手提式挖坑机开合螺母式自动进给机构的设计与试验
马丽娜,王警梁,宗望远,黄小毛,冯 军
手提式挖坑机开合螺母式自动进给机构的设计与试验
马丽娜,王警梁,宗望远※,黄小毛,冯 军
(华中农业大学工学院,武汉 430070)
挖坑机钻头进给量是影响其扭矩和工作效率的重要因素,研究挖坑机进给量与其动态力学参数之间的变化规律对开发挖坑机具有重要意义。该文首先根据开合螺母的工作原理,利用解析法分析了开合螺母机构的运动特性,确定出了其动销轨道角为105°,进而设计出了一种开合螺母式自动进给机构的手提式挖坑机,不仅实现了挖坑作业的自动化,又能迅速完成回程运动。然后基于挖坑机升土理论,分析了挖坑机钻头进给量与其升土效果之间的影响关系,并通过试验进行了验证,从而为挖坑机进给量的设计提供了参考。研究表明,开合螺母螺距为5 mm时,挖坑机扭矩及其波动幅度均较小、工作效率最高。
机械化;设计;土壤;挖坑机;开合螺母;自动进给;钻头进给量;扭矩
0 引 言
挖坑机是一种用途广泛、结构简单、操作方便的挖坑整地机械,主要有悬挂式、手提式、牵引式和自走式四类。而在山地、丘陵、沟壑等复杂地形工况下普遍采用手提式挖坑机进行果树栽植、橡胶定植、小树移植和挖追肥穴等的作业[1]。
目前,国内外学者普遍采用试验研究了挖坑机动态力学参数对其扭矩、功率和工作效率的影响规律[2-6],分析了挖坑机钻头、支撑机构、主轴等结构的动力学特性和振动特性[7-14],对其结构进行了优化。为适应特殊环境作业工况的要求,并达到提高工作效率和降低劳动强度[15-16]的目的,设计了以液压为动力[17-18]或具备新型进给机构[19-24]以及仿生钻头[25]等结构的自动化及智能化的新型挖坑机,甚至设计出了挖坑机器人[26],但其普遍造价高、使用周期短,而且受到工作条件限制[27]。对于挖坑机钻头进给量的控制,多采用液压或手动等方式实现[28-30],尚未明确机械式挖坑机进给量的设计方法。此外,现有手提式挖坑机多无支架,不仅坑穴的垂直度得不到保障,大大增加了挖坑机钻头扭矩,严重制约着结构的可靠性和稳定性,而且增大了挖坑作业过程中的不安全因素。
因此,本文基于挖坑升土理论,确定了挖坑机的进给量,并结合开合螺母机构的工作原理,设计出了一种开合螺母式自动进给机构的手提式挖坑机。
1 手提式挖坑机开合螺母式自动进给机构的设计
1.1 开合螺母式自动进给机构螺距的设计
根据挖坑机升土理论[31]可知,影响钻头顺利升土的主要因素有2个,即钻头转速和钻头进给量。钻头进给量一定时,钻头实际转速超过临界转速时土壤向上流动,挖坑机顺利升土。钻头转速一定时,钻头进给量则是影响钻头升土效果和挖坑效率的关键因素。手提式挖坑机自动进给机构采用丝杠螺母传动的进给方式,该自动进给机构的螺距即决定了挖坑机的进给量。
挖坑机钻头工作时,当土壤垂直运动速度大于土壤堵塞临界速度时钻头能够正常工作,而不发生堵塞现象。
土壤垂直运动速度[1]为
式中v为土壤垂直运动速度,m/s;0为钻头半径,m;为钻头转速,rad/s;为土壤速度损失系数;为钻头升角,(°);2为土壤之间摩擦系数;为钻头半径处的质点速度与水平面的夹角,(°);与为系数;1为土钢摩擦角,一般取20°;为重力加速度,9.8 m/s2。
钻头进给速度[31]v为
避免钻头堵塞临界条件为
式中为钻头进给量,mm/r;为土壤彭松系数,取1.6。
本文中选用的钻头半径为0.15 m,钻头升角为20°。根据文献[1],土钢摩擦角和土壤内摩擦角分别取20°和44°。由式(1)~式(3),可得出土壤垂直速度和堵塞临界速度分别随钻头进给量变化曲线,如图1所示。
由图1可知,土壤垂直速度和堵塞临界速度随进给量变化曲线相交于点(5.3,0.048)。当进给量小于5.3 mm/r时,土壤垂直运动速度大于钻头堵塞临界速度,挖坑机能够正常升运土壤。当进给量大于5.3 mm/r时,土壤垂直速度小于钻头堵塞临界速度,挖坑机钻头发生堵塞。当钻头进给量满足顺利升土条件时,进给量越大,挖坑效率越高。结合螺母丝杠螺距在国标中的规定,开合螺母螺纹规格选为Tr24×5,即直径为24 mm,螺距为5 mm的梯形螺纹。为匹配挖坑机钻头旋向和动力输出轴的转向,自动进给机构螺纹旋向设计为右旋。
1.2 开合螺母结构设计
采用螺纹传动能够实现挖坑机钻头自动进给运动,但若采用闭合螺母与丝杠配合形式,需要动力输出轴反转才能完成钻头的回程运动。但挖坑机动力源是汽油机,其动力输出轴不能反转,故采用闭合螺母与丝杠配合的进给运动形式无法用于实际的挖坑作业。因此,本文采用开合螺母式自动进给机构,当螺母闭合时,挖坑机钻头完成进给运动;挖坑作业完成后,打开开合螺母,手动提起钻头至初始位置,完成回程运动。该方案既实现了挖坑作业的自动化,又能迅速完成回程运动。
本文借鉴汽车轮胎平衡机快速锁紧螺母机构进行开合螺母结构设计,如图2a所示。半螺母上有2个销钉孔,分别装有定销和动销。定销和基座固联,半螺母可绕定销转动。螺母拨片上有2种类型的4个轨道呈对称分布,定销在圆轨道内滑动,动销在直轨道内滑动。螺母拨片绕定销转动时带动动销在直轨道内滑动,从而控制螺母开闭。螺母拨片和基座之间设置有弹簧,保证螺母一直处于闭合状态。开合螺母中心点记为点,其中任意一个定销位置记为点,动销所在滑道末端位置记为点,动销在滑道内的位置记为点,螺母开合运动简图如图2b所示。
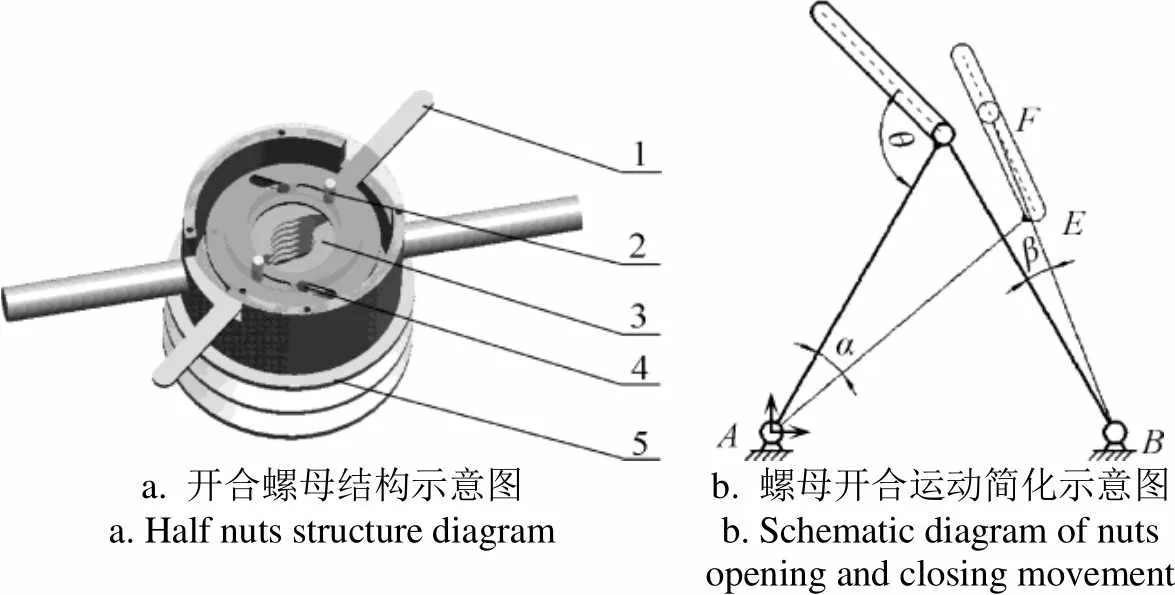
a. 开合螺母结构示意图a. Half nuts structure diagramb. 螺母开合运动简化示意图b. Schematic diagram of nuts opening and closing movement
c. 螺母开合运动分析图
c. Analysis of nuts opening and closing motion
1.螺母拨片 2.定销 3.半螺母 4.动销 5.基座
1.Nut picks 2.Fixed pin 3.Half nut 4.Movable pin 5.Base
注:为杆的摆动角,(°);为杆的摆动角,(°);为动销轨道角,(°);1为点与点之间的长度,m;2为点与点之间的长度,m;3为点与点之间的长度,m;4为点与点之间的长度,m;1为杆与水平线的夹角,(°);2为杆与水平线的夹角,(°);3为杆与水平线的夹角,(°)。
Note:is the swing angle of rod, (°);is the swing angle of rod, (°);is the orbit angle of movable pin, (°);1is the distance between pointand point, m;2is the distance between pointand point, (m);3is the distance between pointand point, m;4is the distance between pointand point, m;1is the angle between rodand horizontal level, (°);2is the angle between rodand horizontal level, (°);3is the angle between rodand horizontal level, (°).
图2 开合螺母机构运动分析图
Fig.2 Movement analysis chart of half nut mechanism
利用解析法对半螺母的开合运动进行运动分析,建立如图2c所示的直角坐标系。各杆件组成了一个封闭的矢量多边形,即。在此封闭矢量多边形中,各矢量和等于0,即满足
式中1为点至点的方向向量;2为点至点的方向向量;3为点至点的方向向量;4为点至点的方向向量。
将封闭矢量方程(4)改写并表示为复数矢量形式为
式中1为点与点之间的长度,m;2为点与点之间的长度,m;3为点与点之间的长度,m;4为点与点之间的长度,m;1为杆与水平线的夹角,(°);2为杆与水平线的夹角,(°);3为杆与水平线的夹角,(°)。
式中为动销轨道角,(°)。
由几何关系知1=3=4,消去未知量2后,将1从0°取到60°,间隔5°,动销轨道角从90°取到120°,间隔5°,代入式(7)得3。由各杆件的杆长关系和初始位置角度(1=60°,3=120°),可知杆转动角为=60°−1,杆转动角为=120°−3。列出不同和组合下的值,如表1所示。
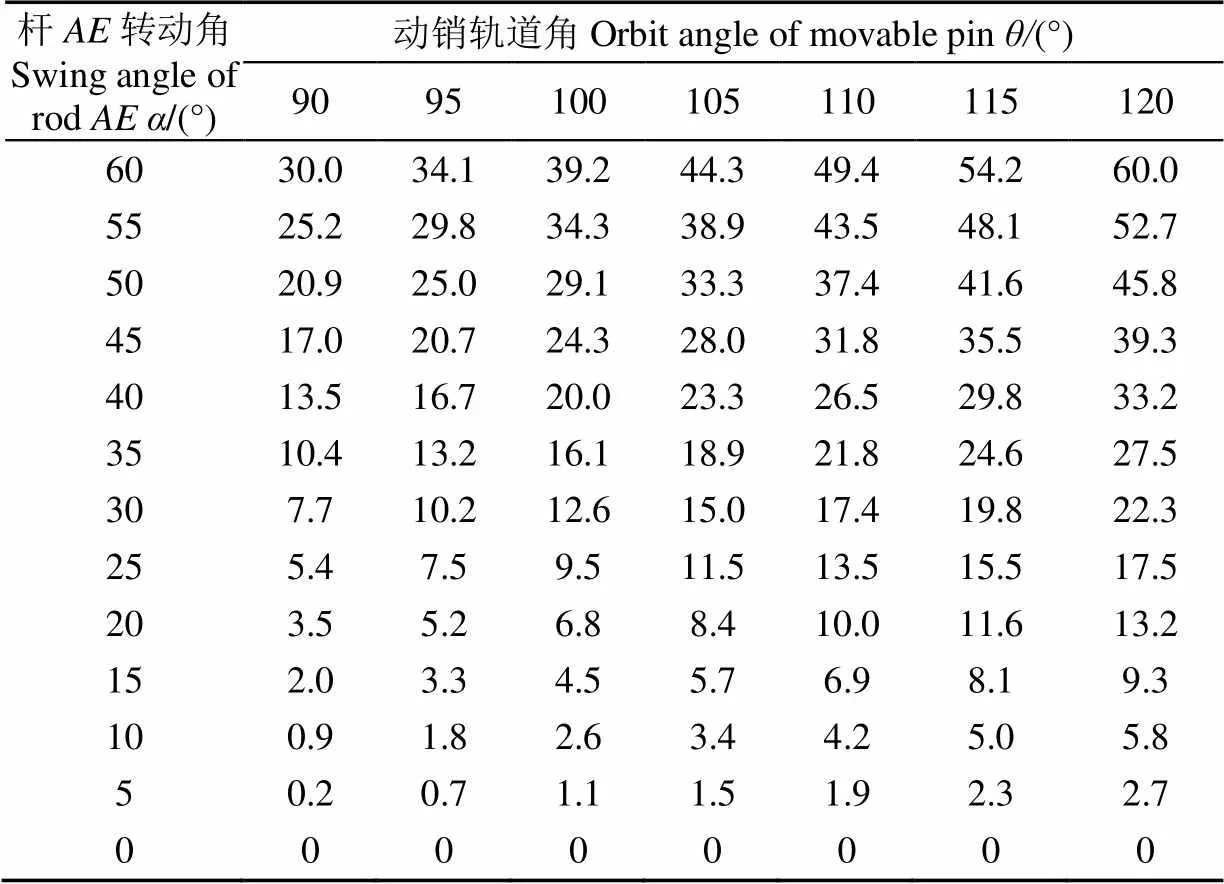
表1 动销轨道角和杆AE转动角对杆BF转动角的影响
表1中杆转动角的变化趋势为:在动销轨道角不变时杆转动角随杆转动角增大而增大,在杆转动角不变时杆3转动角随动销轨道角增大而增大。从工作效率看,相同的杆转动角对应的杆转动角越大螺母开合的效率就越高。从结构尺寸看,杆转动角越大开合螺母机构整体尺寸越大。即,杆转动角越大,螺母开合的效率就越高,但杆转动角变大时开合螺母机构的整体尺寸就会变大。综合考虑开合螺母的工作效率和结构尺寸,取动销轨道角为105°。
1.3 手提式挖坑机整体结构设计
该手提式挖坑机结构如图3所示,主要由机架、汽油机、带轮、开合螺母、支撑架、丝杠、导轨和钻头等组成。汽油机动力在其输出轴处分为两部分:一部分传递给钻头,带动钻头转动;另一部分经带轮传递到开合螺母,开合螺母与丝杠形成螺旋副,带动钻头实现进给运动。在挖坑作业完成后,停止汽油机工作,通过螺母拨片打开开合螺母,将支撑架连同汽油机及钻头提起到初始位置,然后闭合开合螺母以备下次作业。
2 试验与分析
本文采用北京新宇航世纪科技有限公司JN338-100A型扭矩仪实时测量挖坑机作业过程中钻头转速和扭矩。
2.1 试验装置
试验装置如图4a所示,汽油机动力输出轴通过联轴器与扭矩仪的一端相连,扭矩仪的另一端通过联轴器与钻头联接轴相连[32-33]。图4b为试验现场。
2.2 试验方法
试验时间为2016年5月6日至8日,选择华中农业大学现代农业科技试验基地平整地块作为试验区域,试验过程中空气湿度基本一致,试验前首先测定试验区域的土壤坚实度。在试验区域均布取4个测试点,分别测量每个测试点在不同深度处的土壤坚实度,测量结果见表2。由表2可知,土壤坚实度在土层深度变化时基本保持不变,排除了土壤坚实度变化对挖坑机作业中钻头消耗功率的影响。
为分析不同进给量对挖坑作业过程中钻头扭矩变化的影响,选用Tr24×3、Tr24×5和Tr24×8 3种不同螺距的自动进给机构进行挖坑作业对比试验。试验过程中保证挖坑机钻头匀速工作。
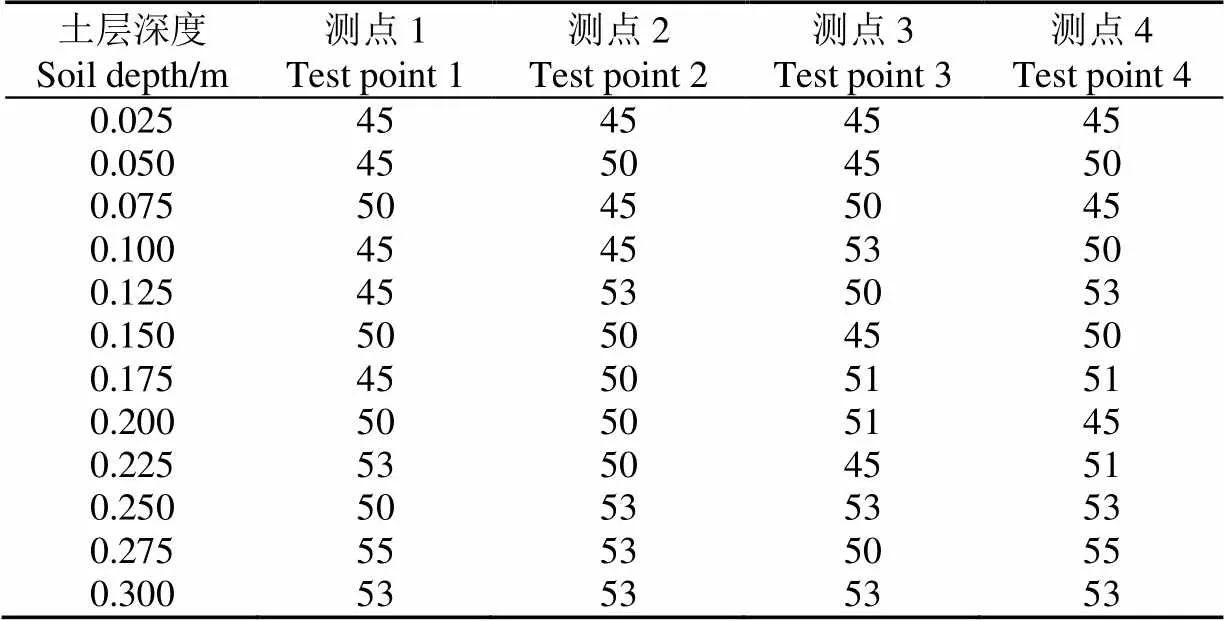
表2 各测点土壤坚实度
2.3 试验数据处理与分析
扭矩仪数据采集卡采集到的数据为各测点对应的钻头转速、钻头扭矩,进而计算出各测点对应的钻头位移。而后将各组数据按时长为1 s分段,计算出扭矩标准差,各组数据见图5、图6和图7。
a. 测点1
a. Test point 1
b. 测点2
b. Test point 2
c. 测点3
c. Test point 3
a. 测点1
a. Test point 1
b. 测点2
b. Test point 2
c. 测点3
c. Test point 3
由图5、图6和图7可知,在钻头速度恒定的前提下,3种试验条件挖坑作业过程中,钻头扭矩均随时间增加呈上升趋势。
对比分析图5、图6和图7可知:1)螺距为8 mm各测点钻头扭矩均比螺距为3和5 mm大,且波动幅度大。螺距为8 mm时,钻头对应的进给量8大于5.3 mm/r,土壤垂直运动速度小于钻头堵塞临界速度,挖坑机钻头发生堵塞,所以扭矩增加且波动幅度增大;2)螺距为3和5 mm时,对应的进给量分别为3和5 mm/r,均小于5.3 mm/r,土壤垂直速度大于钻头堵塞临界速度,挖坑机能够正常升运土壤,因此二者各测点钻头扭矩和波动幅度均相对较小。但是当钻头进给量满足顺利升土条件时,进给量越大,挖坑效率越高,因此开合螺母螺距为5 mm时,不仅可以满足正常升运土壤,而且工作效率最高。
a. 测点1
a. Test point 1
b. 测点2
b. Test point 2
c. 测点3
c. Test point 3
此外,挖坑作业时,闭合开合螺母,开合螺母与丝杠形成螺旋副,带动钻头实现进给运动;挖坑作业完成后,手动打开开合螺母,通过提起开合螺母,能够将钻头顺利提升至初始位置,从而完成钻头的回程运动,以备进行下一个挖坑作业。整个试验过程中,开合螺母机构工作性能均可靠。
3 结 论
1)设计了一种手提式挖坑机开合螺母式自动进给机构,不仅实现了挖坑作业的自动化,而且能迅速完成回程运动。该手提式挖坑机设计有支撑结构,不仅能够保证挖坑的垂直度,而且增强了安全性和可靠性。
2)运用经典挖坑理论,明确了挖坑机钻头进给量对其升土效果的影响关系,并通过试验进行了验证,为挖坑机进给量的设计提供了参考。研究表明,开合螺母螺距为5 mm时,挖坑机扭矩及其波动幅度均较小、工作效率最高。
3)采用解析法分析了开合螺母机构的运动特性,确定出了其动销轨道角为105°。
[1] 于建国,屈锦卫. 国内外挖坑机的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 农机化研究,2006(12):38-41.
Yu Jianguo, Qu Jinwei. Research situation and development trend of earth auger in home and abroad[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2006(12): 38-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 王乃康,刘会敏,茅也冰. 作业参数对挖坑机动态力学参数影响的试验研究(I):挖坑机动态力学参数的测试与研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2002,24(5/6):195-199.
Wang Naikang, Liu Huimin, Mao Yebing. Effects of working parameters on dynamic mechanical parameters for digging machine(I): Test and study of dynamic mechanical parameters for digging machine[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2002, 24(5/6): 195-199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 郭贵生,高梦祥,郭康权,等. 基于MATLAB挖坑机螺旋钻头参数的研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2003,31(3):179-182.
Guo Guisheng, Gao Mengxiang, Guo Kangquan, et al. Study of screw auger parameters of mounted hole digger on the basis of MATLAB[J]. Jour. of Northwest Sci-Tech Univ. of Agri. and For. : Nat. Sci. Ed., 2003, 31(3): 179-182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 高梦祥,郭贵生,郭康权. 基于MATLAB的挖坑机钻头转矩分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2003,31(1):131-134.
Gao Mengxiang, Guo Guisheng, Guo Kangquan. Analysis of screw auger’s torque of digging pit machine by using MATLAB[J]. Jour. of Northwest Sci-Tech Univ. of Agri. and For. : Nat. Sci. Ed., 2003, 31(1): 131-134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 刘少刚. 挖坑机钻头转速及进给量的优化选择[J]. 林业机械,1989(3):27-31.
[6] 王警梁. 自动进给挖坑机设计与参数化研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学,2016.
Wang Jingliang. Design and Parametric Research of Automatic Feed Hole Digger[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李耀明,徐立章,陈航. 4YS-600型树木移栽机铲刀臂的改进设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(3):60-63.
Li Yaoming, Xu Lizhang, Chen Hang. Improved design of spade arm in 4YS-600 tree transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(3): 60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 王保帅,杨永发,高延杰,等. 摆杆式烟苗移栽挖穴机的设计与优化分析[J]. 中国农机化学报,2016,37(8):23-27.
Wang Baoshuai, Yang Yongfa, Gao Yanjie, et al. Design and optimization analysis of the transplanting and digging machine for the tobacco seedling transplanting[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2016, 37(8): 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 杨有刚,刘迎春,吕新民. 挖坑机扭转振动特征对的动力学分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(6):53-55.
Yang Yougang, Liu Yingxin, Lü Xinmin. Dynamic analysis of torsional vibration for a hole digger[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(6): 53-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 孟庆华. 深植挖坑机钻头动态过程数学描述与仿真研究[D]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2007.
Meng Qinghua. Research on Simulation and Mathematical Interpretation of Dynamic Process to Earth Auger for Tree Deep Planting[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 赵忠松. 挖坑机钻头有限元分析和悬挂机构运动仿真[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2010.
Zhao Zhongsong. FEA of the Auger and the Hitch Motion Simulation of Hole Digger[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 屈锦卫. 挖坑机主轴的有限元分析及其悬挂机构的动力学仿真[D]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2007.
Qu Jinwei. Finite Element Analysis of the Principal Axis of Earth Auger and Dynamic Simulation of Hanging Machine[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] Macpherson J D, Jogi P N, Kingman J E E. Application and analysis of simultaneous near bit and surface dynamics measurements[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2001, 16(4): 230-238.
[14] Macpherson J D, Jogi P N, Kingman J E E. Application and analysis of simultaneous near bit and surface dynamics measurements[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2001, 16(4): 230-238.
[15] Vosniak J, Lopes E D S, Fiedler N C, et al. Demanded physical effort and posture in semi mechanical hole-digging activity at forestry plantation[J]. Scientia Forestalis/ Forest Sciences, 2010(88): 589-598.
[16] Silva E P D, Minette L J, Souza A P D. Evaluation an ergonomic of the activity of semi mechanized pit for the planting of eucalyptus[J]. Scientia Forestalis/Forest Sciences, 2007(76): 77-83.
[17] 李肖婷. 3WY-40多功能液压微型挖坑机设计分析及研究[J]. 农业技术与装备,2016(323):68-71.
Li Xiaoting. Design research and analysis on 3WY-40 multi-function hydraulic micro hole digger[J]. Agricultural Technology and Equipment, 2016(323): 68-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 陆建,缪明,卢少颖,等. 车载植树挖坑机研究设计与试验[J]. 中国农机化学报,2014,35(6):44-47,60.
Lu Jian, Miao Ming, Lu Shaoying, et al. Design and test research of digging machine for vehicle planting[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2014, 35(6): 44-47,60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] Wangyuan Z, Jingliang W, Xiaomao H, et al. Development of a mobile powered hole digger for orchard tree cultivation using a slider-crank feed mechanism[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2016, 9(3): 48-56.
[20] 宗望远,王警梁. 高效轻便挖坑机:CN205017820U[P]. 2016-02-10.
[21] 渠聚鑫. 新型自走式植树挖坑机的研究[D]. 北京:中国林业科学研究院,2009.
Qu Juxin. Research on New Self-Propelled Tree Planting Earth Auger[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 姜长笑. 可移动挖坑机:CN105165183A[P]. 2015-12-23.
[23] 赵彩华. 手提式植树挖坑机:CN105474833A[P]. 2016-04-13.
[24] 符翔. 一种农业挖坑机械装置:CN205284090U[P]. 2016-06-08.
[25] 吕有界,王玉兴,唐艳芹,等. 仿生曲面在螺旋桩螺旋叶片上的应用研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2007,23(4):134-137.
Lu Youjie, Wang Yuxing, Tang Yanqin, et al. Application of bionic surface on blades of screw pile[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2007, 23(4): 134-137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] Du Danfeng, Ma Yan, Guo Xiurong, et al. Research on a forestation hole digging robot[C]//2010 International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, 2010: 1073-1076.
[27] 黄亚光. 挖坑机执行机构动力学分析及参数研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2012.
Huang Yaguang. Dynamics Analysis and Parameters Research on Digging Machine Actuator[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] Haga M, Hiroshi W, Fujishima K. Digging control system for hydraulic excavator[J]. Mechatronics, 2001, 11(6): 665-676.
[29] 吴立国,郭克君,满大为,等. 自行式挖坑机液压系统的设计与选型[J]. 林业机械与木工设备,2016,44(5):24-28.
Wu Liguo, Guo Kejun, Man Dawei, et al. Design and model selection of hydraulic systems for a self-propelled hole digger[J]. Forestry Machinery and Woodworking Equipment, 2016, 44(5): 24-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 王有刚. 新型全液压连续式挖坑机研究[D]. 北京:北京林业大学,2012. Wang Yougang. The Design of New Continuous Digging Machine with All-Hydraulic Drive[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 卓凤英. 挖坑机[M]. 北京:中国林业出版社,1989.
[32] 张居敏,贺小伟,夏俊芳,等. 高茬秸秆还田耕整机功耗检测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(18):38-46.
Zhang Jumin, He Xiaowei, Xia Junfang, et al. Design and field experiment of power consumption measurement system for high stubble returning and tillage machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(18): 38- 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 陈度,王书茂,康峰,等. 联合收割机喂入量与收获过程损失模型[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(9):18-21.
Chen Du, Wang Shumao, Kang Feng, et al. Mathematical model of feeding rate and processing loss for combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(9): 18-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Design and experiment of automatic feed mechanism with half nuts structure of portable digging machine
Ma Li’na, Wang Jingliang, Zong Wangyuan※, Huang Xiaomao, Feng Jun
(430070,)
Digging machine is a kind of digging and tillage machine. Because its structure is simple and it can be operated conveniently, it is widely used as a hole digger. There are mainly 4 types of digging machines, i.e. suspension type, portable type, traction type and self-propelled type. On the mountains, hills, ravines and other complex terrain conditions, portable type of digging machine is popularly used to dig a hole so as to plant or transplant trees. Hence, this paper designed a new portable digging machine with a half-nut mechanism to keep the feed rate stable and decrease the torque of the drilling bit as far as possible when drilling the hole. In addition, the support structure was also designed for the digging machine for the sake of guaranteeing the verticality of the hole and ensuring the reliability and stability of the digging machine, as well as making the structure more secure. The feed rate of the digging machine was an important factor, which affected the torque and work efficiency of the drilling bit greatly. Research on the effect of the feed rate on the dynamic mechanical parameters of digging machine was of great significance for developing a new model of digging machine. However, the power of the digging machine was gasoline engine, so the power output shaft could not reversely rotate, and it could not be used for actual digging. Thus there was a great need to design a new structure that could solve the gasoline engine’s problem of rotating only in one direction. Accordingly, the half-nut mechanism was designed. According to the working principle of the half-nut, the motion characteristics of half-nut mechanism were analyzed by using the analytic method. The straight track angle of half-nut picks was decided as 105°, and thus a portable digging machine with half-nut mechanism was designed. The new designed digging machine could not only realize the digging operation automatically, but also complete the return movement rapidly. Then based on the working principle of digging machine, the relationship between the feed rate and the effect of lifting soil was studied. In order to verify the result, the experiment of testing the torque and rotational speed during the process of drilling a hole was conducted by using the torque measuring device JN338-100A made by Beijing Xinyuhang Century Science and Technology Co., Ltd. to collect the data afterward. Therefore it successfully provided a theoretical basis for the determination of feed rate of a new type of digging machine. It showed that when the pitch of half nut was taken as 3 or 5 mm, the torque and its fluctuation both were small. However when the pitch of half nut was taken as 8 mm, for it did not satisfy the working principle of digging machine, the torque and its fluctuation varied greatly, and the digging machine could not lift soil smoothly. In order to improve the work efficiency, the pitch of half nut was taken as 5 mm for this new designed digging mechanism finally. This paper provides a theoretical basis for the design of automatic feed mechanism of a new portable digging machine.
mechanization; design; soils; digging machine; half nuts; feed automatically; feed rate; torque
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.04.004
S776.26+2
A
1002-6819(2017)-04-0025-07
2016-06-06
2017-02-05
公益性行业(农业)科研专项经费(201203047)
马丽娜,女,讲师,山东莱芜人,主要从事农业装备数字化设计技术研究。武汉 华中农业大学工学院,430070。Email:sunnylina@163.com
宗望远,男,河南周口人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事现代农业装备设计与测控技术研究。武汉 华中农业大学工学院,430070。 Email:zongwangyuan@mail.hzau.edu.cn
马丽娜,王警梁,宗望远,黄小毛,冯 军. 手提式挖坑机开合螺母式自动进给机构的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(4):25-31. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.04.004 http://www.tcsae.org
Ma Li’na, Wang Jingliang, Zong Wangyuan, Huang Xiaomao, Feng Jun. Design and experiment of automatic feed mechanism with half nuts structure of portable digging machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(4): 25-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.04.004 http://www.tcsae.org

