84例脓毒性休克患者降钙素原清除率的临床分析
邓林

[摘要] 目的 通过动态监测脓毒性休克患者入住ICU 前3 dPCT清除率,探讨早期降钙素原清除率(procalcitonin clearance ,PCTc)评估预后的价值。方法 采用前瞻性方法进行观察研究,方便选取2015年4月—2016年4月期间入住该院ICU,符合脓毒性休克诊断标准且感染灶无需外科处理的内科患者。入选标准的患者共84例,其中男女各42例,28 d病死率为41.67%。检测入选患者于住ICU第1、2、3日血清PCT 质量浓度(PCT-day1、PCT-day2、PCT-day3),并计算第2、3日的PCT清除率(PCTc-day2、PCTc-day3)。 结果 生存组与死亡组相比,PCT-day1、PCT-day2、PCT-day3差异均无统计学意义(P﹥0.05),生存组的PCTc-day2、PCTc-day3(17%、51%)明显高于死亡组(2%、20%),差异有统计学意义(P=0.018,<0.001)。PCTc-day2、PCTc-day3预测28 d生存的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.651(95%CI,0.53~0.77,P<0.05)与0.758(95%CI,0.66~0.86,P<0.01)。PCTc-day3预测28 d生存最佳截断值为38%,敏感度63.26%,特异度77.14%。 结论 3 d内PCT降钙素原明显下降的脓毒性休克患者生存率较高,早期监测 PCT清除率有助于判断预后。
[关键词] 降钙素原;脓毒性休克;清除率
[中图分类号] R720 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2017)05(c)-0018-04
[Abstract] Objective To study the early procalcitonin clearance by dynamic monitoring of it in the first three days of patients with septic shock in ICU and evaluate the prognosis value. Methods The prospective method was used for observation and research, and the 84 cases of internal patients meeting the septic shock diagnosis standards and whose infection focus had no need for the surgical treatment in ICU from April 2015 to April 2016 were convenient selected and included 42 females and 42 males, and the 28 d morbidity was 41.67%, and serum PCT quality concentrations such as PCT-day1,PCT-day2,PCT-day3 at 1 d, 2 d and 3 d of all patients selected were tested and the PCT clearance of PCTc-day2,PCTc-day3) at 2 d and 3 d was calculated. Results The differences in the PCT-day1,PCT-day2,PCT-day3 were not statistically significant between the survival group and the death group(P>0.05), and the PCTc-day2,PCTc-day3 in the survival group were obviously higher than those in the death group(17.00%,51.00% vs 2.00%,20.00%), and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.018, P<0.001), and the 28 d survival area under ROC curve of PCTc-day2,PCTc-day3 was respectively 0.651(95%CI,0.53~0.77,P<0.05) and 0.758(95%CI,0.66~0.86,P<0.01), and the best cutoff value of 28 d survival, sensitivity and specificity were respectively 38.00%, 63.26% and 77.14%. Conclusion The survival rate of septic shock patients whose PCT obviously decreases in 3 d is higher, and the early monitoring of PCT clearance contributes to determining the prognosis.
[Key words] Procalcitonin; Septic shock;Clearance
膿毒性休克是ICU常见危重症,虽然近年来在诊疗方面取得了很大的进展,但仍是ICU患者的主要死亡原因[1-2]。早期准确评估脓毒性休克患者的预后有助于识别治疗效果不佳的患者,并及时调整治疗方案,有可能改善患者预后。血清降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)作为一种新的炎症指标,与感染和脓毒症的相关性很好,并由于其诊断脓毒症敏感度及特异度均优于CRP、IL-6、IL-8、乳酸、内毒素等传统炎症指标[3-4],PCT已被国际指南推荐,作为脓毒症的诊断重要指标[2]。不仅如此,研究显示动态监测PCT 水平变化趋势有助于判断脓毒症的预后[5],其中,PCT 清除率(procalcitonin clearance,PCTc)是近年提出的被认为能较好评估脓毒症预后的一个指标[6]。该研究通过动态监测2015年4月—2016年4月期间脓毒性休克患者入住ICU 3 d内PCT的浓度及其清除率,探讨降钙素原清除率在判断脓毒性休克患者预后中的价值,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
采用前瞻性方法进行研究,方便选取入住该院ICU,符合脓毒性休克诊断标准[2]且感染灶无需外科处理的患者。排除标准:①入住ICU时间<72 h ,②年龄<18 岁,③合并血液系统、免疫系统疾病,④某些肿瘤(甲状腺癌、肺小细胞癌)等对PCT有影响的疾病,⑤确诊为非细菌感染,⑥放弃积极治疗者。
1.2 资料收集
收集研究对象的临床资料,包括性别、年龄、APACHE II评分(第1个24 h)、住ICU 时间、机械通气时间、28 d临床结局(分为生存、死亡组)等。
1.3 指标检测
入选患者于住ICU第1、2、3日分别抽取血液标本以测定血清PCT 质量浓度(PCT-day1、PCT-day2、PCT-day3),样本采用生物梅里埃公司Mini-VIDAS 分析仪进行检测,测量范围为0.05~200 ng/mL。根据上述获得数据,计算第2、3日的PCT清除率(PCTc-day2、PCTc-day3),计算公式分别为:PCTc-day2(%)=(PCT-day1-PCT-day2)/PCT-day1×100%;PCTc-day3(%)=(PCT-day1-PCT-day3)/ PCT-day1× 100%。
1.4 统计方法
采用SPSS 19.0统计学软件进行数据统计分析,符合正态分布的定量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示, 两组间比较采用两独立样本t检验;非正态分布的计量资料以中位数[M,(P25,P75)]表示,两组间比较采用Mann-whitney U检验。PCT清除率对患者预后的评估价值,采用绘制受试工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)判定,计算曲线下面积(AUC)、敏感度、特异度、约登指数指标,并计算最佳截断值。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 基线资料
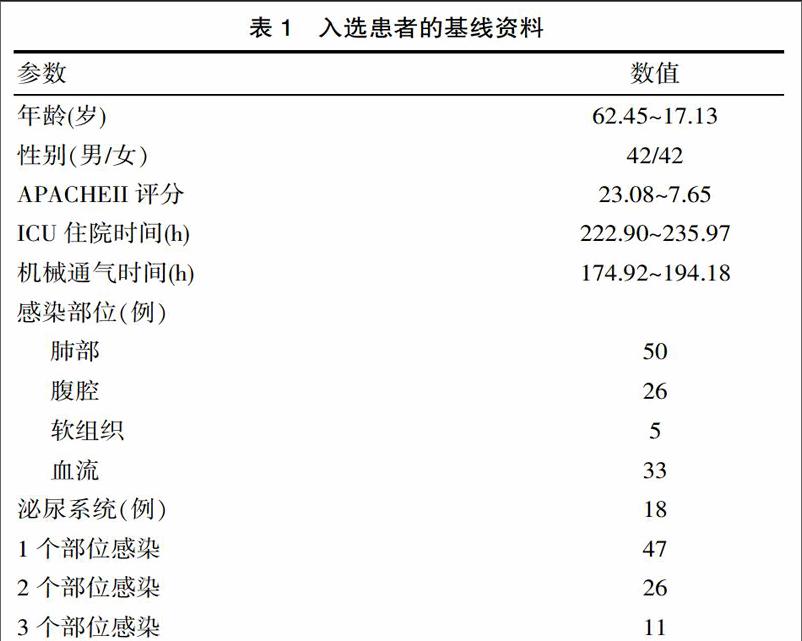
该研究共纳入符合入选标准的患者共84例,其中男女各42例, 28 d病死率为41.67%。感染部位主要为肺部感染、血流感染、腹腔感染及泌尿系感染,其中37例患者存在两个及以上部位感染。患者基线资料见表1。
2.2 生存组与死亡组比较
生存组与死亡组相比, PCT-day1、PCT-day2、PCT-day3差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),生存组PCTc-day2、PCTc-day3明显高于死亡组,差异有统计学意义(P=0.018,<0.001),见表2。
2.3 PCT清除率的ROC曲线分析
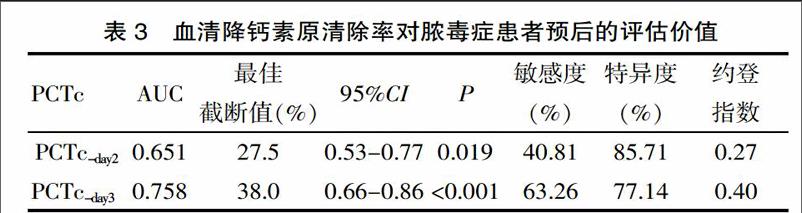
PCTc-day2、PCTc-day3预测28d生存的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.651(95%CI,0.53~0.77,P<0.05)与0.758(95%CI,0.66~0.86,P<0.01)。PCTc-day3对预后的预测价值优于PCTc-day2,其最佳截断值为38.0%,敏感度63.26%,特异度77.14%。见表3。
3 讨论
严重脓毒症和脓毒性休克是导致ICU患者死亡的重要原因,国内的流行病学調查显示其死亡率为28.7%~48.7%[1,7]。该研究纳入的对象全部为感染性休克患者,且病情较重[APACHEII评分为(23.08±7.65)分],总样本28 d病死率为41.67%,与上述国内的流行病学数据相符。尽早给予有效的抗生素是脓毒性休克治疗成败的关键,而病原学培养结果则是作为制定抗感染方案的重要依据,但病原学培养结果往往难以早期获得,且阳性率不高,因此,重症医学科医生更希望某一临床指标可早期识别对经验性抗感染反应不佳的患者,并根据此指导调整抗感染方案。PCT由于其与脓毒症良好的相关性,受到临床医生的重视。
PCT是目前脓毒症领域应用最广泛的生物标志物,它对脓毒症的诊断价值已经得到普遍认可,而PCT绝对值在评估脓毒症预后方面的价值则存在争议。早期Clec'H等[8]研究显示,死亡组脓毒症患者的PCT水平明显高于生存组(中位数第1天:16 ng/mL vs. 6 ng/mL, P=0.045; 第10天:6.5 ng/mL vs. 1.05 ng/mL, P= 0.02);而de Azevedo等[9]研究则显示PCT水平在生存组与死亡组脓毒症患者间差异无统计学意义(中位数24 h:38.32 ng/mL vs. 41.17 ng/mL; 48 h:21.17 ng/mL vs. 20.02 ng/mL;72 h:13.41 ng/mL vs. 11.25 ng/mL)。该研究生存组与死亡组患者第1、2、3天的PCT水平差异无统计学意义,与de Azevedo 等的研究一致。这可能与研究对象各自处于不同的PCT释放时相有关[10]。有关降钙素原的临床价值,2012年中华急诊医学会发表国内专家共识,认为初始PCT水平绝对值的预后意义有限[3]。
PCT清除率(PCTc)是近年提出的用于评估脓毒症预后的新指标,研究显示PCTc评估预后的价值优于PCT绝对值[11],但不同的研究观察的时间点以及截断值各有不同。Pieralli等[12]研究发现,PCT的72 h清除率低于15%可作为预测死亡的独立因素。Karlsson等[11]研究发现,入院72 h内PCT水平下降超过 50%的患者预后较好,而PCT水平没有明显下降的患者死亡率较高。该研究发现,第3天的PCT清除率评估预后的价值优于第2天的PCT清除率,其AUC曲线下面积较高,其最佳截断值为38%,与上述研究结论一致,表明早期监测PCT清除率能作为判断脓毒性休克患者的预后有效指标。
该研究的研究对象全部为感染性休克的内科患者,且感染灶不需要外科处理,可最大限度排除外伤、手术等感染以外的因素对PCT的影响,更能反映PCTc与抗感染疗效的关系。该次研究结果验证了第3天的PCT清除率可有效评估感染性休克患者的预后,具有一定的临床应用价值。同时,该研究亦有不足之处。首先,纳入的患者为单一的内科患者且病情较重,研究结果未必适用于外科及病情较轻的脓毒症患者;其次,样本量偏少。
PCTc具有一定的应用前景。与其它评估脓毒症预后的指标相比具有以下优势:①PCTc不仅可评估预后,还能反映抗生素方案是否合适。Charles等[13]研究发现,经验性抗感染方案有效的患者第2、3天的PCTc明显高于无效的患者。②PCTc在病程早期即可作为评估预后的有效指标,从而识别对经验性抗感染方案反应差的患者。已有大量研究证明,PCT可用于指导抗感染疗程,减少抗生素的应用[14-15],但能否指导调整抗感染方案从而改善预后尚需要更多的临床试验去验证。
综上所述,早期 PCT浓度对脓毒性休克患者的预后判断有一定的局限性,即初始 PCT水平低并不一定提示生存率较高;而即使初始的PCT水平非常高,经过正确的治疗后PCT迅速下降,预后也较好。监测 3 d的PCT清除率能有效判断预后,可作为临床医生评估病情严重程度以及调整抗感染策略的可靠指标。
[参考文献]
[1] Zhou J, Qian C, Zhao M, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in intensive care units in mainland China[J]. PLoS One,2014,9(9):e107181.
[2] Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012[J].Intensive Care Med,2013,39(2):165-228.
[3] 降钙素原急诊临床应用专家共识组.降钙素原(PCT)急诊临床应用的专家共识[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2012,21(9):944-951.
[4] Garnacho-Montero J, Huici-Moreno MJ, Gutierrez-Pizarraya A, et al. Prognostic and diagnostic value of eosinopenia, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and circulating cell-free DNA in critically ill patients admitted with suspicion of sepsis[J]. Crit Care,2014,18(3):R116.
[5] Schuetz P, Maurer P, Punjabi V, et al.Procalcitonin decrease over 72 hours in US critical care units predicts fatal outcome in sepsis patients[J]. Crit Care,2013,17(3):R115.
[6] Ruiz-Rodriguez JC, Caballero J, Ruiz-Sanmartin A, et al. Usefulness of procalcitonin clearance as a prognostic biom arker in septic shock. A prospective pilot study[J]. Med Intensiva,2012,36(7):475-480.
[7] Cheng B, Xie G, Yao S, et al. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in critically ill surgical patients in ten university hospitals in China[J]. Crit Care Med,2007,35(11):2538-2546.
[8] Clec'H C, Ferriere F, Karoubi P, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of procalcitonin in patients with septic shock[J]. Crit Care Med,2004,32(5):1166-1169.
[9] de Azevedo JR, Torres OJ, Beraldi RA, et al. Prognostic evaluation of severe sepsis and septic shock: procalcitonin clearance vs Delta Sequential Organ Failure Assessment[J]. J Crit Care,2015,30(1):219.
[10] 石巖,刘大为. 降钙素原在全身性感染诊治中的研究进展[J]. 中华内科杂志,2011,50(5):444-446.
[11] Karlsson S, Heikkinen M, Pettila V, et al. Predictive value of procalcitonin decrease in patients with severe sepsis: a prospective observational study[J].Crit Care,2010,14(6):R205.
[12] Pieralli F, Vannucchi V, Mancini A, et al. Procalcitonin Kinetics in the First 72 Hours Predicts 30-Day Mortality in Severely Ill Septic Patients Admitted to an Intermediate Care Unit[M]. Jclin Med Res,2015:706-713.
[13] Charles P E, Tinel C, Barbar S, et al. Procalcitonin kinetics within the first days of sepsis: relationship with the appropriateness of antibiotic therapy and the outcome[J].Crit Care,2009,13(2):R38.
[14] Layios N, Lambermont B, Canivet JL, et al. Procalcitonin usefulness for the initiation of antibiotic treatment in intensive care unit patients[J]. Crit Care Med,2012,40(8):2304-2309.
[15] Jensen JU, Hein L, Lundgren B, et al. Procalcitonin-guided interventions against infections to increase early appropriate antibiotics and improve survival in the intensive care unit: a randomized trial[J]. Crit Care Med,2011,39(9):2048-2058.
(收稿日期:2017-02-21)

