Effect of Acupoint Massage on Cognitive Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
You-Hua LIU, Luo YANG, Shao-Hua GONG, Xiao-Ping YI, Hong GUO
School of Nursing, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100013, China
Abstract
Key words: Acupoint massage; Cognitive dysfunction; Systematic review; Meta-analysis
Introduction
With the rapid growth of the aging population, the incident number of of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is growing every year in China[1]. Studies[2-3]have shown that mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is the precursor stage of AD. Only 1%of normal elderly people may convert to AD each year,while about 6.53% of MCI patients convert to AD each year[4]. According to the estimates in the Global Burden of Disease (GBD), AD’s Disability-Adjusted Life Years(DALY) loss accounts for the second largest proportion of chronic diseases in the elderly, and its impact on society and the family is evident[5]. Therefore, the early intervention and prevention of AD is of great significance.Because the pathogenesis of cognitive impairment is not clear, there is a lack of effective treatment. The long-term efficacy of drug intervention is not clear, and the side effects are obvious, so most studies tend to use non-drug intervention in recent years. Acupoint massage is a kind of disease treatment method based on meridian acupoints and massage as the main method. As one of the non-drug interventions, the efficacy and safety of acupoint massage in improving cognitive function have been affirmed in many clinical studies. However, there is no relevant systematic evaluation report, and there is still insufficient evidence to prove the effectiveness of acupoint massage in cognitive function, which affects its popularization and application to some extent. Based on this, the study intends to use meta-analysis method to objectively analyze the intervention effect of acupoint massage on cognitive impairment, in order to provide reference for the clinical application of acupoint massage.
Materials and Methods
Search strategy
CNKI, VIP, Wanfang, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase,the Cochrane Library, and CINAHL were searched by computer. According to the principle of free subject words, the clinical trial studies on the improvement of cognitive function by acupoint massage were systematically collected from inception to June 2019. The Chinese retrieval words included “穴位按摩/穴位按揉/穴位按压/点穴/点穴按摩/经穴推拿” and “认知功能/脑功能/认知功能障碍/认知功能下降/认知功能受损/神经认知障碍/神经系统并发症/脑功能障碍”. The English retrieval words included “acupressure/acupoint pressing/acupoint/acupoint massage”, “cognitive dysfunction/cognitive impairment/cognitive decline/neurocognitive impairment/cerebral dysfunction/neurological complications/alzheimer’s disease/dementia/neuropsychiatric symptom”. In addition, the citations of the included literatures were traced back by snowball.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: (1) The subjects of the study were the elderly population. (2) The intervention measures in the experimental group was acupoint massage combined with routine nursing or acupoint massage alone, while the control group was treated with routine nursing or no intervention measures. (3) The research design was a randomized controlled trial and a quasi-experimental research design. (4) The main outcome indexes were the evaluation of the overall cognitive function at the end of acupoint massage intervention or at the end of followup, such as the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)Scale, Wechlich Memory Scale China revision (WMS-C)and so on.
Exclusion criteria: (1) Combined interventions, such as acupoint massage combined with acupuncture and/or moxibustion in the experimental group. (2) Lectures,reviews, case reports, etc. (3) Repeated publication,incomplete original data, no full text, or incorrect data statistics.
Literature screening and data extraction
After the duplicate literatures were removed by Endnote X8, the literatures were screened independently by two researchers, and the re-screening was completed after reading the full text. If there were differences, the third party would decide. The contents of data extraction included: the first author, the publication time, the sample size of the experimental group and the control group, the intervention method of the experimental group and the control group, the intervention time, the outcome index,the selection of acupoints and so on. The above steps were completed independently by the two researchers and checked with each other. In the event of differences, they were decided after panel discussion.
Literature quality evaluation
Cochrane Handbook (version 5.1.0) was used, the quality of the included literature were evaluated from the generation of random sequences, allocation concealment schemes, blind methods for research subjects, intervention implementers and outcome surveyors, integrity of result data, selective reporting of research results, and other sources of bias[6]. It was completed by two researchers independently and blindly, and then compared with each other. In the event of differences, the third party decided.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis of the extracted study data was performed using RevMan5 software. Continuous variable data were calculated by standardized mean difference (SMD),and 95% confidence interval (CI) was used for interval estimation. The heterogeneity of the literature was determined by χ2test. When P>0.1, I2≤50%, the studies were considered to be homogeneous, the fixed effect model was used to combine the effect value. On the contrary, the random effect model was used.
Results
Inclusion of documents
Totally 547 articles were obtained by preliminary retrieval of literature. After layer by layer screening, such as deleting the repeated literature, browsing the abstract of the text, reading the full text and so on, 10 articles[7-16]were finally included. The literature screening process and results were shown in Figure 1.
Basic information and quality evaluation of the included literature
The total sample size was 818, of which 413 cases of the acupoint massage group and 405 cases in the control group. All the studies used recognized diagnostic criteria at home and abroad and tools with good reliability and validity to evaluate cognitive function, and described the baseline to be consistent. The basic situation and the quality evaluation included in the literature are shown in Table 1.

Figure 1 Document retrieval flow chart
Meta-analysis results
Meta Analysis of MMSE scale score: The MMSE scores of the 2 groups were reported in 9 studies[7-13,15-16]. There were 737 patients in the 2 groups (373 patients in the acupoint massage group and 364 patients in the control group). There was statistical heterogeneity among the studies (P<0.10, I2=68%), so random effects model was used. Meta-analysis showed that the MMSE score of the acupoint massage group was higher than that of the control group after intervention, and the difference was statistically significant [SMD=0.80, 95% CI (0.53, 1.07),P<0.0001]. The results showed that acupoint massage had better results in evaluating the total score of MMSE than the control group. (Figure 2)
Meta Analysis of WMS-C scale score: The WMS-C scores of the 2 groups were reported in 4 studies[7,8,13,15].There were 348 patients in the 2 groups (175 patients in the acupoint massage group and 173 patients in the control group). Because the WMS-C scale is divided into 4 subscales, including picture memory, associative memory,understanding memory and instantaneous memory, the meta-analysis of these 4 dimensions was carried out.
There was statistical heterogeneity between the studies that reporting picture memory score (P<0.10, I2=94%), so random effects model was used. The results showed that the improvement of picture memory score in acupoint massage group was significantly better than that in control group after intervention, and the difference was statistically significant [SMD=-3.69, 95% CI (-5.08,-2.30), P<0.0001]. (Figure 3)
There was statistical heterogeneity between the studies that reporting associative memory score (P<0.10,I2=95%), so random effects model was used. The results showed that the improvement of associative memory score in acupoint massage group was significantly better than that in control group after intervention, and the differencewas statistically significant [SMD 0.24, 95% CI (-0.73,1.20), P<0.0001]. (Figure 4)

Table 1 Basic information of 10 included studies
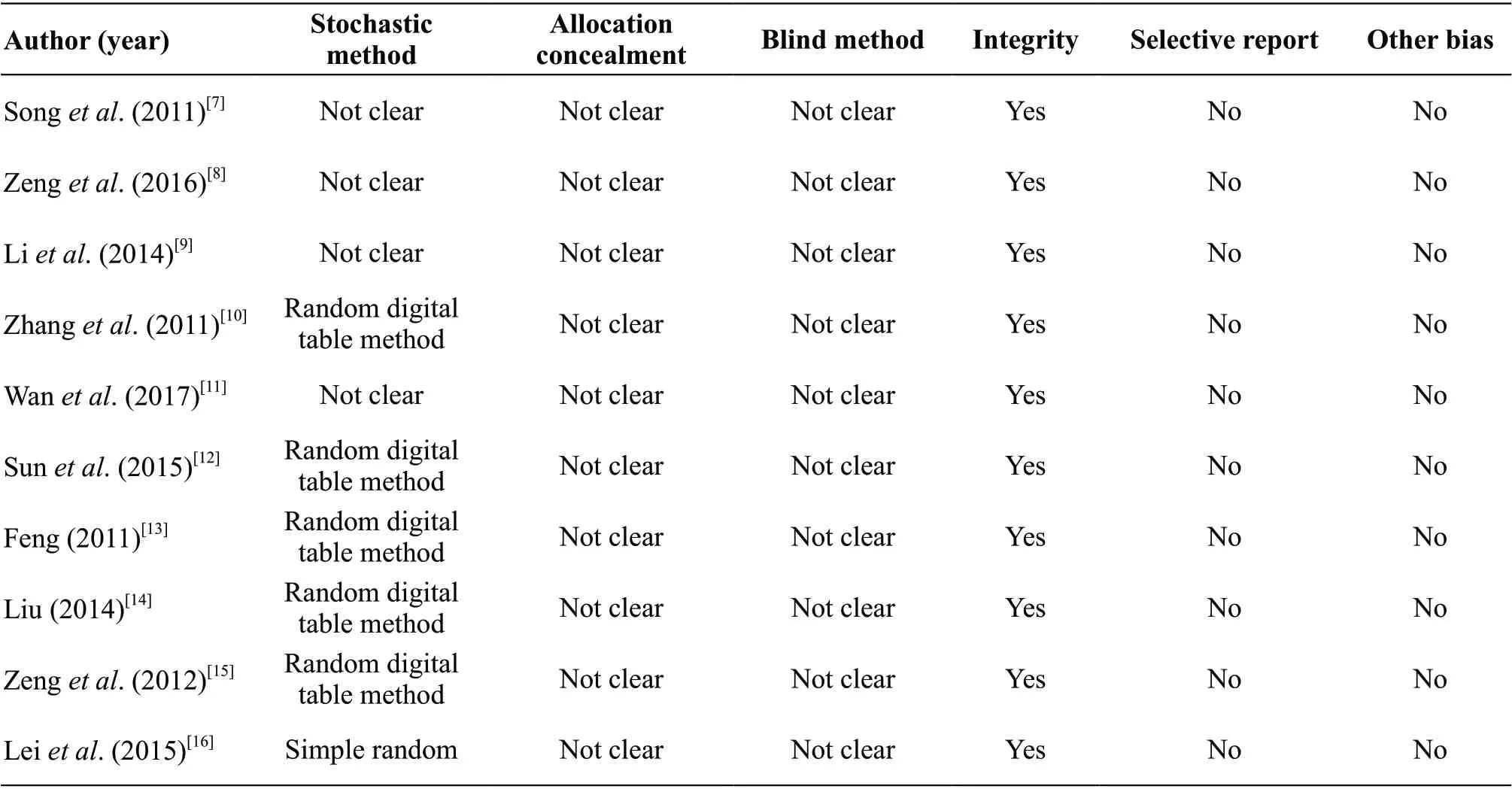
Table 2 Quality evaluation for included articles

Figure 2 Meta-analysis of MMSE scores in 2 groups after intervention
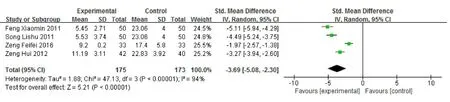
Figure 3 Meta-analysis of picture recall scores in 2 groups after intervention

Figure 4 Meta-analysis of associative memory scores in 2 groups after intervention
There was statistical heterogeneity between the studies that reporting understanding memory score (P<0.10,I2=90%), so random effects model was used. The results showed that the improvement of understanding memory score in acupoint massage group was significantly better than that in control group after intervention, and the difference was statistically significant [SMD=1.33, 95%CI (0.58, 2.09), P<0.0001]. (Figure 5)
There was statistical heterogeneity between the studies that reporting instantaneous memory score, P<0.10,I2=93%, so random effects model was used. The results showed that the improvement of instantaneous memory score in acupoint massage group was significantly better than that in control group after intervention, and the difference was statistically significant [SMD=1.70, 95%CI (0.77, 2.62), P<0.0001]. (Figure 6)
Sensitivity analysis
Because there was heterogeneity in the literature of metaanalysis, sensitivity analysis was carried out to find the source of heterogeneity. The sensitivity analysis of the research data included in each meta-analysis was carried out by using the item-by-item elimination method. There was no significant change in the results of meta-analysis after item-by-item elimination, which indicated that the results of meta-analysis in this study were reliable.
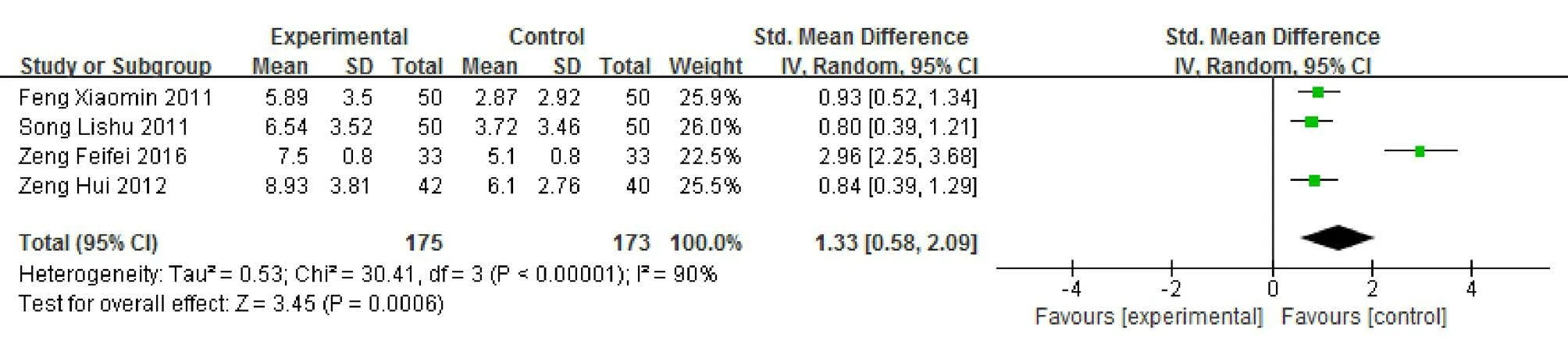
Figure 5 Meta-analysis of understanding memory scores after intervention in 2 groups
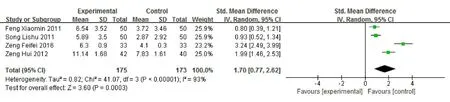
Figure 6 Meta-analysis of instantaneous memory scores in 2 groups after intervention
Discussion
Acupoint massage can improve cognitive impairment
Acupoint massage is based on the theory of meridians and acupoints, with massage as the main treatment,which is used to prevent and cure diseases. The results of meta-analysis showed that the cognitive function in acupoint massage group was significantly better than that in control group after intervention. Compared with the control group, acupoint massage significantly increased the score of MMSE in the elderly [SMD=0.80, 95% CI(0.53, 1.07), P<0.0001]. In addition, acupoint massage also significantly improved the picture memory ability of the elderly [SMD=-3.69, 95% CI (-5.08, 2.30),P<0.0001], associative memory ability [SMD=0.24, 95%CI (-0.73, 1.20), P<0.0001], understanding and memory ability [SMD=1.33, 95% CI (0.58, 2.09), P<0.0001],instantaneous memory ability [SMD=1.70, 95% CI (0.77,2.62), P<0.0001]. These results suggest that acupoint massage can effectively improve the cognitive impairment of MCI patients.
Mechanism of acupoint massage
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) holds that through pressing and stimulating specific points of the body surface, acupoint massage can enhance qi and blood circulation from the surface to the inside, stimulate the qi of meridians and collaterals, and mobilize the disease resistance ability of the body, thus achieving the purpose of preventing and treating diseases[17]. Modern medicine believes that massage of meridians and acupoints of the head can stimulate cerebral nerve activity, promote cerebral blood circulation, improve the blood supply of the central nervous system, and the blood oxygen and nutritional supply of the corresponding brain tissue, so as to promote the recovery of neural structure and brain function related to cognitive function, to slow down brain atrophy, and finally to improve cognitive function[18].In addition, acupoint massage may also improve some immune function of the body through neurohumoral and other factors, sequentially to improve the overall health status of MCI patients[19].
Acupoint selection in included studies
Although the acupoints selceted in the studies were different, the main acupoints were Taiyang (10), Baihui(8), Shenting (8), Shencong (7) and Fengchi (6).
According to the theory of TCM, Taiyang acupoint have the function of calming the heart and focusing attention.Baihui acupoint has the function of calming, awakening the brain, invigorating the mind, opening the orifice,and enhancing people’s undefined memory. Shenting acupoint has the function of nourishing the brain,resuscitation, and tranquilizing mind. Shencong acupoint can stimulate meridian qi, enlighten the mind, wake up the mind and enlighten the orifice. Fengchi acupoint has the effect of promoting clear mind and refreshing the spirit. These acupoints are located in the projection area of frontotemporal and parietal lobe, which is closely related to human advanced thinking and memory.Massage of these acupoints can cause the effect of nerve and periosteum, promote the establishment of collateral circulation of the brain, activate the number of nerve fibers of the nerve cells with low function, thus improving the function of the brain. In addition, some of the studies used other acupoints, such as Sanyinjiao (3), Neiguan acupoint (3), Shenmen acupoint (3), Anmian acupoint(2), Yintang acupoint (1), Qianding (1), Touwei (1), and Chengling acupoint (1).
Limitations of the included researches and meta-analysis
This study strictly follows the reporting specification of meta-analysis, but there are still some limitations to be explained. (1) Meta-analysis is a kind of literature secondary analysis method, which is a retrospective study, and its results will be affected by the quality of the original literature. (2) All included literatures are generally of low quality. There are many problems,such as unclear random method, unknown distribution,unknown blind method and so on. Most studies did not describe withdrawal / loss of follow-up, and did not carry out intentionality analysis. In addition, the choice of outcome indicators is not consistent among the studies.(3) The inclusion of literature is limited to publicly published studies that are hired by databases. (4) The sample size of the researches were small, and there is a certain risk of bias, which may affect the accuracy of the results. Therefore, more large samples, multi-center and high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to verify the intervention effect of acupoint massage on cognitive impairment, so as to provide more reliable medical evidence for clinical decision-making.
Conclusions
Acupoint massage, as traditional medicine in our country,is not only safe and economical, but also can effectively improve the cognitive dysfunction of the elderly, which is worth popularizing and applying in the community. It has certain significance to improve the cognitive function of MCI patients and prevent the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease.
Declaration
All contributing authors declared no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年2期
Journal of Integrative Nursing2019年2期
- Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- Application of Comprehensive Health Education in Nursing of Patients with Metrorrhagia and Metrostaxis Treated by Hysteroscopic Electrotomy
- Application of Stone Needle Therapy Based on Blood Stasis Theory in the Treatment of 36 Cases of Knee Osteoarthritis in Early and Middle Stage
- Quantitative and Qualitative Investigation of Traditional Chinese Medicine Nursing Protocols for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Effect of Auricular Piont Pressing Combined with Thunder-Fire Moxibustion on Abdominal Distension and Constipation After Thoracic Compression Fracture
- Application of Out-of-Hospital Extended Nursing in Brace Treatment of Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis
- The Effects of Simulation-Based Learning Using Virtual Reality in Nursing Student:A Meta-Analysis
