一类含有分布时滞的非自治细胞神经网络的全局指数稳定性
李 宾, 龙述君
(1. 西华大学 理学院, 四川 成都 610039; 2. 乐山师范学院 数学与信息科学学院, 四川 乐山 614004)
一类含有分布时滞的非自治细胞神经网络的全局指数稳定性
李 宾1, 龙述君2*
(1. 西华大学 理学院, 四川 成都 610039; 2. 乐山师范学院 数学与信息科学学院, 四川 乐山 614004)
研究一类具有分布时滞的非自治细胞神经网络的全局指数稳定性,通过建立一个新的微分-积分不等式,并将其运用到非自治细胞神经网络的稳定性研究中,从而得到全局指数稳定性的充分判别准则.结论较以往的文献结果,更具一般性,适用范围更广.最后,通过实例说明所获结论的可行性和优越性.
细胞神经网络; 非自治; 全局指数稳定; 微分-积分不等式; 分布时滞.
自从L.O.Chua等1988年在文献[1-2]中首次提出细胞神经网络理论以来,其相关理论已经成功应用在模式识别、移动图像处理、运动目标识别等领域.网络系统的稳定性是这些应用必须考虑的因素,因此,吸引了很多学者对该动力行为进行研究并获得许多有用的结果[3-13].在现实生活中,时滞现象是普遍存在的,时滞的存在往往会对系统具有一定的破坏作用,如在神经元间信号传输过程中产生的时滞现象会对系统造成震荡、混沌或不稳定现象,因而研究时滞对动力行为的影响是非常有必要的[14-17].
当考虑一个长期的动力行为时,系统的参数常常受到环境干扰而随时间变化,非自治微分系统更能准确描述此类情况.对人工细胞神经网络而言,也不例外.然而对非自治神经网络的研究远比对自治神经网络的研究困难得多.人们尝试各种方法对其进行研究,并获得较好结果.文献[18-19]采用李亚普洛夫楔函数方法研究具有有限时滞的非自治细胞神经网络的动力行为,获得了系统稳定性的充分判据;文献[8-9]通过建立新的微分不等式,运用不等式分析技巧研究几类非自治神经网络的动力行为,拓宽了判定动力行为条件的使用范围.此外,由于具有各种轴突大小和轴突长度的大量平行路径存在,神经网络通常具有空间延展,此类情况下,时滞往往以分布时滞呈现出来,因而有必要研究具有分布时滞的非自治细胞神经网络的动力行为[20-21],但这些成果中都要求判定条件在时间变化范围内一致成立,这在一定程度上影响了成果的适用范围.
基于以上分析,本文将对含有分布时滞的非自治细胞神经网络的全局指数稳定进行研究,得到全局指数稳定性的充分判别准则,从而推广一些现有文献的相关结果.
考虑如下含分布时滞的细胞神经网络模型:
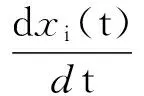

i=1,2,…,n,
(1)
1 预备知识
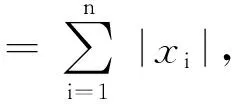
C[X,Y]表示从拓扑空间X到拓扑空间Y的所有连续映射全体.特别地,令CC[(-∞,0],Rn]表示所有有界连续函数φ:(-∞,0]→Rn且|.
定义1如果存在常数λgt;0,M≥1,使得对于系统(1)的任意2个分别满足初值条件φ,φ∈C的解x(t,φ),y(t,φ).对任意t≥t0有
‖x(t,φ)-y(t,φ)‖≤M‖φ-φ‖e-λ(t-t0),
则称系统(1)是全局指数稳定的.
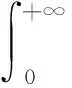
引理1假设p(t)满足如下含有脉冲项的微积分不等式
(2)
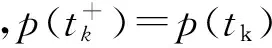
如果当t≤t0时有
p(t)≤me-λ(t-t0),
(3)
则
t≥t0,
(4)
其中,m为正常数,δkmax{1,|pk|+|qk|×k(s)eλsds},λ∈(0,λ0),满足

(5)


下面将证明
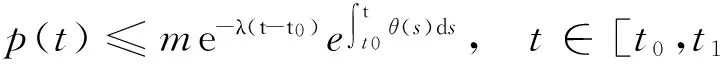
(6)
为了证明(6)式,首先证明,对任意的常数εgt;0有
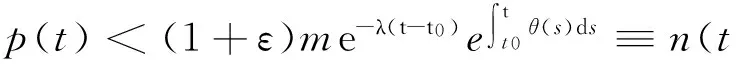
(7)
假设(7)式不成立,则存在一个t*∈(t0,t1),使得
p(t*)=n(t*),D+p(t*)≥n′(t*),
(8)
p(t)≤n(t), t∈(-∞,t*].
(9)
结合(2)、(5)、(7)~(9)式,可以得到
(10)
显然与(8)式的第二个不等式矛盾,因而(7)式成立,在(7)式中,令ε→0,得到(6)式成立.
接下来,结合(2)、(3)和(6)式,得到
(11)
则
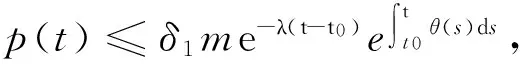
运用与(6)式类似的方法,得到
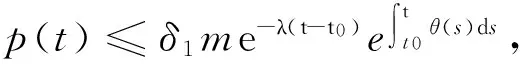
通过归纳得到,对任意的k∈N有
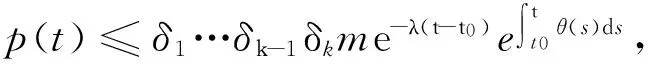
故原命题得证.
注1在引理1中,当t≥t0时,如果α(t)≡0和β(t)≡0,得到文献[13]中的引理1.
2 主要结果
定理1假设如下条件成立:
(A1) 对任意i,j=1,2,…,n和l=1,2,…,m,存在kj和uijl,使得
|fj(x)-fj(y)|≤kj|x-y|,
|gijl(x)-gijl(y)|≤uijl|x-y|;


(12)
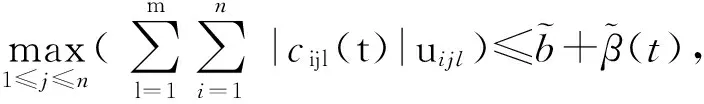
(13)
(A3) 存在常数λgt;γ≥0和h≥0,使得
(14)
其中λ满足
(15)
则系统(1)是全局指数稳定的且指数收敛率不低于λ-γ.
证明设x(t),y(t)是系统(1)的任意2个分别满足初值条件φ,φ∈C的解.令
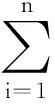
结合系统(1)和条件(A1)、(A2),得到
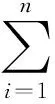
(16)
因为φ,φ∈C,则存在一个正数M≥1,使得
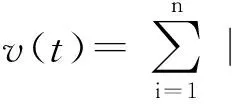
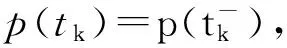
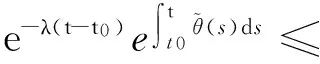
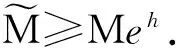

(17)
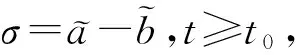
3 实例说明
考虑如下二维含有分布时滞的非自治细胞神经网络系统
(18)

明显地,gi(s)满足李普希兹条件且ui=1(i=1,2),得到(A2)的参数
-b1(t)≤-2.25+δ(t),
-b2(t)≤-2.5+δ(t);
|c11(t)|+|c21(t)|≤1.75,
|c12(t)|+|c22(t)|≤1.6.
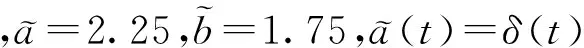
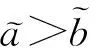
下面计算

对任意tgt;t0≥0,存在正整数n≥m≥0,使得nT≤tlt;(n+1)T,mT≤t0lt;(m+1)T;令t=nT+u,t0=mT+w,其中0≤u,wlt;T.通过计算得到

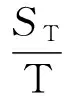
特别地,当k∈N时,令
明显地,δ(s)的周期为2π,易得
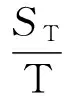
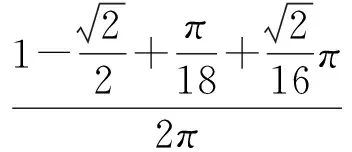

图 1 x1(t)的状态曲线
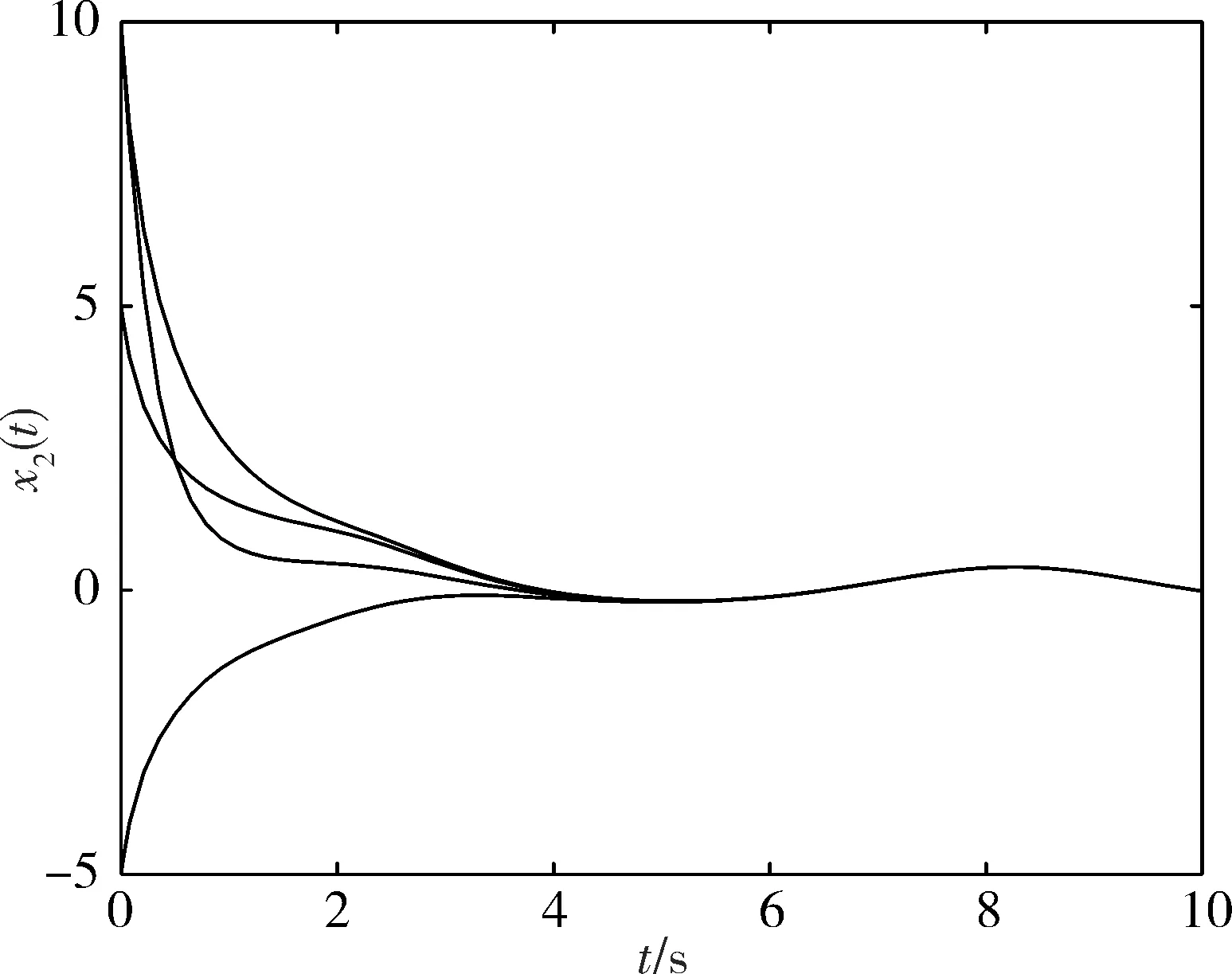
图 2 x2(t)的状态曲线
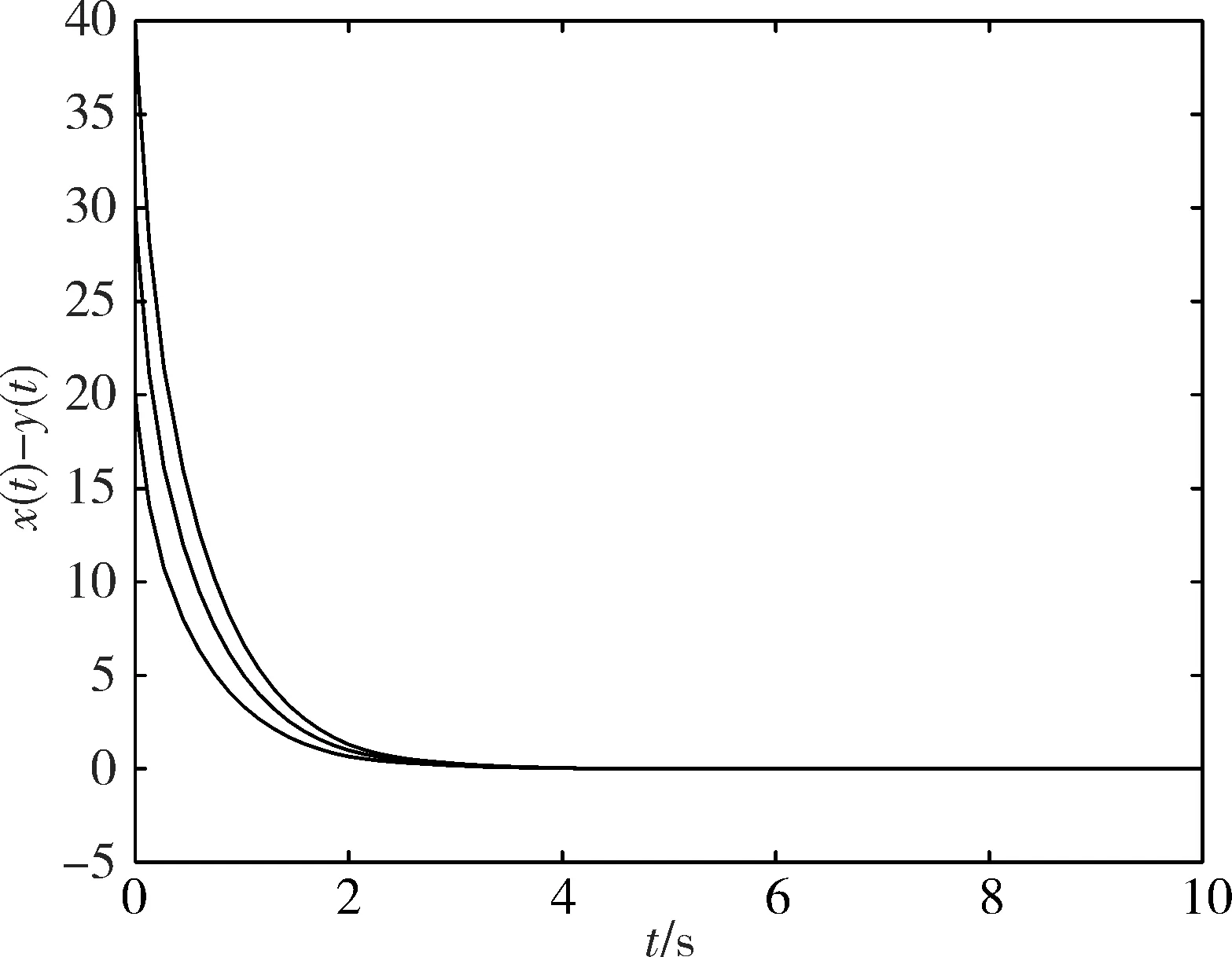
图 3 ‖x(t)-y(t)‖的衰减曲线
注3在文献[20]的条件(H2)中,令ωi=qij=rij=1(i,j=1,2);得到相应的判别条件:
h1(t)=b1(t)-(|c11(t)|+|c21(t)|)=
1.625-cost-sint-δ(t);
h2(t)=b2(t)-(|c12(t)|+|c22(t)|)=
1.75-0.75sint-δ(t).
通过观察图4和5发现,对任意的t≥t0,不存在σgt;0,使得h1(t)gt;σ,h2(t)gt;σ成立,因此,文献[20]中的结论对此例是失效的.

图 4 h1(t)对应的图形
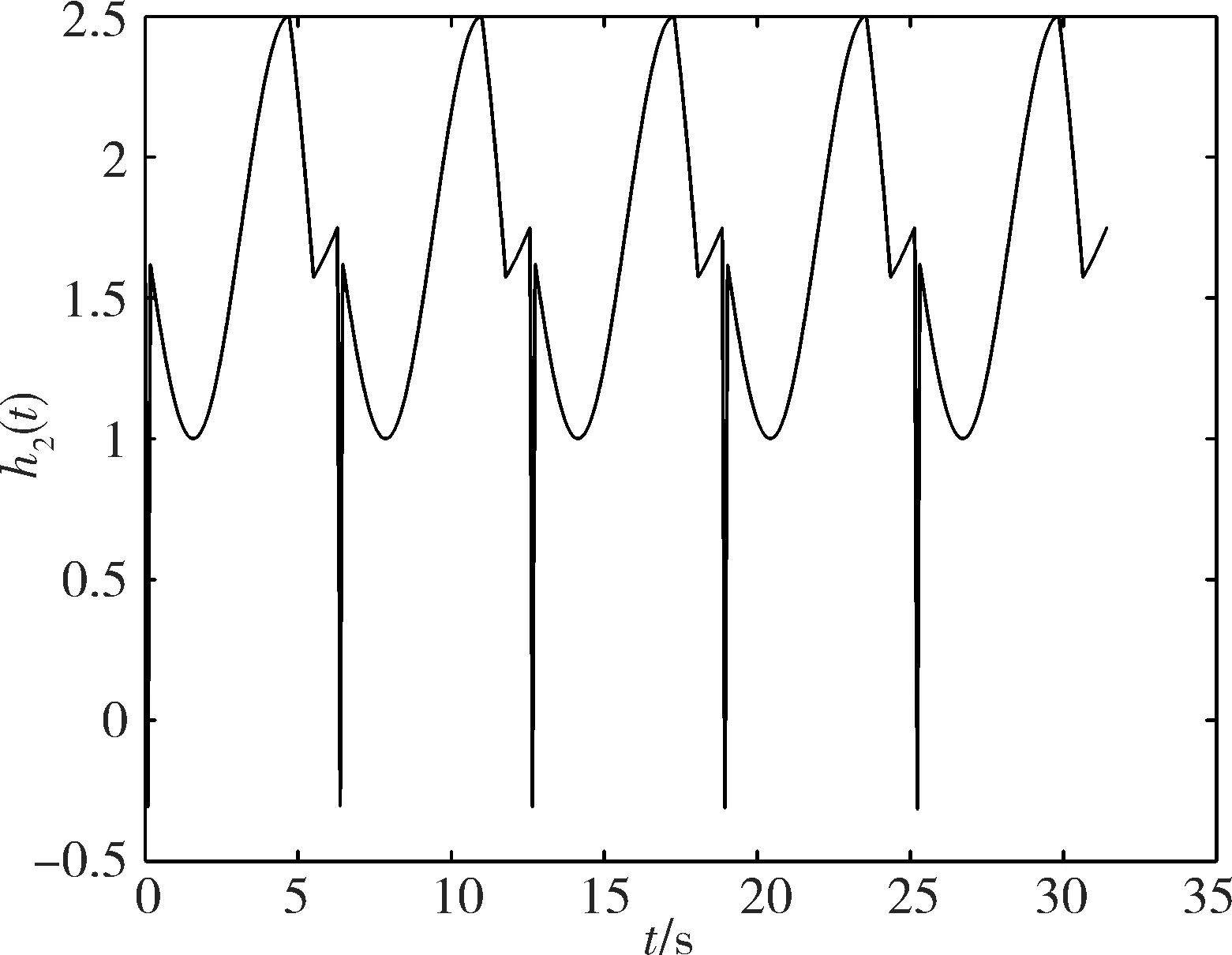
图 5 h2(t)对应的图形
4 结束语
本文研究一类含有分布时滞的非自治细胞神经网络的全局指数稳定性问题,通过运用不等式分析技巧,建立一个新的微分-积分不等式,使得神经网络的全局指数稳定的判别准则得到了进一步放松,较之前的结果适用范围更广.
[1] CHUA L O, YANG L. Cellular neural networks:theory.IEEE trans[J]. Circuits Syst,1988,35(I):1257-1272.
[2] CHUA L O, YANG L. Cellular neural networks:applications.IEEE trans[J]. Circuits Syst,1988,35(I):1273-1290.
[3] ROSKA T, BOROS T, THIRAN P, et al. Detecting simple motion using cellular neural networks[C]//IEEE International Workshop on Cellular Neural Networks and Their Applications,1990. Cnna-90 Proceedings. IEEE,1990:127-138.
[4] CHUA L O, ROSKA T. Cellular neural networks with nonlinear and delay-type template elements[C]//EE Int Workshop Cellular Neural Networks Applications, Cnna-90 Proceeding,1991:12-25.
[5] LIANG J L, CAO J D. Global asymptotic stability of bi-directional associative memory networks with distributed delays[J]. Appl Math Comput,2004,152(1):415-424.
[6] SONG Q K, YAN H, ZHAO Z J, et al. Global exponential stability of complex-valued neural networks with both time-varying delays and impulsive effects[J]. Neural Networks,2016,79(1):108-116.
[7] JIANG M H, MU J, HUANG D S. Globally exponential stability and dissipativity for nonautonomous neural networks with mised time-varying delays[J]. Neurocomputing,2016,205(1):421-429.
[8] LONG S J, XU D Y. Global exponential stability of non-autonomous cellular neural networks with impulses and time-varying delays[J]. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat,2013,18(1):1463-1472.
[9] LONG S J, LI H H, ZHANG Y X. Dynamic behavior of nonautonomous cellular neural networks with time-varying delays[J]. Neurocomputing,2015,168(1):846-852.
[10] CHEN Z W, YANG J, ZHONG S M. Delay-partitioning approach to stability analysis of generalized neural networks with time-varying delay via new integral inequality[J]. Neurocomputing,2016,191(1):380-387.
[11] LONG S J, XU D Y, ZHU W. Global exponential stability of impulsive dynamical systems with distributed delays[J]. Electronic Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations,2007,10(1):1-13.
[12] 龙述君,向丽. 一类具有分布时滞的Hopfleld神经网络的稳定性[J]. 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版),2006,29(5):566-569.
[13] XU D Y, ZHU W, LONG S J. Global exponential stability of impulsive integro-differential equation[J]. Nonlinear Analysis,2006,64(1):2805-2816.
[14] LOU X Y, CUI B T. Boundedness and exponential stability for nonautonomous RCNNs with distributeddelays[J]. Comput Math Appl,2007,54(1):589-598.
[15] LI L L, JIAN J G. Exponential p-convergence analysis for stochastic BAM neural networks with time-varying and infinite distributed delays[J]. Appl Math Comput,2015,266(1):860-873.
[16] 杨德刚. 一种新的时滞细胞神经网络全局渐进稳定性准则[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版),2007,24(3):46-50.
[17] 李建军,杨志春. 双向联想记忆神经网络的指数输入-状态稳定性[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版),2016,33(4):79-84.
[18] LI L L, JIAN J G. Delay-dependent passivity analysis of impulsive neural networks with time-varying delays[J]. Neurocomputing,2015,168(1):276-282.
[19] CHEN G L, XIA J W, ZHUANG H M. Improved passivity analysis for neural networks with Markovian jumping parameters and interval time-varyingdelays[J]. Neurocomputing,2015,155(1):253-260.
[20] JIANG H J, TENG Z D. Boundeness and global stability for nonautonomous recurrent neural networks with distributed delays[J]. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals,2006,30(1):83-93.
[21] ZHANG Q, WEI X P, XU J. Global exponential stability for nonautonomous cellular neural networks with unbounded delays[J]. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals,2009,39(1):1144-1151.
[22] LI X D. Existence and global exponential stability of periodic solution for impulsive Cohen-Grossberg-type BAM neural networks with continuously distributed delays[J].Appl Math Comput,2009,215(1):292-307.
[23] HUANG C X, CAO J D. Almost sure exponential stability of stochastic cellular neural networks with unbounded distributed delays[J]. Neurocomputing,2009,72(1):3352-3356.
[24] RAKKIYAPPAN R, BALASUBRAMANIAM P. LMI conditions for stability of stochastic recurrent neural networks with distributed delays[J]. Chaos Solitons and Fractals,2009,40(1):1688-1696.
[25] ESTEVES S. Global exponential stability of non-autonomous neural network models with continuous distributed delays[J]. Appl Math Comput,2013,219(17):9296-9307.
[26] OLIVEIRA JOSE J. Global stability of a Cohen-Grossberg neural network with both time-varying and continuous distributed delays[J]. Nonlinear Analysis:Real World Applications,2011,12(1):2861-2870.
[27] MOHAMAD SANNAY. Global exponential stability in DCNNs with distributed delays and unbounded activation[J]. J Comput Appl Math,2007,205(1):161-173.
[28] OLIVEIRA JOSE J. Global asymptotic stability for neural network models with distributed delays[J]. Math Comput Modeling,2009,50(1):81-91.
[29] LI Y T, WANG J Y. An analysis on the global exponential stability and the existence of periodic solutions for non-autonomous hybrid BAM neural networks with distributed delays and impulses[J]. Comput Math Appl,2008,56(1):2256-2267.
2010MSC:34D23; 92B20
(编辑 郑月蓉)
Global Exponential Stability of Non-autonomous Cellular Neutral Network Models with Distributed Delays
LI Bin1, LONG Shujun2
(1.SchoolofScience,XihuaUniversity,Chengdu610039,Sichuan;2.CollegeofMathematicsandInformationScience,LeshanNormalUnivesity,Leshan614004,Sichuan)
In this paper, we investigate the global exponential stability of non-autonomous cellular neural networks with distributed delays. We establish a new differential-integro inequality and use it in the investigation the stability of cellular neural networks to obtain a sufficient condition for the global exponential stability for the considered system. Our results improve the known results in the literature. Finally, an example is given to illustrate the effectiveness and superiority of our conclusion
cellular neural network; non-autonomous; global exponential stability; differential-integro inequality; distributed delays
O175.13
A
1001-8395(2017)06-0780-07
10.3969/j.issn.1001-8395.2017.06.012
2016-10-10
四川省教育厅创新团队项目(16TD0029)
*通信作者简介:龙述君(1975—),男,教授,主要从事运筹学与控制论的研究,E-mail:longer207@yahoo.com.cn

