revisited[J]. J Hydrol, 2000,235(3):221-241. [5]FEARNHEAD P. Exact and efficient Bayesian inference for multiple changepoint problems[J]. Stat Comput, 2006,16(2):203-213. [6]LIANG F, WONG W H. Real-parameter evolutionary Monte Carlo with applications to Bayesian mixture models[J]. J Am Stat Assoc, 2001,96(454):653-666. [7]LAVIELLE M, LEBARBIER E. An application of MCMC methods for the multiple change-points problem[J]. Sig Pro, 2001,81(1):39-53. [8]KIM J, CHEON S. Bayesian multiple change-point estimation with annealing stochastic approximation Monte Carlo[J]. Comput Stat, 2010,25(2):215-239. [9]YUAN T, KUO Y. Bayesian analysis of hazard rate, change point, and cost-optimal burn-in time for electronic devices[J]. IEEE Trans Rel, 2010,59(1):132-138. [10]ABBAS-TURKI L A, KARATZAS I, LI Q. Impulse control of a diffusion with a change point[J]. Stoch Int J Probab Stoch Process, 2015,87(3):382-408. [11]MISHRA M N, PRAKASA RAO B L S. Estimation of change point for switching fractional diffusion processes[J]. Stoch Int J Probab Stoch Process, 2014,86(3):429-449. [12]GAPEEV P V, SHIRYAEV A N. Bayesian quickest detection problems for some diffusion processes[J]. Adv Appl Probab, 2013,45(1):164-185. [13]NEGRI I, NISHIYAMA Y. Asymptotically distribution free test for parameter change in a diffusion process model[J]. Ann Inst Stat Math, 2012,64(5):911-918. [14]VOSTRIKOVA, L YU. Detection of a “disorder” in a Wiener process[J]. Theor Probab Appl, 1981,26(2):356-362. [15]HADJILIADIS O, MOUSTAKIDES V. Optimal and asymptotically optimal CUSUM rules for change point detection in the Brownian motion model with multiple alternatives[J]. Theor Probab Appl, 2006,50(1):75-85. (编辑HWJ) DOI:10.7612/j.issn.1000-2537.2016.04.014 收稿日期:2015-11-12 基金项目:国家自然科学基金(61174099); 河南省高等学校重点科研项目(16A110001) *通讯作者,E-mail:chaobing5@163.com 中图分类号O212.8; O212.4 文献标识码A 文章编号1000-2537(2016)04-0084-05 Bayesian Parameter Estimation of Wiener Process with a Change-Point HEChao-bing* (School of Mathematics and Statistics, Anyang Normal University, Anyang 455000, China) AbstractBy introducing a latent variable, the simple likelihood function of Wiener process with a change-point is obtained according to the important property of the normal distribution. All the parameters are sampled by Gibbs sampler together with Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, and the parameters are estimated based on the Gibbs samples. Random simulation results show that the estimations are fairly accurate. Key wordslatent variable; additivity; full conditional distribution; Gibbs sampling; Metropolis-Hastings algorithm