Application of Semantic Core Words in Meaning-Match Listening
Chen Yuwei
【Abstract】“Semantic Core Words”, as the combination of “Semantic Mark Words” and “Semantic Key Words”, plays an important role in the meaning-match listening. They help the listener generally and specifically locate where the missing part is and try to fill the blank with the correct and accurate words or phrases that are required. This paper takes an extract from BEC exercise “Airspeed-Notes on Presentation by Chief Executive” as an instance to exemplify how to use semantic core words to do the meaning match, which aims to help those to have a better understanding of the usage of“Semantic Core Words”, accordingly grasping the listening skill in meaning-match listening.
【Key words】Semantic Core Words; Meaning-Match Listening; Application
【作者簡介】Chen Yuwei, Chengdu Institute Sichuan International Studies University.
1. Introduction
Listening, as the most important part of English listening, has always been the most challenging language skill for most of the English learner. The problem may arise in the grasping the main idea of the semantic passage, or the intensive listening like multiple choice, gap-filling, and etc.. However, the most difficult part of most of them must be the meaning match since it tests how well the students get the main idea of the passage that theyve heard and how they could revise the sentence into the one that in the question sheet. Therefore, it is of great necessity for most English learner to know how to apply “semantic core words” into the meaning-match. This paper intends to give a brief analysis to the application part through the example of the “Gap-Filling” in BEC Vantage.
2. Brief Analysis of Meaning-Match
Gap-filling is one of the most common-seen question in English listening task. If can be divided into two main types, One is literal match and the other is meaning match. The first type mainly tests students word-to-word listening as well as the spelling and speed for the words or sentences, which is supposed to be the much easier part if the students master a certain lever of vocabulary and the listening skill. For example, the question is “Buying presents is a high ________ for a lot of people.” and the listening text is “Buying presents is a high priority for a lot of people.” Thus, It easily can be seen that the blank should be filled with “priority”. While, another one is meaning match. This one asks for the high lever of ones listening skill. In this type of listening, students not only should handle the problems met in the literal meaning, but also should have the ability of total understanding of the sentence or the passage theyve heard instead of the words or phrases that they are listening in the passage. Take the following sentence for example, “Online shopping tends to be more attracted by women for its ________.” and the listening text is “It seems women are now more attracted to the convenience of online shopping than they used to be.” Thus, we cannot get the answer just as easily as the first one. Besides having a full understanding of the sentence, we may get a clue from those words of “women, more attracted, online shopping” to get the answer. That is “convenience”. So the words “women, more attracted, online shopping” are the semantic core words, which are the points of doing meaning-match task in listening.
3. What is “Semantic Core Words”
Semantic belong to the linguistic field, which mainly focuses on the study of the meaning of linguistic units, words and sentences in particular. According to the componential analysis originated with the work of Trubetzkoy (1939) and the Prague School of Linguistics (mainly in phonology), “Semantic markers or sememes help us to index the meanings of words, separate the various meanings of individual words, and help us to analyze relationships between similar or different words.” This specifically suggests that semantic makers refers to the signal of the meaning and structure, which intends to clarify the logic thinking of the speaker or writer. A better grasp of the semantic markers is useful to understand the idea of the targeted speaker or the writer. The semantic markers include the words to summarize, such as “to summarize, in a word”, the words to suggest the time sequence, like “first, second, third”, the words to indicate the causes and reasons, such as “because, as, for, since, as a result”, and the transition connection, like “but, although, though, yet”, the words to emphasize, like “indeed, anyway, in fact”, and the words to express the progressive relationship, such as “besides, whats more, moreover”. However, it is not enough for listeners to only grasp the semantic markers to complete the meaning-match, therefore, core words should be invited to finish the task together.
“Semantic Core Words”, including “Semantic Mark Words” and “Semantic Key Words”, like markers, could help the listeners easily locate where the listening material is and identify the missing part in meaning match. They could be the content words or function words, which depend on the semantic meaning itself. Here, “locate” and “identify” are two main functions of semantic core words. To begin with, the semantic core words should be easily recognized in listening. Thus, those special words could be the first to consider, such as proper names, numbers, abbreviations, phrases with special structure, prepositional phrases, etc.. If there are no such special words, nouns, verbs, adjectives or adverbs will be the helpers. But one thing should be paid attention to is that the latter ones probably would change with different forms or similar meanings, like synonyms.
4. Application of “Semantic Core Words”
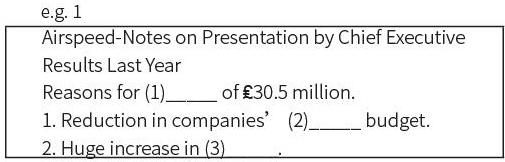
In this part, the writer of this paper aims to take an extract from BEC exercise “Airspeed-Notes on Presentation by Chief Executive” as an instance to exemplify how to use semantic core words to do the meaning match. The following (e.g. 1) is the example.

While students are doing the task, they should follow the following steps:1. Underline the semantic mark key words; 2. Understand the main idea of the whole passage according to the semantic mark key words; 3. Locate where the question belongs to; 4. Match the missing part; 5. Check the form and meaning of the filling words.
In the first blank, “Reasons for (1)_______ of ?30.5 million.” The listening text is “So why did we make a loss of ?30.5 million last year?”Here the special semantic core word “?30.5 million” is easily to recognize, which helps the listener locate where the material is. Students may paste a marker here. “why” is another semantic core word, equal to “reasons”, a marker here, too. “last year” is not important for the understanding of the sentence. Thus, it does not belong to the core word. Therefore, it is easily identified that “loss” is missing in the blank. So, “loss” is the answer to this gap. So the whole sentence is done like this while listening (e. g. 2).
e. g. 2
The second one, “1. Reduction in companies (2)_______ budget.” From the former text, “there are various reasons”, It can be known that the following part is going to present the reasons. The related text, “Firstly, ... we know the amount of money being spent by all firms on their travel budget has generally fallen.” Thus the marker can be pasted like this “1 to firstly”, “reduction to fallen”, “companies to firms”, “budget to budget”, “the amount of money” is similar to budget in meaning. Here, “reduction” has been changed in word form and replaced with the synonym. “companies” was changed with synonym “firms”, too. So, it is a little bit challenging to identify, but not so difficult to find the answer is “travel”. Similarly, the following blank could be done in the same way. “2 to the second reason”, “huge to enormously”, “increase to increase”. So here the answer is “a few costs” or “costs”.
It can be seen that “semantic core words” is of great importance for doing meaning-match listening. They not only take the advantage of the semantic markers to help the listener have a general location of the passage theyve heard, but also enable the listener have a specific location of the exact missing parts. Therefore, for those that always get lost in listening, they could be the effective way to find the missing words or phrases and then match them in the blank.
5. Conclusion
“Semantic Core Words” help the listener generally and specifically locate where the missing part is and try to fill the blank with the correct and accurate words or phrases that are required. However, merely depending on the “semantic Core Words” cannot meet the whole demand of a meaning-match while doing the gap-filling, thereby, the word class, word form and the word meaning in the blank should also be considered. Besides, in order to handle the listening task, the extensive listening with high quality should also be covered in the students daily task, and the intensive listening like dictation is also of great necessity for those students who want to improve their listening score in the test. Generally speaking, listening is closely related to ones reading, speaking as well as writing, which relies on ones comprehensive understanding of the language. Therefore, it is advisable for students to keep practicing in their daily use with perseverance and consistency.
參考文献:
[1]曹彦,沈淼.以语用能力为核心的大学英语听力教学实践[J].鞍山师范学院学报,2011(1):49-51.
[2]戴炜栋主编.新编简明语言学教程[M].上海:上海外语教育出版社,2013.
[3]邓炎昌,刘润清.语言与文化:英汉语言文化对比[M].北京:外语教育与研究出版社,1989.
[4]胡壮麟主编.语言学教程[M].北京:北京大学出版社,2013.
[5]王建荣.语用学理论在中学英语听力教学中的应用研究[D].武汉:华中师范大学,2006.
[6]肖丽莉.英语听说能力培养的语用学阐释[D].昆明:云南师范大学,2006.
[7]谢博鸿,何刚毅,曾覃.高校英语听力教学中的语用策略核心构架[J].校园英语,2016(6):25.
[8]周之南. BEC听力必备手册[M].北京:经济科学出版社,2012.

