德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校校园总体规划
Sasaki事务所
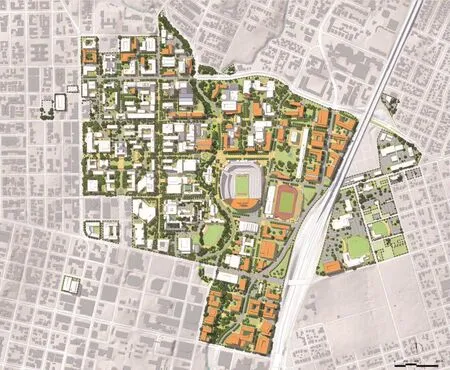
1 德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校总体规划愿景The University of Texas at Austin Campus Master Plan Vision

2 校园排放物的可持续性图示Sustainability diagram mapping campus emissions
3 校园历史演变(人口、校区及大学历史时期)Historic evolution of the campus, with population, campus area, and historic eras of the University

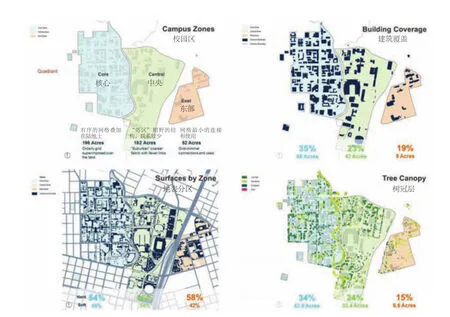
4 记录校区、建筑覆盖、地表分区及树冠层的校园分析Campus analysis documented the campus zones,building coverage, surface areas, and tree canopy
Sasaki为德克萨斯大学所作的总体规划明确了如何精明且持续地投资校园,也找出了推动大学使命、提升学术和研究优势的机会。作为综合规划的范例,Sasaki的规划覆盖发展管理、土地和建筑使用、城市设计和场所营造、交通和停车、历史保护和能源管理等方面。规划以社会、环境和经济的可持续性为导向,并提供数据和分析辅助决策。规划成果是一个能够让德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校实现其使命的综合的、可实现的愿景。
德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校的目标是成为全美公立研究大学20强——这意味着它在未来30年将需要新增超过65万m2的学术研究空间。总体规划在土地和建筑总体使用策略的基础上进一步发展。德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校拥有悠久的校园规划历史,从其独树一帜的建筑和令人难忘的公共空间可见一斑。总体规划在良好的基础上管理未来的发展与设计,创造出21世纪独特的场所感。
规划同样强调从校园核心向邻近社区延伸的重要性,包括连接起校园和市中心的德克萨斯州议会区和新兴医疗创新区。总体规划为医疗区制定了框架并促进后续规划措施的完善。该区超过3亿美元的用于医疗和服务设施的建筑设计正在紧锣密鼓地进行,包括新的戴尔医疗学校、科研建筑、医疗办公建筑、停车场和一座将在大学用地建造的另行投资的教学医院。
校园总体规划创造了系统性的可持续框架,来探索和评估奥斯汀校园的现状条件、目标、规划和想法。这个方法增强了校园建成环境、自然环境、社会和经济的适应力,将规划和设计原则与大学的可持续目标结合起来,帮助确立策略和成功标准。相关的能源研究开启了自持续能源的先河。
在为主题校园和医疗社区所作的景观总体规划中,Sasaki明确了材料、实施和政策来加强景观、自然及城市体系的关系,尤其恢复了先前被忽略的沃勒河。
Sasaki还开发了视觉技术,为大学提供持续的决策支持系统。这项技术还将所有不同元素融入规划,这样大学就可以评估建筑各方面的情况,例如现状、能耗、历史价值、学术临近性、土地利用以及背景环境。这些有力的工具保证总体规划不止是静态的图纸,而是一个持续、互动的过程。
2013年春,德克萨斯大学校董事会通过了校园与医疗区的规划。

5 通过建筑分析来研究课堂、计算机实验室、图书馆和学习空间的分布及建筑类型的使用Building analysis studied the distribution of classrooms, computer labs, library and study space, and building types by use
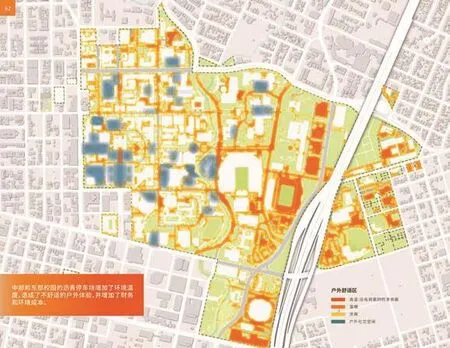
6 通过绘制户外舒适区地图,以了解校园的社交场所及有未遮荫的防渗表面的不舒适区域位置Outdoor comfort zones were mapped to understand where the campus community socialized and where there were uncomfortable areas, with unshaded impervious surfaces
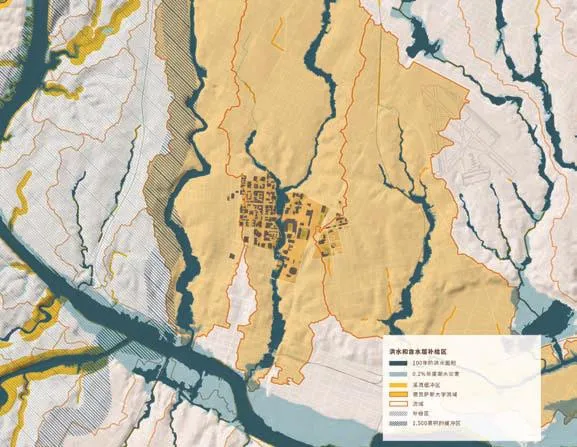
7 洪水及含水层补给区显示了构成校园的集水点和溪流Flood and acquifer recharge zones show the watersheds and creeks that make up the campus
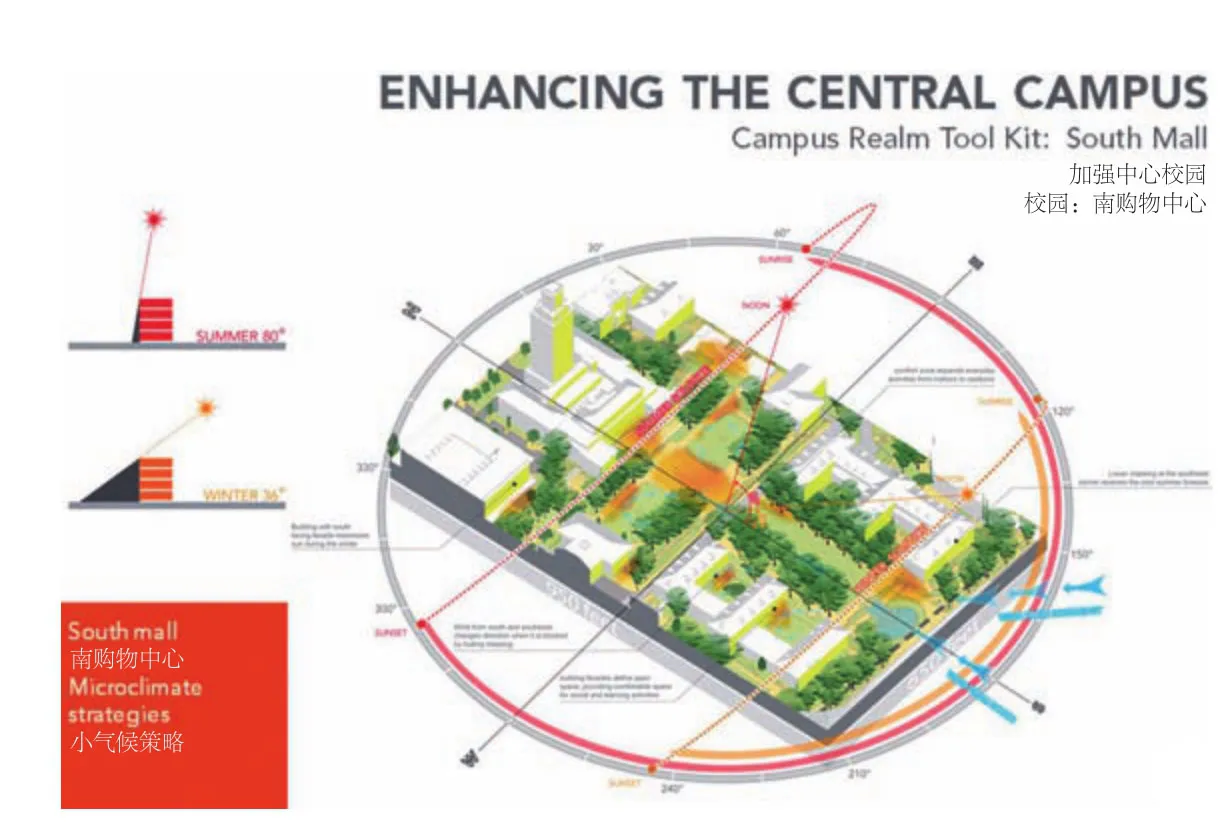
8 小气候策略是基于校园领域工具包创建的,它研究了现有校园中最成功的区域Microclimate strategies were created based on a campus realm toolkit that studied the most successful areas on the existing campus
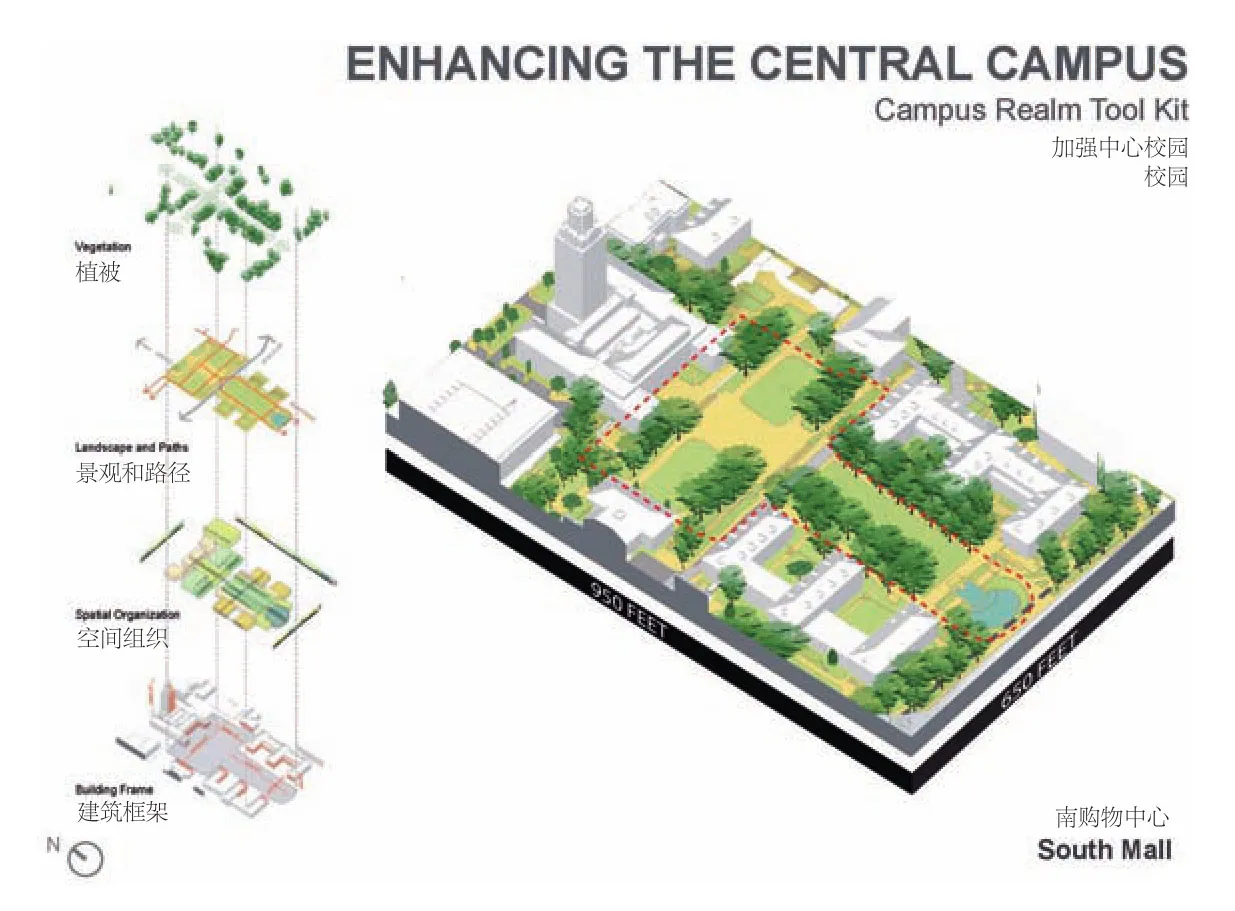
9 校园领域工具包探讨了建筑配置、框架、空间组织、景观、环路以及植被The campus realm toolkit explored building configurations and frames, spatial organization, landscape and circulation paths, and vegetation
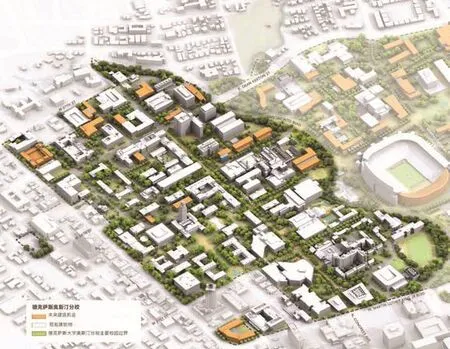
10 核心校园为原先占地40英亩的校园,充满战略的设想Core campus is comprised of the original 40-acre campus is envisioned with strategic infill opportunities
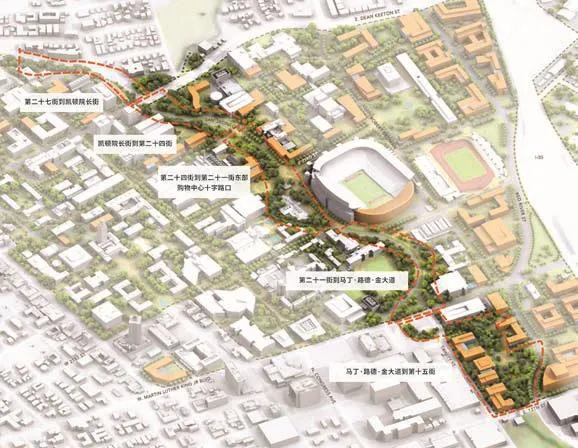
11 沃勒溪走廊被重新设想为与校园拼接在一起的改进的公共设施The Waller Creek corridor was reimagined as an improved public amenity that stitches the campus together

12 中央校园被设计为填充开发的主要区域,适应未来的增长Central campus is designed as a major zone for infill development that accommodates future growth
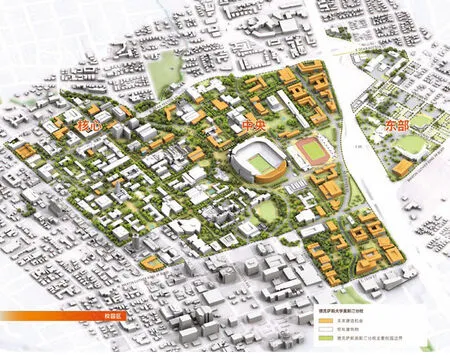
13 大学布置在三个校区的组织结构中:核心校区,中央校区和东校区。每个区域的设计都响应了总体规划的重要思想。The University is designed within the organizational structure of three campus zones∶ Core Campus, Central Campus, and East Campus. Each zone is designed in respond to the Master Plan's big ideas.
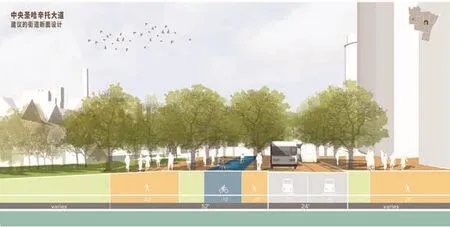
14 拟议中的中央圣哈辛托大道将公共交通、自行车及人流融合为新的街景The proposed Central San Jacinto Boulevard integrates public transportation, bicycle, and pedestrian circulation in a new streetscape

15 拟议中的东21街优先考虑行人及自行车的交通,同时依然提供通往校园的车辆通道The proposed East 21 Street prioritizes pedestrian and bicycle circulation, while still providing vehicular access on campus
项目地点:美国德克萨斯州奥斯汀
业主名称:德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校
完成时间:2013年(设计)
规模:162hm2
服务内容:规划与城市设计、景观设计
Sasaki’s master planning work at the University of Texas at Austin identifies how to invest in the campus intelligently and consistently, and highlights opportunities to further academic and research excellence in support of the university’s mission. A model of integrated planning, Sasaki’s plan addresses growth management, land and building use, urban design and placemaking, mobility and parking, historic preservation, and energy management. The plan is guided by social, environmental, and financial sustainability principles, as well as data and analysis to inform better decisionmaking. The result is an integrated, implementable vision that will enable UT Austin to fulfill its mission.
UT Austin’s goal is to become one of the top 20 public research universities in the nation—which means it may need over seven million square feet of new academic and research space over the next 30 years. The master plan provides for growth in the context of an overall strategy for land and building use. UT Austin also has a long history of campus planning, evident in its distinguished architecture and memorable public spaces. The master plan builds on this legacy,managing growth and design to create a unique sense of place in the 21st century.
The plan also emphasizes the importance of reaching beyond the campus core to its adjacent neighborhoods—the Texas Capitol District and an emerging medical and innovation district that connects the campus and downtown. The master plan includes a framework for the medical district that facilitated a follow-on planning effort. Architectural design is currently underway for over $300 million in new medical and support facilities within the medical district, including the new Dell Medical School, a research building, a medical office building, and a parking structure, as well as a separately-funded teaching hospital to be constructed on UT land. The medical school is expected to open in 2017 and the teaching hospital will follow in 2018.
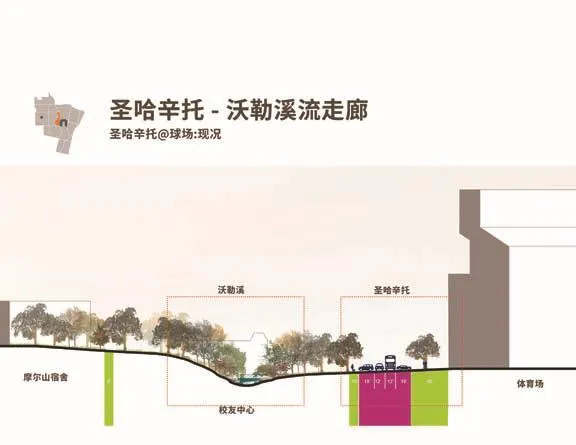
16 圣哈辛托-沃勒溪流走廊将流动性网络与小溪的公共领域改进融为一体The San Jacinto-Waller Creek Corridor weaves the mobility network with the public realm improvement of the creek

17 建议的圣哈辛托-沃勒溪流走廊通过在体育场交通枢纽附近新街景的设计,可容纳公共交通、骑车人及行人的穿行The proposed San Jacinto-Waller Creek Corridor accommodates public transportation,bicyclists, and pedestrians with a new streetscape design, near the Stadium transportation hub

18 为校园总体规划提出八大构想Eight big ideas were generated for the campus master plan
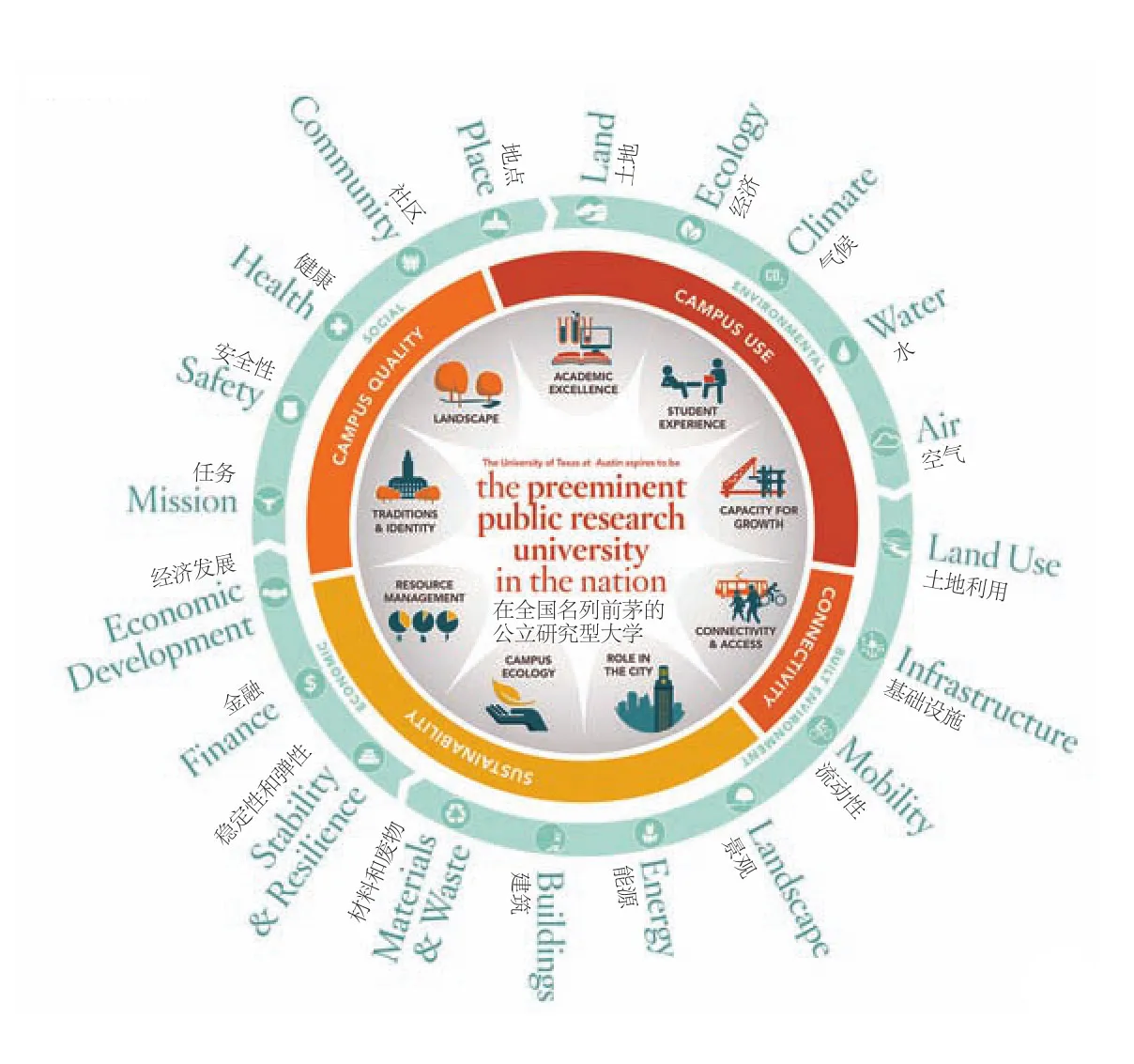
19 可持续目标已被纳入校园规划方法Sustainability goals were integrated to the campus planning approach
The campus master plan creates a systems-based sustainability framework to explore and evaluate current conditions, goals, plans, and ideas at UT Austin.This approach contributes to the resilience of the campus’s built environment,natural environment, society, and economy.Integrating planning and design principles with the university’s sustainability goals, the framework helps establish strategies and metrics for success.A related energy study creates a model for selfsustaining energy initiatives.

20 校园领域工具包研究了现有校园中的成功区域,以此帮助重新思考中央带的欠发达区域A campus realm toolkit studied successful areas on the existing campus as a means to help rethink underdeveloped areas in the central zone

21 校园领域工具包图示分析了建筑结构和框架、空间组织、景观、环路和植被The campus realm toolkit diagrams analyze building configurations and frames, spatial organization, landscape and circulation paths, and vegetation
In a related landscape master plan that addresses both the main campus and medical district, Sasaki defines landscape materials,practices, and policies to enhance the landscape’s relationship to the larger natural and urban systems of which it is part. In particular, the plan restores the previously neglected Waller Creek.
Sasaki also developed visualization technology that provides the university with an ongoing decision support system. These powerful tools ensure the master plan is not a static document but an ongoing, responsive process. The technology also integrates all the different components of the plan, so the university can evaluate buildings,for example, in regards to condition, energy use,historical significance, academic adjacencies, land use, and environmental context.
In the spring of 2013, the UT Board of Regents approved the plans for both the campus and the medical district.
Project location:Austin, TX, USA
Client:University of Texas at Austin
Completion date:2013 (Design)
Size:162 hm2
Services:Landscape Architecture, Planning and Urban Design
——走出萧条

