糖尿病对上尿路尿路上皮癌根治术后发生膀胱内肿瘤的风险分析
郭玉婷 李长平 崔壮 刘媛媛 马骏
糖尿病对上尿路尿路上皮癌根治术后发生膀胱内肿瘤的风险分析
郭玉婷李长平崔壮刘媛媛马骏
目的:探讨合并糖尿病(diabetes mellitus,DM)的上尿路尿路上皮癌(upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma,UUT-UC)患者行根治性肾输尿管切除术(radical nephroureterectomy,RNU)及膀胱袖口状切除术后是否增加膀胱内肿瘤发生的风险。方法:回顾性分析天津医科大学第二医院2005年1月至2013年12月282例行根治性肾输尿管切除术及膀胱袖口状切除术,且既往无膀胱肿瘤病史的UUT-UC患者临床病理资料,比较非DM组(233例)与DM组(49例)无复发生存期(recurrence-free survival,RFS)及肿瘤特异性生存期(cancer-specific survival,CSS),并分析年龄、DM、病理分级及分期等因素对患者术后膀胱内肿瘤发生的影响。结果:纳入研究的患者术后中位随访时间为41个月,282例中80例(28.4%)发生膀胱内肿瘤,中位发生时间为11个月。非DM患者RFS较DM患者显著延长(P=0.013)。Cox回归模型多因素分析显示,DM(P=0.014)、肾孟癌合并输尿管癌(P=0.001)与术后化疗(P=0.024)是术后膀胱内肿瘤发生独立影响因素。结论:DM增加UUT-UC患者术后膀胱内肿瘤发生风险,因此需要加强对合并DM患者术后的密切随访及血糖控制。
糖尿病尿路上皮癌根治性肾输尿管切除术膀胱肿瘤发生
上尿路尿路上皮癌(upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma,UUT-UC)是一种相对少见的肿瘤,约占尿路上皮癌的5%。根治性肾输尿管切除术(radical nephroureterectomy,RNU)及膀胱袖口状切除术是治疗UUT-UC的金标准[1],以下统一表述为RNU术。术后膀胱内肿瘤发生率为20%~50%[2]。糖尿病(diabetes mellitus,DM)是一种常见的慢性疾病,目前已经证实DM是多种恶性肿瘤的高危影响因素[3]。有研究表明DM与膀胱肿瘤的发生有关[4],但目前关于DM是否为术后膀胱内肿瘤发生的危险因素尚存在争议。本研究回顾性分析UUT-UC患者的各项临床病理及随访资料,以探讨DM是否为术后膀胱内肿瘤发生的影响因素。
1 材料与方法
1.1临床资料
收集天津医科大学第二医院2005年1月至2013 年12月收治的肾盂癌、输尿管癌患者349例,行开放性RNU或腹腔镜RNU术,术后病理诊断为上尿路尿路上皮癌。其中排除RNU术前合并膀胱肿瘤45例、RNU术前肿瘤远处转移5例、RNU术后放疗7例及失访10例,最终纳入282例UUT-UC患者,分为非DM (233例)与DM(49例)两组。术前诊断包括尿脱落细胞学、膀胱镜和影像学检查。RNU术后2年内每3~4个月行尿脱落细胞学、膀胱镜、B超和CT检查,第3年每6个月复查1次,5年以后每年复查1次。术后所有患者均行即刻膀胱灌注化疗。本研究通过天津医科大学第二医院伦理委员会批准,所有患者的记录和信息均匿名且在分析之前消除了识别信息。
1.2方法
本研究中膀胱内肿瘤发生的时间确定为UUT-UC患者行RNU术后至随访期间内首次发生膀胱肿瘤的时间,肿瘤特异性生存期的死亡时间确定为因肿瘤直接或间接原因引起死亡的时间,研究终止日期为2015年12月。主要从年龄、性别、高血压、糖尿病、肾积水、临床病理分级及分期、淋巴血管侵犯、肿瘤位置和术后化疗方面分析术后影响膀胱内肿瘤发生的因素。分为年龄≤65岁、年龄>65岁;DM定义为空腹血糖≥7.0mmol/L,和/或餐后2 h血糖≥11.1 mmol/L;肾积水分为轻度、中度及重度;淋巴血管侵犯定义为肿瘤细胞存在淋巴或静脉导管内;肿瘤位置包括肾盂、输尿管及肾盂合并输尿管;肿瘤病理诊断依据WHO分级(2004年)及TNM分期(2002年)标准。
1.3统计学处理
采用SPSS 21.0统计软件进行分析。应用Kaplan-Meier法分析3年及5年无复发生存率和肿瘤特异性生存率,采用Log rank检验行单因素分析,采用Cox回归模型行多因素分析。以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1患者临床病理特征
纳入研究的282例UUT-UC患者中,男性168例(59.6%)、女性114例(40.4%),中位年龄为68.0 (60.0~74.8)岁,RNU术后中位随访时间为41(29~64)个月。随访期间内282例患者中77例(27.3%)死亡,80例(28.4%)发生膀胱内肿瘤的患者中包括59例非DM与21例DM,中位发生时间为11(7~15)个月。80例术后1、2年内发生膀胱内肿瘤的患者为62.5% (50/80)、85.0%(68/80),见表1。
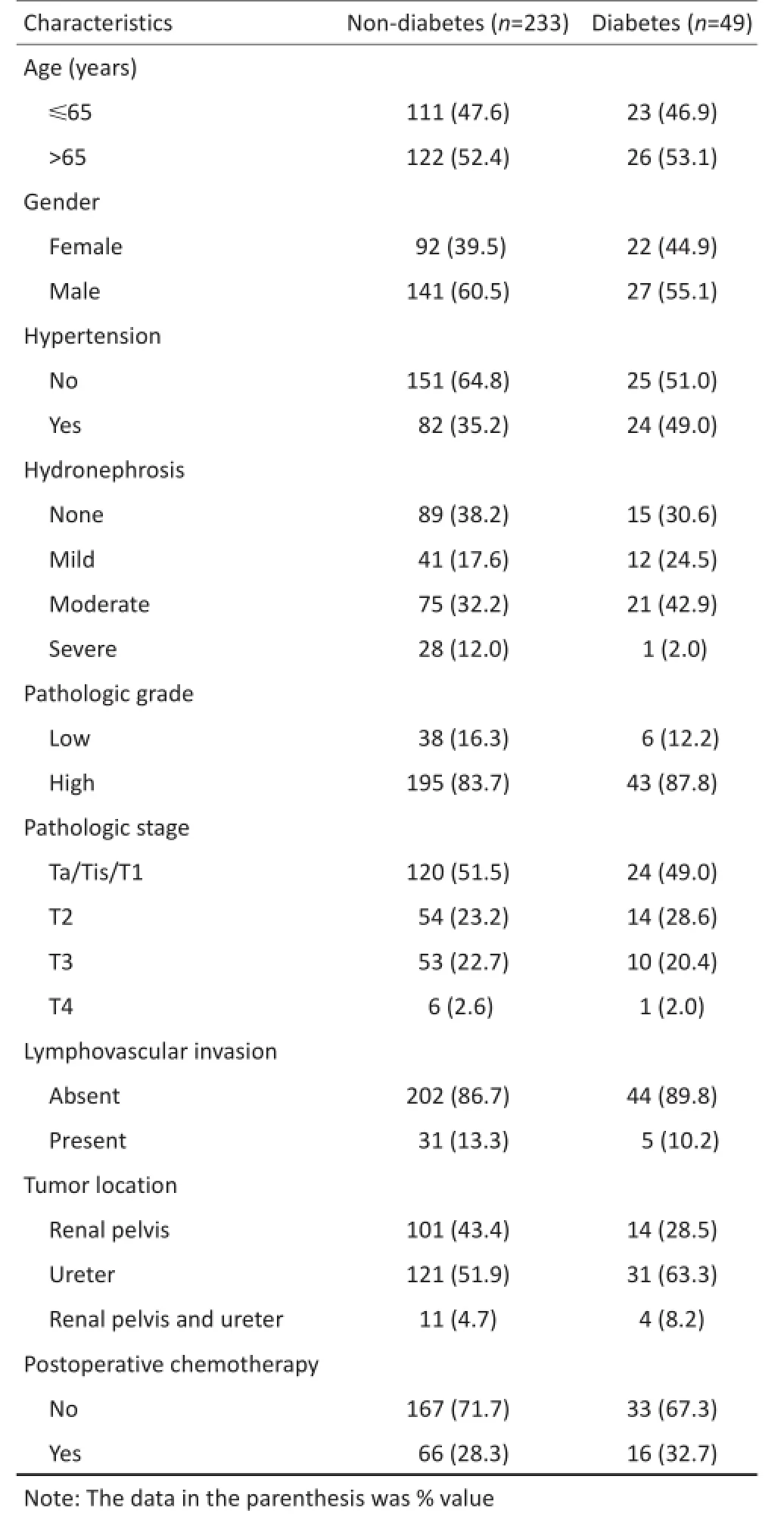
表1 282例UUT-UC患者临床病理特征Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 282 patients with UUT-UC
2.2两组患者生存情况比较
非DM与DM组患者膀胱内肿瘤发生率分别为25.3%(59/233)与42.9%(21/49)。非DM组患者无复发生存期(recurrence-free survival,RFS)高于DM组患者,差异具有统计学意义(P=0.013),5年无复发生存率分别为72.4%、57.7%(图1A)。两组患者肿瘤特异性生存期(cancer-specific survival,CSS)差异无统计学意义(P=0.255),5年肿瘤特异性生存率分别为75.0%、60.5%(图1B)。
2.3UUT-UC患者临床特征对术后RFS影响
单因素分析显示,年龄、性别、高血压、肾积水、病理分级和分期及淋巴血管侵犯对患者术后膀胱内肿瘤发生无影响。DM、肾盂癌合并输尿管癌与术后化疗是影响术后膀胱内肿瘤发生因素,差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05,表2)。
Cox回归模型多因素分析显示,DM和肾盂癌合并输尿管癌是术后膀胱内肿瘤发生独立危险因素,而术后化疗是其独立保护因素(P<0.05,表3)。
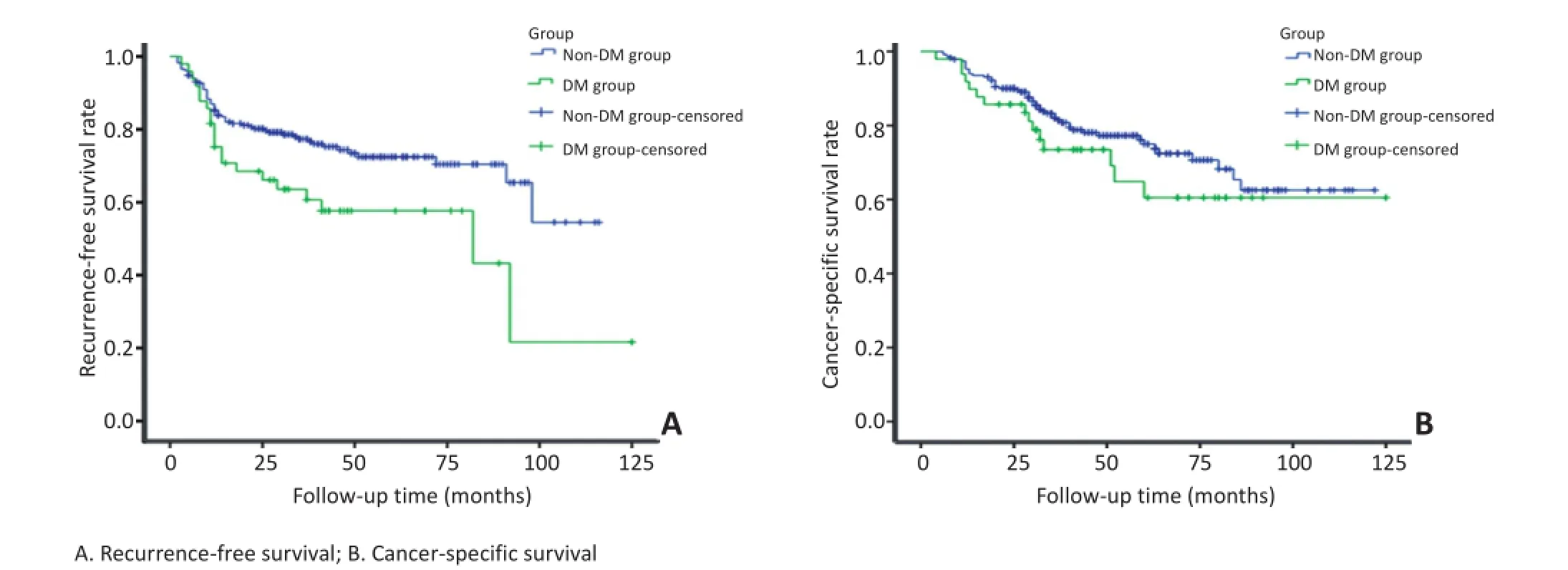
图1非DM与DM患者生存曲线比较Figure 1 Comparison of survival curves in non-diabetic and diabetic patients
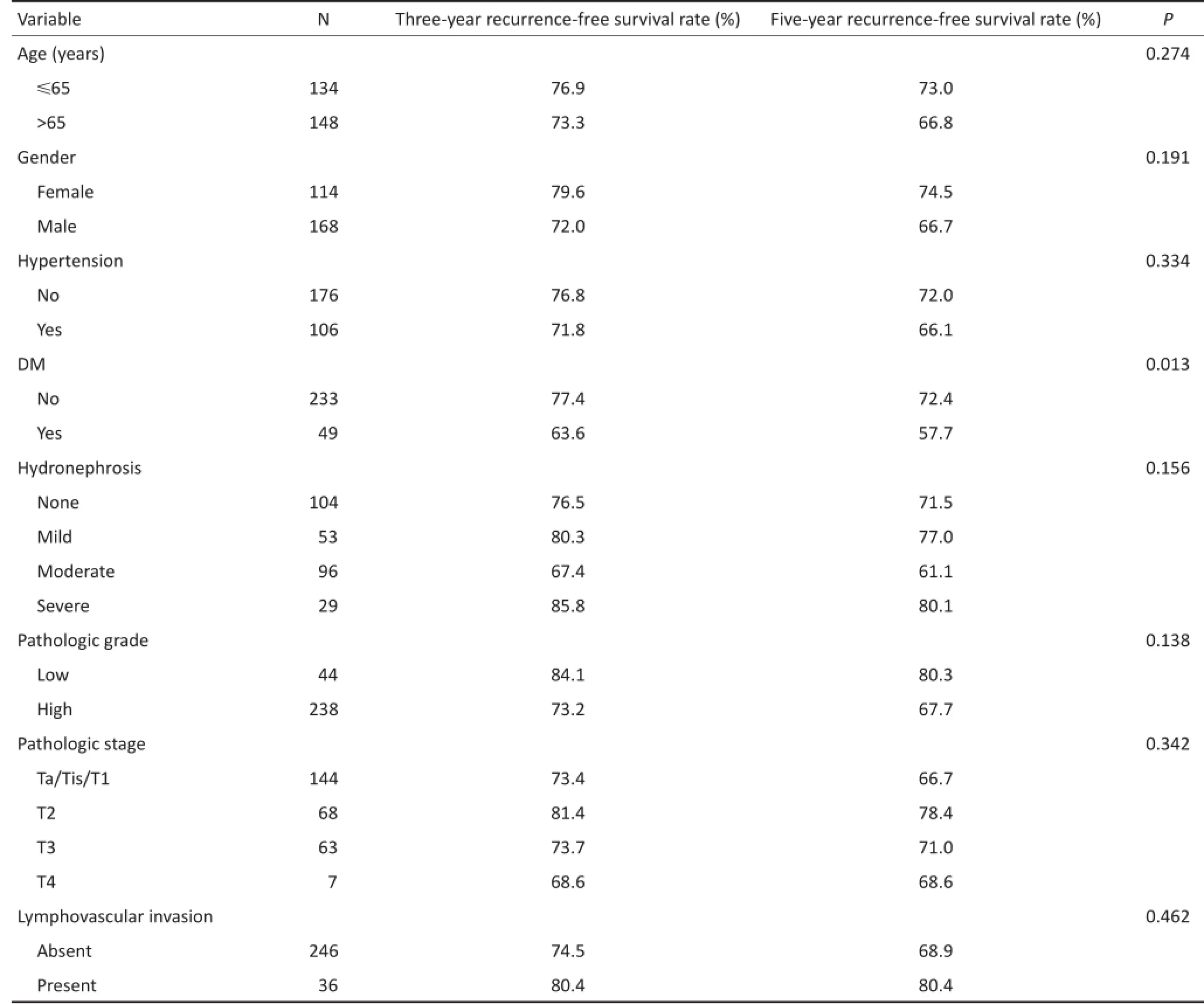
表2 UUT-UC患者术后RFS的单因素分析Table 2 Univariate analysis of recurrence-free survival in patients with UUT-UC after RNU
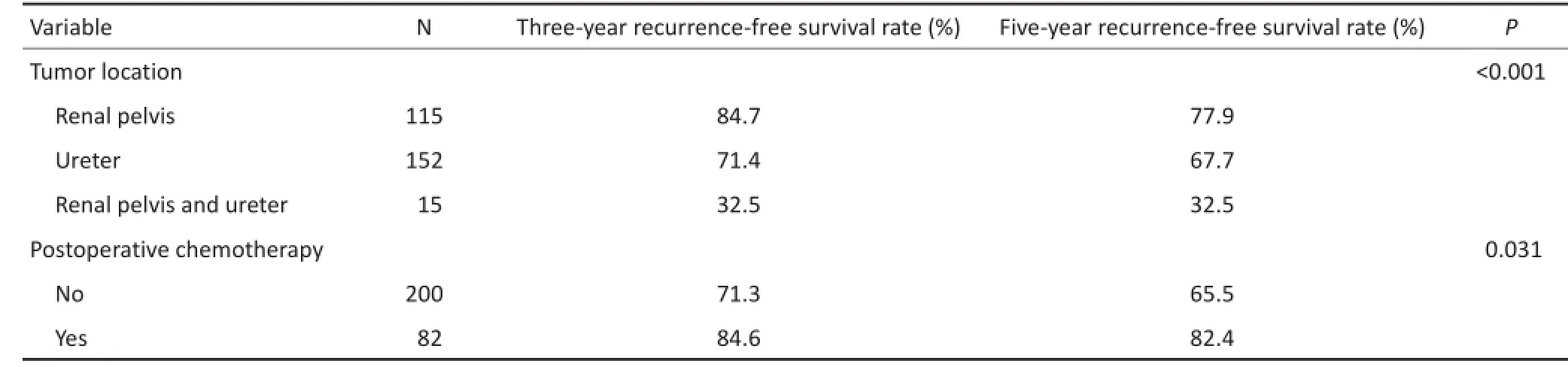
表2 UUT-UC患者术后RFS的单因素分析(续表2)Table 2 Univariate analysis of recurrence-free survival in patients with UUT-UC after RNU

表3 UUT-UC患者术后RFS的Cox回归模型多因素分析Table 3 Multivariate analysis using Cox's regression model of recurrence-free survival in patients with UUT-UC after RNU
3 讨论
本研究中28.4%(80/282)患者RNU术后发生膀胱内肿瘤,与Novara等[2]的研究结果一致。同时对膀胱内肿瘤发生的影响因素行Cox回归模型多因素生存分析发现,UUT-UC合并DM患者的术后膀胱内肿瘤发生风险是非DM患者的1.883倍,肾盂癌合并输尿管癌患者的术后膀胱内肿瘤发生风险是肾盂癌患者的3.760倍,DM与肾盂癌合并输尿管癌是引起术后膀胱内肿瘤发生的独立危险因素,而术后化疗较未化疗患者的膀胱内肿瘤发生率显著降低。有报道RNU术后膀胱内即刻灌注,1年内膀胱肿瘤发生率可降低11.0%~14.9%[5],因此建议UUT-UC患者不仅要行术后即刻膀胱灌注,还需行术后化疗。
DM是一种全球范围内的流行疾病,可引起心血管疾病、视网膜病变、神经病变、肾病、膀胱功能障碍、性功能障碍、勃起功能障碍及尿路感染等并发症。有文献报道DM是肝癌、胆管癌、胰腺癌、结肠癌、子宫内膜癌和肾癌等的高危影响因素[3],同时也与这些肿瘤的不良预后相关[6]。还有文献报道DM会增加膀胱肿瘤发生的风险,但潜在机制尚不清楚[4,7],而体外实验发现高剂量胰岛素促进膀胱尿路上皮细胞的增殖[8]。通常认为胰岛素和胰岛素样生长因子-I (insulin-like growth factor-I,IGF-I)及膀胱尿路上皮癌细胞的有丝分裂机制是DM引起膀胱肿瘤发生的关键,IGF-I通过激活IGF-I受体(insulin-like growth factor-I receptor,IGF-IR)从而促进肿瘤细胞的增殖[9],这种内环境的改变可促进细胞增殖、抗凋亡甚至诱导基因突变,进而引起膀胱肿瘤的发生。在尿路上皮细胞表面,DM通过增加致癌物质的浓度或细胞暴露于致癌物质的时间,增加尿路感染和膀胱功能障碍的概率[3],进而增加膀胱肿瘤发生的风险[10]。DM患者尿液pH值降低使其产生具有致癌性质的芳香胺[11-12],芳香胺有利于尿道结石的形成,从而导致膀胱炎症,进一步促进膀胱肿瘤的发生[8]。同时,超过50%DM患者会继发膀胱功能障碍,泌尿道感染的发生概率是正常人群的2~3倍[3]。有文献报道膀胱肿瘤和细菌感染呈显著相关性[13-14],细菌的细胞壁可引起炎症和促进细胞增殖,进而发生膀胱肿瘤。Kawai等[14]发现将人尿路上皮细胞表面的大肠杆菌移入小鼠体内可以产生亚硝胺,亚硝胺的致癌作用进而会影响动物膀胱肿瘤的发生。另有文献报道,DM患者中服用二甲双胍较未服用二甲双胍者的膀胱肿瘤发生率及肿瘤特异性死亡率显著降低[15],但具体机制还需进一步研究。
综上所述,DM是UUT-UC患者RNU术后发生膀胱内肿瘤的一个独立危险因素,而且本研究中85.0% (68/80)患者术后2年内发生膀胱肿瘤,因此术后2年内应该加强患者的随访和检查,高度警惕膀胱肿瘤发生的风险。
[1]Xylinas E,Colin P,Audenet F,et al.Intravesical recurrence after radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinomas:predictors and impact on subsequent oncological outcomes from a national multicenter study[J].World J Urol,2013,31(1):61-68.
[2]Novara G,De Marco V,Dalpiaz O,et al.Independent predictors of metachronous bladder transitional cell carcinoma(TCC)after nephroureterectomy for TCC of the upper urinary tract[J].BJU Int,2008,101(11):1368-1374.
[3]Brown JS,Wessells H,Chancellor MB,et al.Urologic complications of diabetes[J].Diabetes Care,2005,28(1):177-185.
[4]MacKenzie T,Zens MS,Ferrara A,et al.Diabetes and risk of bladder cancer:evidence from a case-control study in New England[J]. Cancer,2011,117(7):1552-1556.
[5] Ito A,Shintaku I,Satoh M,et al.Prospective randomized phase II trial of a single early intravesical instillation of pirarubicin(THP)in the prevention of bladder recurrence after nephroureterectomy for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma:the THP Monotherapy Study Group Trial[J].J Clin Oncol,2013,31(11):1422-1427.
[6] Hwang EC,Kim YJ,Hwang IS,et al.Impact of diabetes mellitus on recurrence and progression in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma:a retrospective cohort study[J].Int J Urol,2011,18(11):769-776.
[7]Woolcott CG,Maskarinec G,Haiman CA,et al.Diabetes and urothelial cancer risk:the Multiethnic Cohort study[J].Cancer Epidemiol,2011,35(6):551-554.
[8]Liu S,Li Y,Lin T,et al.High dose human insulin and insulin glargine promote T24 bladder cancer cell proliferation via PI3K-independent activation of Akt[J].Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2011,91(2):177-182.
[9]Metalli D,Lovat F,Tripodi F,et al.The insulin-like growth factor receptor I promotes motility and invasion of bladder cancer cells through Akt-and mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent activation of paxillin[J].Am J Pathol,2010,176(6):2997-3006.
[10]Jiang X,Castelao JE,Groshen S,et al.Water intake and bladder cancer risk in Los Angeles County[J].Int J Cancer,2008,123(7):1649-1656. [11]Alguacil J,Pfeiffer RM,Moore LE,et al.Measurement of urine pH for epidemiological studies on bladder cancer[J].Eur J Epidemiol,2007,22(2):91-98.
[12]Cameron MA,Maalouf NM,Adams-Huet B,et al.Urine composition in type 2 diabetes:predisposition to uric acid nephrolithiasis [J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2006,17(5):1422-1428.
[13]Kanda Y.Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software'EZR' for medical statistics[J].Bone MarrowTransplant,2013,48(3):452-458.
[14]Kawai K,Kawamata H,Kemeyama S,et al.Persistence of carcinogenaltered cell population in rat urothelium which can be promoted to tumors by chronic inflammatory stimulus[J].Cancer Res,1994,54(10):2630-2632.
[15]Rieken M,Xylinas E,Kluth L,et al.Diabetes mellitus without metformin intake is associated with worse oncologic outcomes after radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol,2014,40(1):113-120.
(2016-05-05收稿)
(2016-07-22修回)

郭玉婷专业方向为慢性病流行病学与综合评价研究。
E-mail:guoyuting_mcdull@163.com
Analysis of diabetes mellitus increasing the risk of intravesical recurrence in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy
Yuting GUO,Changping LI,Zhuang CUI,Yuanyuan LIU,Jun MA
Correspondence to:Jun MA;E-mail:majun@tmu.edu.cn
Department of Health Statistics,College of Public Health,Tianjin Medical University,Tianjin 300070,China
Objective:To investigate whether the risk of intravesical recurrence increases in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma(UUT-UC)and diabetes mellitus(DM)after radical nephroureterectomy(RNU)with bladder cuff excision.Methods:We retrospectively analyzed the clinicopathological data of 282 UUT-UC patients with no history of bladder neoplasm and who underwent RNU with bladder cuff excision in the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University from January 2005 to December 2013.The recurrence-free survival(RFS)and cancer-specific survival(CSS)were compared between the non-diabetic(233 patients)and diabetic(49 patients)patients. The factors influencing intravesical recurrence in patients with UUT-UC after RNU were analyzed.These factors included age,DM,pathologic grade,and stage.Results:Among the 282 patients included in the study,80(28.4%)patients developed intravesical recurrence during the median follow up of 41 months,and the median time to recurrence was 11 months.Non-diabetic patients had a significantly longer duration of bladder neoplasm RFS than diabetic patients(P=0.013).Multivariate analysis using Cox's regression model indicated that DM(P=0.014),renal pelvis and ureter tumor(P=0.001),and postoperative chemotherapy(P=0.024)were independent influential factors for intravesical recurrence in patients with UUT-UC after RNU with bladder cuff excision.Conclusion:DM posed an increased risk for intravesical recurrence after RNUwithbladder cuff excisioninpatients withUUT-UC.Therefore,these patients needtobe closely monitored,andtheir bloodglucose must be controlled.
diabetes mellitus,urothelial carcinoma,radical nephroureterectomy,bladder neoplasm,recurrence
10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2016.15.522
天津医科大学公共卫生学院卫生统计学教研室(天津市300070)
马骏majun@tmu.edu.cn

