Differences in pain and inflammation between Diclofenac 0.1% and Nepafenac 0.1% after cataract surgery
, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2
(作者单位:155284印度尼西亚日惹, Gadjah Mada大学/Dr. Sardjito 综合医院眼科;255284印度尼西亚日惹,Dr. Yap眼科医院)
Abstract
•KEYWORDS:phacoemulsification; senile cataract; flare and cell; Diclofenac; Nepafenac
INTRODUCTION
The use of anti-inflammatory eye drop for cataract surgery has become a standard procedure to prevent postoperative intraocular inflammation and reduce pain level[1-4]. Hence, it increases patients comfort and accelerate the recovery of visual acuity[5]. Postoperative inflammation might cause pain, photophobia and increase of intraocular pressure as well as associated with posterior capsule opacity (PCO) and cystoid macular edema[2]. Previously, steroid was mostly used agent, however, it might lengthen corneal recovery, increase intraocular pressure and risk of infection[6]. Recently, nonsteroidal anti-inflammation drugs (NSAID) has been found having similar effectivity as steroid in order to control inflammation reaction postoperatively[7]. Administrations of Diclofenac before or after cataract surgery has been shown equal effectivity as steroid in reducing inflammation[3-4]. Most recently, Nepafenac, a more neutral and a prodrug, is able to penetrate cornea 6x faster than Diclofenac group[8].
This study was aimed to compare pain and inflammation level between Diclofenac 0.1% and Nepafenac 0.1% as preoperative medications for phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Primary outcomes (as inflammation signs) were pain score, blepharospasm, conjunctival hyperemia, and flare-cells in anterior chamber. Furthermore, endothelial cells are prone to injury that is caused by either mechanical injury (surgical techniques and manipulation) or intracellular injury (inflammation). Furthermore, the examination of corneal endothelial cells parameters might help to determine the level of endothelial trauma and injury caused by phacoemulsification[1]. Therefore, secondary outcomes of this study were corneal endothelial cells counts, coefficient of variance, hexagonal cells percentage and central corneal thickness.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
StudyDesignandPatientsEnrollmentThis study was a prospective randomized controlled trial design (RCT). The sample size was calculated based on the hypothetical test formula of two unpaired means for flare mean calculation:n1=n2=2[(Z+Z)S/(X1-X2)]2,n=estimated sample size, Zα=critical value of the normal distribution at=0.05 (1.96); Zβ=critical value of the normal distribution atβ=0.2 (0.84), standard deviation (SD) =1.52[2], X1-X2=the minimum mean difference is considered significant=1.2[2]. The calculation was then added by estimated sample drop out (10%) and became 28 samples. The inclusion criteria were patients (aged 40-80 years old) with senile cataract (Burrato grade II-III), and willing to provide and sign the informed consent form prior to examination and surgical procedure. Exclusion criteria for this research were patients with previous other ophthalmic disease (i.e. history of glaucoma, uveitis, lens luxation and exfoliation syndrome), diabetes mellitus, surgical complications (posterior capsule rupture or vitreous prolapse), preoperative corneal endothelial cell count <1500 cell/mm2, surgery duration >15min, ultrasound (US) time >2min. The drop out criteria for this research were patients not presented at postoperative monitoring, emergence of complications such as endophthalmitis, persistent corneal edema, and not compliance of postoperative medication. The study followed the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. The Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada/Dr. Sardjito General Hospital (Indonesia) has approved the study protocol.
StudyProtocolThis study was conducted at Dr. Yap Eye Hospital Yogyakarta, Indonesia, from June 2017 until August 2017. Subjects were divided equally into 2 groups (DiclofenacvsNepafenac groups). Surgical procedure was performed by a single operator using a single surgical technique. Patients and operator were kept blind regarding the interventions. Preoperative examinations included uncorrected and best-corrected visual acuity (Snellen’s chart), anterior segment biomicroscopy and cataract morphology examination, tonometry (Shin-nippon non-contact Tonometry), ultrasonography, and biometry (IOL calculation). Cataract morphology and grading was done by a single observer.
SurgicalTechniqueEyes were anaesthetized with topical anesthesia [Pantocaine 0.5% (Cendo®)] on a maximally dilated eye. Eyes were then irrigated with povidone-iodine 5%, eye lids and area around the eye were done aseptic and antiseptic procedures with povidone-iodine 10%. Cornea were incised with a keratome, followed by intracameral injection of 0.5 mL preservative-free (PF) lidocaine hydrochloride 1%, hydroxypropil methylcellulose (HPMC) OVDs were injected into anterior chamber followed by capsulotomy using the continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis (CCC) technique, cataract lens was hydrodissected. Centurion® Vision System was applied for phacoemulsification with the vertical chop technique, residual cortex were irrigated and aspirated until clean, implantation foldable acrylic hydrophilic intraocular lens (Rohto neo eye®) in the bag. Intracameral injections were then administered [0.1 mL dexamethasone (4 mg/mL) and 0.1 mL solution containing 0.5 mg 0.5% levofloxacin].
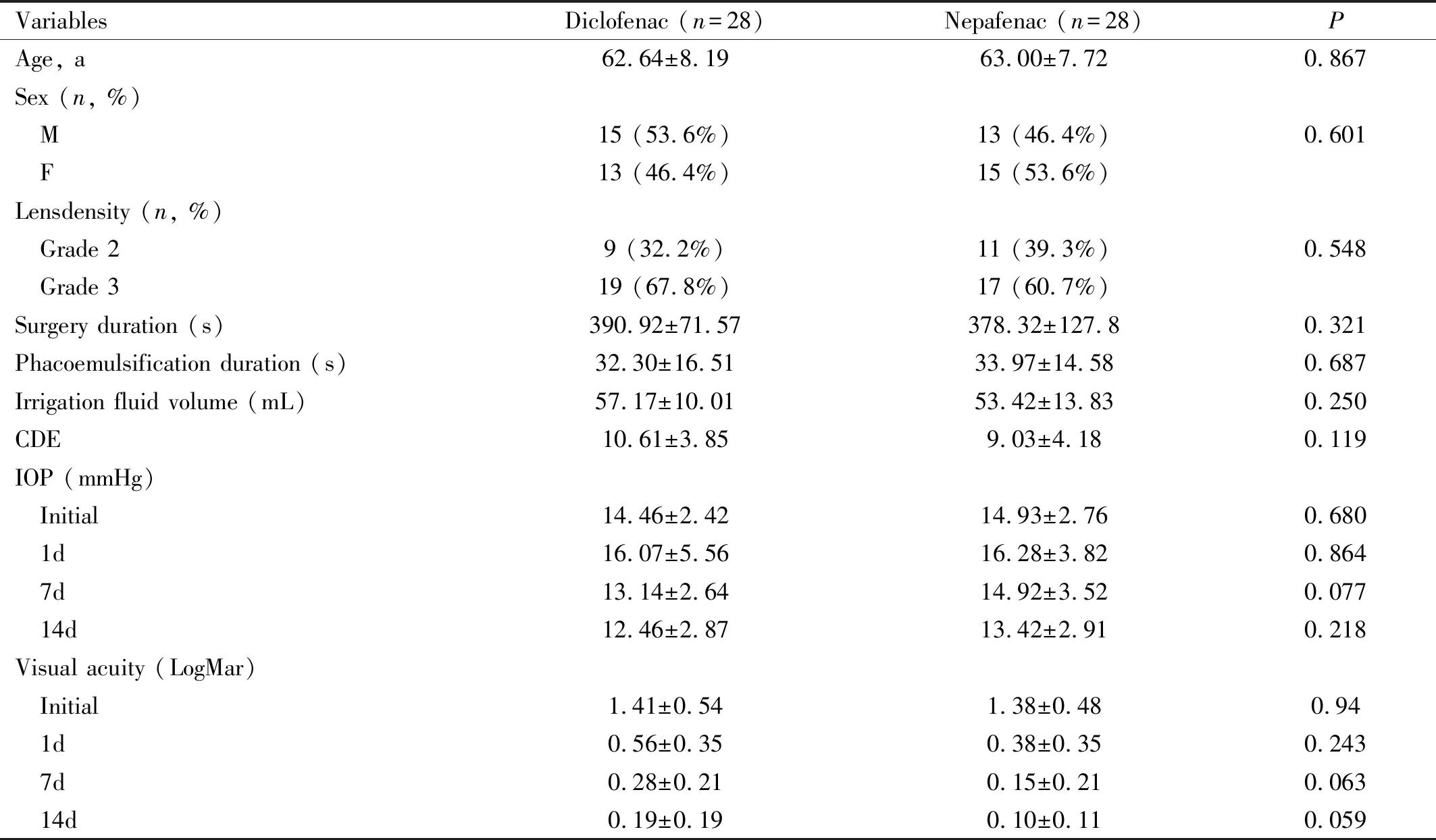
Table 1 Subject characteristics
Parameters are in Mean±SD (except: sex and lens density); CDE: Cumulative dissipated energy; IOP: Intraocular pressure.
EPT (effective phaco time) was calculated by multiplying US (ultrasound) time with US average power /100.
OutcomesMeasuresThe primary outcomes were the inflammation variables, such as: pain score based on Visual Analogue Score[9], blepharospasm based on the Jankovicetal[10], conjunctival hyperemia based on the Cornea and Contact Lens Research Unit (CCLRU)[11], flare and cell in the front chamber of the eye using the grading system from Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group[12]. Follow-up was done on the 1, 7 and 14d postoperative. The secondary outcomes were the measurement of corneal endothelial density, morphology, and corneal thickness (Topcon SP-3000®). The operator who measured and examined the outcome was kept blind regarding the treatment groups.
StatisticalAnalysisStatistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 22.0 for Windows software. Continuous data were expressed as the mean±SD and range, normality was first confirmed by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. For subject characteristics, categorical data was analyzed using Chi square test and independent samplest-test for numerical data if normally distributed (Mann-Whitney test if not normally distributed). Inflammation variable is analyzed using the Chi square test. Difference in density and corneal endothelial cell morphology between the two groups is analyzed using independent samplest-test followed by comparison between the follow-up days.
RESULTS
Fifty-six eyes(56 patients) were enrolled in this study (no loss of follow-up subject and no adverse events were found during and after the administration of treatment to the participants). There were no statistically significant differences in subject characteristics between diclofenac and nepafenac group (Table 1).
There were no significant differences between Diclofenac and Nepafenac in conjunctival hyperemia and blepharospasm both groups at 1d (P=0.284, effect size=0.29, 95%CI=-0.09 to 0.31;P=0.254, effect size=0.31, 95%CI=-0.13 to 0.49, respectively), and 7d (P=1.000 andP=0.556, effect size=0.18, 95%CI=-0.08 to 0.16, respectively) postoperatively. In pain score, Nepafenac group was found significantly lower during surgery (P=0.006, effect size=0.77, 95%CI=0.24 to 1.34), 1d postoperative (P=0.045, effect size=0.39, 95%CI=-0.10 to 0.62) and 7d postoperative (P=0.014, effect size=0.69, 95%CI=-0.06 to 0.50). In flare-cell score, Nepafenac group was also found significantly lower at 1d postoperative (P=0.029, effect size=0.59, 95%CI=0.02 to 0.36) (Table 2).
Table 3 shows the corneal endothelial parameters at 7d and 14d postoperative. The decrease in hexagonal cell percentage was found lower in Nepafenac group at 7d postoperative (P=0.042, effect size: -0.55, 95%CI=-2.33 to -0.03). There were no significant correlations between phacoemulsification duration and loss of endothelial cell counts (7d and 14d) in Diclofenac (7d:r=-0.167,P=0.424; 14d:r=-158,P=0.452) as well as in Nepafenac group (7d:r=0.125,P=0.543; 14d:r=0.039,P=0.850). Therefore, the endothelial loss in this study was not dependent of the duration of phacoemulsification.

Table 2 Primary outcomes: inflammations parametersMean±SD

Table 3 Secondary outcomes: corneal endothelial parameters
CV: Coefficient of variance; CCT: Central corneal thickness.
DISCUSSION
Recently, preoperative medication using NSAIDs (for instances: Diclofenac or Nepafenac) is important to reduce metabolic stress and inflammation caused by phacoemulsification cataract surgery. In this RCT study, the administration of Nepafenac eye drop prior to surgery was found effective in reducing post-operative pain and inflammation. The pain (during surgery, 1d and 7d postoperative) and flare-cell score (1d postoperative) were found lower in Nepafenac group.
The results of the present study, might be caused by greater ability of Nepafenac to penetrate cornea and convert into its active substance, amfenac[13-15]. It has been known to have 6x faster corneal penetration (with longer duration of action) than Diclofenac[16]. The results of this study was in line with a study by Nardietal[15]that found subjects who receiving Nepafenac had milder pain sensation if compared to subjects receiving Ketorolac and Diclofenac. Similarly, Laneetal[2]has found that Nepafenac administration 3d prior to phacoemulsification was more effective to reduce postoperative flare-cell than other NSAIDs. No statistically significant difference of flare-cell score at 7d might be caused by the administration of topical steroid therapy. The surgical methods in this study produced very mild degree of hyperemic and blepharospasm that result in no difference between 2 groups. Previous surgical methods, such as: the application of retrobulbar or peribulbar anesthesia and peritomy of the conjunctiva were prone to produce more hyperemic and conjunctival edema[13].
In severe inflammation condition, inflammation cells are able to replace normal endothelial cells that cause sloughing of the endothelial cells into aqueous humor[17-18]. In the present study, there were no statistically significant difference between 2 groups in the corneal endothelial cells parameters (corneal endothelial cells counts, coefficient of variance and central corneal thickness). It could be assumed that corneal endothelial cells parameters changes were not dependent of NSAIDs administration but rather than the surgical manipulation itself[19]. However, the decrease of hexagonal cell was lower in Nepafenac at 7d but not at 14d, that showed morphology plasticity of endothelial cells[20]. In the present study, the similarity of type and cataract turbidity would standardize the use of phacoemulsification energy.
In conclusion, pain level and flare-cell score at the first day after phacoemulsification in Nepafenac group was lower than Diclofenac group. Reduction of hexagonal cell percentage at the seventh day after phacoemulsification was lower for Nepafenac group than Diclofenac group. The limitation of this study was the short period of follow-up, therefore, for future researches, follow up time could be conducted in longer period to assess the occurrence of cystoid macular edema post phacoemulsification.

