Effects of medicinal diets on patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy
Liang Lei, Li-Sen Wang
Abstract Chemotherapy is the main treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but it often leads to serious side effects.Modern studies indicated that medicinal diets can reduce the side effects of chemotherapy. However, blindly taking medicinal diet always fails to achieve curative effect and even aggravates the patient's condition. In order to provide dietary guidance for NSCLC patients undergoing chemotherapy, based on the basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine, the article elaborates the application of medicinal diets in those NSCLC patients who have been treated by chemotherapy.
Key words: Medicinal diets, Non-small cell lung cancer,Chemotherapy, Syndrome differentiation and treatment,Mechanisms
Introduction
I n traditional Chinese medicine theory, lung cancer belongs to the category of "pulmonary carbuncle","pulmonary accretion", "Xi Fen","cough", "phlegm and fluid retention","chest stuffiness" and the like. The basic etiological factors and pathogenesis of lung cancer is deficiency of healthy-qi, then pathogenic factors invade the lung and lead to blood stasis and sputum block, which blocks functional activities of qi and further develops into cancer [1]. As reported in Zhu Bing Yuan Hou Lun "tumor are caused by the discord of yin and yang, which cause the weakness of the viscera, then easily invaded by the wind pathogen, and then block the qi of the viscera [2]". Chemotherapy is an important method for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. However, it not only kills cancer cells, but can also kill the normal cells, damaging the immunity, which can affect the quality of life, even leads to the termination of chemotherapy treatment.
1 Syndrome differentiation and treatment for patients with NSCLC undergoing chemotherapy
Chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression is the most common dose-limiting and potentially fatal complication. Chemotherapy drugs not only can inhibit the activity and induce the apoptosis of hematopoietic precursors, affect the division of stem cells, it can also break the balance between proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow cells and cell senescence in peripheral blood, reduce the concentration of peripheral blood cells. For NSCLS patients, the most common chemotherapeutic agent Platinum could kill cancer cells and destroys the differentiation of bone marrow stem cells [3,4]. Gastrointestinal distress are common side-effects of chemotherapeutic medications that kill fast-dividing cells, which cause nausea, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhoea,abdominal cramps, and constipation.Higher concentrations of paclitaxel can induce apoptosis of smooth muscle cells [5,6]. Chemotherapy drugs can stimulate gastrointestinal
chromaffin cells to release 5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT), and combine with 5-HT3 receptors then activate chemoreceptor triggers and vomiting centers, causing nausea and vomiting.In addition, chemotherapeutic drugs can also cause stomatitis and gastrointestinal mucosal edema by damaging the proliferative mucosal epithelial tissue which leads to diarrhea or constipation. Chemotherapy can also can cause organs damage, such as cardiotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity.
Chemotherapy drugs in traditional Chinese medicine are considered to be exogenous "ill-effect of drug", which can directly damage human's qi, blood, Yin and yang,and affected the function of viscera. Diagnosed by the clinical symptoms of bone marrow depression, nausea,vomiting and alopecia, the basic pathogenesis of patients after chemotherapy is deficiency both the spleen and kidney, disorder of vital energy and blood [7,8]. Spleen can promote the activation of qi. The deficiency of qi can lead to abnormal movements, nausea and vomiting. Spleen is also the biochemical source of qi and blood. Deficiency of spleen qi can lead to deficiency of immunity. Ling Shu Jue qi has recorded that, the kidney has hematopoietic functions. Kidney is innate and it dominates bone hidden essence, in charge of the growth and development, aging,death of the entire process. Chemotherapy could lead the deficiency of kidney qi, then damage the hematopoietic functions and further lead to hair loss. In addition, based on the Cold Heat Syndrome, the cold and heat attributes can be changed after chemotherapy. Tian et al. [9] randomly divided 58 patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation into two groups, 38 in the cold group and 20 in the heat group. After 30 days of treatment with gemcitabine, 12 cases in the cold group turned into heat syndrome, while 20 cases in the heat group did not change.There was significant difference between the two groups(P < 0.05), which indicates that gemcitabine, a chemotherapeutic drug for NSCLC, could change the syndrome type of patients. Liu et al. [10] adopted a retrospective study found that syndrome of deficiency both the lung and spleen deficiency was common in NSCLC patients at the early stage of chemotherapy, and kidney-yang deficiency and phlegm-dampness stopping were common after chemotherapy. Jie et al. [11] observed the effects of docetaxel and cisplatin chemotherapy, gemcitabine and cisplatin chemotherapy and albumin-bound paclitaxel monotherapy on the syndromes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer,found that the syndrome of spleen qi deficiency, phlegm dampness and blood stasis were more common in docetaxel and cisplatin chemotherapy group; the syndrome of lung deficiency, phlegm heat and spleen deficiency, phlegm dampness were more common in gemcitabine and cisplatin chemotherapy group; and the syndrome of qi stagnation,blood stasis and phlegm dampness in lung in paclitaxel monotherapy is common. Through dialectical analysis of the syndrome of NSCLC patients after chemotherapy, and under the principle of dialectical diet, drug and food are reasonably compatible to regulate Yin, Yang, qi and blood of patients, so as to achieve the purpose of strengthening the body and dispelling pathogens.
2 Mechanisms of medicinal diet to improve the side effects of chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
Medicinal diets treatment of bone marrow depression caused by NSCLC chemotherapy originates from the summary of clinical experience of dialectical prescription treatment. Many experimental studies have found that chemotherapy drugs for NSCLC can cause digestive tract reaction, alopecia and bone marrow suppression, and the most common bone marrow suppression is leukopenia[12-15]. Medicinal diets can reduce the adverse reactions of chemotherapy through different mechanisms. It can directly promote hematopoiesis of bone marrow and alleviate the inhibition of bone marrow by chemotherapy. It founded that pig's trotter soup with Astragalus [16] (Dang Gui Bu Xue decoction and Pig's Foot Composition) could significantly increase the number of white blood cells and shorten the time of leukopenia. Radix Angelicae Sinensis[17] can Promote the synthesis of DNA of bone marrow nucleated cells, increase the number of bone marrow nucleated cells, stimulate the formation of hematopoietic stem progenitor cells, accelerate the differentiation and maturation of blood cells, and ultimately directly affect the formation of white blood cells [18,19] Medicinal diets also can promote the formation of blood cells through the regulation immune system. Modern medicine has proved that amino acids (such as glycine and arginine) can regulate hematopoietic function and promote the synthesis of hemoglobin. A variety of amino acids in pig hooves can promote the maturation of immature cells into leukocytes with special functions and eventually release into the blood system. Chen et al. [20] explored the effects of medicated diet of Astragalus on the gastrointestinal tract of rats after chemotherapy (consisting of Astragalus membranaceus,Dioscorea opposite Thunb, Semen Raphani, Rice and Endothelium corneum gigeriae galli). It was found that medicated diet of Astragalus membranaceus could repair the gastrointestinal injury caused by chemotherapy in rats by regulating the tight junction proteins of Claudin-1 and JAM-1. Recent researchers have found that Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide can reduce the expression of TLR4 gene and inhibit myocardial hypertrophy induced by TNF [21-23]; amylase and pepsin in Endothelium corneum gigeriae galli can promote gastrointestinal digestive function; Dioscorea opposite Thunb can stimulate the activation of CD4+, CD25+T cells by tonifying spleenqi, destroy the balance between pro-inflammatory factors and anti-inflammatory factors, and protect gastrointestinal mucosa; Semen Raphani can eliminate phlegm and dissipate qi. In addition to distension, improve the syndrome of spleen and stomach qi deficiency, inhibit the expression of intestinal NF-kB, thereby improving gastrointestinal symptoms. Medicinal diet has been proved to be effective in countering the side effects of cancer chemotherapy.

Figure 1: The mechanism of medicated diet to improve myelosuppression
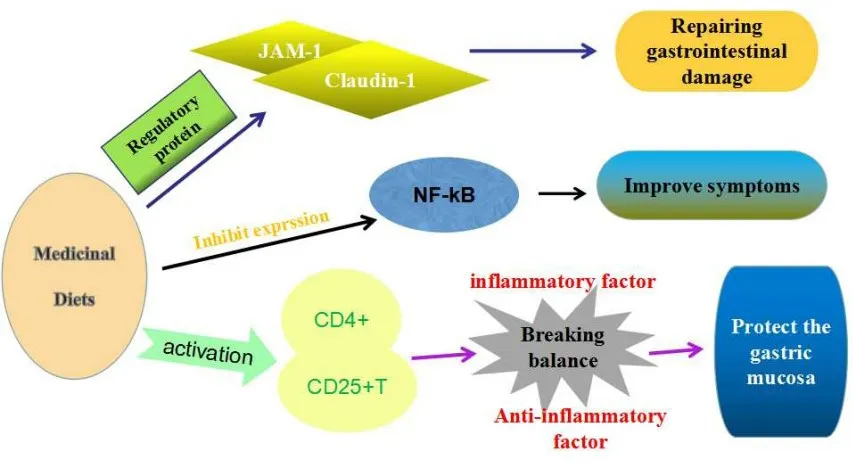
Figure 2: The mechanism of medicinal diets on gastrointestinal adverse reactions
3 Clinical effects of Medicinal Diets on Adverse Reactions of NSCLC Chemotherapy
TCM medicinal diet has been widely valued in tumor adjuvant therapy, and clinical benefits for the adverse reactions of NSCLC chemotherapy drugs have been well reported. Li et al. [24] randomly divided 45 patients with advanced NSCLC into self-control group (alternate chemotherapy cycle combined with Shen Qi San Dou Decoction), experimental group (combined with Shen Qi San Dou Decoction) and control group (paclitaxel chemotherapy alone). Shen Qi San Dou Decoction includes Radix Pseudostellariae, Astragalus membranaceus, Glycinemax-(L.)merr, Vigna umbellate, Vigna radiata, Adenophora stricta Miq., Ophiopogon japonicus, Radix Asparagi,Psoralea corylifolia Linn, Jujube. The synergistic and attenuating effects of advanced NSCLC chemotherapy were compared with KPS scores. The total effective rate was 66.7%, 86.67%, 46.67% in self-control group, experimental group and control group, respectively. The incidence of digestive tract adverse reactions in the three groups were 46.7%, 40% and 66.7%, respectively. The incidence of bone marrow suppression was 46.7%, 33.3% and 60%,respectively. KPS of three groups were statistically analyzed, the difference was significant (P < 0.05), indicating that Shen Qi San Dou Decoction in the treatment of advanced NSCLC patients can improve the clinical efficacy,reduced adverse reactions of patients. Yang Shuyan et al.[25] has randomly divided 60 patients with lung adenocarcinoma into medicated diet group and control group.The leukopenia caused by chemotherapy with TP regimen was observed in patients with lung adenocarcinoma treated with eels' soup with Astragalus membranaceus (consisting of Astragalus membranaceus, Dioscorea oppositifolia L., eel and ginger), twice a day, from three days before chemotherapy to two weeks after the end of chemotherapy. After 4, 7 and 14 days of chemotherapy treatment,the blood samples were collected. Statistical t-test showed that 28 cases of leukopenia were improved effectively in the medicated diet group, and the total effective rate of symptom improvement was 93.3%, while 14 cases in the control group, and the total effective rate of symptom improvement was 46.7% (P < 0.05).This indicated that eels soup with Astragalus could prevent and treat bone marrow depression caused by chemotherapy for lung adenocarcinoma. In the study of Zhu Ling et al. [26], 62 NSCLC patients were randomly divided into control group and treatment group, by comparing and observing the quality of life, immune indicators, toxic and side effects of the two groups after chemotherapy, the effect of medicated diet in improving the toxicity and synergy of cancer chemotherapy was evaluated. According to the theory of dialectical diets, the treatment group was treated with boiled eggs with walnut branches (composed of walnut green shell,walnut kernels and eggs) and Bai Di porridge (composed of Selaginella doederleinii Hieron, Fresh radix rehmanniae, Coix seed, jujube) for those with deficiency of both of lung and kidney, and radish porridge (composed of radish,carrot and japonica rice) for those with phlegm-heat accumulation of lung, while the control group was treated with chemotherapy alone. After 21 days of treatment, compared with the Karl's score before and after treatment in the two groups, 17 cases in the treatment group were improved, 8 cases were stable, 6 cases were decreased, the total effective rate was 80.6%. In the control group, 8 cases were improved, 7 cases were stable,16 cases were decreased, the total effective rate was 48.3% (P < 0.05). The incidence of visceral toxicity was 51.5% in the control group, 35.4% in the experimental group. The incidence of gastrointestinal reactions was 67.7%, 41.9% in the control group, experimental group, respectively. The incidence of hepatotoxicity was 16.1% in the treatment group and 29% in the control group. The incidence of leukopenia, gastrointestinal reactions and hepatotoxicity in the treatment group was significantly lower than that in the control group (P < 0.01).The combination of medicated diet and chemotherapy has a certain synergistic effect on the treatment of advanced NSCLC patients, and has a significant effect on improving the quality of life and reducing the side effects of chemotherapy.
4 Discussion and Prospect
Food can treat cancer disease but may activate it as well.In the theory of Chinese medicine, it has long been recorded as "thin taste can nourish qi and blood", fat and fat diet can produce phlegm and dampness, which maybe lead to cancer, but fish and other high-protein flesh and blood sentimental products are conducive to strengthen qi and blood and anti-cancer. Recent researches have proved that medical diet has definite curative effect in cancer intervention therapy, especially in reducing the adverse reaction of chemotherapy in NSCLC patients. The medicated diet selected for patients with NSCLC undergoing chemotherapy is mainly based on patient's syndrome, as syndrome differentiation is the essence of Chinese medicine and the basis of medicated diet. Different diets are chosen for NSCLC patients in different stages. By collecting and analyzing disease syndromes, according to "Balance of yin and yang ", "five flavors blend each other", "compatibility and taboos", the dietary program was made. Which is suitable for patients' condition. therefore, medicinal diet has certain indications. Su Wen [27] has recorded that patients with spleen disease have better to eat rice, beef, jujube and sunflower; people with heart disease are recommended to eat wheat, mutton, apricot and garlic; people with kidney disease are suggested to eat soybean yellow roll, pork, chestnut; people with liver disease should eat hemp, dog meat,plum and leek; people with lung disease are suggested to eat yellow millet, chicken, peach and onion. Spicy food is forbidden to patients with liver disease, salty patients with heart disease should avoid salty food, and patients with spleen disease should avoid some acid food. Ancient physicians had summed up the principles of "eighteen incompatible medicaments", "nineteen nedicaments of nutual antagonism" and "seven emotions" of drug compatibility,which should be listed as taboos of drug-diet compatibility. In addition, some studies proposed by modern medicine should also be considered as taboos of medicinal diet. For examples, foods high in calcium such as milk should not be eaten with foods high in calcium oxalate such as spinach laver and bamboo shoots; eggs, don't eat eggs, crab and persimmon at the same time [28, 29].
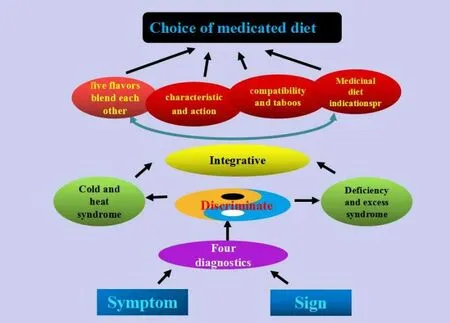
Figure 3: Dialectical principle of Medicinal diet
Traditional Chinese medicine diet is an important treasury of traditional Chinese medicine, but it is not a panacea.At present, there are still many problems and difficulties in the nursing work of traditional Chinese medicine diet for cancer patients. When using traditional Chinese medicine diets, the principle of syndrome differentiation and treatment should be followed. in addition, there are many case reports on medicated diet of alleviating the side effects of chemotherapy in NSCLC patients at present, but systematic and standardized large sample experimental study are lack. More research is needed to understand not only potential therapies but also how to select appropriate patients for these therapies.
- Food and Health的其它文章
- Progress of Bai He Di Huang decoction on intestinal flora of mouse with depression
- Reporting and methodological quality of systematic reviews or meta-analyses in nasogastric and nasojejunal enteral nutrition for severe acute pancreatitis
- Green tea and its active compounds in cancer prevention andtreatment
- Intestinal microflora in patients with liver disease

