Application of Comprehensive Health Education in Nursing of Patients with Metrorrhagia and Metrostaxis Treated by Hysteroscopic Electrotomy
Fei YANG, Qing-Wen GENG, Jing WANG, Yan-Min LI, Ya-Li WANG
1Department of Gynecology, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to the Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100010, China; 2Department of Brain Diseases, Dongzhimen Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, 100700, China
Abstract
Key words: Health education; Metrorrhagia and metrostaxis; Abnormal uterine bleeding; Hysteroscopy;Complications
Introduction
Benglou refers to metrorrhagia and metrostaxis in TCM. It is a common and multiple disease in clinical gynecology,mainly caused by diseases such as submucosal myoma of uterus, endometrial polyp, dysfunctional uterine bleeding,etc.[1], manifested as excessive volume of menses,irregular menstrual cycle, frequent menstruation, and prolonged menstruation[2]. Patients with severe illness can also cause anemia, which is a great threat to the life and health of patients. Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive technology. With the continuous progress of medical technology in recent years, it is widely used in gynecological examination and treatment[3]. The application of hysteroscopy in surgery can let us observe the tissue structure on the surface of the lesion more carefully, and determine the scope and location of the lesion more accurately. Moreover, it has the advantages of intuition, effectiveness, safety and simple operation,which greatly makes up for the shortcomings of traditional diagnosis and treatment methods[4-5]. Although hysteroscopy causes less pain and less trauma to patients,patients are vulnerable to bad emotions such as anxiety and nervousness due to lack of awareness of hysteroscopy,which is not conducive to the smooth implementation of the operation. Health education can increase patients’awareness of disease and the operation of hysteroscopy,effectively alleviate patients’ anxiety and depression,make patients actively face the disease, and thereby to reduce complications and promote early recovery of patients[6]. This study investigated the application of health education in the nursing care of metrorrhagia and metrostaxis patients treated by hysteroscopy, and explored the application value of health education and its influence on the complications of patients.
Materials and Methods
General information
70 patients with metrorrhagia and metrostaxis admitted from March 2018 to March 2019 were selected as the study subjects. Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) All patients were diagnosed as metrorrhagia and metrostaxis by blood routine, gynecological examination, general examination and other related clinical examinations,which met the relevant diagnostic criteria of gynecology and obstetrics: accompanied by different degrees of bleeding; menstrual arrest occurred suddenly in several months. (2) All patients underwent hysteroscopic electrotomy for treatment, without contraindications for operation. (3) Patients had clear consciousness. (4) All patients signed the informed consents. Exclusion criteria:(1) patients with genital organic diseases; (2) patients with systemic diseases; (3) patients with gynecological organic diseases; (4) patients with other serious diseases such as liver, kidney, heart, blood vessels, etc. patients with a history of mental and neurological diseases; (5) patients with coagulopathy.
According to the random number table method,patients were divided into two groups. The control group consisted of 35 patients, aged 25-43 years, with the mean age of 33.5. The bleeding time ranged from 5 to 28 days, with the mean bleeding time of 15.6 days. The observation group consisted of 35 cases, The patients aged 23-45 years, with the average age of 33.6, the bleeding time ranged from 4 to 29 days, with the average bleeding time of 15.7 days. The differences of the general data such as age and average bleeding time between the two groups were not statistically significant (P>0.05).
Methods
The control group was given routine health education.Generally, the duty nurse explains the surgery related knowledge and matters needing attention for the patient,introduces the surgery successful cases, alleviates the patient’s anxiety, and helps the patient to establish the confidence. In addition, nurse tells patients to have the routine examinations of vaginal secretions, hematuria,liver and kidney function and coagulation function performed before operation.
The observation group was given comprehensive health education in preoperative, postoperative and discharge stages.
Preoperative stage: Duty nurse introduces the hospital environment and ward environment for patients when they are admitted to hospital, meticulously explains the relevant knowledge of disease for patients, and emphasize the advantages of hysteroscopy technology, such as good curative effect, short hospitalization time, less bleeding,less trauma, less pain, no need of laparotomy, etc., to reduce the psychological pressure of patients. Duty nurse also understand the patient’s medical history carefully,evaluate the patient’s condition, knowledge level and psychological state, and communicate patiently with the patient[7]. Before operation, she needs to inform patients of correct operation position, introduce operation steps and methods in details, let patients understand the safety and advancement of operation, possible discomforts and treatment methods after operation, so that reducing patients’ psychological burden, fear and worry can ensure that patients have a good psychological status to face the forthcoming operation, and ensure the successful completion of the operation[8]. Additionally, nurse should instruct patients to flush vagina with 10% povidone solution, and advise patients to eat foods that are easy to digest, rich in vitamins and proteins before operation.Fasting water was started 8 hours before operation[9].
Post-operation stage: After the patient is awake after the operation, patients can eat a small amount of semifluid diet, mainly high in vitamins and protein, which helps to strengthen the patient’s physique, promote wound healing as soon as possible, and repair the body. Patients are urged to keep clothes clean and dry, and actively cooperate with symptomatic treatment such as hemostasis and anti-infection[10]. Inform the patient that there will still be a small amount of vaginal bleeding or fluid flow generally lasting for about 2 weeks after the operation,and urge the patient to pad toilet paper, etc.. If the blood volume increases abnormally, immediately notify the doctor for corresponding treatment. Inform the patient that there will be a certain degree of aches and abdominal distension after the operation, which is caused by the pulling of autonomic nerve during the operation and will usually relieve itself. If the patient’s acid pain and abdominal distension become worse, immediately notify the doctor for corresponding treatment[11].
Discharge stage: Before the discharge, the patient is instructed to observe the vaginal fluid nature, pay attention to improve the their self-care ability. Patients need to take a break for at least 2 weeks, and forbidden tub bath for at least 8 weeks. Additionally, patients should have proper exercises, a good diet and nutrition and personal hygiene.If there is any abnormal situation, patients should contact the doctor in time. The patients are supposed to return to hospital for consultation one month after discharge,and have a general physical examination done every 6 months[12].
Observation indicators
Two groups of patients were evaluated by Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA) and Hamilton Depression Scale(HAMD) before and after nursing intervention[13]. HAMA and HAMD were compiled by Hamilton in the 1950s and 1960s. HAMA scale is an important diagnostic tool often used to diagnose and classify anxiety symptom. It consists of 14 items, using a 5-point scale ranging from 0 to 4,4 points indicates very severe, 3 points severe, 2 points moderate, 1 point mild, and 0 points not present. Total score ≤7 points indicates no anxiety symptom; 8-13 points indicates there may be anxiety symptom; 14-20 points indicates there must be anxiety symptom; 21-28 points indicates there are obvious anxiety symptom; ≥29 points indicates there are severe anxiety symptom. HAM-D is the most widely used scale for evaluating depressive state in clinical application. It is easy to master, clear in standard and simple in evaluation method. It can evaluate depressive symptoms of many diseases, such as neurosis, manic depression and depression, especially for depression. 17 items of HAMD scale, the 4th, 5th, 6th, 12th, 13th, 14thand 16thitems adopt a 3-point scale ranging from 0 to 2, and the other items adopt 5-point scale ranging from 0 to 4,the total score >24 points indicates severe depression, 17-24 points indicates depression symptom must be present,7-16 points indicates there may be depressive symptom,<7 points indicates no depressive symptom. HAMA and HAMD were assessed by two trained caregivers through observation and conversation. The higher the patient score,the more severe the bad mood.
The hospitalization time, operation time and intraoperative bleeding volume were compared between the two groups. The blood volume, operation time and hospitalization time of the two groups were recorded and sorted out. Surgical time is from the beginning of anesthesia to the completion of surgery. Intraoperative blood loss refers to the amount of bleeding in the blood-stained gauze,which was calculated by the weighing method.
The postoperative complications and degree of cooperation between the two groups were compared.Complications include massive hemorrhage and uterine perforation. The degree of coordination was divided into good, passable and poor. Poor indicates that the patient does not cooperate with the operation and has resistance.Passable indicates that the operation was successfully completed and the patient cooperated with the operation under the supervision of the medical staff. Good indicates that the operation was completed smoothly, and the patient could cooperate actively with the operation. degree of coordination (%) = (good+passable) cases/total number of cases ×100%.
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed by SPSS18.0 software, in which the count data were expressed as percentage (%), and difference between groups was analyzed using χ2test.The measurement data was expressed as (± s), and the difference within groups was analyzed using paired sample t test, and the difference between groups were analyzed using independent sample t test. The inspection level was α=0.05, and a value of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Anxiety and depression scores between before and after nursing intervention
The HAMD and HAMA scores of the patients in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (P<0.05), as shown in Table 1.
Hospitalization time, operation time and intraoperative bleeding volume between the two groups
A shorter hospitalization time, a shorter operation time and a less intraoperative bleeding volume were found in the observation group compared with the control group (P<0.05), as shown in Table 2.
Postoperative complications and operative coordination between the two groups
The incidence rate of complications such as massive hemorrhage and uterine perforation in the observation group was lower than that in the control group (5.7% vs.20.0%, P<0.05), and the degree of patients’ cooperation in surgery in the observation group was higher than that in the control group (94.3% vs. 60.0%, P<0.05), as shown in Table 3.
Discussion
Abnormal uterine bleeding belongs to Benglou category of TCM. Non-menstrual bleeding is not only metrorrhagia, but also metrostaxis. There is a certaincorrelation between metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, so it is collectively called Benglou[14]. With the improvement of people’s living standards in recent years, eating habits have undergone tremendous changes, and more and more women have abnormal uterine bleeding, which seriously affects women’s quality of life and physical health. At present, hysteroscopic surgery is mainly used to treat such disease. Patients who should have the uterus removed after failure to conservative treatment of benign lesions in the uterine cavity can be treated with hysteroscopic surgery to preserve the uterus without affecting the ovarian blood supply. Based on its rapid postoperative recovery, significant curative effect, minimally invasive,etc, hysteroscopic surgery is widely used in clinical gynecology at present[15].
Table 1 Comparison of anxiety and depression scores between two groups (±s)
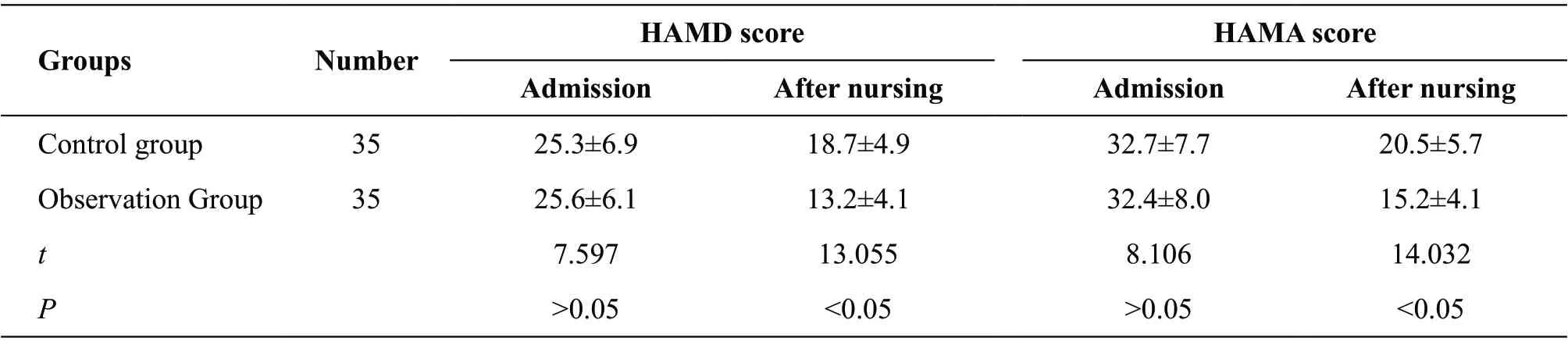
Table 1 Comparison of anxiety and depression scores between two groups (±s)
GroupsNumber HAMD scoreHAMA score AdmissionAfter nursingAdmissionAfter nursing Control group3525.3±6.918.7±4.932.7±7.720.5±5.7 Observation Group3525.6±6.113.2±4.132.4±8.015.2±4.1 t 7.59713.0558.10614.032 P>0.05<0.05>0.05<0.05
Table 2 Comparison of hospitalization time, operation time and intraoperative bleeding volume between two groups (±s)
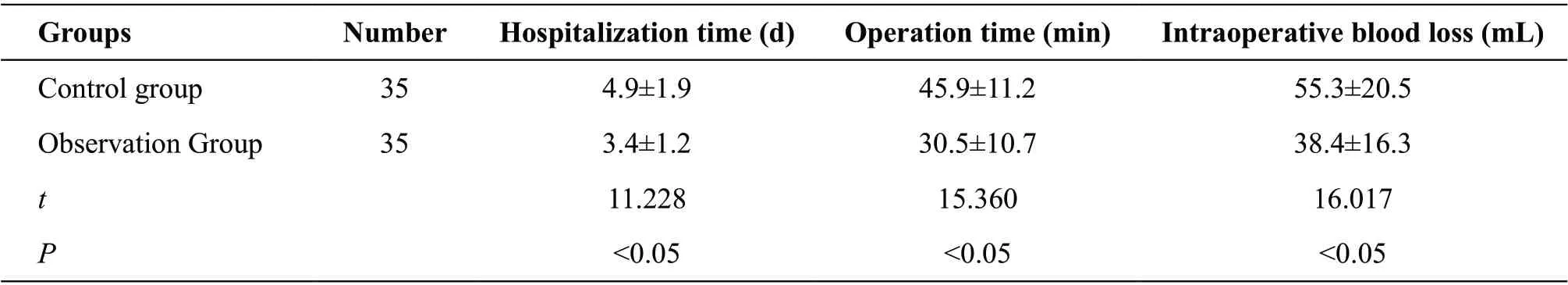
Table 2 Comparison of hospitalization time, operation time and intraoperative bleeding volume between two groups (±s)
GroupsNumberHospitalization time (d)Operation time (min)Intraoperative blood loss (mL)Control group354.9±1.945.9±11.255.3±20.5 Observation Group353.4±1.230.5±10.738.4±16.3 t 11.22815.36016.017 P<0.05<0.05<0.05
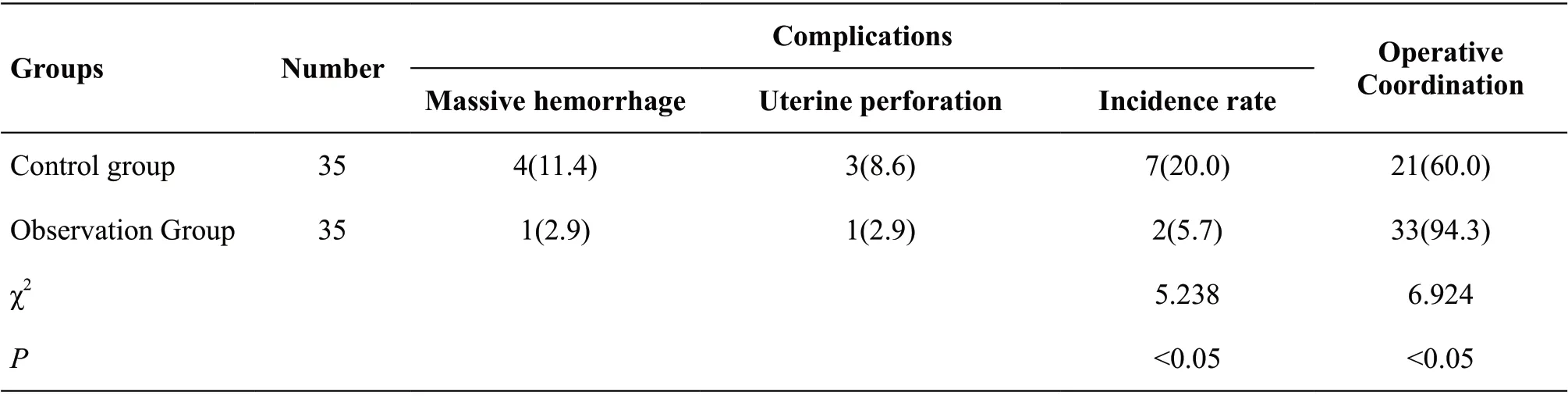
Table 3 Complications and operative coordination between the two groups [n(%)]
Comprehensive health education is helpful for nurses to have a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition, to makes nurses timely and accurately judge the psychological state and take appropriate measures to deal with it. Moreover, it makes the psychological burden and physical pain of patients greatly reduced, and ensure the smooth completion of the operation and accelerate the prognosis recovery of patients[16]. The results of this study showed that the psychological state, hospitalization time,operation time and postoperative complications of the observation group with comprehensive health education were better than those of the control group with routine nursing. It is hence proved that health education plays an important and positive role in nursing, and comprehensive health education is applied in the nursing of metrorrhagia and metrostaxis patients, with remarkable nursing effect,and the advantages are as follows: (1) Nursing staff can take the initiative to educate and help patients. In their work, they can clearly define their responsibilities and have a clear awareness of their educators so as to achieve the goal of education. (2) Nurses’ prestige in patients’minds has been improved, and comprehensive health education has promoted nurses to pay more attention to new nursing technologies and knowledge, enhance their awareness of studying professional knowledge, and realize their own value. (3) After the implementation of comprehensive health education, the patients have a more in-depth understanding and mastery of relevant disease knowledge, which is conductive to enhance their ability to judge and participate in treatment, to find out their own adverse reactions in time, to reflect their own feelings correctly, and to play an active and auxiliary role.
With the improvement of people’s demand for treatment, health education has become an important part of nursing. Nurses pay more and more attention to health education for patients. In order to successfully implement health education, firstly, nursing workers should be patiently and meticulously communicate with patients while implementing health education. As far as possible,the patient’s psychological and physiological needs should be fully understood to improve the patient’s trust in the nursing workers. The second is to fully obtain the support and understanding of the patient’s family members,improve the nursing ability of the patient’s family members, and implement better care and treatment for the patients. The third is to pay attention to the relationship between doctors and patients, and to seek the support and understanding of doctors, so that nursing workers can better implement health education.
To sum up, the application of health education in the nursing of metrorrhagia and metrostaxis patients can relieve the patients’ anxiety and depression, improve their understanding and mastery of relevant disease knowledge and their ability to cope with bleeding and their selfcare, as well as reduce the incidence of complications and the length of hospital stay and promote the prognosis of patients. Therefore, it is worthy of clinical application.
Declaration
All authors of this article declare that they have no conflict of interests.
 Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年2期
Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年2期
- Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- Application of Stone Needle Therapy Based on Blood Stasis Theory in the Treatment of 36 Cases of Knee Osteoarthritis in Early and Middle Stage
- Quantitative and Qualitative Investigation of Traditional Chinese Medicine Nursing Protocols for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Effect of Auricular Piont Pressing Combined with Thunder-Fire Moxibustion on Abdominal Distension and Constipation After Thoracic Compression Fracture
- Application of Out-of-Hospital Extended Nursing in Brace Treatment of Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis
- The Effects of Simulation-Based Learning Using Virtual Reality in Nursing Student:A Meta-Analysis
- Effect of Acupoint Massage on Cognitive Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
