成人先天性巨趾畸形两例报告
卢明峰 曹学伟
. 病例报告 Case report .
成人先天性巨趾畸形两例报告
卢明峰 曹学伟
趾;先天畸形;趾
先天性巨趾畸形是一种非常罕见的先天性畸形[1],目前病因尚未明确,该病无明显的遗传因素,染色体研究也尚未发现异常,2015 年 2 月至 2016 年 4 月我院收治成人先天性巨趾畸形 2 例。现报告如下。
临床资料
例 2,患者,男,19 岁。左足趾巨大畸形 19 年来我院就诊。患者出生后家人遂发现其左足第 1、2 趾变大畸形,随着年龄增长,左足第 1、2 趾不断长大畸形,无伴足趾疼痛,现影响美观及日常生活。专科检查:左足第1、2 趾巨大畸形,第 1 趾长约 7 cm,周长 25 cm,第 2 趾长约 5 cm,周长 12 cm,局部无红肿,无压痛,无胼胝体形成;足趾关节活动无明显受限,趾端感觉和血运良好。患者无先天畸形家族史。左足 X 线片 ( 图 4 ) 提示左足第1 跖骨增大,第 1、2 趾骨软组织影稍增厚,诊断为先天性巨趾 ( 左足第 1、2 趾 )。2015 年 6 月 15 日在腰麻下行左趾先天性巨趾畸形远节趾骨截骨术+左长屈伸肌腱止点重建术+左足第 2 趾近端趾间关节融合术,术后复查左足 X 线片 ( 图 5 ) 左足趾截除远节趾骨,第 1 跖骨较前片缩小,第 2 趾近段趾间关节行小关节融合,术后患趾血运感觉和活动较好。术后随访 9 个月肢端血运感觉良好,外观及功能明显改善,无复发病例。
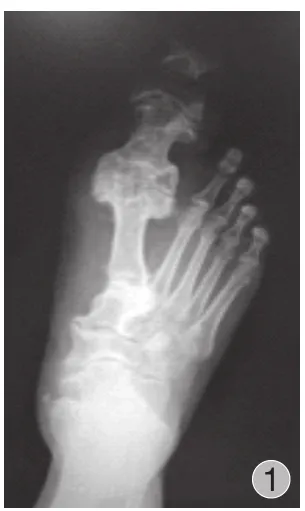
图1 术前右足正位片:右足趾改变,符合先天性巨趾畸形Fig.1 The preoperative anterioposterior film of the right foot: The form of the right hallux was abnormal.Congenital gigantism of the foot was conformed
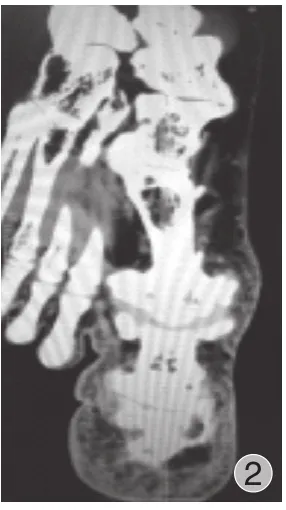
图2 足部螺旋 CT 平扫片:右足第 1 跖趾骨粗大,关节增生肥大及周围软组织增生,符合先天性巨趾畸形并创伤性关节炎,第1 跖趾关节半脱位Fig.2 The CT scan of the right foot: The first plantar phalanges of the right foot became large, with the joint and surrounding soft tissue hyperplasia.Congenital gigantism of the foot with traumatic arthritis was conformed
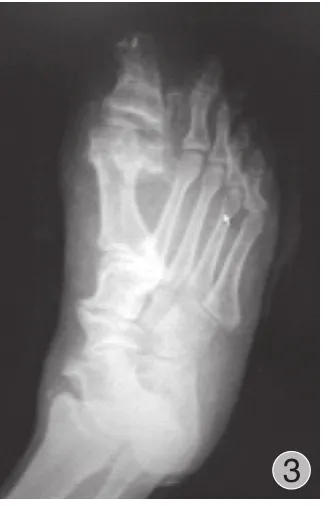
图3 术后复查片:与前片相比,右足?趾截除远节趾骨,第1 跖骨较前片缩小,患者足趾功能及外观很好地改善,右足?趾关节对位正常,形态良好,呈术后改变Fig.3 The postoperative film: The distal phalange of the right hallux was cut.The first metatarsal of the left foot shrank.The function and appearance of the 2 patients’ toes were improved after the surgery.The hallux of the right foot joint was normal.The shape was well after the surgery
讨 论
先天性巨趾畸形是非常少见的足部畸形,可以发生于单趾或者多个足趾[1],尤其是第 2、3 趾的发生率最高,其次是趾,多见于单侧发病。王海华等[2]报道多趾巨大畸形患者多于单趾畸形的患者,胫侧足趾好发。本研究2 例患者巨趾畸形均是单侧发病,第 1 例是趾单趾发病,第 2 例是多趾发病。巨趾症在四肢先天性畸形疾病中的发病率非常低,约为 1 / 18 000[3],男女的发病率无明显的差异,并且也没有明显的遗传倾向[4]。该病的发病原因目前尚不明确,最新观点认为由于生长抑制因子缺乏或局部内因子表达,导致了足趾神经损害和脂肪、纤维组织过度增殖蓄积而成[4-5];一般来说,患此病的婴儿出生后即出现。对于出生时不明显,随年龄增长患趾增粗变长的患者较少见。而本次报告的病例 1 属于上述情况。先天性巨趾以足趾软组织和骨的过度生长为主要特征,累及神经较少[6],常发生在侧方或跖面,不对称的肥大足趾亦导致侧弯,异常增大的脚趾常导致患者穿鞋困难和行走不便,从而导致患者前去医院就诊。临床中,先天性巨趾畸形分两种类型:静止型和进展型;静止型患者肥大的足趾出生时已伴有,但不会再发展,与其它足趾同等比例生长,并且治疗效果较好;进展型的患者巨趾亦为出生伴有,然而肥厚增大的足趾的生长速度远远超过正常足趾,而且往往影响其它足趾。
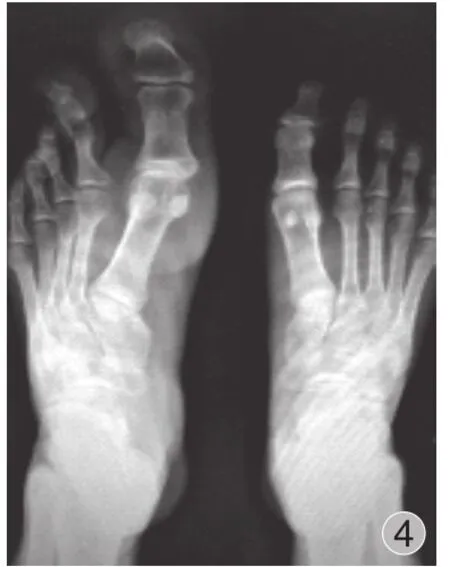
图4 术前双足正位片:左足第 1 跖骨增大,第 1、2 趾骨软组织影稍增厚,诊断为先天性巨趾 ( 左足第 1、2 趾 )Fig.4 The preoperative anterioposterior film of the feet: The first metatarsal of the left foot was enlarged.The soft tissue shadows of the first and second phalanges were slightly thickened.Congenital gigantism of the foot was diagnosed

图5 左趾先天性巨趾畸形远节趾骨截骨术 + 左长屈伸肌腱止点重建术 + 左足第 2 趾近端趾间关节融合术后改变,左足趾截除远节趾骨,第 1 跖骨较前片缩小,形态大小基本正常,第2 趾近段趾间关节行小关节融合,术后发现患趾血运感觉和活动较好Fig.5 Osteotomy of the distal phalanges of the left hallux, the check point revascularization of the left long toe flexion tendons, the joint arthrodesis of the second left proximal interphalangeal joint were performed.The distal phalange of the left hallux was cut.The first metatarsal of the left foot shrank.The form and size were normal.The joint arthrodesis was performed on the second proximal interphalangeal joint.The blood supply, feelings and activities of the 2 patients’ toes were well after the surgery
对于成人巨趾畸形的治疗,手术矫形是首选,其目的是使患足和健足能穿同样的鞋,并且行走无痛,最后是美观问题。由于畸形的形式形态多种多样,故对应的手术方式也多种多样,主要是在改善外形和功能的基础上进行。巨趾的常用手术治疗方法有:软组织切除术、骨骺遏止术、截骨术、趾列切除术等。王海华等[2]对 12 例患者进行手术治疗,术式包括软组织缩容、截骨术等,效果都比较显著;Kalen 等[7]和 Ishida 等[8]研究发现处于进展型巨趾畸形复发率较高,采用截趾联合缩容手术更为适合。本组 2 例均处于进展期,严重影响美观、功能和生活。为了保存患趾功能,选择远节趾骨截骨矫形术外加肌腱止点重建术,能很好改善患者足趾功能及外观,术后随访 2 例患趾血运感觉和活动较好。
[1] 张保付.先天性巨趾畸形2例.中医正骨, 2015, 27(4):78-80.
[2] 王海华, 田光磊, 诸寅, 等.巨趾畸形12例临床分析.中华外科杂志, 2008, 46(6):434-436.
[3] Kowtharapu DN, Thawrani D, Kumar SJ.Drennen’s the child’s foot and ankle.Ed2.Baltimore: Lippincot Williams and Wilkins, 2009: 443-449.
[4] 余庆雄, 盛玲玲.先天性巨(指)趾畸形的研究进展.中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(23):2371-2374.
[5] 姚栋, 苏巍, 张邵军, 等.巨趾症1例报道及文献复习.山西医科大学学报, 2005, 36(4):520-521.
[6] 周礼祥, 袁长深, 梅其杰, 等.巨趾症1例报告.医药前沿, 2013, 14(14):329-329.
[7] Kalen V, Burwell DS, Omer GE.Macrodactyly of the hands and feet.J Pediatr Orthop, 1988, 8(3):311-315.
[8] Ishida O, Ikuta Y.Long -term results of surgical treatment for macrodactyly of the hand.Plast Reconstr Surg, 1998, 102(5): 1586-1590.
( 本文编辑:李贵存 )
Two cases of adult congenital macrodactylia
LU Ming-feng, CAO Xue-wei.
The second Clinical College, Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510000, PRC
Objective To analyze and discuss the clinical therapy and treatment outcomes of congenital gigantism of the foot.Methods The clinical documents of 2 cases of congenital gigantism of the foot were retrospectively analyzed.The 2 patients’ average age was 20 years old.All the deformities were found at birth.The cases of multiple toes involved were more than that of single toe, and the cases of tibial toe involved were more than that of fibular toe.The forefoot was enlarged.All the phalanges involved and partial metatarsal bones were enlarged.Marked increase in subcutaneous fat was found in all the cases in the operation, which infiltrated the interossei and articular capsules.The appearance of the nerves and their branches in the foot were normal and fatty infiltration was not discovered.Corrective osteotomy and reconstruction of tendon check point were performed on the 2 patients, who were followed up for 1 year.The appearance and function of the limb were observed.Results The 2 patients were satisfactory with the postoperative function and appearance.Conclusions According to the age, clinical classification, degree of pathological changes and limb function, the 2 cases of the digital gigantism of the foot are in progress.To save the function, we choose corrective osteotomy and reconstruction of tendon check point.The function and appearance of the 2 patients’ toes get improved after the surgery.The blood supply, feelings and activities of the toes are well during the follow-up.
Toes; Congenital abnormalities; Hallux
10.3969/j.issn.2095-252X.2000.12.014
R684.2
510000 广州中医药大学第二临床医学院研究生 ( 卢明峰 );510000 广东省中医院骨三科 ( 曹学伟 )
曹学伟,Email: 1543896277@qq.com
2016-05-18 )

