Fascioliasis presenting as colon cancer liver metastasis on 18Ffluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography:A case report
Sami Akbulut,Egemen Ozdemir,Emine Samdanci,Selver Unsal,Murat Harputluoglu,Sezai Yilmaz
Sami Akbulut,Sezai Yilmaz,Liver Transplant Institute,Inonu University,Malatya 44280,Turkey
Egemen Ozdemir,Department of Surgery,Inonu University Faculty of Medicine,Malatya 44280,Turkey
Emine Samdanci,Department of Pathology,Inonu University Faculty of Medicine,Malatya 44280,Turkey
Selver Unsal,Department of Nursing Service,Liver Transplant Institute,Inonu University,Malatya 44280,Turkey
Murat Harputluoglu,Department of Gastroenterology,Inonu University Faculty of Medicine,Malatya 44280,Turkey
Abstract
Key words: Colon cancer liver metastasis;Fasciola hepatica;Positron emission tomography;Misdiagnosis;Case report
INTRODUCTION
Fascioliasis (liver fluke) is a parasitic disease of the liver caused by a type of trematode of the speciesFasciola hepaticaand less frequently byF.gigantica.Humans are infected by ingesting metacercariae-containing watercress and similar freshwater plants or drinking contaminated water.After ingestion of contaminated water or beverages,the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum,and the larvae migrate through the intestinal wall into the peritoneum.After penetrating the liver capsule,the larvae pass through the liver parenchyma and reach the biliary ducts,where they develop into adult flukes[1,2].During this migration,they cause destruction in the liver parenchyma,which is characterized by necrosis and fibrosis.The larval form matures to a 3-cm long and 1-cm wide leaf-shaped adult form in approximately 12 wk.Parasites in the biliary ducts remain asymptomatic for years in most patients and are usually detected incidentally during radiological examinations for other reasons.The most important steps in the diagnosis of fascioliasis are clinical suspicion,detection of eggs in the stool,serological tests,molecular tests,and endoscopic and radiological examinations.Radiologically,fascioliasis can be confused with many other benign and malignant diseases of the liver and biliary tract[3].We aimed to present the diagnosis and treatment process of a patient with fascioliasis radiologically mimicking liver metastasis of colon cancer.
CASE REPORT
Chief complaints
A 35-year-old female patient who underwent right hemicolectomy for cecal cancer was referred to our Liver Transplant Institute for surgical treatment of colon cancer liver metastasis.
Personal History
Patient stated that she had been eating watercress for a long time.
History of past illness
The patient stated that she underwent colonoscopy at another clinic because of exhaustion,fatigue,and anemia,and right hemicolectomy was performed upon detection of a cecal tumor on colonoscopy.Histopathological examination revealed cecal adenocarcinoma with subserosal fat tissue invasion and five metastatic lymph nodes in 32 lymph nodes.Preoperative contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed hypodense and heterogenous lesions with soft tissue density that were 40 mm x 33 mm in diameter in the right lobe of the liver (Figure 1).At the 3rd postoperative week,multiple hypermetabolic lesions with SUVmax of 5.3 in segments V,VII,and VIII of the liver were detected on performing18Ffluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/CT (18F-FDG-PET/CT) after 5.5 mCi18F-FDG injection (Figure 2).In addition,hypermetabolic lesions were detected in the subhepatic (SUVmax:7.1),superior mesenteric (SUVmax:7.1),and aortocaval window (SUVmax:7.3).Six cycles of adjuvant FOLFOX (folinic acid,fluorouracil,oxaliplatin) and bevacizumab were administered to the patient.In control18F-FDGPET/CT,the SUVmax values of liver lesions decreased to 3.8,and the SUVmax values of the lymph nodes did not regress.Thus,the same chemotherapy regimen was continued,and control18F-FDG-PET/CT was performed at the end of 12th chemotherapy course.In the last18F-FDG-PET/CT,all previously seen lesions were stable,whereas they regressed significantly both dimensionally and metabolically.Subsequently,the patient was referred to our center.Dynamic liver magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) performed immediately after the 12th chemotherapy course showed regression of the lesions in the liver.After 6 weeks,dynamic MRI at our center revealed that the lesions were more prominent than those on previous magnetic resonance images.Because the patient had colon cancer,the lesions in the liver were hypermetabolic in18F-FDG-PET/CT,and the lesions started to regrow after chemotherapy,and the patient planned to undergo surgery.Right hepatectomy was performed to include all lesions with intraoperative ultrasonography.In addition,all lymph nodes in the hepatoduodenal ligament,celiac,and aortocaval window were resected,and a frozen section was sent for analysis,and no tumor was detected in the lymph nodes.In the histopathological examination of the hepatectomy specimen,the lesions had granulomatous foci on a tract,characterized by suppuration enriched with eosinophils (Figure 3-4),which was noted to be compatible withF.hepaticainfection by a pathologist.Based on this result,preoperative blood tests of the patient were reexamined,and eosinophil count was 0.78 × 109/L (normal range:0-0.5).F.hepaticaIgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Synlab MVZ Leinfelden GmbH,Leinfelden-Echterdingen,Germany) was positive.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The final diagnosis of the presented case is fascioliasis mimicking colon cancer liver metastasis.
TREATMENT
The patient was administered two doses (10 mg/kg/dose) of triclabendazole (Egaten,Novartis Pharma,Switzerland) 24 h apart.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
At the 4th postoperative month follow-up,the alkaline phosphatase and gammaglutamyl transferase values were elevated,and the common bile duct was significantly dilated on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)images.SeveralFasciolaparasites were extracted from the common bile duct with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) (Figure 5).Triclabendazole(10 mg/kg/dose) therapy was administered to the patient after ERCP.The patient is still followed up without hepatobiliary complications.Although blood alphafetoprotein (AFP) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels were normal during the follow-up period,the CA19-9 level showed changes in the postoperative period(Figure 6).However,the CA19-9 level dramatically decreased after ERCP and returned to normal limits (normal range:0-35 U/mL).No findings of dead or living parasites were detected in the last control ERCP.
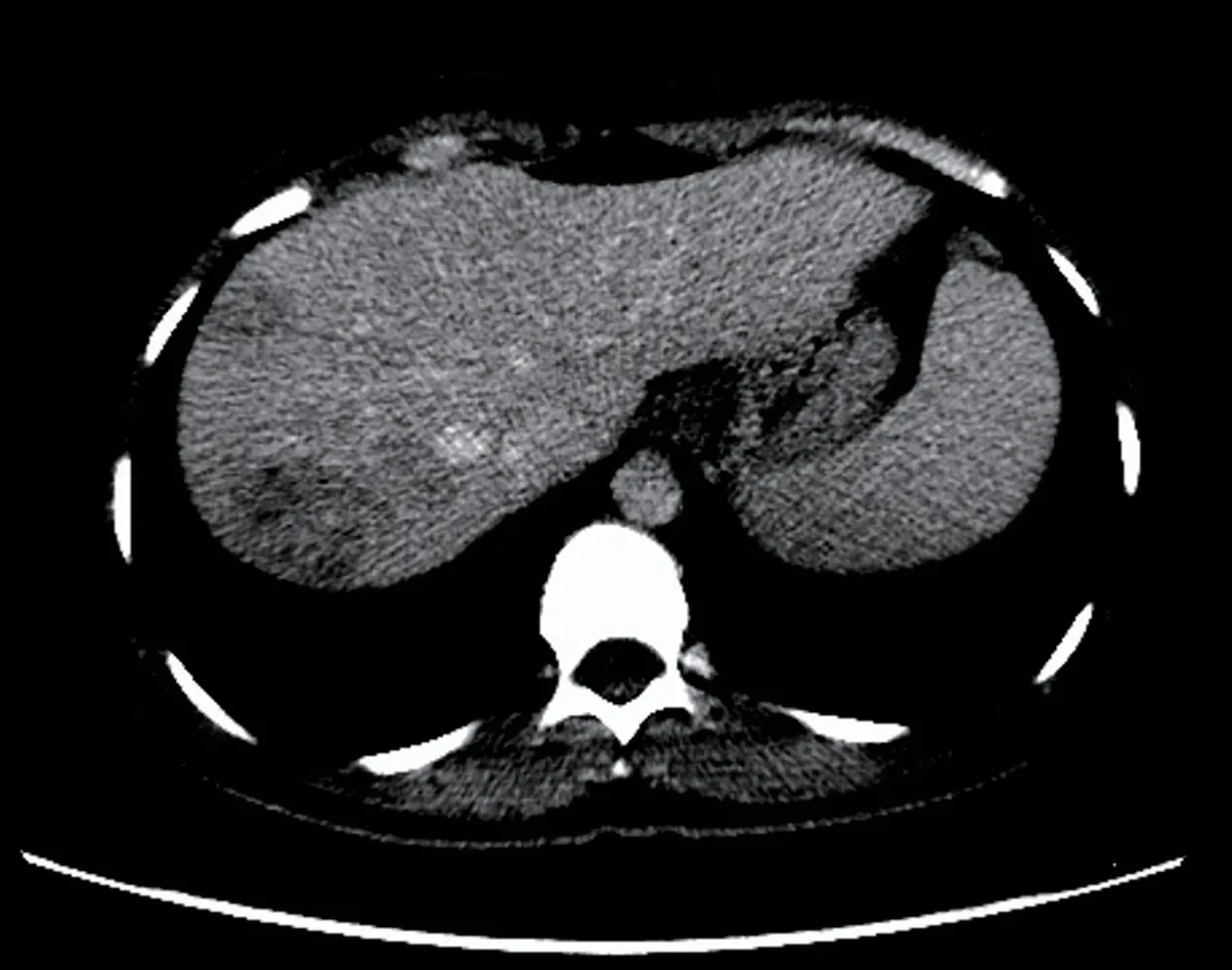
Figure1 Computed tomography image after contrast medium injection.
DISCUSSION
Two phases in the life cycle ofF.hepaticahave been defined:acute (hepatic) and chronic (biliary).The phase where the parasite penetrates through the liver capsule and invades the liver parenchyma is the hepatic phase.In this phase,parasites digest hepatocytes,open tunnels in the parenchyma,and remain in the parenchyma for months[2,4].Signs and symptoms in the hepatic phase commonly mimic those of liver abscess[2,5].Patients in this phase usually experience non-specific symptoms,such as loss of appetite,weight loss,right upper quadrant pain,fever,sweating,urticaria,and arthralgia[6].Hepatomegaly,right upper quadrant pain,and prominent eosinophilia can be seen[4,5].The phase where the parasite becomes visible in the bile ducts is the biliary phase.In this phase,signs and symptoms,such as biliary colic,epigastric pain,and jaundice,which are related to biliary tract obstruction,develop.The level of cholestatic enzymes and bilirubin may increase[7].Symptoms of acute pancreatitis may develop in patients with distal bile duct obstruction[8].
The following diagnostic modalities are used in the diagnosis of fascioliasis:clinical suspicion,parasite eggs observed by direct microscopy (stool,bile,or duodenal aspirate),detection of DNA of the parasite with real-time polymerase chain reaction(stool,bile or duodenal aspirate),serological tests (immunoelectrophoresis,counterimmunoelectrophoresis,metacercarial precipitin test,indirect hemagglutination),complement fixation,immunofluorescence assay,radioimmunoassays,enzyme-linked immunofiltration assay (ELIFA),enzyme-linked immuno-electrotransfer blot (EITB)or western blot,Falcon assay screening test-ELISA (FAST-ELISA),micro-ELISA,dot-ELISA],radiological examination of lesions of the liver parenchyma and biliary ducts(CT,MRI,MRCP,and18F-FDG-PET/CT),endoscopic examination of parasite directly(ERCP,endo-ultrasonography) and histopathological examination of the parasite on tissue biopsy[3,9,10].
Appearance of parasite eggs in the stool has a diagnostic value only in the biliary phase[5,9].Eosinophilia and anemia may be seen in biochemical tests[3,11].ELISA is the leading serological test with high sensitivity and rapid results[6].However,it should be supported by radiological findings due to its high false positive and negative rates[12].Appearance of tunnel-like linear and branched hypodense lesions on CT is characteristic[3].In most patients,iso-hyperintense (T2) and iso-hypointense (T1)lesions can be seen on MR and MRCP images,and these lesions can mimic malignant diseases of the biliary tract.ERCP and endoscopic ultrasonography are very useful in the biliary phase[9,11].Similar to this case,ERCP is the most appropriate treatment modality both to remove parasites from the bile ducts and to decompress the bile ducts.
由表5可知,旅游目的地马尼拉(103.61)的整体风险感知最高,薄荷岛(102.75)则在第二,马尼拉和薄荷岛的整体风险感知均超出了平均水平(102.61)。同时游客对马尼拉和薄荷岛两地的社会治安类风险感知都较高,其原因可能是2017年4月至5月期间,马尼拉发生两起严重爆炸事件以及薄荷岛发生武装交火事件,使游客普遍产生惶恐情绪。
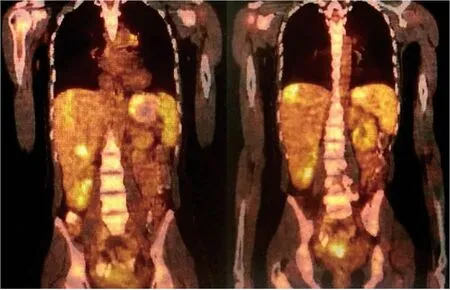
Figure2 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/Computed tomography was performed using 5.5 mCi of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose injection.
Diagnosis,staging,response to treatment,and recurrence of malignant diseases can be determined successfully by18F-FDG-PET/CT.However,false-positive results can be obtained in inflammations due to radiotherapy and surgery or in various chronic infections.These can sometimes mimic malignancy[13-15].Similar to this case,carefully evaluating high FDG uptake in PET/CT is particularly important in a patient with malignancy.Otherwise,because patients can only be cured with anti-helminthic treatment,they may undergo unnecessary major surgical procedures or chemotherapy.
The most common diseases confused with fascioliasis are viral hepatitis,liver abscess,cholecystitis,sclerosing cholangitis,AIDS-associated cholangitis,ruptured hydatid cyst,and ascariasis,clonorchiasis,and primary and metastatic tumors of the liver and biliary tract[2,5,9].Therefore,misinterpretation of these signs and symptoms in areas where fascioliasis is not endemic is possible,and thus,diagnosis may be delayed[9].Similar to this case,in a patient with colon cancer,it is expected that liver lesions will be interpreted as a tumor by a radiologist or nuclear medicine specialist without experience in fascioliasis.
The first and best option for the treatment of fascioliasis is triclabendazole,and another alternative drug is nitazoxanide.Triclabendazole is used in two doses (10 mg/kg/dose) 24 h apart and is effective at all stages regardless of the phase of the disease.Nitazoxanide is a good alternative to triclabendazole,and it is administered as 500 mg twice daily for 7 d[16].Other drugs that were used previously and are no longer recommended due to drug resistance or toxicity,including bithionol,praziquantel,emetine,dehydroemetine,metronidazole,albendazole,niclofolan,and chloroquine.In this case,we had to administer it twice in a few months.
CONCLUSION
Fascioliasis may mimic many benign and malignant diseases of the liver due to its non-specific signs and symptoms.Differential diagnosis is quite difficult,if there is no clinical suspicion,especially in patients with simultaneous fascioliasis and gastrointestinal malignancy.Therefore,careful evaluation of diagnostic imaging tools in patients living in endemic areas and the use of other diagnostic tools in suspected cases are vital.
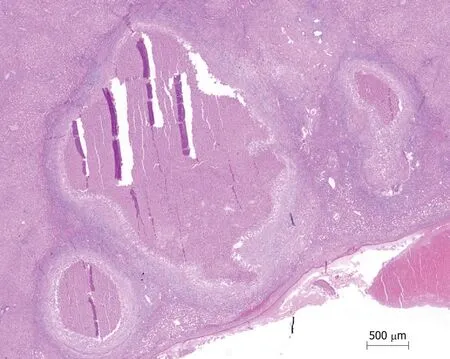
Figure3 Granuloma with central necrosis (HE ×100).
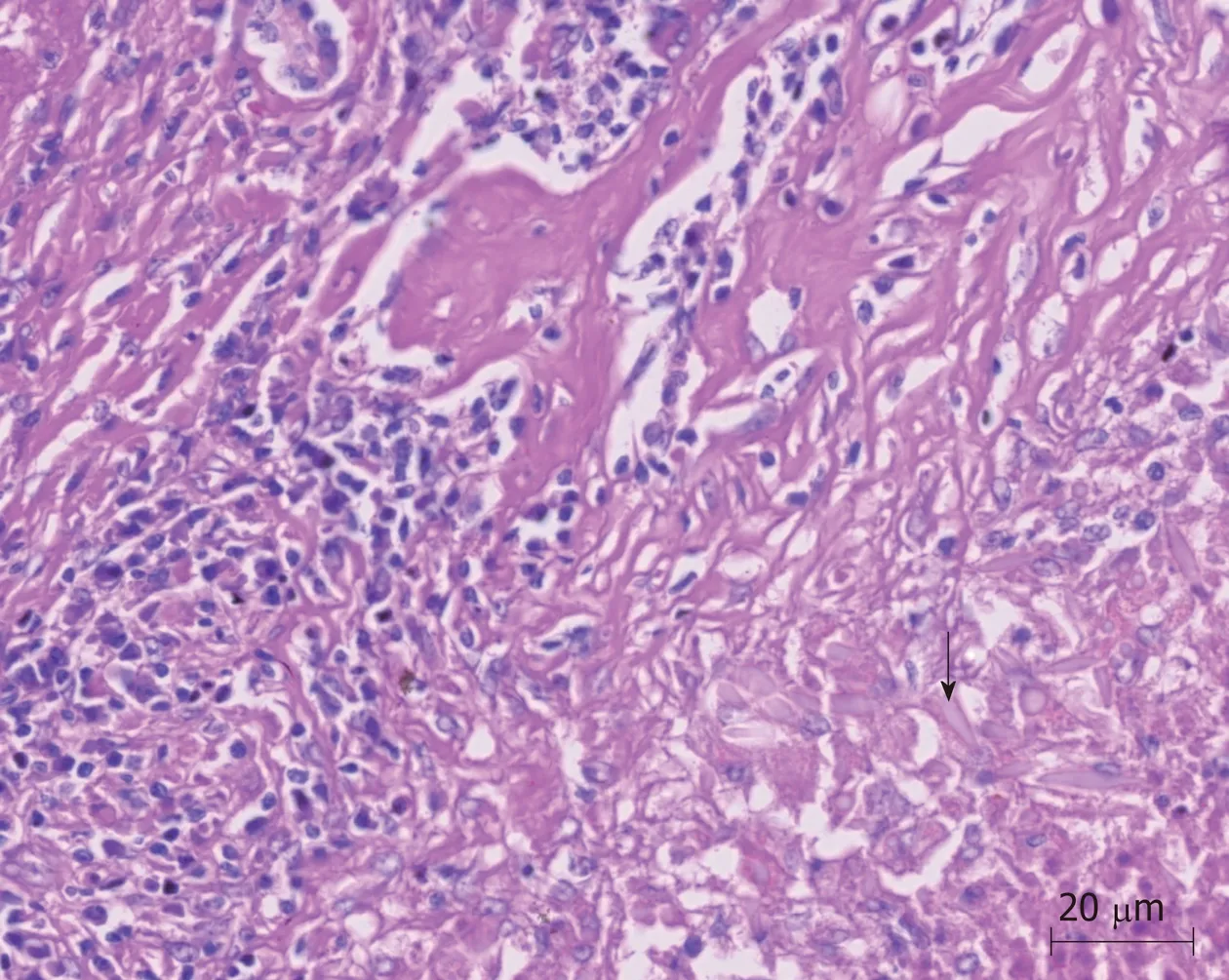
Figure4 Charcot-Leyden crystals near granuloma (arrows) (HE ×100).

Figure5 Endoscopic view of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography procedure.
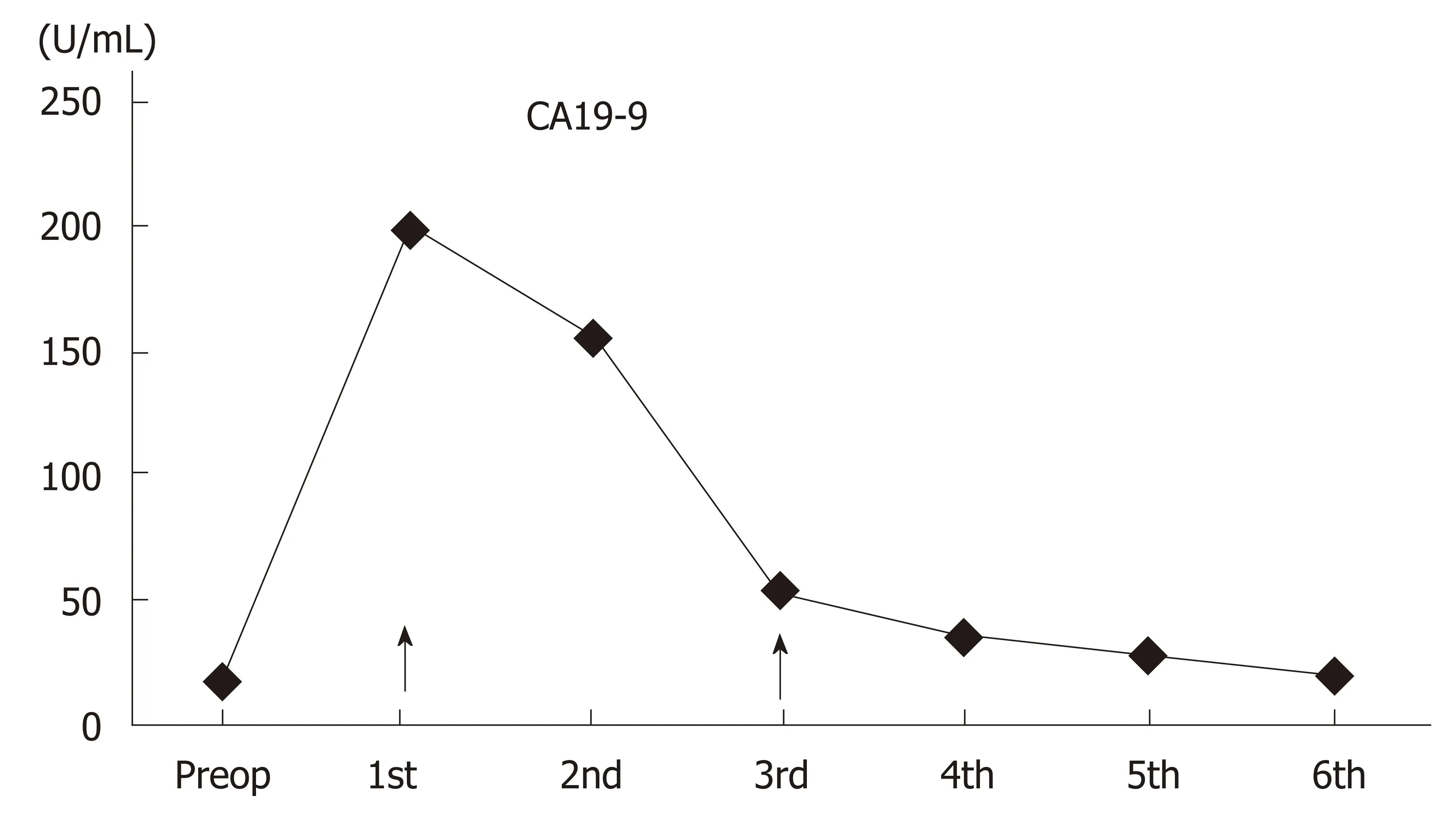
Figure6 Course of blood CA19-9 levels.
 World Journal of Hepatology2019年8期
World Journal of Hepatology2019年8期
- World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- ls porto sinusoidal vascular disease to be actively searched in patients with portal vein thrombosis?
- Prolonged high-fat-diet feeding promotes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alters gut microbiota in mice
- lmpact of psychosocial comorbidities on clinical outcomes after liver transplantation:Stratification of a high-risk population
- Outpatient telephonic transitional care after hospital discharge improves survival in cirrhotic patients
