French Spine Surgery Society guidelines for management of spinal surgeries during COVID-19 pandemic
Solène Prost,Yann Philippe Charles,Jérôme Allain,Jean-Luc Barat,Henri d'Astorg,Manuel Delhaye,Chistophe Eap,Fahed Zairi,Pierre Guigui,Brice Ilharreborde,Jean Meyblum,Jean-Charles Le Huec,Nicolas Lonjon,Guillaume Lot,Olivier Hamel,Guillaume Riouallon,Stéphane Litrico,Patrick Tropiano,Benjamin Blondel,the French Spine Surgery Society
Solène Prost,Patrick Tropiano,Benjamin Blondel, Aix-Marseille Université,APHM,CNRS,ISM,CHU Timone,Unité de Chirurgie Rachidienne,Marseille 13005,France
Yann Philippe Charles, Service de Chirurgie du Rachis,Hôpitaux Universitaires de Strasbourg,Strasbourg 67200,France
Jérôme Allain, Institut Parisien du dos,Paris 75005,France
Jean-Luc Barat,Service de Neurochirurgie,Hôpital privé Clairval - Ramsay santé,Marseille 13009,France
Henri d'Astorg, Unité de Chirurgie du Rachis,Centre Orthopédique Santy,Lyon 69008,France
Manuel Delhaye, Centre Francilien du dos,Versailles 78000,France
Chistophe Eap,CHU Reims,Hôpital Maison Blanche,Neurochirurgie,Reims 51100,France
Fahed Zairi,Hôpital Privé Le Bois Ramsay Santé,Lille 59000,France
Pierre Guigui, Hôpital Européen Georges-Pompidou HEGP,Paris 75015,France
Brice Ilharreborde, Service de Chirurgie Orthopédique Pédiatrique,CHU Robert Debré,APHP,Université de Paris,Paris 75019,France
Jean Meyblum,Service de Chirurgie Orthopédique,Groupe Hospitalier Paris Saint-Joseph,Paris 75014,France
Jean-Charles Le Huec,Polyclinique Bordeaux Nord Aquitaine,Bordeaux 33300,France
Nicolas Lonjon, Service de Neurochirurgie,Hôpital Gui de Chauliac,Montpellier 34090,France
Guillaume Lot,Hôpital - Fondation Rothschild,Service de Neurochirurgie,Paris 75019,France
Olivier Hamel,Clinique Des Cèdres Service de Neurochirurgie,Château D'Alliez,Cornebarrieu 31700,France
Guillaume Riouallon, Hôpital Paris Saint-Joseph,Paris 75014,France
Stéphane Litrico, Unité de Chirurgie Rachidienne,Hôpital Pasteur 2,CHU de Nice,Nice 06001,France
Abstract
Key words:COVID-19;Spine;Surgery;Guidelines;Organization;Cluster region
INTRODUCTION
Since the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19)in December 2019 in China,a worldwide dissemination of the virus has been reported,leading on March 11,2020 to a declaration of pandemic situation by the World Health Organization[1].In France,the sanitary response is based on the ORSAN REB plan[2]with two goals:Management of COVID-19 patients and virus containment.Due to an active circulation of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2)in France,the decision was made to activate Phase 3 of the plan on March 14,2020,which included a graduate response of the sanitary system in order to attenuate the impact of the virus on the population.Asides from complete mobilization of sanitary resources and standard precautions against viruses,national lockdown was decided on March 17,2020.Since this date,elective surgeries have been postponed in order to avoid potential unnecessary use of intensive care unit resources.
With regard to spine surgery,French physicians are devoted to take place in the national plan against COVID-19 with various actions such as screening and triage of patients or direct help in intensive care units.However,spine surgeons also have to take care(with a restricted access to operating theaters)of patients with various spinal conditions.The French Spine Surgery Society therefore decided to elaborate specific guidelines for management of spinal disorders during COVID-19 pandemic in order to prioritize management of patients.
FRENCH SPINE SURGERY SOCIETY GUIDELINES
The actual sanitary crisis led to a massive mobilization of sanitary system towards intensive care units and management of COVID-19 patients.This unstable period of time is therefore drastically reducing the possibility for surgical procedures.Furthermore,social distancing measures limit outpatient's visits or hospitalizations.
Common spinal procedures were then classified in three groups according to emergency criteria.
Level I:Urgent surgical indications
(1)Cervical or lumbar radiculopathy with acute motor deficit;(2)Disc herniation with cauda equina syndrome;(3)Spinal epidural hematoma;(4)Septic conditions including epidural abscess;(5)Spinal fractures with neurologic deficit;and(6)Spinal tumors(metastases)with neurologic deficit.
Of note,these conditions that require urgent procedures would be performed according to each structure's possibilities,including a potential transfer of patients to another center if the initial structure's capacities are overloaded.The surgical strategy should favor the least invasive approach whenever possible,in order to reduce hospitalization length of stay and the need for postoperative intensive care.
Level II:Surgical indications associated to a potential loss of chance for the patient
(1)Radiculopathy with hyperalgesia(requiring hospitalization);(2)Cervical myelopathy with rapidly progressive neurologic signs;(3)Unstable vertebral fracture without neurologic deficit;and(4)Unstable spine tumor without neurologic deficit.
These procedures need to be scheduled in a reasonable delay according to each structure's possibilities,which include potential transfer of patients to another center if the initial structure's capacities are overloaded.Similarly to urgent indications,the surgical strategy will favor less invasive approach if possible,in order to reduce the length of hospital stay and the need for intensive care postoperatively.
Level III:Non-urgent surgical indications
(1)Degenerative spinal conditions without neurologic deficit:Chronic radiculopathy,discopathy,degenerative spondylolisthesis,spinal canal stenosis with neurogenic claudication;(2)Spinal deformities(scoliosis and kyphosis of any etiology);and(3)Revision surgery related to previous instrumentation failure without instability or neurologic deficit.
For these indications,surgical procedures should be postponed to a later date that will depend on the pandemic evolution and necessary time for health structures to go back to normal activities.
It is important to note that this 3 levels list reported here is not exhaustive and the surgical and anesthesiologist teams must analyze together each clinical situation that requires surgery.Furthermore,these guidelines need to be taken into account in the light of the pandemic evolution and its consequences on each health structure.Some regional particularities due to large COVID-19 clusters and a high need for intensive care unit beds must also be considered to select patients eligible for surgery.
Every patient eligible for a spinal surgical procedure during the COVID-19 pandemic should also be informed of the potential risk of contamination during hospitalization.
ORGANIZATION IN A COVID-19 CLUSTER REGION
The degree of emergency of spinal surgical indications highly depends on human resources(i.e.intensive care and anesthesiology medical and paramedical staff)as well as the availability of mechanical ventilation.In COVID-19 cluster regions,postanesthesia care units and/or operative rooms might have been turned into intensive care units,thus resulting in limited availability for operated patients.Furthermore,pathways of remaining operating theaters need to be divided into a COVID+ sector and a COVID- sector.In case of COVID+ theaters,a specific protocol needs to be applied.During the preparation phase,the anesthesiologist and nurse work in the theater,whereas the surgical team prepares the required devices and implants outside the theater.Whenever possible,the surgical team should be reduced to a minimum(surgeon and scrub nurse).A second scrub nurse stays outside to provide additional devices if required.After surgery,the patient might be extubated and immediate postoperative care should be provided in the operating theater as post-operative care units might not be accessible.If one of these units remains operational,it should be allocated to COVID- patients.The operated COVID patient will be directly transferred from the theater to a dedicated COVID hospitalization ward.When the patient has left the operating theater,cleaning of the room should only be performed after one hour,as a high concentration of SARS-CoV-2 virus might still be present in the air.These considerations lead to very limited access to urgent surgical procedures in COVID-19 patients,which needs to be taken into account preoperatively by the surgeon when formulating a surgical indication.
From a medical standpoint,if one of the urgent surgical indications listed above is considered,one should take into account that a COVID-19 patient with mild or moderate respiratory symptoms might quickly deteriorate between day 5 and 10 of the disease.Therefore,COVID-19 patients should only be operated after the critical time point of 10-14 d,once respiratory recovery is clearly demonstrated.Two cases of COVID-19 patients might illustrate the unusual strategy of treating spinal fractures.
Case 1
A 56-year-old male was admitted to the emergency room after falling from a roof while working.His past medical history included hypertension and a prostate cancer.He presented back pain.The neurologic exam was normal.He was coughing without evidence of dyspnea.His body temperature was 37.9 °C.He was tested positive for COVID-19 by polymerase chain reaction.A chest X-ray was carried out,showing no major opacity.An additional computed tomography(CT)-scan performed because of suspected spinal trauma evidenced COVID-19 typical thoracic signs of peripheral ground glass opacities(Figure 1).The CT further evidenced a vertebral compression fracture of L1 without significant posterior wall involvement,thus classifying the fracture as stable and without risk for neurologic complications(Figure 2).Since the patient presented a compensated respiratory function,he was confined at home.The L1 fracture was treated conservatively although a significant vertebral body collapse was present.A secondary operation might be carried out once the patient is free of symptoms and the OR and postoperative care unit availability have improved.
Case 2
A 71-year-old female with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis fell and was admitted to the emergency room.Her past medical history included hypertension and diabetes type 2.She was febrile(38.6 °C)and presented with dyspnea.The polymerase chain reaction was positive for COVID-19 and her chest X-ray showed moderate bilateral opacities.A CT-scan was performed,showing an unstable nonneurologic T7-T8 fracture(Figure 3).Furthermore images of a COVID-19 typical thoracic CT-scan with bilateral ground glass opacities were present(Figure 4).A first line treatment of the COVID-19 respiratory distress syndrome was considered.A secondary operation was indicated after 16 days once the respiratory function had improved(Sat02 95%),since ambulation was impossible because of the highly unstable fracture.A cement augmented percutaneous instrumentation T5-T10 was performed(Figure 5)and the patient was transferred to a specific surgical COVID-19 unit for postoperative care.A postoperative X-ray control apart from intraoperative fluoroscopy was avoided in order to limit any possible contact of the patient with other patients and staff at the radiologic department.She was discharged and confined after 5 d at home,once she was able to walk and her respiratory symptoms had returned to normal.Ambulatory care by a nurse was continued at home.
DISCUSSION
In such an unstable period of time,everyday practice needs to be completely reinvented for every medical area.Emergency and intensive care specialists are currently on the first line of the crisis according to the important number of patients that require hospitalization in intensive care.As reported by Zangrilloet al[3]about the Italian experience,fast and large reshaping of intensive care units has been a priority in France and in many other countries.Concerning operative rooms,many adaptations are also necessary with specific isolated rooms for COVID+ patients and a need for perfect coordination between all healthcare professionals[4,5].
Spine surgeons might not be the first physicians concerned by management of COVID-19 patients,but,similarly to others surgeons they can actively take part in the common crisis response by helping in many ways other departments of the hospital.They are also responsible for the organization of spinal care during the pandemic within a globally tight organization[6].According to Zouet al[7]the first step of management is related to screening for COVID-19 symptoms and triage of the patients that would require a surgical procedure.The next step is to develop guidelines for spinal surgical indications according to emergency criteria,and then eventually to the surgical procedures with all needed precautions.
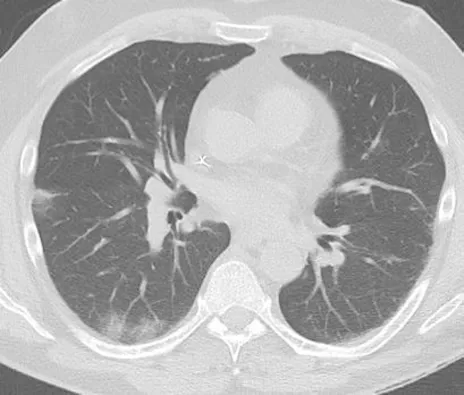
Figure 1 Chest computed tomography-scan revealing coronavirus disease 2019 typical thoracic signs of peripheral ground glass opacities.
CONCLUSION
We hope that the guidelines formulated by the French Spine Surgery Society and the experience of spine surgeons from a cluster region will be helpful in order optimizing the management of patients with urgent spinal conditions during the pandemic.It is also important to note that with confinement of the population,a drastic decrease of urgent cases have been noted in France(trauma and degenerative).This may also be related to an apprehension of patients towards potential COVID infection in health structures and difficulties to reach a physician for appointment.Finally,we also have to prepare the end of the crisis and this 3 levels list will be modulate according to pandemic evolution.Supplementary protection devices will be needed for patients and physicians and adapted pathways will be necessary for COVID- and COVID+patients in order to prevent second wave effect.

Figure 2 Spine computed tomography scan.A:Sagittal view;B:Axial view.The images showed that the stable vertebral compression L1 fracture without significant posterior wall involvement.A conservative treatment was carried out.
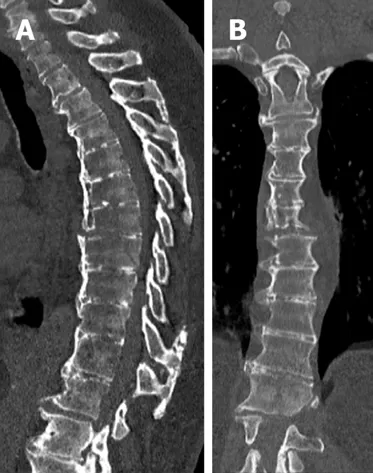
Figure 3 Sagittal and coronal spine computed tomography scan showing an unstable non-neurologic T7-T8 fracture on ankylosing spine.A:Sagittal;B:Coronal.

Figure 4 Coronavirus disease 2019 typical thoracic computed tomography-scan with bilateral ground glass opacities.

Figure 5 Intra-operative lateral and anteroposterior fluoroscopic control after T5-T10 cement augmented percutaneous posterior fixation.A:Intra-operative lateral;B:Anteroposterior.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年10期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年10期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Prophylactic and therapeutic roles of oleanolic acid and its derivatives in several diseases
- Macrophage regulation of graft-vs-host disease
- Antiphospholipid syndrome and its role in pediatric cerebrovascular diseases:A literature review
- Remotely monitored telerehabilitation for cardiac patients:A review of the current situation
- Keystone design perforator island flap in facial defect reconstruction
- Cross electro-nape-acupuncture ameliorates cerebral hemorrhageinduced brain damage by inhibiting necroptosis
